L4 Diffusion potentials UNFINISHED
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Define:
Isosmotic
Hypoosmotic
Hyperosmotic
Isotonic
hypotonic
Hypertonic
Two solutions with the same osmolarity (same total solute concentration).
A solution with lower osmolarity than another.
A solution with higher osmolarity than another.
A solution that does not change cell volume (no net osmosis).
A solution that causes cells to swell (water enters).
A solution that causes cells to shrink (water leaves).
What is charge (q) measured in?
Coulombs (C).
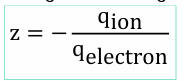
What is valence (z)?
what is its equation
The charge number of an ion (e.g., Na⁺ = +1, Cl⁻ = -1)
What is Faraday’s constant (F)?
the charge per mole of ions, approximately 96,485 C/mol
Formula for charge using ion quantity?
q = zFn (z = valence, F = Faraday constant, n = moles)
What is voltage (V)?
The potential difference that drives charge movement (like pressure in fluids)
What is current (I) and its unit?
what is its formula
The rate of charge flow, measured in amperes (A)
q=it
What causes charge separation across membranes?
Selective permeability — only certain ions move (e.g., Na⁺ moves, Cl⁻ stays)
Goes down chemical gradient and is repelled by electrical gradient
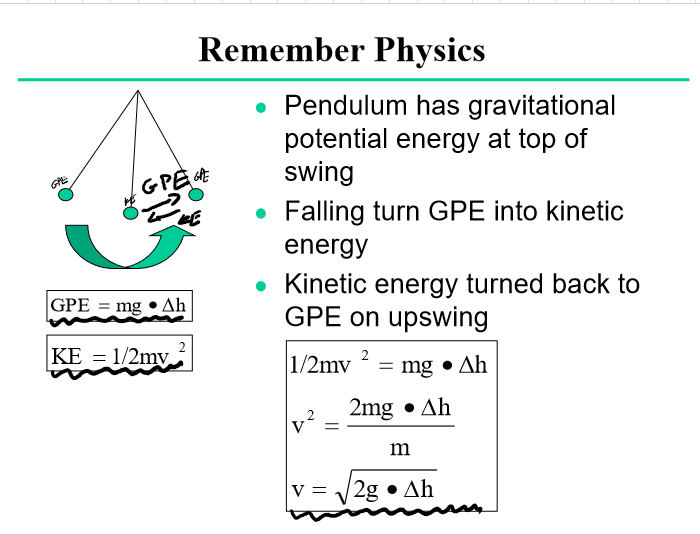
GPE and KE formulas