Intracranial Regulation
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
CSF is clear and colorless, with a similar composition to other ___. It has a specific gravity of 1.00_ and minimal ____ and no ____
ecf. 7, wbc, rbc
CSF is produced in choroid plexus of ____ and circulates around brain and spinal cord surface. It is drained by the ___ ventricle
ventricles, fourth
obstructive hydrocephalus is a blockage of CSF flow in the ____ system
ventricular
CSF produced at ____ml/day rate, ventricle and subarachnoid space has about _____ fluid
500, 125-150
brain doesnt store ___ so it requires a constant supply of ____
nutrients, oxygen
Brain receives around ___% of cardiac output, which is ___mL per minute of blood flow
15, 750
arterial and venous vessels are ___ parallel in the brain. The blood vessels have ___ layers instead of 3, which make them more prone to rupture
not, 2
In the brain veins dont follow ____ ___ and also don’t have ____
arterial circulation, valves
BBB is formed by ____ cells of the brains capillaries that form ___ __
endothelial, tight junctions
disorders affecting LOC
IICP patho
brain swelling, increased icp, hypoxia, further secondary injury, more swelling, more icp
IICP causes
HTN, strokes
IICP infant manifestations
bulging fontanelles, separated sutures, downward deviation of eyes, cushings triad, sensitive to stimuli, fixed and dilated pupils
cushings triad
increased systolic and pulse pressure, bradycardia, decrease respirations
IICP adult clinical manifestations
ams, incontinent, change in pupil size and light reaction, cushings, unilateral weakness, posturing, meningeal irritation
decorticate is arms ____ and indicates issue with ____ ____
in, cerebral cortex
decerebrate is arms ___ and indicates issue with ____. its the worst
out, midbrain
meningeal irritation clinicals
kernigs, brudzinskis
kernigs is pain and jerking when ____ raised. Brudzinskis is ____ rigidity so entire upper region moves with it
legs.nuchal
GCS grid
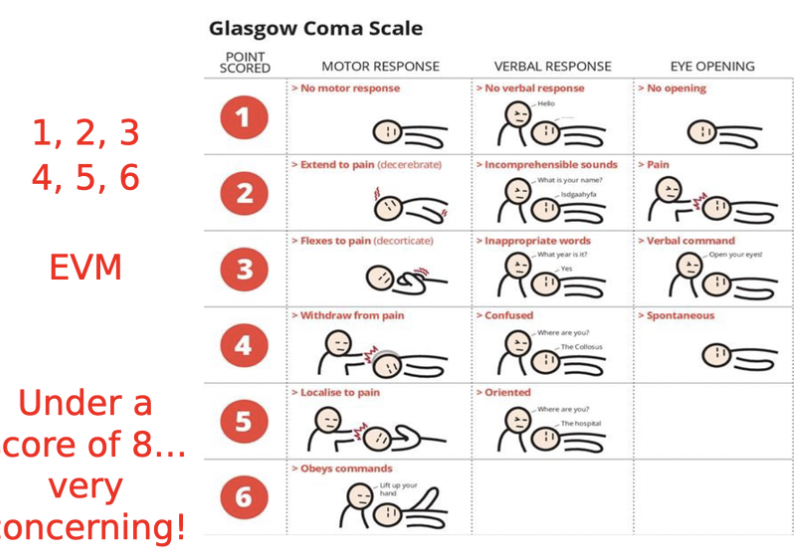
early IICP ss

Late ss of IICP

IICP Dx
ABGs, ICP monitoring, lumbar puncture
Increased ___ and ___ will vaso ____ and increase ___ bc more acidity
co2, h, dilate, icp
lumbar puncture isnt common because it can ____ the brain
herniate
IICP complications
herniation, DI, SIADH, hyponatremia
IICP medical tx
diuretics, hypertonic saline, corticosteroids for cerebral edema , antiseizure, NM blocking agents, Ca blockers, vasopressors, mannitol
mannitol role to reduce ICP
pulls water out of brain tissue and diuresis
IICP interventions table
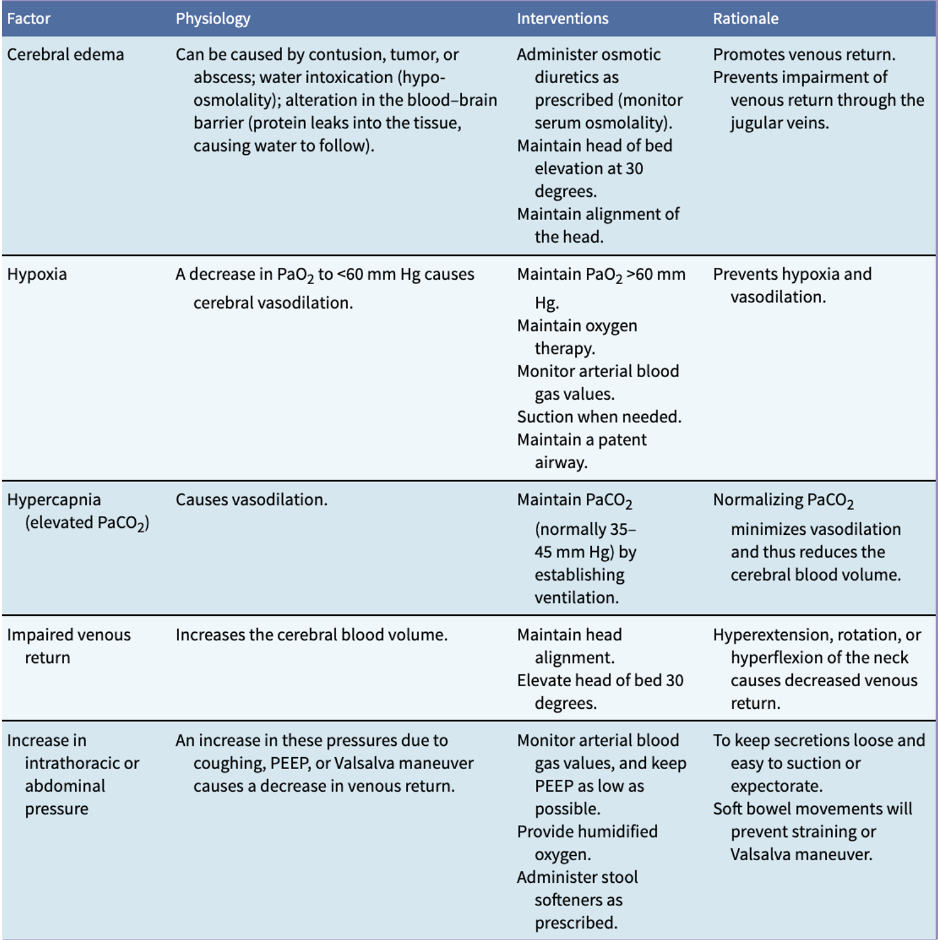
IN IICP, BP, pulse, LOC, pupils, and motor function are checked
hourly
Aneurysm precautions
bed rest, HOB up, constipation, DVT
Vasospasm ss
headache, decreased response, aphasia or partial paralysis
vasospasm tx
ca blocker
hydrocephalus is blood in subarachnoid space. ss is x3. Tx with a _____ shunt
drowsiness, behavior change, ataxic gait. Ventriculoperitoneal
IICP positioning
HOB up, neutral head and neck, no flexion, log roll
IICP oxygenation nursing cares
suction 15s2m, auscultate q8h, TBI mgmt
PaCO2 should be under ___mmHg after hyperventilation
30
IICP GI nursing care
stool softeners, bowel protocol, no coughing or enemas/cathartics
IICP temperature nursing cares
acetaminophen, cooling blankets. Shivering means increase metabolic rate and ICP
rotation/flexion of neck or hip causes intraabdominal and intrathoracic _____ ____ which means ICP increase
pressure increase
Before suctioning IICP should _____ with 100 o2 before and limit to 15 secs
hyperventilate
neutral/midline position of head promotes
venous drainage
IICP fluid balance nursing cares
diuretics, corticosteroids for edema, hypertonics, slow IVs, oral hygiene
hyperhypoiso
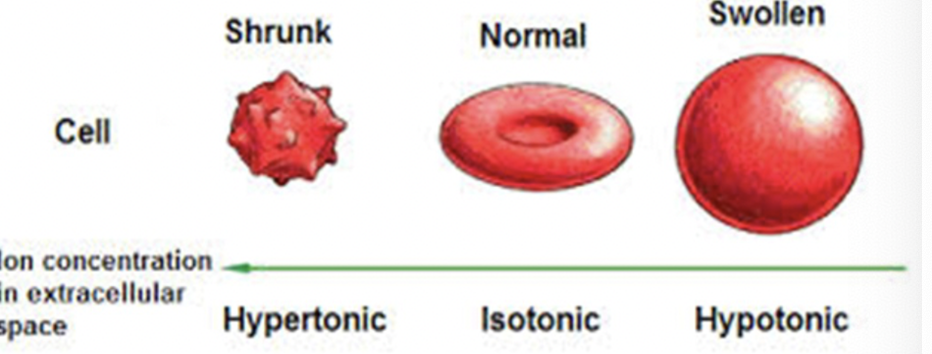
if UO is GREATER than 200/mL for 2+ hrs this indicates
diabetes insipidus
TIA is early warning signs of a ____ stroke, lasts from a few mins up to 24 hrs
ischemic
TIA Tx
carotid endardectomy, stenosis
TIA complications
stroke, CN injury, infection/hematoma, carotid artery disruption, hypotension to ischemia
Stroke dx
noncontrast CT, ECG afib, ultrasound
Stroke prevention
antithrombotics, anticoagulation, BP control, statins
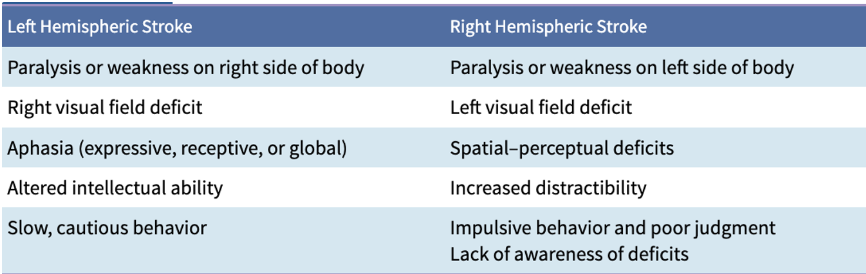
Ischemic vs hemorrhagic clinicals
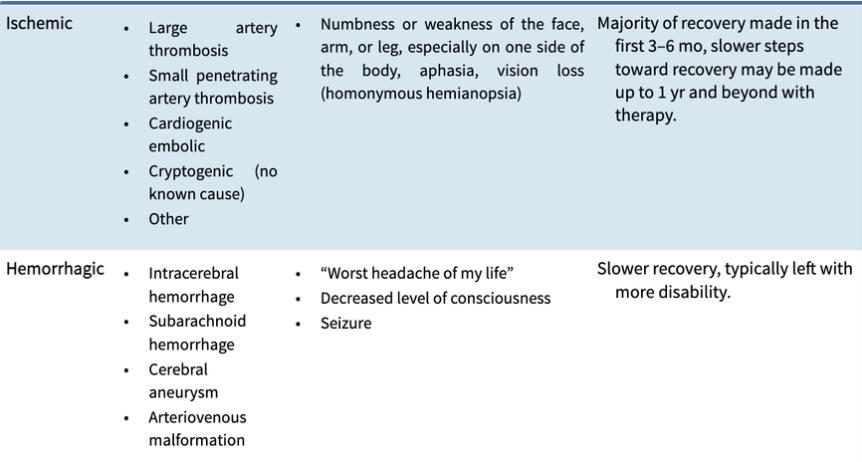
Right vs left side hemispheric stroke
thrombolytic therapy reqs

door to needle time needs to be under ____ and should start tpa within ____ hrs of onset
one hour, 4-6
tpa moa
convert plasminogen to plasmin to break down fibrin
tpa guidlines of ____mg/kg with a max dose of ___. The first 10% is given ____ over one minute, the rest is given over ___ hour
0.9, 90. IVB, 1
Contraindications for tPA
4.5, INR under 1.7, warfarin, intracranial issue hx
in Afib INR target of ___, BP should be under ____mmhg
2-3, 185/110
ischemic stroke nursing tx
HOB up, bedrest, permissive HTN, no oversedation or rapid diuresis, alignment, prone position to promote hyperextension, ROM , fiber and 2-3L water, dysphagia help, regular toilet
ischemic stroke complications
swallowing, IICP, meningeal irritation, UTI, arrhythmias, hyperglycemia
most common hemorrhagic stroke is x2
intracerebral and subarachnoid
Causes of hemorrhagic strokes
cerebral amyloid angiopathy, aneurysms, avms
cerebral amyloid angiopathy def
damage from deposit of beta amyloid proteins in vessels
aneurysms def
dilation of cerebral artery walls
avms def
tangle of vessels that lack a cap bed with leaves it prone to rupture
most common cause of stroke for young people is dt
avms
hemorrhagic stroke from IICP and meningeal irritation signs
ha, photophobia, nuchal rigidity
hemorrhagic stroke clinicals
projectile vomit, severe headache
catecholamine surger from hemorrhagic stroke can lead to x2 complications
htn and arrhythmias
it avm/aneurysm that leaks blood and has a clot that seals the rupture site there is either no ss or severe bleeding and a fast
death
intracerebral hemorrhage is bleeding in the
brain tissue
subdural hematoma is when blood collects between . it is a _ problem and the worst one
dura and brain, venous
epidural hematoma is blood between _____ and it is an issue of the ____
skull and dura, arterial
hemorrhagic stroke complications
vasospasm, seizures, hydrocephalus, rebleeding, hypona, pneumonia, cerebral hypoxia
vasospasm is usually ____ after hemorrhage and to tx you ___ aneurysm or use meds like ____ blockers
7-9 days, clip, ca
hemorrhagic strok eroutine meds
htn, analgesics, sedation, seizures, nv, gastric protection, steroids, antispasm
sbp goal is
140