ROMANESQUE
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
roman like
Romanesque means _________
Romanesque
(800-1180) It refers to the architecture of the 11th and 12th centuries in medieval Europe to Roman Architecture, based on similarities of forms and materials.
Architectural Characteristics
Sober And Dignified
Solemn Spaces
Exterior Is Simple, Severe
Modest Height
Horizontal Lines
Multiple Units
Blind / False Arches
Carolingian architecture
It is the style of north European Pre-Romanesque architecture belonging to the period of the Carolingian Renaissance of the late 8th and 9th centuries, when the Carolingian dynasty dominated west European politics.
Ex. Lorsch Abbey, a monastery in Lorsch Germany
Ottonian architecture
It is an architectural style which evolved during the reign of Emperor Otto the Great.
Ex. Church of St. Cyriakus
Geographical
It is the combination of Roman and Byzantine Architecture basically roman in style.
Geological
common material used for construction were stone, brick, marble or terra cotta, as well as ready-made columns and features from the old Roman buildings.
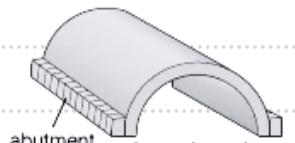
barrel vault
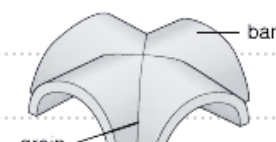
groin vault
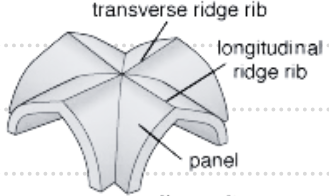
rib vault
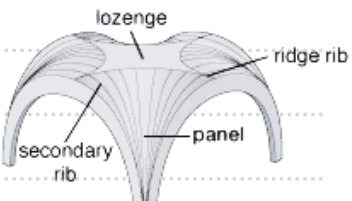
fan vault
Churches, Monasteries, Castles
3 Main topologies
Churches
The main building and symbolized God's Kingdom.
apse
The holiest part of churches
Symbolism
Circular parts reflect perfection so they were linked to God.
Squared parts are related to human.
Monasteries
Designed as a microcosm, as the City of God.
1. Church
2. Cloister
3. Chapter Room
4. Abbot's House
5. Monks/Nuns Rooms
6. Refectory
7. Hospital
St. Gallen Monastery
It was one of the most important spiritual centres of Europe. And the spirit of the Benedictine monks can still be felt here today as you enter the Abbey District of St.Gallen. It was rightly designated a UNESCO World Cultural Heritage site in 1983.
Castles
Used for defensive purposes.
They were fortified for providing shelter
Tend to be build in steppedareas, easier to defend.

Worms Cathedral
Also known as the Cathedral of St. Peter. It is claimed to be the representative cathedral of the period due to its castle-like features such as its distinctive conical towers. The structure was constructed in phases throughout the 12th century and mostly completed by 1181.

Notre Dame de Port
Founded by the Bishop of Clermont Avitus of Clermont during the 6th century and was rebuilt during the 12th century after being burned down by the Normans. The church was declared as a basilica manor on May 3, 1886, and was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1998. Its name comes from the Latin word ‘portus’ since the church was built in a ‘port’ district. It characterized by the use of inlaid decoration formed of different colored lavas.

Santiago de Compostela
Considered as a religious pilgrimage site housing the relics of Apostle St. James and the Pértico de la Gloria. Together with its Romanesque essence, the church was reinvented with Baroque touches shaping its current structure. It wasconstructed during the reign of Afonso V1in 1075 and was built under the direction of Bishop Diego Pelaez.

Durham Cathedral
The Cathedral has a symmetrical, Latin cross layout. Two towers were built on the main facade, and the third tower was built in the intersection of the four points of the cross. The central tower is the tallest. The cathedral is considered the earliest example in the use of ribbed vaults.

Worcester Cathedral
The cathedral was founded in 680. The chapter house dates from 1120, and the nave was extended the 1170s. Between 1224 and 1269 the east end was rebuilt in the Early English Gothic style. The earliest surviving fabric dates from 1084, when the cathedral was rebuilt in the Romanesque style by Bishop Wulfstan.

Canterbury Cathedral
One of the oldest and most historic Christian structures in England. Originally established by St. Augustine of Canterbury and located in Canterbury, Kent, England, UK. The cathedral was rebuilt from the Tith -12th century and from the 14th - 16thcentury, when the present nave and the Bell Harry tower were built.

Loaree Castle
One of the oldest castle in Spain. It has an irregular floor plan and a double wall with cylindrical towers.

Rochester Castle, Kent, England
One of the best preserved and finest examples of Norman architecture in England. Its great keep, square, massive and is one of the tallest in the country, measures 113 feet high, 70 feet square and has walls 12 feet thick in places.

Cardiff Castle, England
The imposing Norman Keep at Cardiff Castle sits atop a man made mound (or motte) 10.67m (over 35ft) high. The stone shell keep replaced an original wooden structure in the mid 12th century, the tower that defends the gatehouse is 17.02m high (over S5ft).

Pisa Cathedral
The cathedral is one of the finest of the Romanesque period and has a strongly marked individuality. It resembles other early Basilican churches in plan, with long rows of columns connected by arches,double aisles, and a nave which has the usual timber roof.
Construction began 1063 under the direction of Architect Buscheto.
Its architecture includes various stylistic elements: classical,Lombard-Emilian, Byzantine, and Islamic, which reflects the international presence of Pisan merchants at the time. This new style was called ‘Pisan Romanesque’.
The facade, of grey marble and white stone set with discs of coloured marble.
The original central door was in bronze and made around 180 by Bonanno Pisano, while the other two were probably in wood. Above the doors there are four rows of open galleries

Pisa Baptistery
Construction started in 1152 to replace the older baptistery and completed 1363.
Designed by Diotisalvi.
The lower section is in the Romanesque style with round |arches, while the upper sections are in the Gothic Style.
Circular in plan with total circumference is 107.25m and height of 54.86m.

Pisa Baptistery Font
Constructed of marble which is often used in Italian Architecture.

Pisa Campanile “Leaning Tower of Pisa”
Free standing bell tower, known worldwide for its unintended tilt.
By Architect Bonanno Pisano
15.5m in diameter with blind arcades.
|55.86m in height from the ground on the low side and 56.67m on the high side. Angle of slant: 3.97 degrees

Pisa Camposanto
Also known as “holy field". The outer wall is composed of 43 blind arches. The walls of the vast structure were covered in over 2600 meters squared of frescoes.

Wheel Window
A rose window having distinctly radiating mullions or bars. Also called Catherine Wheel, marigold window.
Ex Worms Cathedral, Germany

Tympanum
The space between an arch and the horizontal head of a door or window below, often decorated with sculpture.
Ex Tympanum of Vezelay Abbey, France

Tremeau
A column supporting the tympanum of a doorway at its center.
Ex Trumeau of Vezelay Abbey, France

Campanile
A bell tower, usually near but not attached to the body of a church.

Order
Any of several concentric rings of masonry forming an arch, esp. when each projects the one below.
Ex. Order of the Manila Cathedral (Neo-Romanesque Church)

Tabernacle
A canopied recess for a religious image or icon.