Chapter 6: Bone Tissue and the Skeletal System
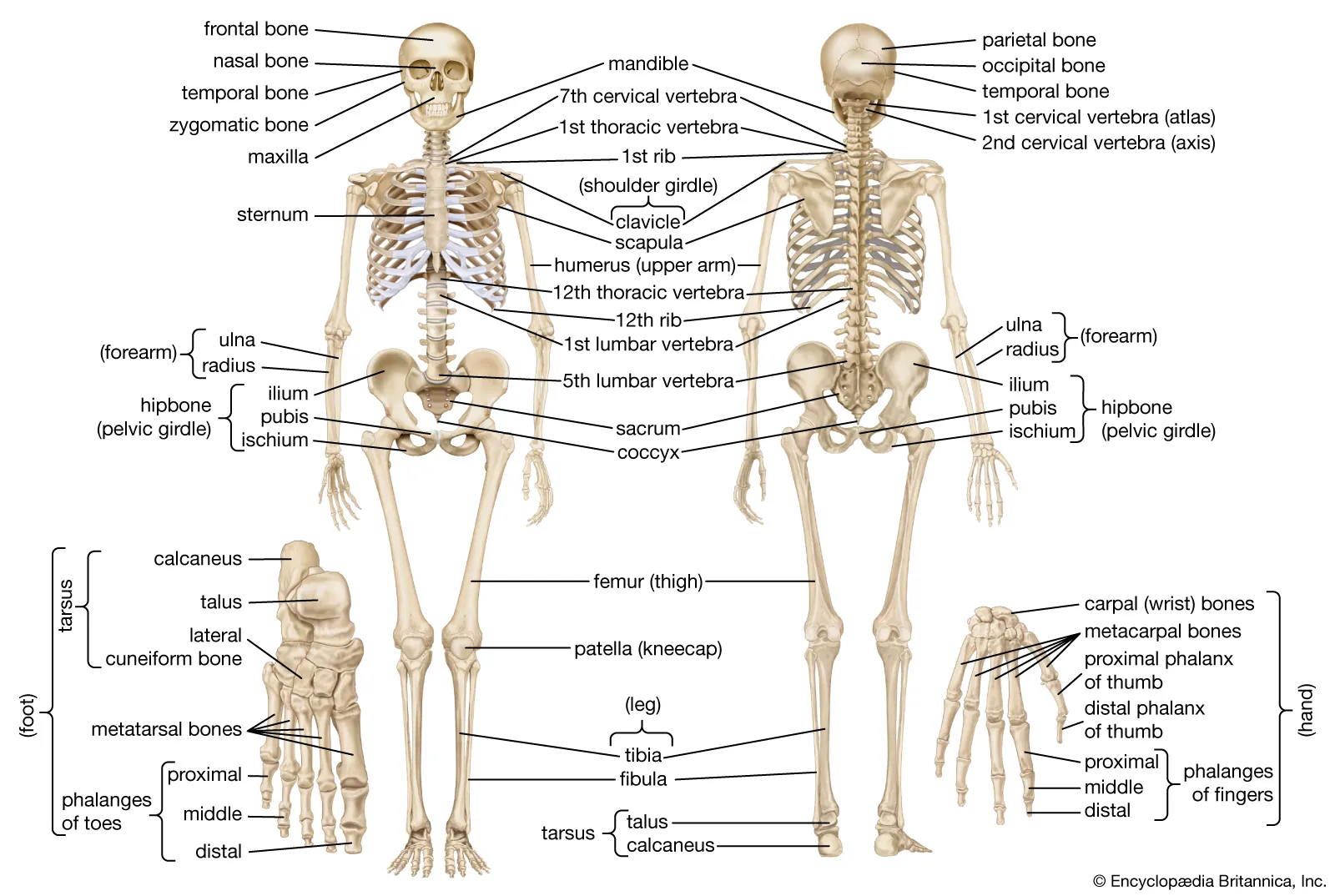
The Functions of the Skeletal System
- Bone, or osseous tissue, is a hard, dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton, the support structure of the body.
- The skeletal system is the body system composed of bones and cartilage and performs the following critical functions for the human body:
- supports the body
- facilitates movement
- protects internal organs
- produces blood cells
- stores and releases minerals and fat
Mineral Storage, Energy Storage, and Hematopoiesis
- Yellow marrow contains adipose tissue; the triglycerides stored in the adipocytes of the tissue can serve as a source of energy.
- Red marrow is where hematopoiesis—the production of blood cells—takes place. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are all produced in the red marrow.
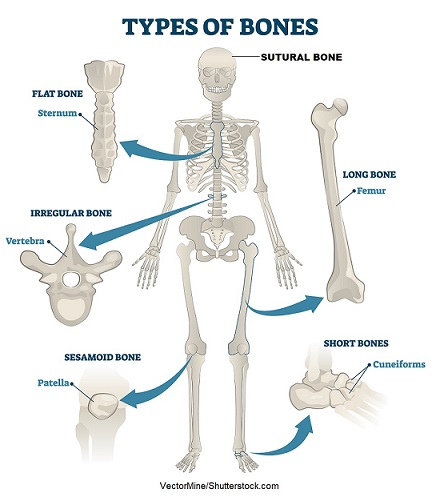
Bone Classification
The 206 bones that compose the adult skeleton are divided into five categories based on their shapes.
Their shapes and their functions are related such that each categorical shape of bone has a distinct function.
\n Long Bones
A long bone is one that is cylindrical in shape, being longer than it is wide.
- Keep in mind, however, that the term describes the shape of a bone, not its size.
- Long bones are found in the arms (humerus, ulna, radius) and legs (femur, tibia, fibula), as well as in the fingers (metacarpals, phalanges) and toes (metatarsals, phalanges).
- Long bones function as levers; they move when muscles contract.
\n Short Bones
A short bone is one that is cube-like in shape, being approximately equal in length, width, and thickness.
The only short bones in the human skeleton are in the carpals of the wrists and the tarsals of the ankles.
Short bones provide stability and support as well as some limited motion.
Flat Bones: The term “ flat bone” is somewhat of a misnomer because, although a flat bone is typically thin, it is also often curved.
Irregular Bones: An irregular bone is one that does not have any easily characterized shape and therefore does not fit any other classification.
Sesamoid Bones
- A sesamoid bone is a small, round bone that, as the name suggests, is shaped like a sesame seed.
- These bones form in tendons (the sheaths of tissue that connect bones to muscles) where a great deal of pressure is generated in a joint.
- The sesamoid bones protect tendons by helping them overcome compressive forces.
Bone Classifications
| Bone classification | Features | Function(s) | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long | Cylinder-like shape, longer than it is wide | Leverage | Femur, tibia, fibula, metatarsals, humerus, ulna, radius, metacarpals, phalanges |
| Short | Cube-like shape,approximately equal in length, width, and thickness | Provide stability, support, while allowing for somemotion | Carpals, tarsals |
| Flat | Thin and curved | Points of attachment for muscles; protectors ofinternal organs | Sternum, ribs, scapulae, cranialbones |
| Irregular | Complex shape | Protect internal organs | Vertebrae, facial bones |
| Sesamoid | Small and round; embedded in tendons | Protect tendons fromcompressive forces | Patellae |
Bone Structure
- Bone tissue (osseous tissue) differs greatly from other tissues in the body.
- Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness.
Gross Anatomy of Bone
- The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone. A long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis.
- The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone.
- The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow marrow.
- The walls of the diaphysis are composed of dense and hard compact bone.
- Each epiphysis meets the diaphysis at the metaphysis, the narrow area that contains the epiphyseal plate (growth plate), a layer of hyaline (transparent) cartilage in a growing bone.
- The medullary cavity has a delicate membranous lining called the endosteum (end- = “inside”; oste- = “bone”), where bone growth, repair, and remodeling occur.
- The outer surface of the bone is covered with a fibrous membrane called the periosteum (peri- = “around” or “surrounding”).
- The epiphyses are covered with articular cartilage, a thin layer of cartilage that reduces friction and acts as a shock absorber.
- Flat bones, like those of the cranium, consist of a layer of diploë (spongy bone), lined on either side by a layer of compact bone.
Bone Markings
- An articulation is where two bone surfaces come together (articulus = “joint”).
- These surfaces tend to conform to one another, such as one being rounded and the other cupped, to facilitate the function of the articulation.
- A projection is an area of a bone that projects above the surface of the bone.
- A hole is an opening or groove in the bone that allows blood vessels and nerves to enter the bone.
Bone Cells and Tissue
- Bone contains a relatively small number of cells entrenched in a matrix of collagen fibers that provide a surface for inorganic salt crystals to adhere.
- The osteoblast is the bone cell responsible for forming new bone and is found in the growing portions of bone, including the periosteum and endosteum.
- As the secreted matrix surrounding the osteoblast calcifies, the osteoblast become trapped within it; as a result, it changes in structure and becomes an osteocyte, the primary cell of mature bone and the most common type of bone cell.
- Each osteocyte is located in a space called a lacuna and is surrounded by bone tissue.
- They can communicate with each other and receive nutrients via long cytoplasmic processes that extend through canaliculi (singular = canaliculus), channels within the bone matrix.
- The cell responsible for bone resorption, or breakdown, is the osteoclast.
Bone Cells
| Cell type | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Osteogenic cells | Develop into osteoblasts | Deep layers of the periosteum and the marrow |
| Osteoblasts | Bone formation | Growing portions of bone, including periosteum and endosteum |
| Osteocytes | Maintain mineral concentration of matrix | Entrapped in matrix |
| Osteoclasts | Bone resorption | Bone surfaces and at sites of old, injured, or unneeded bone |

Compact Bone
- Compact bone is the denser, stronger of the two types of bone tissue. It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones, where it provides support and protection.
- The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon, or Haversian system.
- Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal, or Haversian canal, which contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels.
- These vessels and nerves branch off at right angles through a perforating canal, also known as Volkmann’s canals, to extend to the periosteum and endosteum.
Spongy (Cancellous) Bone
- Like compact bone, spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone, contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but they are not arranged in concentric circles.
- Instead, the lacunae and osteocytes are found in a lattice-like network of matrix spikes called trabeculae (singular = trabecula).
Blood and Nerve Supply
- The spongy bone and medullary cavity receive nourishment from arteries that pass through the compact bone.
- The arteries enter through the nutrient foramen (plural = foramina), small openings in the diaphysis.
- Blood vessels and nerves enter the bone through the nutrient foramen.
Bone Formation and Development
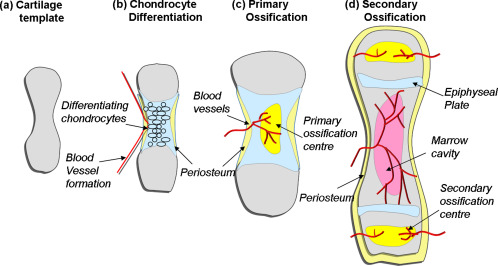
Cartilage Templates
- Bone is a replacement tissue; that is, it uses a model tissue on which to lay down its mineral matrix. For skeletal development, the most common template is cartilage.
- Throughout fetal development and into childhood growth and development, bone forms on the cartilaginous matrix.
- By the time a fetus is born, most of the cartilage has been replaced with bone.
Intramembranous Ossification
- During intramembranous ossification, compact and spongy bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal (undifferentiated) connective tissue.
- Although they will ultimately be spread out by the formation of bone tissue, early osteoblasts appear in a cluster called an ossification center.
- The osteoblasts secrete osteoid, uncalcified matrix, which calcifies (hardens) within a few days as mineral salts are deposited on it, thereby entrapping the osteoblasts within.
Endochondral Ossification
- In endochondral ossification, bone develops by replacing hyaline cartilage.
- The perichondrium, a membrane that covers the cartilage.
- By the second or third month of fetal life, bone cell development and ossification ramps up and creates the primary ossification center, a region deep in the periosteal collar where ossification begins.
- After birth, this same sequence of events (matrix mineralization, death of chondrocytes, invasion of blood vessels from the periosteum, and seeding with osteogenic cells that become osteoblasts) occurs in the epiphyseal regions, and each of these centers of activity is referred to as a secondary ossification center.
- The reserve zone is the region closest to the epiphyseal end of the plate and contains small chondrocytes within the matrix.
- The proliferative zone is the next layer toward the diaphysis and contains stacks of slightly larger chondrocytes.
- Chondrocytes in the next layer, the zone of maturation and hypertrophy, are older and larger than those in the proliferative zone.
- Most of the chondrocytes in the zone of calcified matrix, the zone closest to the diaphysis, are dead because the matrix around them has calcified.
- All that remains of the epiphyseal plate is the epiphyseal line.
- The erosion of old bone along the medullary cavity and the deposition of new bone beneath the periosteum not only increase the diameter of the diaphysis but also increase the diameter of the medullary cavity. This process is called modeling.
Fractures: Bone Repair
- A fracture is a broken bone. It will heal whether or not a physician resets it in its anatomical position.
- If the bone is not reset correctly, the healing process will keep the bone in its deformed position.
- When a broken bone is manipulated and set into its natural position without surgery, the procedure is called a closed reduction.
- Open reduction requires surgery to expose the fracture and reset the bone.
Types of Fractures

| Type of fracture | Description |
|---|---|
| Transverse | Occurs straight across the long axis of the bone |
| Oblique | Occurs at an angle that is not 90 degrees |
| Spiral | Bone segments are pulled apart as a result of a twisting motion |
| Comminuted | Several breaks result in many small pieces between two large segments |
| Impacted | One fragment is driven into the other, usually as a result of compression |
| Greenstick | A partial fracture in which only one side of the bone is broken |
| Open (or compound) | A fracture in which at least one end of the broken bone tears through the skin; carries ahigh risk of infection |
| Closed (or simple) | A fracture in which the skin remains intact |
Bone Repair
- The blood begins to clot, and about six to eight hours after the fracture, the clotting blood has formed a fracture hematoma.
- Within about 48 hours after the fracture, chondrocytes from the endosteum have created an internal callus (plural = calli) by secreting a fibrocartilaginous matrix between the two ends of the broken bone, while the periosteal chondrocytes and osteoblasts create an external callus of hyaline cartilage and bone, respectively, around the outside of the break.
Nutrients and Bone Health
| Nutrient | Role in bone health |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Needed to make calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate, which form the hydroxyapatite crystals that give bone its hardness |
| Vitamin D | Needed for calcium absorption |
| Vitamin K | Supports bone mineralization; may have synergistic effect with vitamin D |
| Magnesium | Structural component of bone |
| Fluoride | Structural component of bone |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Reduces inflammation that may interfere with osteoblast function |
Hormones That Affect the Skeletal System
| Hormone | Role |
|---|---|
| Growth hormone | Increases length of long bones, enhances mineralization, and improves bone density |
| Thyroxine | Stimulates bone growth and promotes synthesis of bone matrix |
| Sex hormones | Promote osteoblastic activity and production of bone matrix; responsible for adolescent growth spurt; promote conversion of epiphyseal plate to epiphyseal line |
| Calcitriol | Stimulates absorption of calcium and phosphate from digestive tract |
| Parathyroid hormone | Stimulates osteoclast proliferation and resorption of bone by osteoclasts; promotesreabsorption of calcium by kidney tubules; indirectly increases calcium absorption by small intestine |
| Calcitonin | Inhibits osteoclast activity and stimulates calcium uptake by bones |
Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems
- Calcium is the most prevalent mineral in bone and the body.
- Calcium ions are needed for bone mineralization, dental health, heart rate and strength modulation, blood coagulation, smooth and skeletal muscle contraction, and nerve impulse conduction.
- Calcium is normally 10 mg/dL. Hypo- or hypercalcemia occurs when this level is not maintained.
- Hypocalcemia - a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of calcium, can have an adverse effect on a number of different body systems including circulation, muscles, nerves, and bone.
- Hypercalcemia - a condition characterized by abnormally high levels of calcium, the nervous system is underactive
- Symptoms: lethargy, sluggish reflexes, constipation and loss of appetite, confusion, and in severe cases, coma.