Everything
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
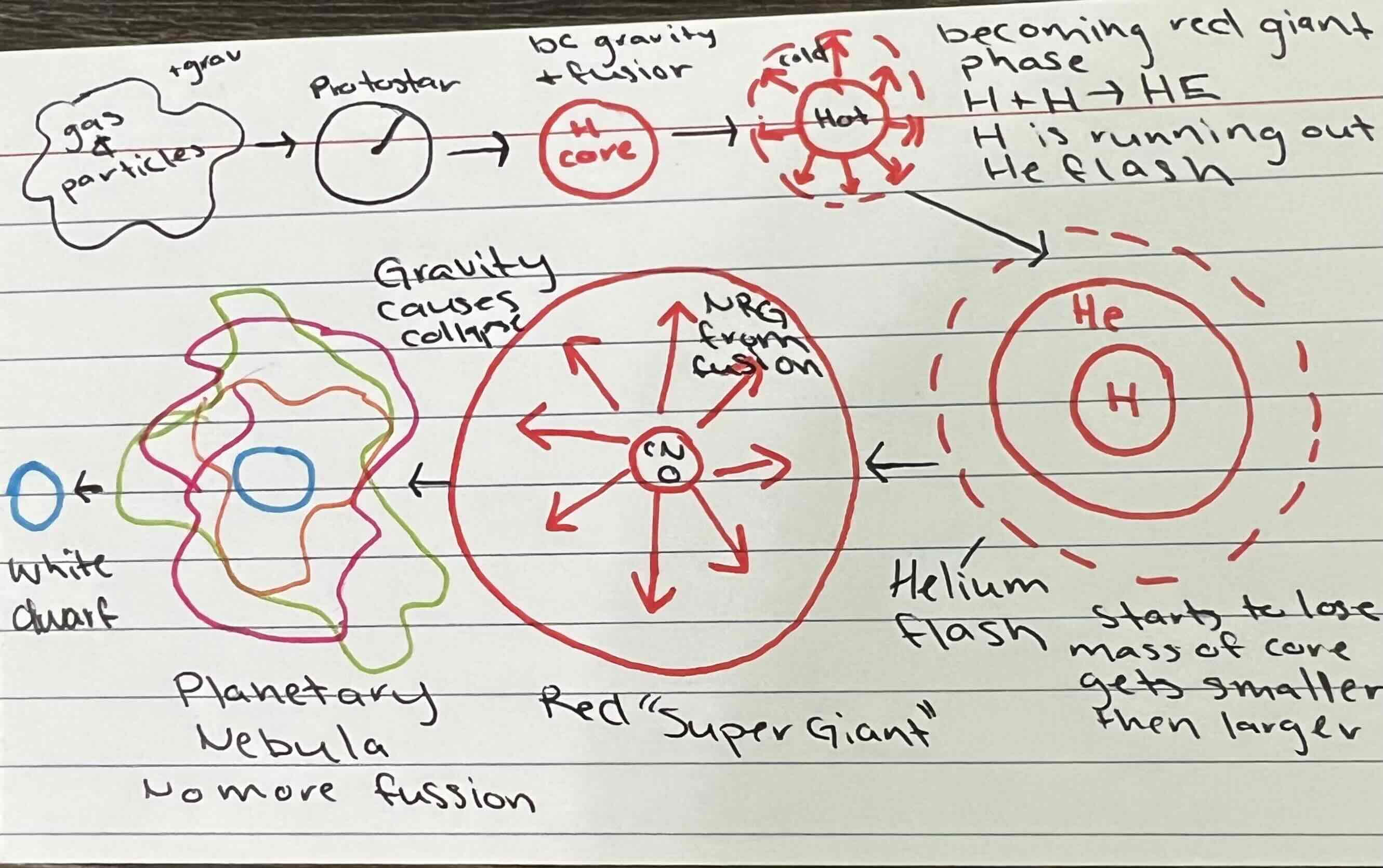
Stellar Evolution mass less than 1.4 times the mass of the sun
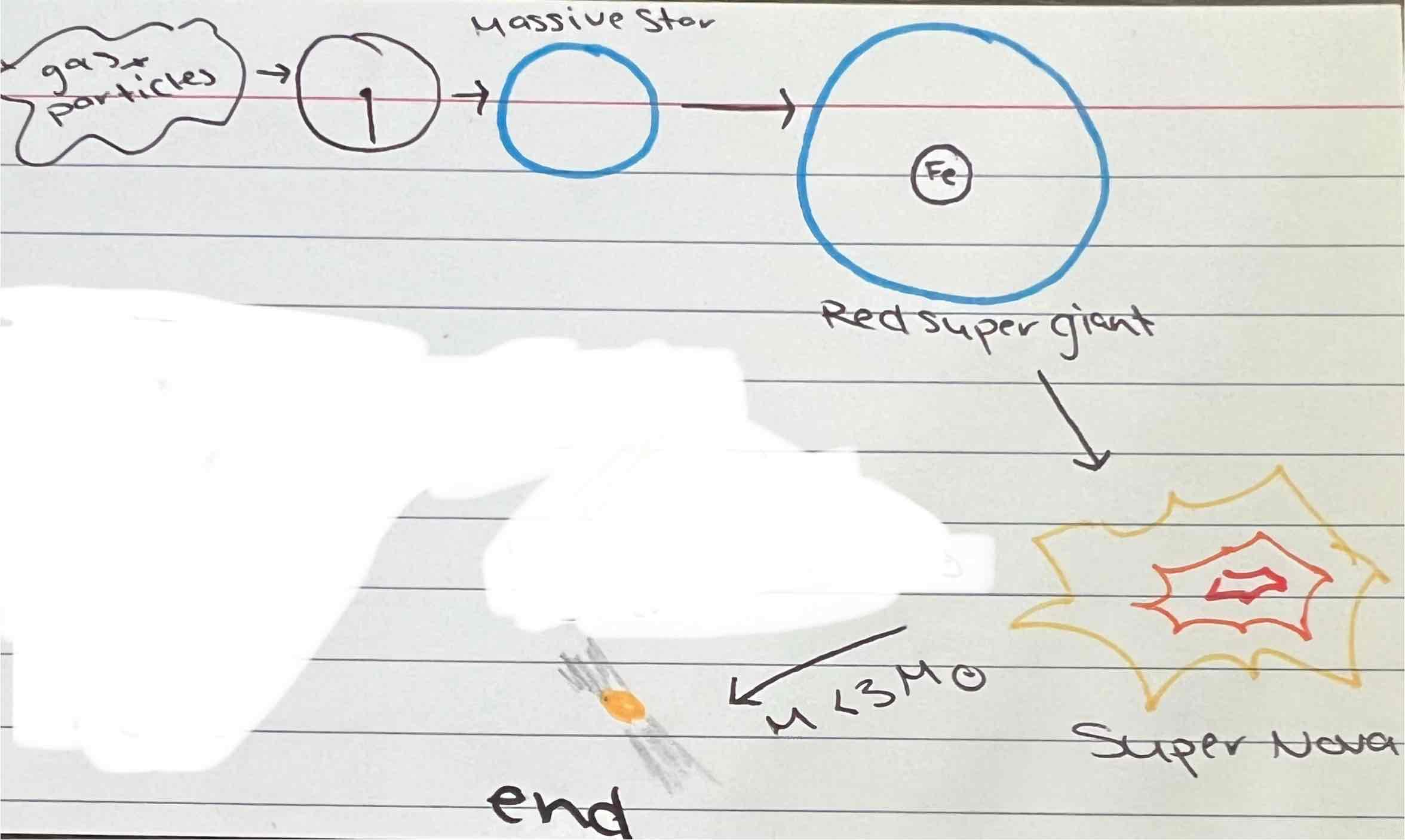
Stellar evolution with a mass greater than 1.4 times the mass of the sun and greater than 3 times the mass of the sun
Stellar evolution with a mass greater than 1.4 times the mass of the sun and less than 3 times the mass of the sun
Kinetic molecular theory of gas
Large number of identical molecules
Volume of gas is negligible
No forces between molecules
Motion is random
All collisions are elastic (Energy is conserved)
When Is the kinetic theory of gas no longer usable
Molecules are compressed
Close to a phase change(All internal energy is potential)
What is the Oppenheimer Volkoff limit
when the mass of a star is greater than three times the mass of the sun, it will become a black hole
When the mass of the star is less than three times the mass of the sun, it will turn into a neutron star
Why are scaphoid variables not stable
Because fusion increases as they burn the remaining parts of an element then temperature increases surface area decreases due to gravity, pulling it in and then surface area increases and temperature decreases so we pulsating brightness
What are the top five greenhouse gases?
Water vapor
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Oxygen and ozone
Nitrogen oxide
Kilo
10³
Centi
10-²
Milli
10-³
Micro
10^-6
Nano
10^-9
v=u+at
v= final velocity m/s
u= initial velocity m/s
a= acceleration m/s²
t= time s
s= ut+ ½ at²
s= displacement m
u= initial velocity m/s
a= Acceleration m/s²
t= time s
Energy
Joules
Si units kg m²/s²
Power
Watt (w)
Si units kg m²/s³
Gas laws
Boyles law
Charles law
Pressure law
Boyle law
As volume increases pressure decreases
Charles law
As temperature increases volume increases
Pressure law
And temperature increases pressure increases
Emmisivity
Amount reflected my a surface
e≈ power radiated by a surface
Power radiated from a black body radiator of the same temperature and area
Albedo
Albedo =power scattered by a surface
incident power
Reflected ex. Snow
Albedo and emissivity
are always between 0 and 1 Usually add up to one
hubbles constant
70 km/s Mpc
Hubbles law
The red shift due to the growth of the universe. The growth of the universe stretches space and time increasing the distance between objects this then stretches the wave length, leading to an observed red shift.

Blue shift
Decreased wavelength decreased distance form and an object
Object is moving towards you in space
Redshift
Increased wavelength increased distance
Object is moving away from us in space
Doppler shift
Doppler shift
Z= change in wavelength /original wavelength = v/c
Z= shift
v= velocity
c= speed of sound
Black body radiator
emissivity = 1
range of wavelengths when heated
Effects of green house gasses
Rising sea level
Increased humidity
Melting glaciers
Less sea ice
Less snow cover
As peak wavelength increases
Temperature decreases and frequency increases
Cosmic scale factor
z = R/Intial R-1
Luminosity
Power emitted by a star
Watts (W)
L = oAT^4
Brightness
The intensity of a star
Wm²
b= L/4(pi)(r²)
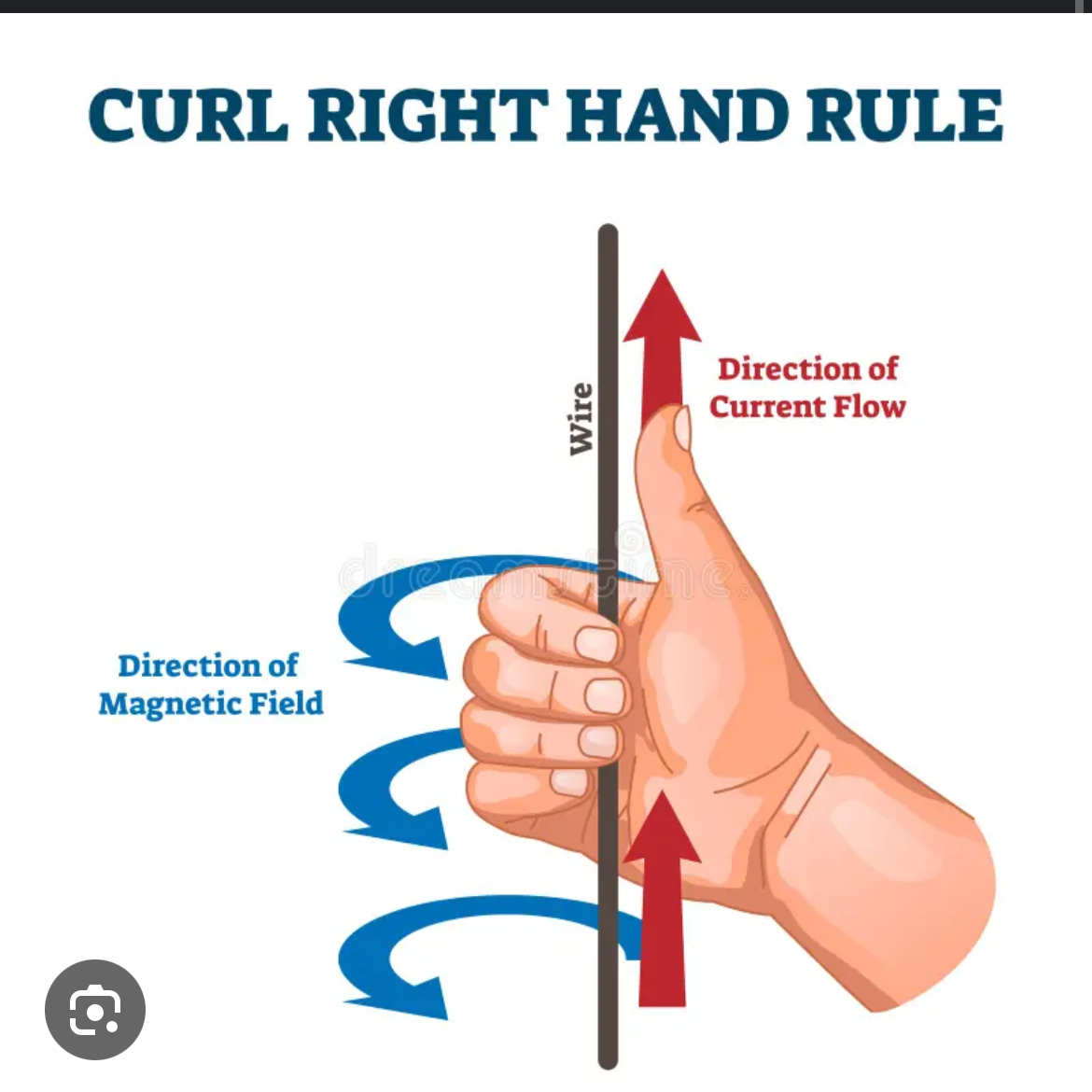
Right hand rule
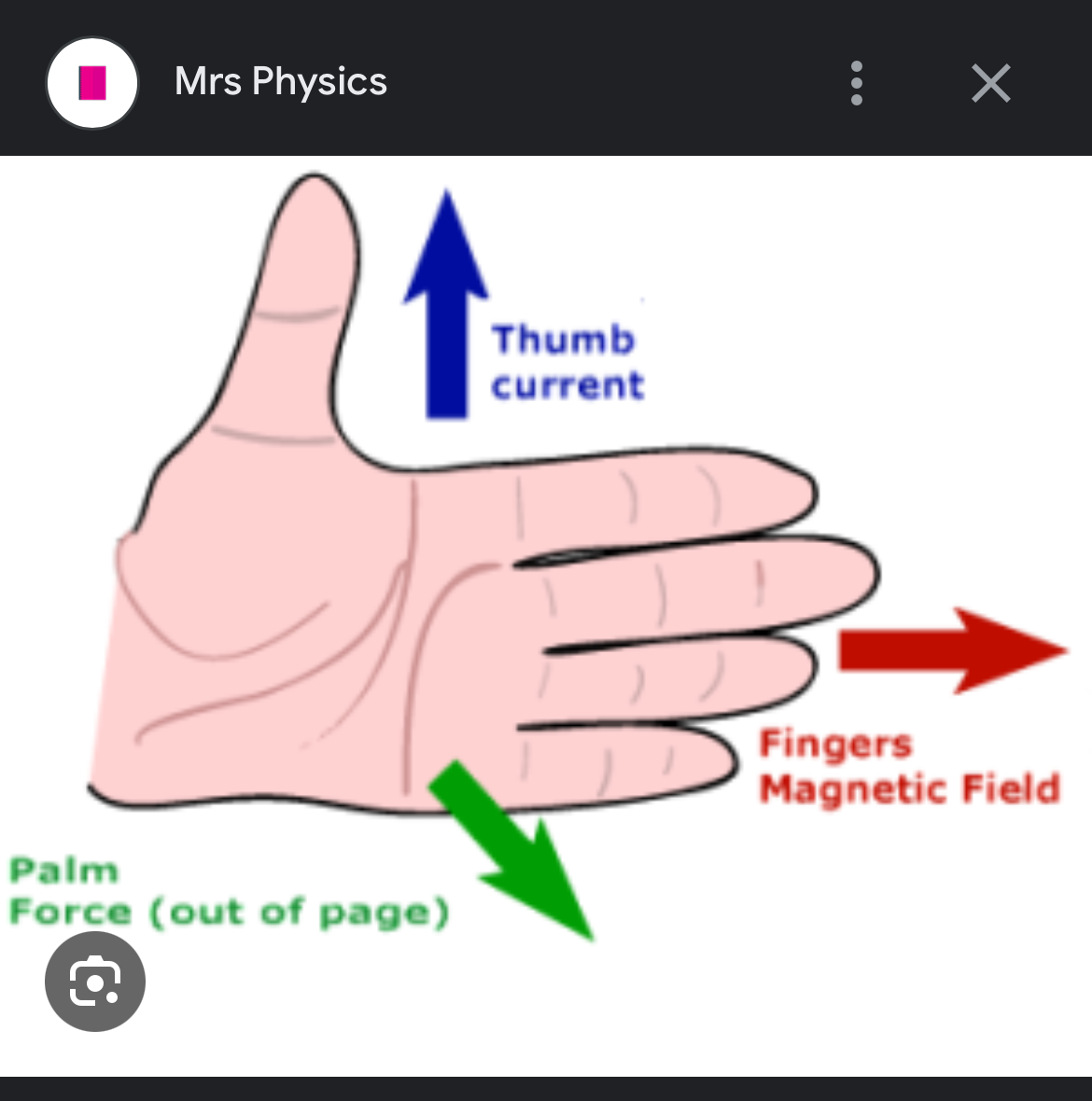
Slap rule
Temperature
Measuring how hot or cold something is
Average kinetic energy
Absolute zero
All molecules stop moving
Relation ship between larger objects and energy
Bigger objects have higher internal energy because it has more mass - more mass= more total energy
Heat transfers
From hot to cold
Because fast moving particle collide with slow moving particles and increase their velocity, kinetic energy and temperature
Specific heat
Amount of energy required to heat one kilogram by one degree kelvin
Conductor
Material that energy can be transferred as heat
Insulator
Material that transfers energy poorly
Q = MC(change in temperate)
Q = heat energy ( J)
M = mass ( kilograms )
C = specific heat capacity (J/kg)
Change in temperature ( C and K)
Force
Newtons (N)
Si units 1 kg m/s²
Patents heat of fusion
Q=ML
Q = j
M= kg
L = j / kg
Pressure
When many molecules collide with the side of a container it’s measured
Pa pascahals
Si units kg/ms² or N/m²
Ways gets can be transferred
Conduction - direct contact
Convection - circulating of fluids with different temperatures
Radiation - transferred through a vacuum waves
visible light
Frequency - 10^14
Wavelength- 400nm -700nm
Electromagnetic spectrum from longest to shortest wavelength
Radio waves
Microwaves
Infrared waves
Visible light
Ultraviolet
X-ray
Gamma rays
P= eoAT^4
P = watts
e = emissivity
o = 5.67× 10^-8 Wm^-2k-4
T = absolute temperature (k)
Weird displacement law
When a black body radiator is heated up it emits a range of different wavelengths
Max wavelength = 2.9×10^-3/T
Temperature increases peak wavelength increases
Peak wavelength increases frequency increases
Intensity
I = P/A
Wm^-2= W/m²
Green house effect
Energy introduced
some energy is absorbed
Un absorbed energy is bounced around off gassed in the atmosphere and trapped in earth’s atmosphere
Frequency
Si units - J*s
Energy can be categorized as
either a wave or a photon
ev
Electron volt is a unit if energy
How are the absorption spectra and emission spectra
They are the approximate inverse of eachother
what is the units and si units for power
Unit: watt (W)
Si units: 1kgm²s-³
Units for voltage and definition
Units: voltage (v)
Definition: potential difference
Unit for current
Unit: amps (A)
Si units: 1Cs^-1
Units and so units for Energy
Units: joules (J)
Si units: 1kgm²s-²
Rules for a parallel circuit
Voltage is equal throughout the circuit
Currents add up to the total current
1/R total is = 1/R +1/R2
Rules for a series circuit
Current is equal throughout the circuit
Total voltage = v1+v2
Total resistance = R1+R2
What is the most stable nucleotide
Iron-56
When is a photon emitted
When ever a electron jumps down an energy level
What is emitted during alpha decay
A helium nucleus

What is emitted in beta negative decay
An anti neutrino
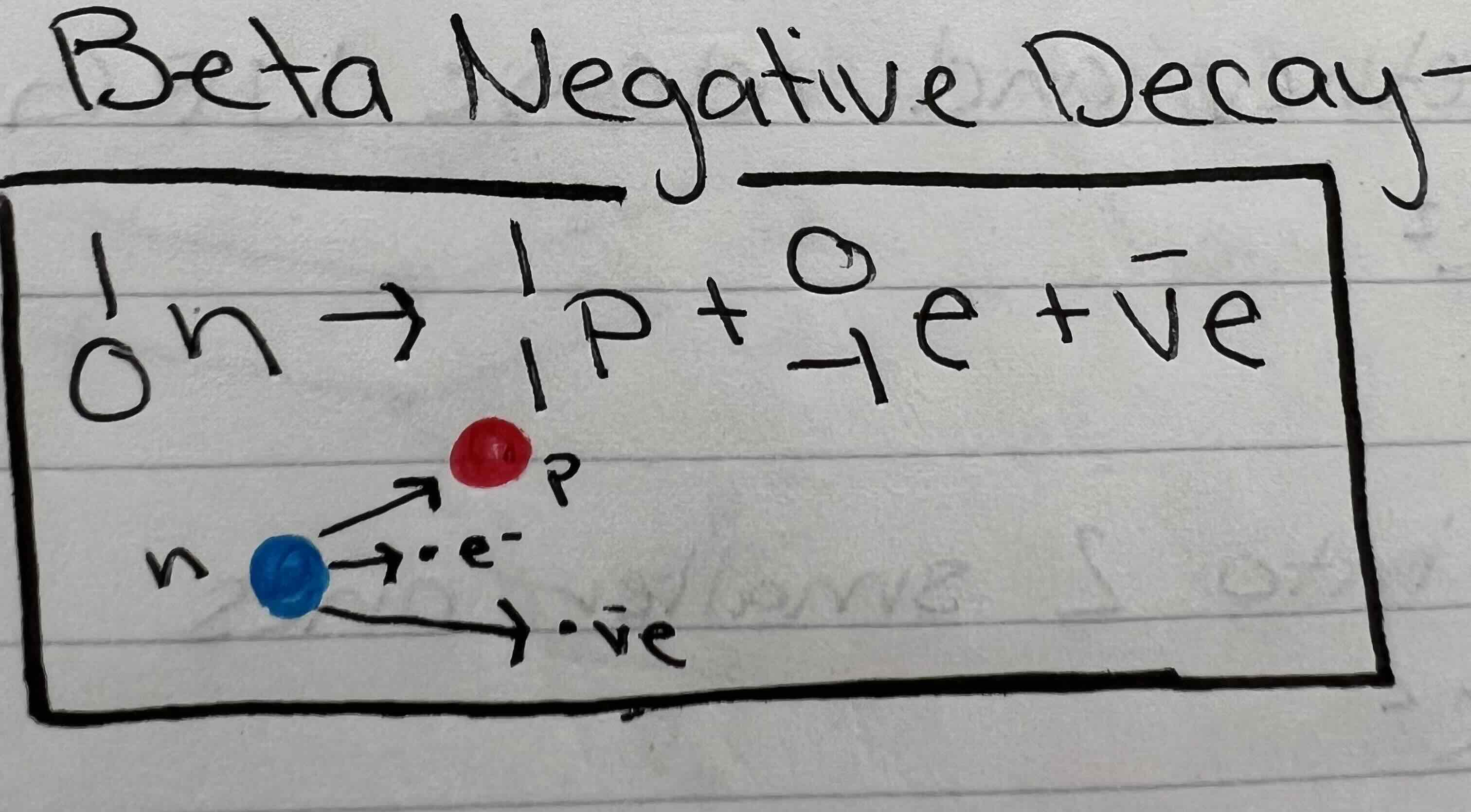
What is emitted during beta positive decay
A neutrino
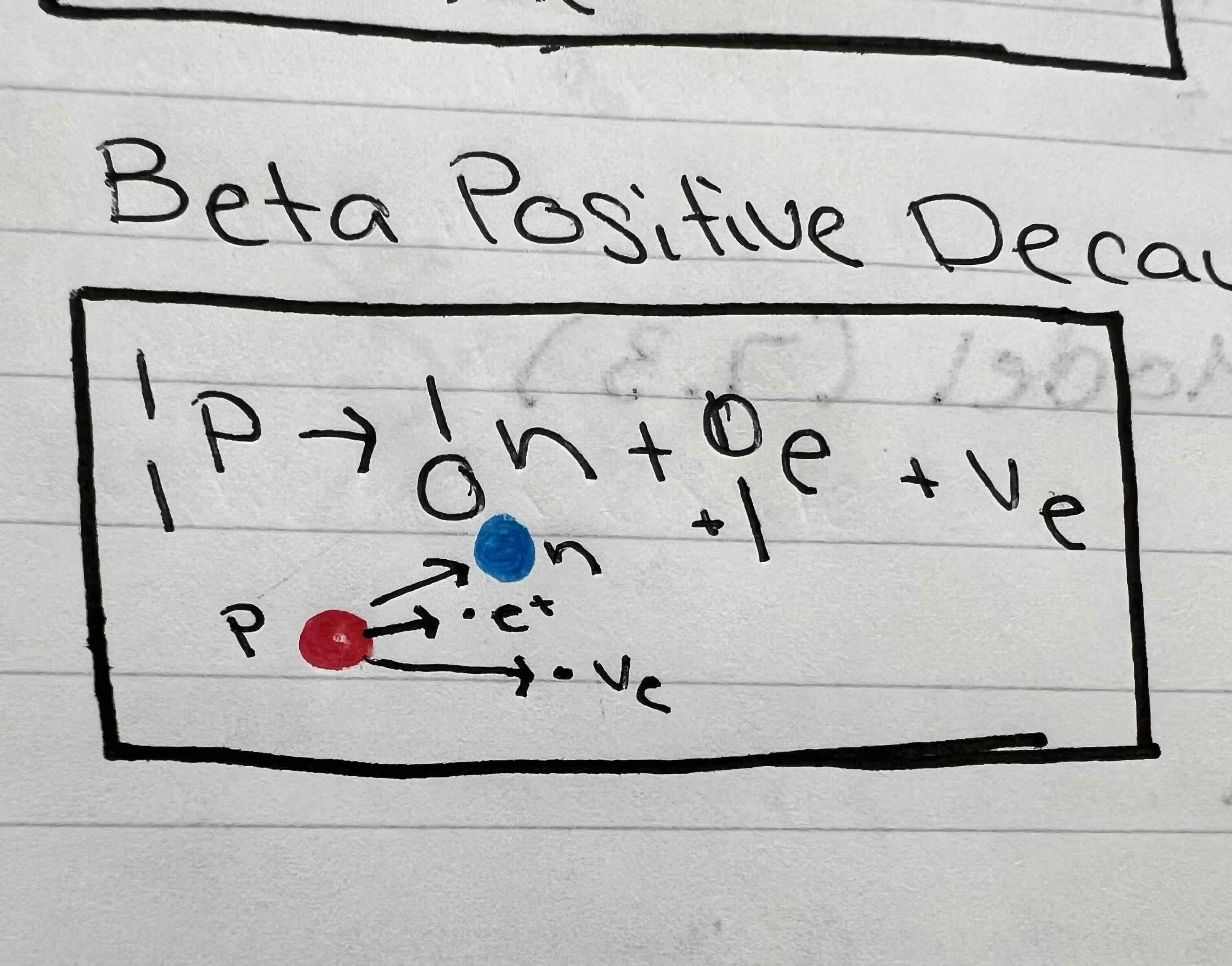
What is emitted during gamma decay
An alpha or beta particle (energy)
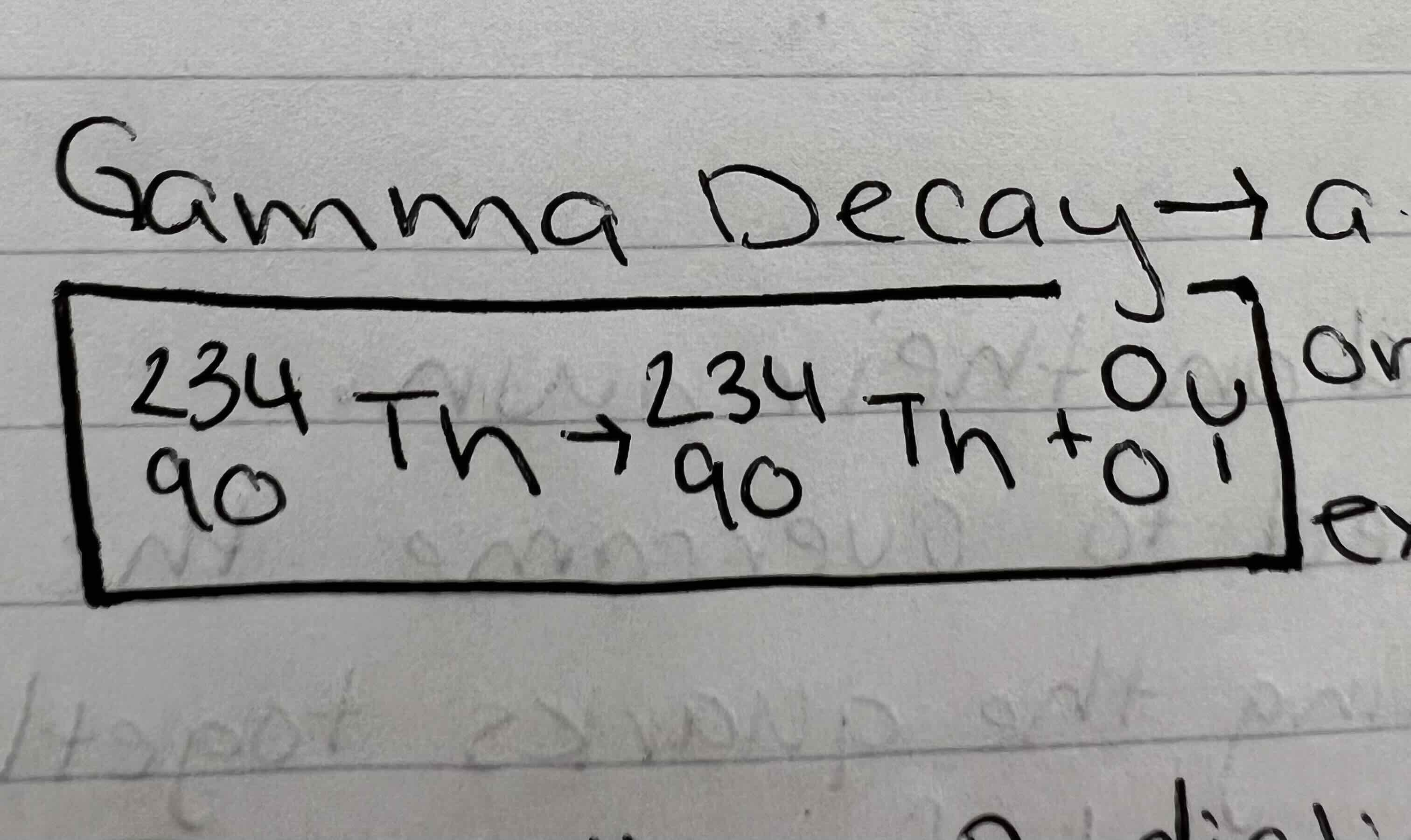
Proton
uud
Neutron
udd
kaon
ds
Meson
du
When are photon used a boson
When there is total animation or spontaneously forming protons and electrons
1 degree
3600 arc second (as)
What happens to a white dwarf when it has a mass greater than 1.4
It collapses in on itself
How to find distance in Astro physics
Parallax d=1/p
Cepheid. b=L/4pid²
H.R diagrams. Max wavelength(T)= 2.9×10-³mk
Red shift. z=new wavelength/og wavelength ≈v/c