11/3 Difference between Series and Parallel
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Number of paths for an electron to travel in series?
Only one path
Number of paths for an electron to travel in parallel?
Multiple paths for current to travel
Equation used to find Equivalent Resistance in Series
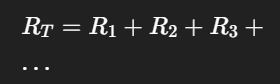
Equation used to find Equivalent Resistance in Parallel
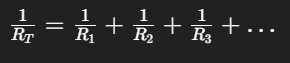
Equation used to find Voltage or Current in Series

Equation used to find Voltage or Current in Parallel
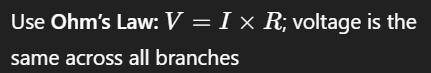
Without adding resistances, what remains constant in series?
Current remains constant throughout
Without adding resistances, what remains constant in parallel?
Voltage remains constant across each branch
What happens to the circuit’s total resistance as more resistance is added in series?
Total resistance increases
What happens to the circuit’s total resistance as more resistance is added in parallel?
Total resistance decreases
What happens to “total” current when adding more resistances in series?
Total current decreases
What happens to “total” current when adding more resistances in parallel?
Total current increases (more paths allow more current)
What voltage goes into each resistance of the circuit in series?
Voltage is divided among resistors
What voltage goes into each resistance of the circuit in parallel?
Voltage is the same across each resistor
When you have 2 or more resistances in the circuit, what happens when 1 breaks, creating a gap in that section of the circuit in series?
The whole circuit stops working (open circuit)
When you have 2 or more resistances in the circuit, what happens when 1 breaks, creating a gap in that section of the circuit in parallel?
Only that branch stops working; the rest continue to function
What must be the difference in voltage from just leaving the voltage source and just before returning to the voltage source in series?
The sum of voltage drops across resistors equals the total voltage of the source
What must be the difference in voltage from just leaving the voltage source and just before returning to the voltage source in parallel?
The voltage drop across each branch equals the total voltage of the source