Chem light unit
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
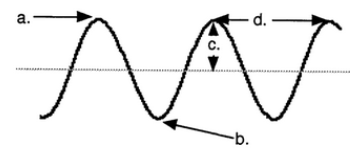
Part of a wave
a. crest
b. trough
c. amplitude
d. wavelength
If the wavelength is short does it have high or low energy
high
If the wavelength is long does it have high or low energy
low
what color has the shortest wavelegth and highest energy
violet
what color has the longest wavelength and lowest energy
red
1 meter is how many nano meters
10^9 nanometers
1 nanometer is how many meters
10^-9 meters
frequency
number of wave cycles
what has the highest frequency
gamma rays
what has the lowest frequency
radio waves
what has the shortest wavelength
gamma rays
what has the longest wavelength
radio waves
Explain how atoms of different elements can emit different colors/wavelengths. Your explanation should include the terms: energy levels, electrons, energy
because of the unique arrangement of their electrons in energy levels. When an atom absorbs energy, its electrons move to higher energy levels and when the move to lower energy levels, they release the absorbed energy in the form of light. Each element has specific energy level spacings, so when electrons transition between these levels, the emitted light corresponds to specific colors or wavelengths for each element.

What spectrum is this
Continuous spectrum: contains all wavelengths of light in a certain range (white light —> diffraction grating —> spectrum)
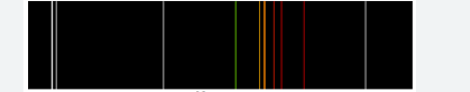
What spectrum is this
Emission spectrum: showing the light in the wavelengths in a line with the color they emitted (hot gas —> diffraction grating —> spectrum)

What spectrum is this
Absorption spectrum: oppisite of emission soectrum, the color that would be emitted would be a balck line and the “background” would be the rainbow (white light —> diffraction grating —> spectrum)
how can we identify an element based on an emission spectrum
bright lines will show up corresponding to the difference between energy levels of the elements
What are the 2 parts of salt
an atomic compound made of a positive ion and a negative ion.
What is the purpose of the flame or what does the flame provide to the salt?
to determine the identity of an unknown metal and the flame provided energy to the electrons
Why do different salts give off different colored light?
As the salt burns, the extra energy is lost — as light. The color of that light depends on the amount of energy being released.
staircase analogy
The stairs represent the energy levels, it requires specfic amounts of energy for the electron to gain and loose energy to chnage energy levels, all energy levels require differnet amount of energy.
Electromagnetic radiation
A form of energy that is produced by eletric & magnetic feild working together
Amplitude
a measurement of the amount of energy transferred by a wave, lower amplitude makes light less bright ( symbol - A)
Frequency
number of wave cycles (full wave) used in hertz, high frequecny = short wavelength symbol = v (nu)
Quanta
specific individual seprate amounts of energy
Quantized
electrons can pass certain energy values
photoelectric effect
When light shines on a metal, electrons can be ejected from the surface of the metal
The photoelectric effect tells us the energy is quantized, it is discrete and absorbed into packets or photons of energy. SO important because it supports why electrons gain and lose energy in certain amounts of packets.
photon
quantum of electromagnetic radiation
prism
when light passes through the color spectrum shows
wavelength
lambda λ
how is light produced
For light to be produced electrons must absorb a quanta of energy and move to a higher energy level than the electrons need to release the quanta of energy to produce light
Does brightness afccts the energy
does not affect the energy same wavelength and energy
to take in
absorb
to give off
emit
where is visible light located on the electromagnetic spectrum
bewteen infrared and ultra violet