Human Nuero final 3 other exams
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Last updated 4:23 AM on 12/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
Septal lesions can cause which of the following?
A. Enhanced aggression
B. Decreased motivation
C. Inability to learn tasks such as mirror-writing
D. Inability to create delcarative memories
E. Increased susceptibility to addiction
A. Enhanced aggression
B. Decreased motivation
C. Inability to learn tasks such as mirror-writing
D. Inability to create delcarative memories
E. Increased susceptibility to addiction
Enhanced aggression
2
New cards
Type 2 muscle fibers have __ mitochondria and fatigue __ quickly than type 1 muscle fibers
A. less, more
B. less, less
C. more, more
D. more,less
A. less, more
B. less, less
C. more, more
D. more,less
less,less
3
New cards
Which of the following is true
A. Norephinphrine receptors are expressed on the membranes of muscle fibers, at the neuromuscular junction
B.Primary motor cortex is located on the postcentral gyrus of the frontal lobe
C. An adult muscle fiber is generally targeted by multiple neuromuscular junctions
D.More space in the primary motor cortex is devoted to the hips than to the hands
E. Most lower motor neuron somata are found in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
A. Norephinphrine receptors are expressed on the membranes of muscle fibers, at the neuromuscular junction
B.Primary motor cortex is located on the postcentral gyrus of the frontal lobe
C. An adult muscle fiber is generally targeted by multiple neuromuscular junctions
D.More space in the primary motor cortex is devoted to the hips than to the hands
E. Most lower motor neuron somata are found in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
most lower motor nueron somata are found in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
4
New cards
Unilateral damage to motor cortex leads to paraylisis mainly on the __ side of the body. Unilatera damage to the spinal cord leads to paralysis mainly on the __ side of the body.
A. Ipsilateral, ipsilateral
B. Contralateral, ipsilateral
C. Ipsilateral, contralateral
D. Contralateral, contralateral
A. Ipsilateral, ipsilateral
B. Contralateral, ipsilateral
C. Ipsilateral, contralateral
D. Contralateral, contralateral
Contralateral, ipsilateral
5
New cards
Which of the following is NOT needed for a muscle contraction?
A. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
B.ATP
C. Actin
D. Myosin
E. Calcium ions
A. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
B.ATP
C. Actin
D. Myosin
E. Calcium ions
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors Which of t
6
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a function of the Basal ganglia?
A. Reflexes
B. Voluntary movement
C.Skill learning
D motivation and emotion
E informing the thalamus of actions
A. Reflexes
B. Voluntary movement
C.Skill learning
D motivation and emotion
E informing the thalamus of actions
Reflexes
7
New cards
What structure divides the striatum?
A Internal capsule
B. Caudate
C. Putamen
D. Nucleus accumbens
E. Substantia nigra
\
A Internal capsule
B. Caudate
C. Putamen
D. Nucleus accumbens
E. Substantia nigra
\
internal capsule
8
New cards
Which type of nuerons are concentrated in the substantia nigra, pars compacta (SNc)
A. Dopamine neurons
B. Gluatamate neurons
C. GABA neurons
D. Acetylcholine neurons
A. Dopamine neurons
B. Gluatamate neurons
C. GABA neurons
D. Acetylcholine neurons
Dopamine neurons
9
New cards
The striatum synapses onto the __ and releases __ .
A. Globus padillus pars externa, glutamate
B. Substantia nigra pars reticulate, dopamine
C. Globus padillus pars interna, GABA
D. Cortex, glutamate
E. Substantia nigra pars compacta, dopamine
A. Globus padillus pars externa, glutamate
B. Substantia nigra pars reticulate, dopamine
C. Globus padillus pars interna, GABA
D. Cortex, glutamate
E. Substantia nigra pars compacta, dopamine
Globus pallidus pars interna, GABA
10
New cards
The middle cerebellar peduncles are conncented to the?
A. Midbrain
B. Medulla
C. Pons
D.thalmus
E.Telencephalon
A. Midbrain
B. Medulla
C. Pons
D.thalmus
E.Telencephalon
Pons
11
New cards
Parallele fibers orginiate from which of hte following?
A.Granule cells
B. Purkinje cells
C. Inferior olive
D. Spinocerebellar tract
E. Dentate nucleus
A.Granule cells
B. Purkinje cells
C. Inferior olive
D. Spinocerebellar tract
E. Dentate nucleus
Granule cells
12
New cards
Which of the cerebellar functional domains receives information on muscle length and tension
A.Spinocerebellar tract
B. Cerebrocerebellum
C.Flocculondular lobe
E Dentate nucleus
A.Spinocerebellar tract
B. Cerebrocerebellum
C.Flocculondular lobe
E Dentate nucleus
Spinocerebellum
13
New cards
Which of the following correctly matches a cerebellar region with an output nucleus?
A. Floculonodular lobe-- Dentate nuclei
B. Spinocerebellum-- vestibular nuclei
C. Cerebrocerebellum --fastigial nuclei
D. vestibulocerebellum--interposed nuclei
E. Lateral cerebellar hemispheres -- dentate nuclei
A. Floculonodular lobe-- Dentate nuclei
B. Spinocerebellum-- vestibular nuclei
C. Cerebrocerebellum --fastigial nuclei
D. vestibulocerebellum--interposed nuclei
E. Lateral cerebellar hemispheres -- dentate nuclei
Lateral cerebellar himisphers-- dentate nuclei
14
New cards
Which of the following cranial nerves does NOT control a parasympathetic ganglion?
A. CN 3
B. CN 6
C. CN 7
D. CN 9
E. CN 10
A. CN 3
B. CN 6
C. CN 7
D. CN 9
E. CN 10
CN 6 (abducens)
15
New cards
What neurotransmitter is released by sympathetic pre-ganglionic neurons?
A. Acetylcholine
B. Nicotine
C. Epinephrine
D. GABA
E. Norepinephrine
A. Acetylcholine
B. Nicotine
C. Epinephrine
D. GABA
E. Norepinephrine
Acetylcholine
16
New cards
Neurons in the ___ control the secretion of digestive fluids?
A. Circular muscle layer of the gut
B. Myenteric plexus of the gut
C. submuscosal plexus of the gut
D. outer serosal layer of the gut
E. logitudinal muscle of the gut
A. Circular muscle layer of the gut
B. Myenteric plexus of the gut
C. submuscosal plexus of the gut
D. outer serosal layer of the gut
E. logitudinal muscle of the gut
Submucosal plexus of the gut
17
New cards
The enteric nervous system in humans is estimated to contain as many neurons as..?
A. The dorsal root ganglia of a human
B. The human spinal cord
C. the human brain
D. The brain of a blue whale
E. a rock
A. The dorsal root ganglia of a human
B. The human spinal cord
C. the human brain
D. The brain of a blue whale
E. a rock
the human spinal cord
18
New cards
Which of the following is not a conjugate eye movement?
A. vergence
B. vesstibulo-ocular reflex
C. saccades
D. Optokinetic movements
E. Smooth pursuit
A. vergence
B. vesstibulo-ocular reflex
C. saccades
D. Optokinetic movements
E. Smooth pursuit
Vergence
19
New cards
Which crainal nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle?
A. Abducens
B. oculomotor
C. Trochlear
D. Optic
E. Trigeminal
A. Abducens
B. oculomotor
C. Trochlear
D. Optic
E. Trigeminal
Abducens
20
New cards
What system is activated when you rotate your head, but the image on the fovea remains stationary?
A. Vestibular ocular reflex
B. Smooth pursuit
C. Optokinetic nystagmus
D. Saccades
E. Fixation
A. Vestibular ocular reflex
B. Smooth pursuit
C. Optokinetic nystagmus
D. Saccades
E. Fixation
Vestibular ocular reflex
21
New cards
The internuclear neurons cause which of the following to happen when looking to the left?
A. Cause the left medial rectus to contract
B. Cause the left lateral rectus to contract
C. Cause the right medial rectus to relax
D. Cause the right lateral rectus to contract
E. Cause the right medial rectus to contract
A. Cause the left medial rectus to contract
B. Cause the left lateral rectus to contract
C. Cause the right medial rectus to relax
D. Cause the right lateral rectus to contract
E. Cause the right medial rectus to contract
Cause the right medial rectus to contract
22
New cards
In the Papez circuit, the mammillary bodies receive input directly from the __ and then project their axons to the __
A. Hypothalamus via the fornix, septal nuclei
B. Hippocampus via the fornix, anterior nucleus of the thalamus
C. Cingulate gyrus, anterior nucleus of the thalamus
D. Anterior nucleus of the thalamus, fornix tract
E. Anterior nucleus of the thalamus, cingulate gyrus
A. Hypothalamus via the fornix, septal nuclei
B. Hippocampus via the fornix, anterior nucleus of the thalamus
C. Cingulate gyrus, anterior nucleus of the thalamus
D. Anterior nucleus of the thalamus, fornix tract
E. Anterior nucleus of the thalamus, cingulate gyrus
Hippocampus via the fornix, anterior nucleus of the thalamus
23
New cards
Urbach-Wiethe disease, which results in the bilateral loss of te amygdala, leads to…
A. Extreme irritability
B. decreased feelings of fear
C. confabulation
D. inability to form new declarative memories
E. loss of procedural memories
A. Extreme irritability
B. decreased feelings of fear
C. confabulation
D. inability to form new declarative memories
E. loss of procedural memories
decreased feelings of fear
24
New cards
Phinease gage experienced perhaps the ultimate job-related injury when a 1-1/2inch iron rod was shot through his skull. What part of the limbic system did it damage?
A. mammillary bodies and anterior nucleus of the thalamus
B. hippocampus and medial temporal lobe
C. Amygdala and anterior temporal lobe
D. Prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex
E. septal nuclei and anterior commissure
A. mammillary bodies and anterior nucleus of the thalamus
B. hippocampus and medial temporal lobe
C. Amygdala and anterior temporal lobe
D. Prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex
E. septal nuclei and anterior commissure
Prefrontal cortex and antieror cingualte cortex
25
New cards
In the papez circuit, the mamillary bodies receive input directly from the --- and then project their axons to the ---
\
\
Hippocampus via the fornix, anterior nucleus of the thalamus
26
New cards
Golgi tendon organs relay information via__ about __
A. la, weight bearing
B. la, phase of walk
C. la, posture
D. lb, phase of walk
E. lb, weight bearing
A. la, weight bearing
B. la, phase of walk
C. la, posture
D. lb, phase of walk
E. lb, weight bearing
lb, weight bearing
27
New cards
How is the subthalamic motor region involved with locomotion?
A. It initiates walking
B. it identifies where the limbs are in space
C. It’s part of the central pattern generator
D. It modulates speed of walking
E. It causes walking to cease ie it switches off the central pattern generator
A. It initiates walking
B. it identifies where the limbs are in space
C. It’s part of the central pattern generator
D. It modulates speed of walking
E. It causes walking to cease ie it switches off the central pattern generator
It modulates speed of walking
28
New cards
What is TRUE about the effects of the brain on locomotion
A. Glutamate is required to initate walking via descending pathways
B. The more intensly the mesencephalic locomotor region is stimulated, the slower the walking speed will be
C. Gait is not modulated by descending pathways
D. The cerebellum only receives information from ascending pathways
A. Glutamate is required to initate walking via descending pathways
B. The more intensly the mesencephalic locomotor region is stimulated, the slower the walking speed will be
C. Gait is not modulated by descending pathways
D. The cerebellum only receives information from ascending pathways
Glutamate is required to initiate walking via descending pathways
29
New cards
What is the effect in mice of knocking out the gene for EphA4
A. The axon of an ihibitory interneuron is unable to cross the midline
B. The spinocerebellar tract doesn’t form
C. Motor neuron axons become misguided and attempt to exit the spinal cord via dorsal roots
D. The axon of an excitatory interneuron is unable to corss the midline
E. The left and right legs extend in sychrony
A. The axon of an ihibitory interneuron is unable to cross the midline
B. The spinocerebellar tract doesn’t form
C. Motor neuron axons become misguided and attempt to exit the spinal cord via dorsal roots
D. The axon of an excitatory interneuron is unable to corss the midline
E. The left and right legs extend in sychrony
The left and right legs extend in sychrony
30
New cards
Which of the following statements is ture?
A. Ghrehlin release enhances appetite
B. Orexin is released by white fat
C. leptin release increases activity levels, which result in increased feeding
D. Lesions of the lateral hypohtalamus decrease feeding
E. Lesions of the medial hypothalamus increase feeding
A. Ghrehlin release enhances appetite
B. Orexin is released by white fat
C. leptin release increases activity levels, which result in increased feeding
D. Lesions of the lateral hypohtalamus decrease feeding
E. Lesions of the medial hypothalamus increase feeding
Ghrelin release enchaces appetite
31
New cards
What do you expect to see as a result of stimulating the dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus?
A. Increased blood pressure
B. Maturation of gametes
C. Maturation of gametes
D. Motor excitation
E. Tiredness
A. Increased blood pressure
B. Maturation of gametes
C. Maturation of gametes
D. Motor excitation
E. Tiredness
Increased blood pressure
32
New cards
Which of the following is an effect of oxytocin?
A. Slows the progression of labor at the end of pregnancy
B. Reduces milk let-down and ejection in females who have recently borne children
C. Increases the likehood of being dishonest in order to benefit your social group
D. Decreases racist behavior in males
E. Increases promiscuity in males in a monogamous relationship
A. Slows the progression of labor at the end of pregnancy
B. Reduces milk let-down and ejection in females who have recently borne children
C. Increases the likehood of being dishonest in order to benefit your social group
D. Decreases racist behavior in males
E. Increases promiscuity in males in a monogamous relationship
Increases likelihood of being dishonest in order to benefit your social group
33
New cards
They hypothalamus doesn’t act in isolation. Interactions of the preoptic nucleus with the limbic system might result in which of the following?
A. Hypothyroidism due to decreased
B. Hypothyroidism due to decreased release of thyrotropin-releasing hormone
C. Tightening your belt to reduce your hunger pangs
D. Purchasing four large orders of fries from McDonald’s when you’re really hungry
E. Putting on a sweater when your body temperature drops
A. Hypothyroidism due to decreased
B. Hypothyroidism due to decreased release of thyrotropin-releasing hormone
C. Tightening your belt to reduce your hunger pangs
D. Purchasing four large orders of fries from McDonald’s when you’re really hungry
E. Putting on a sweater when your body temperature drops
Putting on a sweater when your body temperature drops
34
New cards
During the two-point discrimination test, the mean distance which students could discern was 2mm on the index finger and 20mm on the forehead. P value was sig (.03
Density of sensory recptors in the skin of the index finger is higher than that of the sensroy receptors in the skin of the forehead
35
New cards
Which statement about the fovea is true
A. There is a high density of rods in this region of the retina
B. This is the region of the retina respoinsible for peripheral vision
C. This is the region of the retina where the optic nerve exits the eye
D. This is the region of the retina responsible for reading vision
A. There is a high density of rods in this region of the retina
B. This is the region of the retina respoinsible for peripheral vision
C. This is the region of the retina where the optic nerve exits the eye
D. This is the region of the retina responsible for reading vision
This is the region of the retina responsible for reading vision
36
New cards
Which thalamic nucleus is a relay for nucleus for visual stimuli?
A. Medial geniculate nucleus
B. inferior colliculus
C. Lateral geniculate nucleus
D. Superior colliculus
E. Ventrolateral nucleus
A. Medial geniculate nucleus
B. inferior colliculus
C. Lateral geniculate nucleus
D. Superior colliculus
E. Ventrolateral nucleus
Lateral geneiculate nucleus
37
New cards
The inferior colliculus…
A. Is a strucutre in the pons
B. Responds primarily to visual stimuli
C. Is located at the level fo the cerebral aqueduct
D. Can be found at the same level as fasciculus gracilis
E. Is a ventral structre
A. Is a strucutre in the pons
B. Responds primarily to visual stimuli
C. Is located at the level fo the cerebral aqueduct
D. Can be found at the same level as fasciculus gracilis
E. Is a ventral structre
Is located at the elvel of the cerebral aqueduct
38
New cards
Which of the following is not a structure in the caudal medulla?
A. Sensory decussation
B. Spinal trigeminal nucleus
C. Cuneate fasciculus
D. Cerebral aqueduct
E, Nucleus gracilis
A. Sensory decussation
B. Spinal trigeminal nucleus
C. Cuneate fasciculus
D. Cerebral aqueduct
E, Nucleus gracilis
Cerebral aqudeuct
39
New cards
Which of the following forms a prominent gross structure of the rostral medulla?
A. inferior olive
B. Vestibular nuclei
C. Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
D. Solitary tract
E. hypoglossal nucleus
A. inferior olive
B. Vestibular nuclei
C. Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
D. Solitary tract
E. hypoglossal nucleus
Inferior olive
40
New cards
Which sub-region of the striatum is only present rostral to the thalamus?
A. Putamen
B. caudate nucleus
C. Nucleus accumbens
D. Globus pallidus
E. Subthalamic nucleus
A. Putamen
B. caudate nucleus
C. Nucleus accumbens
D. Globus pallidus
E. Subthalamic nucleus
nucleus accumbens
41
New cards
The medial geniculate nucleus relays__ inofmation
A. Motor
B. vision
C. hearing
D. Touch and pain
E. olfactory
A. Motor
B. vision
C. hearing
D. Touch and pain
E. olfactory
hearing
42
New cards
Layer 4 of the neocortex receives input from which of the following?
A. superior colliculus
B. Contralateral cerebral cortex
C. olfactory bulb
D. brainstem and spinal cord
E. Thalamus
A. superior colliculus
B. Contralateral cerebral cortex
C. olfactory bulb
D. brainstem and spinal cord
E. Thalamus
Thalamus
43
New cards
The two halves of the thalamus are seperated by which space
A. 3rd ventricle
B. 4th ventricle
C. cerebral aqueduct
D. lateral ventricle
E. Interpeduncluar fossa
A. 3rd ventricle
B. 4th ventricle
C. cerebral aqueduct
D. lateral ventricle
E. Interpeduncluar fossa
Third ventricle
44
New cards
All of the following crainal nerves innervate skeletal muscle,\]. Which of these crainal nerves innvervates something in addition to skeletal muscle
A. Hypoglassal
B. Glossopharyngeal
C. Abducens
D. Spinal accessory
E. Trochlear
A. Hypoglassal
B. Glossopharyngeal
C. Abducens
D. Spinal accessory
E. Trochlear
Glossopharyngeal
45
New cards
Injury to the trigemnial nerve would most likely result in impairment in which of the following?
A. Salivating
B. Smiling
C. Balancing
D. Swallowing
E. Chewing
A. Salivating
B. Smiling
C. Balancing
D. Swallowing
E. Chewing
chewing
46
New cards
Which of the following is FALSE?
A. The glossopharyngeal nerve detects blood pressure in the carotid artery
B. The vagus nerve senses blood oxygenation in the aortic arch
C. parts of the optic nerves cross the midline on the ventral surface of the brain
D. The trigeminal nerve exits the dorsal surface of the brain
E. The oculomotor nerve innervates the inferior rectus
A. The glossopharyngeal nerve detects blood pressure in the carotid artery
B. The vagus nerve senses blood oxygenation in the aortic arch
C. parts of the optic nerves cross the midline on the ventral surface of the brain
D. The trigeminal nerve exits the dorsal surface of the brain
E. The oculomotor nerve innervates the inferior rectus
The trigemnial nerve exits the dorsal surface of the brain
47
New cards
Which is NOT a function of the facial nerve?
A. Innervating skeletal muscle
B. Special sensation of taste
C. general sensation near the ear
D. sensing of blood oxygenation and CO2
E. Autonomic input to nose, eyes and mouth
A. Innervating skeletal muscle
B. Special sensation of taste
C. general sensation near the ear
D. sensing of blood oxygenation and CO2
E. Autonomic input to nose, eyes and mouth
Sensing of blood oxygenation and CO2
48
New cards
Which of the following is True?
A. Golgi tendons sense muscle length
B. TRPV1 light mechanical stimuli and temperatures between 31 and 40 degrees C
C. The main somatosensory nerve for the head is the facial nerve
D. Dorsal roots contain both motor and sensory axons
E. The axons of thalamic neurons do not cross the midline as they project to the somatosensory cortex
A. Golgi tendons sense muscle length
B. TRPV1 light mechanical stimuli and temperatures between 31 and 40 degrees C
C. The main somatosensory nerve for the head is the facial nerve
D. Dorsal roots contain both motor and sensory axons
E. The axons of thalamic neurons do not cross the midline as they project to the somatosensory cortex
The axons of thalamic neurons do not cross the midline as they project to the somatosensory cortex.
49
New cards
Damage to the __ of the thalamus could impair the relay of somatosensory information to the cerebral cortex
A. Lateral geniculate nucleus
B. Medial geniculate nucleus
C. Ventral posterior lateral nucleus
D
A. Lateral geniculate nucleus
B. Medial geniculate nucleus
C. Ventral posterior lateral nucleus
D
Ventral posterior lateral nucleus
50
New cards
Neurons that sense vibration and light touch
A. Have axons that are usually unmyelinated
B. Terminate in free nerve endings in the skin
C. have primary afferent cell bodies located ini muscles
D. Have axons that ascend through the dorsal columns
E. Frequently also sense itch
A. Have axons that are usually unmyelinated
B. Terminate in free nerve endings in the skin
C. have primary afferent cell bodies located ini muscles
D. Have axons that ascend through the dorsal columns
E. Frequently also sense itch
have axons that ascend through the dorsal columns
51
New cards
Which of the following accuratley describes Piezo2?
A. It responds to noxious heat and capsaicin
B. It has a G-protien coupled receptor
C. it has two subunit arms
D. It can form a channel through which ions pass, causing the cell to depolarize
E. The nobel prize was awarded for its discovery in 1921
A. It responds to noxious heat and capsaicin
B. It has a G-protien coupled receptor
C. it has two subunit arms
D. It can form a channel through which ions pass, causing the cell to depolarize
E. The nobel prize was awarded for its discovery in 1921
It can form a channel through which ions pass, causing the cell to depolarize
52
New cards
Stimulation of the periaqueductal gray results in
A. Increased muscle tone
B. Decreased visual acuity
C. altered hearing
D. analgesia
E. increased pain perception
A. Increased muscle tone
B. Decreased visual acuity
C. altered hearing
D. analgesia
E. increased pain perception
analgesia
53
New cards
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. Mechanical nociceptors have large receptive fields
B.TRPV1 is activated by tempratures between below 0 degrees C
C. persistent pain leads to a smaller nocieptive response
D. Stimulating the rostral ventromedial medulla can facilitate pain
E. Pain afferents generally have high conduction velocities
A. Mechanical nociceptors have large receptive fields
B.TRPV1 is activated by tempratures between below 0 degrees C
C. persistent pain leads to a smaller nocieptive response
D. Stimulating the rostral ventromedial medulla can facilitate pain
E. Pain afferents generally have high conduction velocities
Stimulating the rostral ventromedial medulla can facilitate pain
54
New cards
Which of the following type of pain can be characterized as outlasting the duration of healing?
A. Chronic pain
B. Persistent pain
C. acute pain
D. nociceptive pain
A. Chronic pain
B. Persistent pain
C. acute pain
D. nociceptive pain
Chronic pain
55
New cards
Complete the sentance correctly. Rods…
A. aid in the detection of motion
B. are less sensitive than cones to light intesity
C. synapse directly onto ganglion cells
D. provide information about color to the brain
E. are important for high acuity vision
A. aid in the detection of motion
B. are less sensitive than cones to light intesity
C. synapse directly onto ganglion cells
D. provide information about color to the brain
E. are important for high acuity vision
aid in the detection of motion
56
New cards
Which of the following statements is false?
A. In the dark, photoreceptors are depolarized
B. Zinc deficiency can lead to night blindness
C. amacrine cells enhance contrast through lateral interactions
D. The highest desity of cones is in the fovea
A. In the dark, photoreceptors are depolarized
B. Zinc deficiency can lead to night blindness
C. amacrine cells enhance contrast through lateral interactions
D. The highest desity of cones is in the fovea
Amacrine cells enchance contrast through lateral interactions
57
New cards
Which of the following is an attribute of an M-type cell
They are important for motion perception
58
New cards
Which of the following is TRUE?
A. The highest density of cone photorecptors is located at the head of the optic nerve
B.Retinal ganglion cells synapse in the suprachiasmatic nucleus
C. in the visual cortex, inputs from the thalamus synapse in layer 2
D. the visual cortex mediates the pupillary light reflex
E. Strabismus lead sto all layers of the visaul fortex being binocular
A. The highest density of cone photorecptors is located at the head of the optic nerve
B.Retinal ganglion cells synapse in the suprachiasmatic nucleus
C. in the visual cortex, inputs from the thalamus synapse in layer 2
D. the visual cortex mediates the pupillary light reflex
E. Strabismus lead sto all layers of the visaul fortex being binocular
Retinal ganglion cells synapse in the suprachiasmatic nucleus
59
New cards
Axons in the temporal retina __ cross in the optic chiasm, axons in the nasal retina -- cross in the optic chiasm
A. don’t, do
B. do, don’t
C. do, do
D. Don’t, don’t
A. don’t, do
B. do, don’t
C. do, do
D. Don’t, don’t
don’t, do
60
New cards
Which gives the correct path visual information takes to get to the thalamus?
A. optic tract, optic nerve, lateral geniculate
B. optic tract, lateral geniculate, optic nerve
C. optic nerve, lateral geniculate, optic tract
D. optic nerve, optic tract, lateral geniculate
E. lateral geniculate, opotic tract, optic nerve
A. optic tract, optic nerve, lateral geniculate
B. optic tract, lateral geniculate, optic nerve
C. optic nerve, lateral geniculate, optic tract
D. optic nerve, optic tract, lateral geniculate
E. lateral geniculate, opotic tract, optic nerve
Optic nerve, optic tract, lateral geneiculate
61
New cards
Cutting the right optic tract would be expected to result in?
A. Loss of central vison
B. loss of peripheral vison
C. loss of right half of one’s visual field
D. loss of the left half of one’s visual feild
E. Loss of the lower halves of both visual fields
A. Loss of central vison
B. loss of peripheral vison
C. loss of right half of one’s visual field
D. loss of the left half of one’s visual feild
E. Loss of the lower halves of both visual fields
Loss in the left half in on’s visual vield
62
New cards
Which o fthe following statements is FALSE?
The cell bodies of vestibular afferents are found in the sprial gnaglion
63
New cards
Supose a tone with a frequnecy of 110hz resonates 2 mm from the apex of the cochlea, a tone with a frequency of 440 hz resonates 5 mm from the apex of the cochlea, where will a tone with a frequency of 1760 hz resonate?
8 mm from the apex of the cochlea
64
New cards
Which is NOT a cranial nerve nucleus that the vestibular nuclei project to?
CN 5, trigeminal
65
New cards
If the stapes was removed from the ear, vibrations from sound would not be passed directly onto the…
oval window
66
New cards
The cell bodies of the primary afferent neurons that sense smell are located in which of the following?
Nasal epithelium
67
New cards
How many odorant receptors are expressed by each olfactory primary afferent neuron?
1
68
New cards
Which cranial nerve provides taste senestaion in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
Facial
69
New cards
T2-type taste receptors are involved with sensing which of the following tastes?
Bitter
70
New cards
Which of the following histochemical staning methods is most helpful for visualzing dendritic spines?
Golgi stain
71
New cards
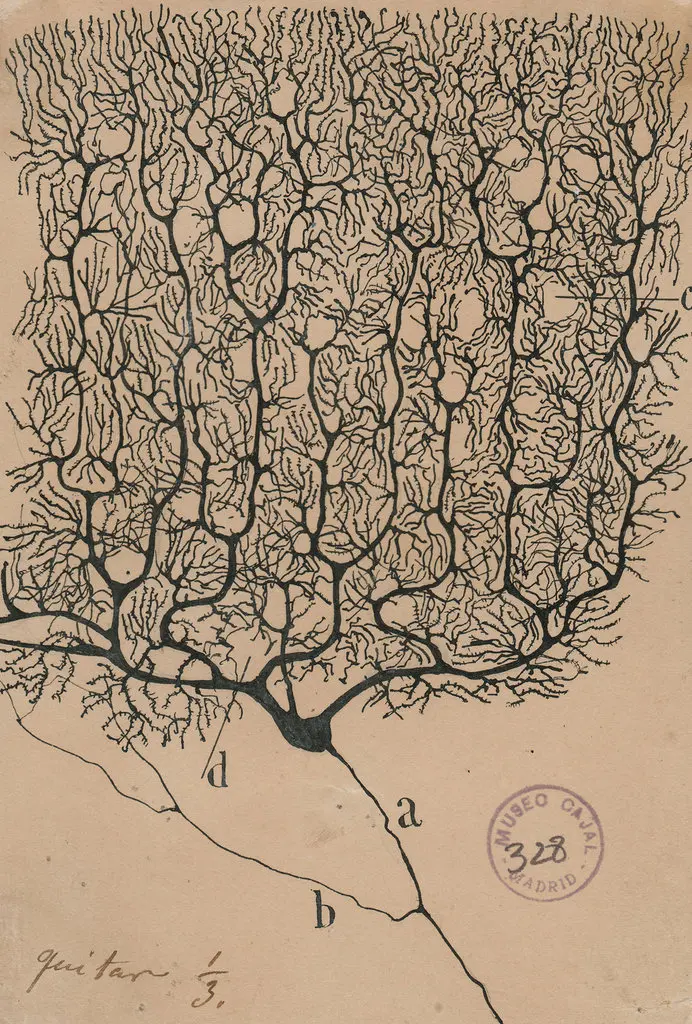
Which brain region is the most likely location for the drawing of the cell shown below?
Cerebellum
72
New cards
What brain region is shown in the Nissil-stained image below
Hippocampus
73
New cards
Neurons have a large amount of nissle substance that can be stained with dyes like cresyl violet. What cell structure makes up this substance?
Rouch endoplasmic reticulum
74
New cards
The resting memebrane potential of a neuron is closest tot eh equilibrium potential of which of the following ions?
Potassium
75
New cards
What is responsible for the rising phase of the neuronal actoin potential?
Voltage-gated sodium channels
76
New cards
Why do changes in the concentration of extracellular sodium affect the resting membrane potetial less than changes in the concentration of extracellular potassium?
There are more potassium channels in the neuronal membrane
77
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a gilal cell type
Parietal cells
78
New cards
What plane of sectioning would divide the rostral part form the caudal part of the cerebral cortex?
Coronal
79
New cards
In the peripheral nervous system, gropus of neuronal somata are called __, and bundles of axons are called --
Ganglia, nerves
80
New cards
The two hemispheres of the brain are separated by which of hte following?
Interhemisphereic fissure
81
New cards
What does ectoderm give rise to?
Skin, nervous system
82
New cards
What occurs during the G0 phase of the cell cycle?
Mitosis no longer occurs
83
New cards
The __ induces the __ to become the neural plate
mesoderm, ectoderm
84
New cards
The basal plate develops into __ neurons __ the spinal cord.
motor, exiting
85
New cards
Pick best answer. What structure produces most of the cerebrospinal fluid?
Choroid plexus
86
New cards
What is major result of the CSF not draining properly?
Hydrocephalus
87
New cards
The cerebral aqueduct allows cerebrospinal fluid to move directly from the __ ventricle to the __ ventricle?
third, fourth
88
New cards
In principle, there are multiple sites from which CSF could be sampled. From which of the following sites is the sampling LEAST likely to result in damage to the CNS?
the space between the L3 and the L4 vertebra
89
New cards
The anterior cerebral artery primarily supplies blood flow to which of the following?
midline of the cerebral cortex
90
New cards
What do the dural venous sinuses drain into?
Internal jugular vein
91
New cards
The right ventricle pumpls __ blood to the __
deoxygenated, lungs
92
New cards
What alleviates decreased oxygen to the brain
Vasodilation
93
New cards
Synthesis of mRNA from DNA in the nucleus is a process called…
Transcription
94
New cards
What mechanism moves microtubules and neurofilaments away form the cell body?
Slow anterograde transport
95
New cards
Nissl substance is composed of which of the following?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
96
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a function of astrocytes?
Increases axonal conduction velocity
97
New cards
What is the resting membrane potential?
about -70mv
98
New cards
Which of these comes first during an action potential?
Depolarization of the cell to its threshold
99
New cards
Which of the following is a result of the refractory period?
Ensures that the action potential is only propogated in one direction
100
New cards
Which of the following has the greatest effect on axonal conduction velocity?
Diameter of the axon