Mammals Concept List (Part 1)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
What type of ancestor did mammals evolve from?
mammal-like, reptilian **Cynodont** Therapsid
2
New cards
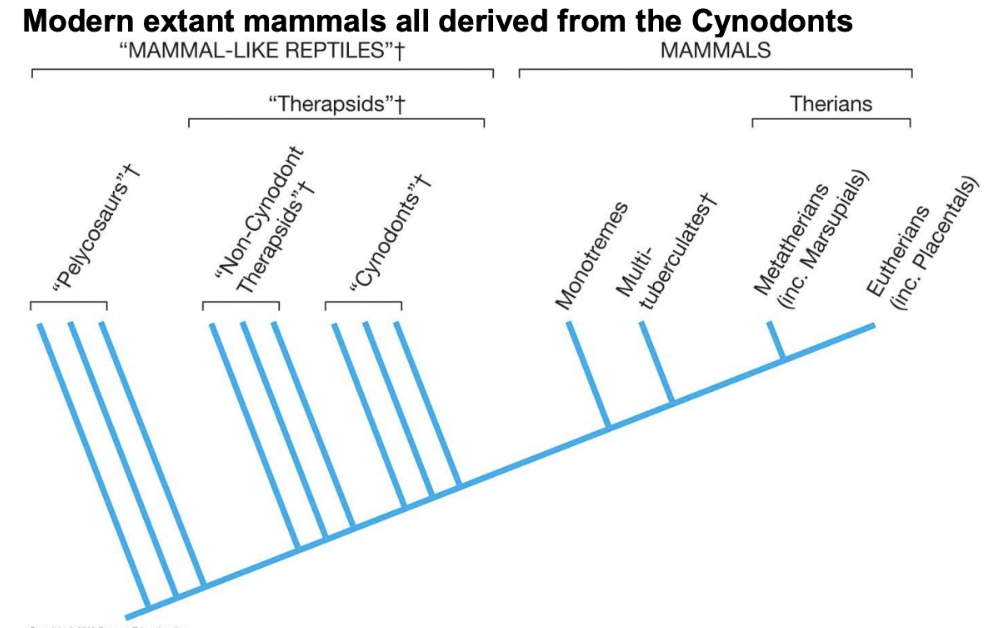
Be able to create a cladogram for mammals
see image
3
New cards
what main events opened the door for the radiation of mammals?
* Synapsid reptiles (including therapsids, aka mammal-like reptiles) dominated the terrestrial environment
* Major extinction event and formation of Pangaea wiped out 70% of terrestrial species
* Mammals evolved from a Therapsid Cynodont ancestor
* sail-backed synapsid → basal therapsid → cynodont therapsid → mammals
* Major extinction event and formation of Pangaea wiped out 70% of terrestrial species
* Mammals evolved from a Therapsid Cynodont ancestor
* sail-backed synapsid → basal therapsid → cynodont therapsid → mammals
4
New cards
what are the defining characteristics of mammals?
* **Endothermic**: main source of body heat is metabolism; requires __subcutaneous fat__ w/in the subdermis to insulate body, and extra energy to be create this subcutaneous fat; only avians and mammals are true endotherms
* __Hair__ at some point during lifetime; insulation and sensory purposes
* **Lactogenic**: presence of mammary glands that nourish young with milk
* __Hair__ at some point during lifetime; insulation and sensory purposes
* **Lactogenic**: presence of mammary glands that nourish young with milk
5
New cards
what are the three main types of mammals?
**Monotremes** – more reptilian gait, oviparious, have a cloaca,
* Shoulder girdle placement
* Includes platytpuses and echidnas
\
**Metatherians/Marsupials**– mammalian gait, have separate openings for reproduction and excretion, viviparous (live birth), have a placenta, nipples, and marsupial pouch, where the altricial young go to to continue developing
* Diamond-shaped nasal bones, 5 upper incisors and 4 lower
* Includes kangaroos, koalas, sugar gliders, opposums, etc
\
**Eutherians/Placentals** – mammalian gait, have separate openings for reproduction and excretion, viviparous (live birth), have a placenta to give the fetus nutrients, and nipples for the babies/young to feed on
* Rectangle-shaped nasal bones, 3 upper and lower incisors
* Includes many mammals like rabbits, dogs, bears, etc
* Shoulder girdle placement
* Includes platytpuses and echidnas
\
**Metatherians/Marsupials**– mammalian gait, have separate openings for reproduction and excretion, viviparous (live birth), have a placenta, nipples, and marsupial pouch, where the altricial young go to to continue developing
* Diamond-shaped nasal bones, 5 upper incisors and 4 lower
* Includes kangaroos, koalas, sugar gliders, opposums, etc
\
**Eutherians/Placentals** – mammalian gait, have separate openings for reproduction and excretion, viviparous (live birth), have a placenta to give the fetus nutrients, and nipples for the babies/young to feed on
* Rectangle-shaped nasal bones, 3 upper and lower incisors
* Includes many mammals like rabbits, dogs, bears, etc
6
New cards
what are some evolutionary changes of the mammalian __brain__?
* expanded cerebral portion (responsible for higher-level processes like language and memory)
7
New cards
what are some evolutionary changes of the mammalian __sweat and sebaceous glands__?
* **Eccrine (sweat) glands** allow for evaporative cooling
* **Sebaceous (oil) glands** produce sebum to protect the hair and also for scent
* **Sebaceous (oil) glands** produce sebum to protect the hair and also for scent
8
New cards
what are some evolutionary changes of the mammalian __circulatory system__?
* **Four-chambered heart**: allows for complete separation of pulmonary and systemic circulation
* **Pulmonary circuit** – right atrium → right ventricle –(pumps gently to)→ lungs
* **Systemic cricuit** – left atrium → left ventricle –(pumps strongly to)→ body
* __Separate__ renal artery and vein (rather than renal portal system)
* **anucleated (no nucleus) blood cells** can carry more oxygen, allowing for higher metabolic rates
* **Pulmonary circuit** – right atrium → right ventricle –(pumps gently to)→ lungs
* **Systemic cricuit** – left atrium → left ventricle –(pumps strongly to)→ body
* __Separate__ renal artery and vein (rather than renal portal system)
* **anucleated (no nucleus) blood cells** can carry more oxygen, allowing for higher metabolic rates
9
New cards
what are some evolutionary changes of the mammalian __respiratory system__?
* **Muscular diaphragm**: used to inhale and exhale via negative pressure
* contracts (flattens out) to inhale
* relaxes (goes back to inverted U shape) to exhale
* contracts (flattens out) to inhale
* relaxes (goes back to inverted U shape) to exhale
10
New cards
In general, small mammals (like mice) have _____ metabolic rates and don’t live very long, whereas large mammals (like elephants) have ___ metabolic rates and live longer.
high; low
11
New cards
what are some evolutionary changes of the mammalian __musculoskeletal system__?
* changes in the jaw
* presence of a secondary palate
* changes in teeth
* increased structures for muscle attachment in face
* changes in axial skeleton (spine)
* changes in appendicular skeleton (limbs)
* presence of a secondary palate
* changes in teeth
* increased structures for muscle attachment in face
* changes in axial skeleton (spine)
* changes in appendicular skeleton (limbs)
12
New cards
what are some characteristics of the mammalian __jaw__?
* lower jaw consists of a single bone (the dentary)
* other bones have moved to the inner ear of mammals
* **Tympanic bone**: derived from the __ancestral angular__; supports the tympanum (eardrum)
* **Three ear ossicles – malleus, incus, and stapes**: transmit sound waves from the tympanum to the inner ear; important for sensing vibrations because mammals’ heads are lifted farther off the ground
* ancestral Articular → malleus
* ancestral Quadrate → incus
* ancestral Columella → stapes
* other bones have moved to the inner ear of mammals
* **Tympanic bone**: derived from the __ancestral angular__; supports the tympanum (eardrum)
* **Three ear ossicles – malleus, incus, and stapes**: transmit sound waves from the tympanum to the inner ear; important for sensing vibrations because mammals’ heads are lifted farther off the ground
* ancestral Articular → malleus
* ancestral Quadrate → incus
* ancestral Columella → stapes
13
New cards
what are some characteristics of the mammalian __secondary palate__?
* separation of trachea and esophagus
* allows mammals to __breathe and eat at the same time__ (allows young to __suckle__)
* single opening into nasal cavity, but two external nares (nostrils)
* **respiratory turbinates** (bones) in nasal cavity to mitigate respiratory water loss
* allows mammals to __breathe and eat at the same time__ (allows young to __suckle__)
* single opening into nasal cavity, but two external nares (nostrils)
* **respiratory turbinates** (bones) in nasal cavity to mitigate respiratory water loss
14
New cards
what are some characteristics of the mammalian __teeth__?
* **Heterodont dentition**: different teeth have different shapes and functions (molars, premolars, canine, incisors)
* **Diphyodont**: two generations of teeth
* **Thecodont**: teeth rooted in a socket
* **Multicuspate**: teeth have lots of cusps/bumps
* mammals do NOT have palatal teeth; teeth are only on the jaw margins in mammals
* **Diphyodont**: two generations of teeth
* **Thecodont**: teeth rooted in a socket
* **Multicuspate**: teeth have lots of cusps/bumps
* mammals do NOT have palatal teeth; teeth are only on the jaw margins in mammals
15
New cards
what are some characteristics of the mammalian __skull__?
* increased structures (arches and ridges) for increased muscle attachment in face
* increase in facial muscles allows for facial expression, important in communication
* allows for chewing and thus easier digestion
* increase in facial muscles allows for facial expression, important in communication
* allows for chewing and thus easier digestion
16
New cards
what are some characteristics of the mammalian __Axial Skeleton (Spine/Vertebral Column)__?
* **atlas/axis complex:** modification of the first cervical (neck) vertebrae to allow for rotation of head
* **double occipital condyle**: allows for articulation between skull and vertebral column (contrast to single one in non-mammals)
* extreme __regionalization of vertebrae__ into the **cervical** (usually 7 vertebrae in the neck) region, **thoracic** (usually 12-13 vertebrae in the upper back), **lumbar** (lower back), **sacral** (pelvis), and **caudal** (tail).
* __Ribs only__ present near the __thoracic__ vertebrae
* muscular diaphragm is used to regulate breathing
* **double occipital condyle**: allows for articulation between skull and vertebral column (contrast to single one in non-mammals)
* extreme __regionalization of vertebrae__ into the **cervical** (usually 7 vertebrae in the neck) region, **thoracic** (usually 12-13 vertebrae in the upper back), **lumbar** (lower back), **sacral** (pelvis), and **caudal** (tail).
* __Ribs only__ present near the __thoracic__ vertebrae
* muscular diaphragm is used to regulate breathing
17
New cards
what are some characteristics of the mammalian __Appendicular Skeleton (Limbs)__?
* **Epiphyses:** __caps__ at the end of limb bones; separated from the shaft by cartilage that ossifies during development
* **Calcaneum**: the __heel bone__ where the achilles tendon inserts; provides leverage for extending the foot
* __Reduction in the number of bones / increase in fusion__ in pelvic and pectoral girdles
* **Mammalian gait**: changes to pectoral and pelvic girdles allow legs to be directly beneath the body, allows for independent movement of limbs (also seen in dinos)
* **Calcaneum**: the __heel bone__ where the achilles tendon inserts; provides leverage for extending the foot
* __Reduction in the number of bones / increase in fusion__ in pelvic and pectoral girdles
* **Mammalian gait**: changes to pectoral and pelvic girdles allow legs to be directly beneath the body, allows for independent movement of limbs (also seen in dinos)
18
New cards
Compared to other vertebrates, mammals are generally long-lived and thus take a long time to reach sexual maturity and reproduce. This confuses scientists because of how rapidly they have undergone evolutionary change to achieve such high diversity in a short geological time period. What is one potential explanation?
* because they are endothermic, mammals have high metabolisms and thus replicate their DNA more often
* more potential for mutations during DNA replication
* more potential for mutations during DNA replication
19
New cards
what are the major similarities and differences between mammals and other vertebrates?
similarities -- all vertebrates have vertebrae
* also often have jaws, bones that ossify from cartilage, and four limbs
differences -- mammals are lactogenic, have hair at some point in their lifetime, and are endothermic
* also often have jaws, bones that ossify from cartilage, and four limbs
differences -- mammals are lactogenic, have hair at some point in their lifetime, and are endothermic
20
New cards
what are the similarities in reproduction and fetal development of all extant mammal groups?
* internal fertilization
* lactogenic (nourish young with milk from mammary glands)
* lactogenic (nourish young with milk from mammary glands)
21
New cards
what are the differences in the reproduction and fetal development of Prototherians (aka Monotremes), Metatherians (aka Marsupials), and Eutherians (aka Placentals)?
__**Prototherians (Monotremes)**__
* cloaca
* oviparous (lay eggs)
__**Metatherians (Marsupials)**__
* separate openings for excretion and reproduction
* Simpler **Choriovitelline placenta** delivers nutrition, oxygen, and other materials needed for embryo to develop
* fetus is born when NOT yet fully developed, so the young are __highly altricial__ and must move to the **marsupium** (pouch) to suckle off the teat and finish development
* young DO have well-developed forelimbs and large lungs
__**Eutherians**__
* separate openings for excretion and reproduction
* **Choriovitelline placenta** develops first, then is __replaced by__ a more complex **chorioallantoic membrane**
* fetus is born at various stages and more developed, so the young do not need to be carried on the teat at all times and can __range from altricial to precocial__
* young have well-developed auditory bullae
* cloaca
* oviparous (lay eggs)
__**Metatherians (Marsupials)**__
* separate openings for excretion and reproduction
* Simpler **Choriovitelline placenta** delivers nutrition, oxygen, and other materials needed for embryo to develop
* fetus is born when NOT yet fully developed, so the young are __highly altricial__ and must move to the **marsupium** (pouch) to suckle off the teat and finish development
* young DO have well-developed forelimbs and large lungs
__**Eutherians**__
* separate openings for excretion and reproduction
* **Choriovitelline placenta** develops first, then is __replaced by__ a more complex **chorioallantoic membrane**
* fetus is born at various stages and more developed, so the young do not need to be carried on the teat at all times and can __range from altricial to precocial__
* young have well-developed auditory bullae
22
New cards
what are the anatomical differences between Phocidae (seals) and Otariidae (sea lions)?
__**Phocidae (seals)**__
* NO external ear pinnae
* smaller front flippers
* INflexible wrist and ankle joints
* placement of limbs more towards sides of body for hydrodynamic shape → beneficial for swimming, not as much for moving on land
__**Otariidae (sea lions)**__
* external ear pinnae
* larger front flippers
* flexible wrist and ankle joints
* placement of limbs more directly beneath body (subterminal), and back limbs can rotate beneath the body to allow for walking/waddling locomotion on land
* NO external ear pinnae
* smaller front flippers
* INflexible wrist and ankle joints
* placement of limbs more towards sides of body for hydrodynamic shape → beneficial for swimming, not as much for moving on land
__**Otariidae (sea lions)**__
* external ear pinnae
* larger front flippers
* flexible wrist and ankle joints
* placement of limbs more directly beneath body (subterminal), and back limbs can rotate beneath the body to allow for walking/waddling locomotion on land
23
New cards
what happens in the terrestrial exercise response vs the dive response?
* **Terrestrial exercise response:** increase in ventilation, increase in heart rate, increase in peripheral vasodilation to send more oxygenated blood to the working muscles, decrease in blood flow to digestive tract
* **Dive response**: decrease in ventilation, decrease in heart rate, increase in peripheral __vasoconstriction__ to redirect blood to the vital organs (thus the muscles in the limbs rely on anaerobic metabolism more, which tires faster and builds up lactic acid)
* **Dive response**: decrease in ventilation, decrease in heart rate, increase in peripheral __vasoconstriction__ to redirect blood to the vital organs (thus the muscles in the limbs rely on anaerobic metabolism more, which tires faster and builds up lactic acid)