Chp7 - Sampling Distributions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
parameter
a # that describes the population. it is a fixed #, but in practice we don’t know it
statistic
a # that describes the sample. known # but can change sample to sample → used to estimate parameter
mean parameter
μ (population)
mean statistic
x bar (sample)
stand deviation parameter
σ (population)
stand deviation statistic
Sx (sample)
proportion parameter
p (population)
proportion statistic
p hat (sample)
variance parameter
σ² (population)
variance statistic
sx² (sample variance)
biased
consistently overestimates or underestimates the true population parameter
unbiased
mean of sampling distribution = population parameter
statistic/sampling mean = parameter/population mean
M of x bar = M
As n (sample size) increases…
the variability of the sample distribution decreases
a good stat has
a low bias (accurate)
a low variability (precise) (so high sample size)
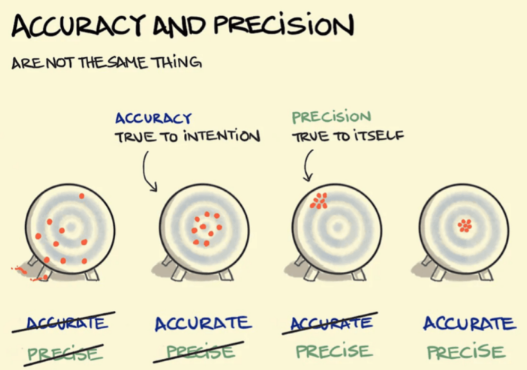
accuracy means
true to intention
precision means
true to itself

the variability of a stat is described by
the spread of tis sampling distribution. this spread is determined by the sampling design & the size of the sample
larger sample = smaller spread