Bio 006 - Cell Respiration
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Endothermic
Losing heat.
Exothermic
Gaining heat.
Endergonic
Energy absorbed.
Exergonic
Energy released.
Anabolic
Building bonds.
Catabolic
Breaking bonds.
Reduction
Gaining electrons/hydrogen
Oxidation
Losing electrons/hydrogen
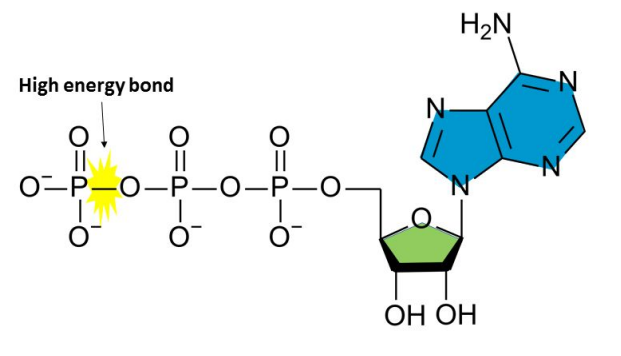
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate.
Energy stored in bonds between extra phosphates
Cellular Respiration
Process which converts ADP back into ATP.
it’s a Anabolic Reaction
Anabolic Reaction
Adding phosphate = building.
Energy Coupling
Pairing anabolic and catabolic reactions.
The process of using energy released from one reaction to drive another reaction.
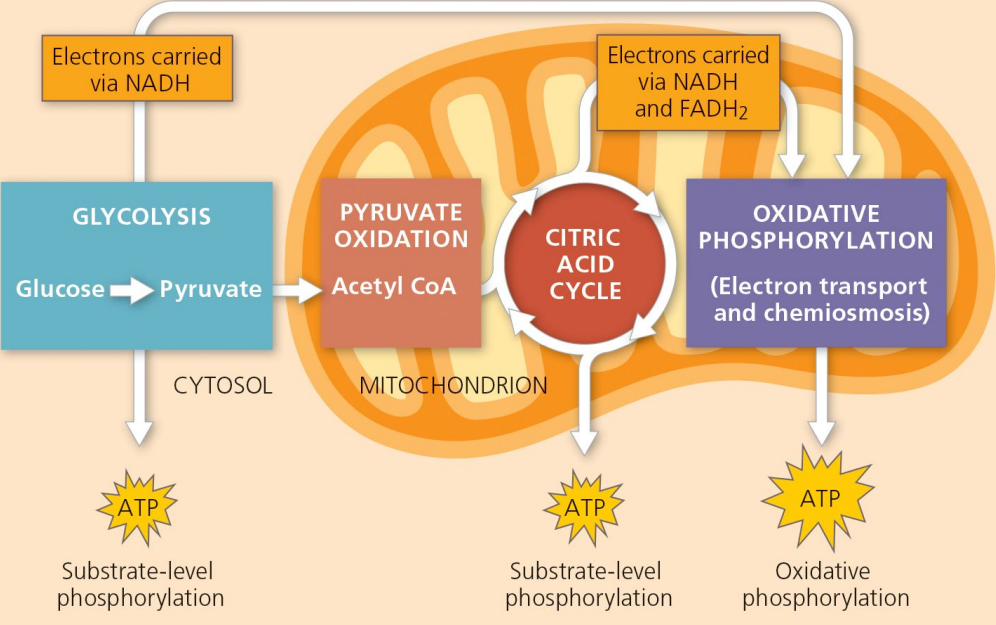
Stages of Cell Respiration
Glycolysis
Pyruvate Oxidation
Citric Acid Cycle / Krebs Cycle
Oxidative Phosphorylation.
Glycolysis
Stage 1 of cell respiration. Only stage which happens outside the mitochondria; occurs in the cytoplasm.
Input: Glucose, NAD
Output: Pyruvate, NADH, H2O
ATP: 2
NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, reduced to NADH
NADH
Reduced form of NAD+
FAD
Flavin adenine dinucleotide, reduced to FADH2.
FADH2
Reduced form of FAD.
Carbon Dioxide
Produced from the breakdown of glucose.
ATP Production
1 molecule of glucose produces ~ 30 ATP.
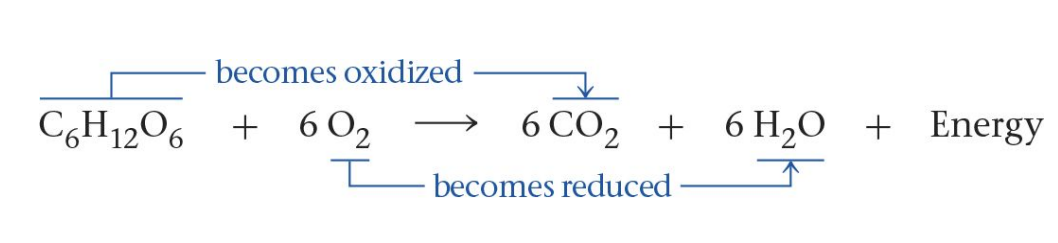
Oxidation
NADH → NAD+; FADH2 → FAD.
Catabolic Reaction
Glucose → CO2; energy released.
Energy in Respiration
Energy from catabolism of glucose is used to build intermediate molecules.
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important energy source in living organisms.
Pyruvate
The output of glycolysis, which is converted into Acetyl-CoA.
Pyruvate Oxidation
Stage 2 of cellular respiration where pyruvate is converted into Acetyl-CoA.
happens in the matrix
Input: Pyruvate, NAD, O2
Output: Acetyl-CoA, CO2, NADH
ATP: NONE
Acetyl-CoA
A molecule that enters the citric acid cycle after pyruvate oxidation.
CO2
Carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration.
Citric Acid Cycle
Stage 3 of cellular respiration that takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
Input: Acetyl-CoA, NAD, FAD
Output: CO2 (lots), NADH, FADH2
ATP: 2
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Stage 4 of cellular respiration where ATP is produced using the electron transport chain.
Happens across the inner membrane
Input: NADH, FADH2, O2
Output: H+, H2O
ATP: 26 or 28
Enzymes
Proteins that act as catalysts to speed up biochemical reactions.
Dehydrogenase
An enzyme that removes hydrogen atoms from substrates.
Works with NAD and FAD
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
A method of generating ATP by directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP.
an enzyme sticks a phosphate onto ADP, making ATP.
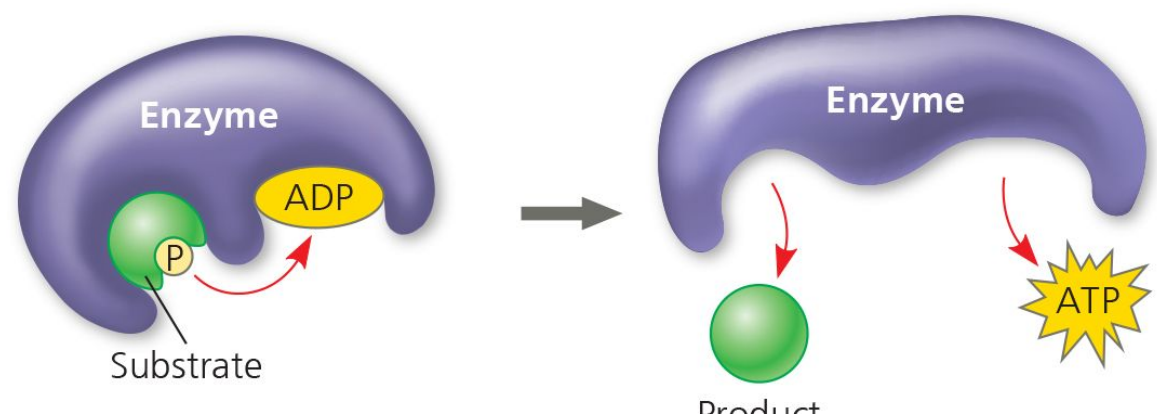
GAPDH
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, an enzyme that produces ATP and NADH in glycolysis.
Pyruvate Kinase
The 2nd important enzyme in glycolysis
An enzyme that converts phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate, producing ATP.
Glycolysis
The first stage of cellular respiration that occurs in the cytoplasm and produces pyruvate.
Phosphorylation
The addition of a phosphate group to a molecule, often to ADP to form ATP.
2
The total ATP yield from glycolysis is ___ ATP.
2
The total ATP yield from substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis is __ ATP.
Complete Reaction of Cellular Respiration
Glucose is converted to carbon dioxide through a series of reactions.
Anaerobic vs Aerobic
Anaerobic processes occur without oxygen, while aerobic processes require oxygen.
NAD
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a coenzyme involved in redox reactions.
Pyruvate
The end product of glycolysis, which is converted into Acetyl CoA in the mitochondria.
H2O
Water, produced as a byproduct of oxidative phosphorylation.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, the primary energy carrier in cells, with a yield of 2 during glycolysis.
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
An enzyme that converts pyruvate into Acetyl CoA, producing CO2 and NADH.
Acetyl CoA
The molecule formed from pyruvate that enters the citric acid cycle.
Citric Acid Cycle
A series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of Acetyl CoA.
FAD
Flavin adenine dinucleotide, a coenzyme involved in redox reactions, similar to NAD.
FADH2
The reduced form of FAD, which also carries electrons to the electron transport chain.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The process in cellular respiration that produces ATP using energy derived from redox reactions.
ATP Synthase
An enzyme that synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate, powered by H+ ions.
Inner Membrane Space
The space between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondria where H+ ions accumulate.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of integral proteins in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transfer electrons and pump H+ ions.
Chemiosmosis
The process of H+ ions moving down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase to generate ATP.
Active Transport
The movement of ions or molecules across a membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring energy.
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
The direct synthesis of ATP from ADP during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
Mitochondrial Membranes
The double membrane structure of mitochondria that separates the mitochondrial matrix from the cytoplasm.
Matrix
The innermost compartment of the mitochondria where the citric acid cycle occurs.
CO2
Carbon dioxide, a waste product produced during pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle.
H+
Hydrogen ions that are used to power ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation.
O2
Oxygen, the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
Stage 3: Citric Acid Cycle
The stage where Acetyl CoA is oxidized to produce CO2, NADH, and FADH2.
Stage 4: Oxidative Phosphorylation
The final stage of cellular respiration where ATP is produced using the energy from NADH and FADH2.
ATP Yield
The total number of ATP produced during cellular respiration, which can be 26 or 28 during oxidative phosphorylation.
30
1 molecule of Glucose = ____ ATP