BIS 2C Lab Practical
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/210
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
1
New cards
phylogenetic tree
a diagram that represents the pattern of **ancestor-descendent relationships** among a group of organisms
2
New cards
phylogenies
these are routinely used in many areas of biology, including biogeography, conservation biology, epidemiology, forensics, pharmaceutical chemistry and medicine.
3
New cards
speciation
in the simplest model, this is shown through the rise of new species when an ancestral lineage splits into two descendents
4
New cards
taxon
we use the term ____________ forever to a group group of organisms at an unspecified taxonomic rank. A ____________ can be a family, phylum, genus, or any other rank of in the Linnaean hierarchy.
5
New cards
node
the intersection of each split in a phylogenetic tree is referred to as a ____________ and it represents the MCRA of two or more descendent lineages, each one represents a speciation event
6
New cards
root node
what represents the MCRA of **ALL** taxa on the phylogeny
7
New cards
internal node
all nodes that are not the root node are referred to as a what?
8
New cards
sister taxa
the pair of taxa resulting from a lineage split are referred to as ___________ _____________. By definition the arise at the same time.
9
New cards
rotate
When deciphering the pattern of lineage splitting it is important to note that each node is free to ____________ without changing our interpretation of relationships.
10
New cards
cladogram
only shows the pattern of lineage splitting; the lengths of the branches have no meaning
11
New cards
phylogram
shows the pattern of lineage splitting and the proportion of genetic change on each branch, the length of the branches on these vary and they are typically accompanied by a scale bar proportional to the amount of genetic change. The amount of change is expressed as the as the average number of changes per site in DNA sequence. Therefore, the longer a branch is on a ____________, the more divergent taxa are from each other.
12
New cards
chronogram
shows the pattern of lineage splitting associated with specific (absolute) geologic times, often presented in millions of years ago (MYA)
13
New cards
characters
heritable traits or features are often referred to as ____________, the most common ones that are used by phylogeneticists are morphology, genetics and behavior
14
New cards
ancestral
a character state present in the MRCA of a group (node) is often referred to as ____________.
15
New cards
derived
any states that evolved after the ancestral character are referred to as ____________.
16
New cards
homology
a key concept that refers to the similarity in characteristics among organisms that is due to a **shared ancestry**. A classic example of this bones within the limbs of humans, birds and bats.
17
New cards
homoplasies
characters that appear similar, but are a result of convergent evolution, are called ____________. A good example is wings.
18
New cards
parsimony
when using ____________, we seek a phylogeny that minimizes the number of evolutionary changes; so the tree with the fewest number of character changes is our preferred hypothesis.
19
New cards
ingroup
organisms which are the specific focus of a study are referred to as what?
20
New cards
outgrip
An ____________ is one or more taxa that are as closely related to the in-group as possible without actually being part of it, ideally they would be the sister taxon of the ingroup.
21
New cards
taxonomy
the naming and description of species is a science onto itself and it is known as ____________
22
New cards
binomial nomenclature
In this system, each species gets a two part name where the first part is the genus (homo) and the second part is the specific epithet (sapiens). Note that genus is capitalized and specific epithet is lowercase, both are underlined or italicized.
23
New cards
monophyletic group
a group that contains all descendants of the MRCA, another name for it is a clade
24
New cards
polytomy
these are used to reflect uncertainty, whether it be missing or incomplete data (soft) or just rapid divergence (hard).
25
New cards
congruence
common branching pattern
26
New cards
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
Carl Woese was the first to propose a system where all living organisms are separated into three domains, what are the three domains?
27
New cards
prokaryotes
Bacteria and Archaea are often collectively referred to as _______________ because they lack a nucleus (it’s important to note that they are not each other’s closest relatives though
28
New cards
microbe
this term is used to refer to microscopic organisms in **any** of the domains and **viruses**
29
New cards
two domain
current studies have shown some support for the alternative “___________ ___________” tree of life
30
New cards
Asgard
In the two domain hypothesis, the sister group of eukaryotes are a subset of archaea called what? (hint, think Marvel)
31
New cards
coccus
this morphology of bacteria and archaea is sphere shaped
32
New cards
bacillus
this morphology of bacteria and archaea is rod-shaped
33
New cards
helical or spiral
this morphology of bacteria and archaea is an elongate spiral, goes by two names
34
New cards
biofilm
a group of microbes that is bound to a surface
35
New cards
binary fission
most bacteria and archaea reproduce through ___________ ____________ , where the chromosome is copied so that each daughter cell is genetically identical
36
New cards
energy, electron, and carbon
what three components (sources) drive metabolism
37
New cards
photography
energy is captured from light
38
New cards
chemotrophy
energy is taken from chemical reactions
39
New cards
lithotrophs
organisms that use inorganic electron donors, like hydrogen sulfide
40
New cards
organotrophs
organisms that use organic electron donors, like methane
41
New cards
autotrophs
organisms that utilize inorganic compounds as a carbon source, like CO2
42
New cards
heterotrophs
organisms that utilize organic, more complex compounds as a carbon source that include C, H and O, such as sugars
43
New cards
extremophiles
habitats for _______________ included the most acidic or basic conditions, temperatures fall to -12° C or rise to 113° C; the water is too salty to support any other life and the radiation irreparably damages the DNA of most other organisms
44
New cards
mesophiles
organisms that live in more ‘normal’ temperatures are called _____________.
45
New cards
acidophile
lives in pH less than 2
46
New cards
alkaliphile
lives in pH greater than 8
47
New cards
psychrophile
lives in temperatures less than 15°C
48
New cards
halophile
lives in salty conditions
49
New cards
thermophile
lives in temperatures about 40°C
50
New cards
xerophile
lives in extremely dry temperatures
51
New cards
lateral gene transfer
In ____________ ____________ ____________, DNA moves from one organism to another via specialized processes
52
New cards
transformation
this is a process of LBT whereby DNA found in the environment (e.g., DNA that came from a cell that is dead and lysed) are moved into an intact cell. The DNA can replace a portion of the recipient’s chromosome or it can add new DNA to the recipient cell’s chromosome. It can also stay as a separate replicating entity.
53
New cards
conjugation
this is a process of LGT that looks similar to mating, but it can occur between distantly related cells and does not result in offspring. It generally involves the transfer from one cell to another of a small piece of DNA known as a plasmid. In ______________ a tube called a sex pilus forms between two cells and a plasmid in the donor cell replicates and one copy passes through the pilus. The plasmid duplicates inside the daughter cell and the pilus breaks.
54
New cards
transduction
_____________ is the incorporation of new genetic material into a host throughout the action of viral particles. Virus particles carry DNA from one host to another and once in the new host, the DNA can be incorporated into the cell’s chromosome or replicate as a separate entity.
55
New cards
great plate count anomaly
the discrepancy between observed microbes in the field and those that can be grown in pure lab cultures in know as the what?
56
New cards
false
True or false, scientists have been able to study most bacteria and archaea directly in a lab
57
New cards
last universal common ancestor
what does LUCA stand for?
58
New cards
mutualism
both organisms benefit from this interaction
59
New cards
parasitism
the parasite benefits while the host is harmed
60
New cards
commensalism
an interaction where one organism benefits but the effect on the other is unknown or negligible
61
New cards
microbial eukaryotes
As with all eukaryotes, _________ ______________ have a nucleus, mitochondria and a cytoskeleton. Some lineages also have chloroplasts that are used for photosynthesis. They can be unicellular, multicellular and colonial. This group also shows great diversity in morphology.
62
New cards
protists
historically, microbial eukaryotes were referred to as what?
63
New cards
locomotion
there are many different body forms of microbial eukaryotes but, unlike Bacteria and Archaea, their body morphologies tend to be associated with forms of ______________.
64
New cards
Ciliate
The _______________ form has numerous short hair like structures in rows across the cell surface, some _______________s are capable of very rapid movement and often use their hair like structures to feed. (the hair like structures are a shortened version of the name of this form)
65
New cards
Amoeboid
The _______________ form has an irregular shape and moves by cytoplasmic streaming using pseudopodia, this type of movement is typically slow.
66
New cards
Flagellate
This body form has one to many whip like structures and are capable of very fast movement. It is important to note that this structure is **not** homologous among bacterial and eukaryotes
67
New cards
microtubules, microfilaments
______________ are part of a cilium or a flagellum, whereas _________________ are active in amoeboid movement.
68
New cards
phagocytosis
the lack of a cell wall the use of a cytoskeleton allows many eukaryotes to perform _____________ where soil food particles are taken directly into the cell
69
New cards
symbiosis
Eukaryotic cells are most likely the product of a _______________ between bacteria and a eukaryotic cell.
70
New cards
Lynn Margulis
who was the the first person to synthesize all of the evidence and eventually many of her arguments formed the foundation of endosymbiotic theory?
71
New cards
asexual reproduction
the genotype is copied into a new body and the all organisms are gentically identical, aside from mutations. However in many taxa, these genetically identical organisms do not have the same body morphology.
72
New cards
1\.778
When calculating the size of an organism in a microscope, the field diameter depends on the lens. What is the field diameter of a microscope at 10x magnification (in mm)?
73
New cards
0\.55
When calculating the size of an organism in a microscope, the field diameter depends on the lens. What is the field diameter of a microscope at 40x magnification (in mm)?
74
New cards
euglena
these use ciliate movement, size approximately 0.05 mm

75
New cards
blepharisma
these use ciliate movement, size approximately 1 mm
76
New cards
chlamydomonas
they use flagellate movement, size approximately 0.01 mm
77
New cards
paramecium
they use ciliate movement, size approximately .05 to 0.32 mm
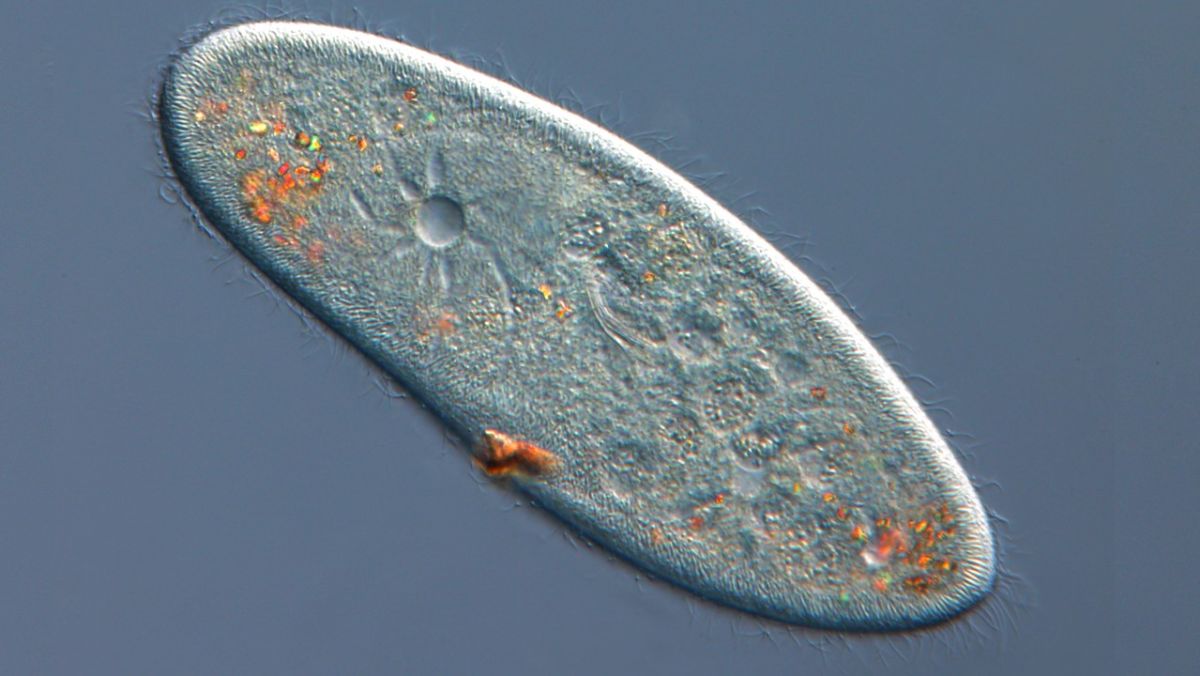
78
New cards
stentor
large and green with irregular trumpet shape, they use ciliate movement, size approximately 2mm
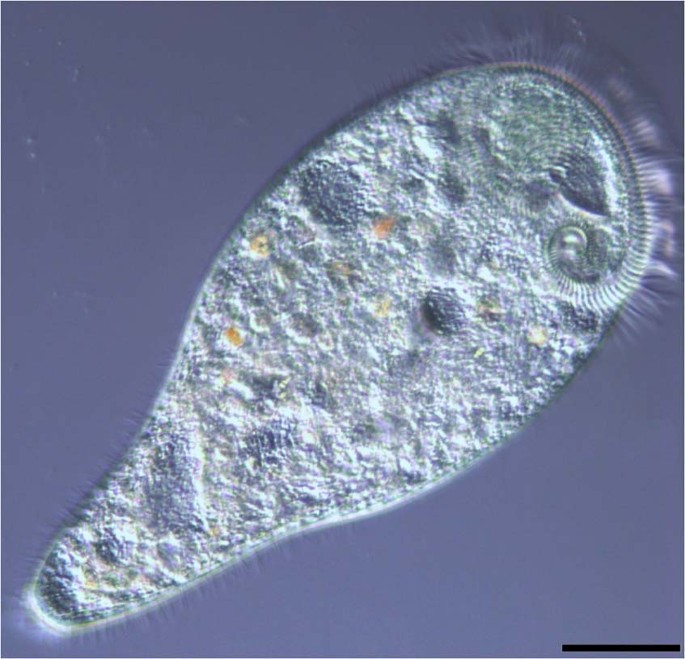
79
New cards
distance matrix
a way of summarizing the percent difference between taxa
80
New cards
eukaryote
what type of organism is being consumed during secondary endosymbiosis? Is it a bacterium or a eukaryote?
81
New cards
primary endosymbiosis
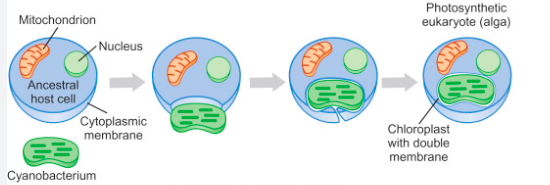
82
New cards
secondary endosymbiosis
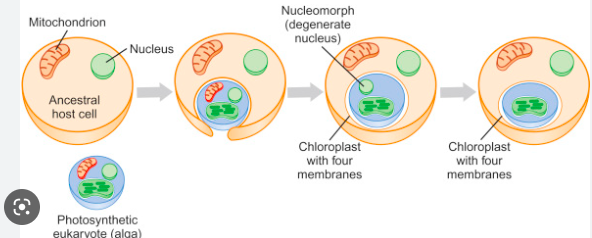
83
New cards
tertiary endosymbiosis
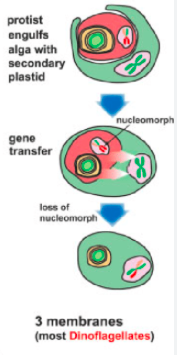
84
New cards
apicomplexa
a phylum of diverse obligate intracellular parasites including Plasmodium spp., the cause of malaria;
85
New cards
plasmodial slime mold
A ___________ ________ _________ is enclosed within a single membrane without walls and is one large cell. This "supercell" (a syncytium) is essentially a bag of cytoplasm containing thousands of individual nuclei.
86
New cards
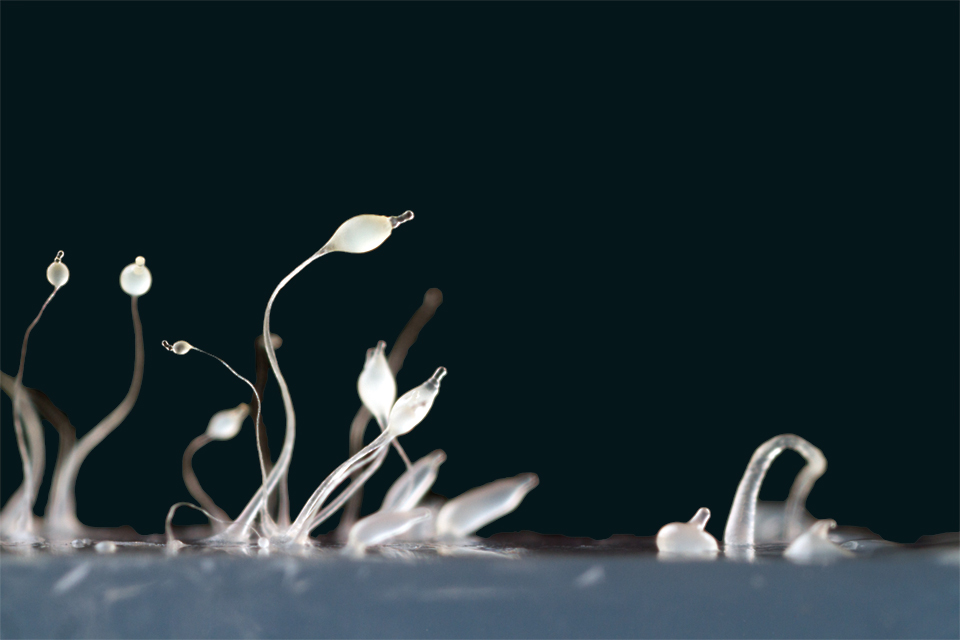
cellular slime mold
___________ ________ _________(dictyostelids) are groups of unicellular amoebae that collaborate to form fruiting structures to disperse spores

87
New cards
Naeglaria
a microbial eukaryote that has the unusual ability to change its body form from amoeboid to flagellate and back again. We performed an experiment with this microbial eukaryote where we removed food and observed them given different time intervals. This helped show us how body morphology changed in response to time without food.
88
New cards
eukaryotes
_______________ are characterized by the presence of a mitochondrion, a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
89
New cards
Plantae, embryophytes, algae
___________ is a lineage that includes the familiar land plants (___________)__ but also includes a variety of unicellular and multicellular photosynthetic eukaryotes often referred to as _____________. (put a common between three answers)
90
New cards
synapomorphy
a characteristic present in an __ancestral__ species and shared exclusively (in more or less modified form) by its __evolutionary__ __descendants__.
91
New cards
embryophytes
these are synapomorphies of what group?
* waxy cuticle
* alternation of generations
* multicellular gametangia with sterile jacket
* multicellular embryo
* apical cell with 2 or more cutting faces
* waxy cuticle
* alternation of generations
* multicellular gametangia with sterile jacket
* multicellular embryo
* apical cell with 2 or more cutting faces
92
New cards
lycopodium and selaginella
what two groups of plants have microphylls?
93
New cards
selaginella
where did heterospory **first** evolve?
94
New cards
tracheophytes
these are synapomorphies of which group?
* vascular tissue (xylem and phloem)
* traceids
* apical meristem
* reduced gametophyte
* dominate branched sporophyte
* vascular tissue (xylem and phloem)
* traceids
* apical meristem
* reduced gametophyte
* dominate branched sporophyte
95
New cards
euphyllophytes
these are synapomorphies of which group
* chloroplast DNA inversion
* megaphylls
* chloroplast DNA inversion
* megaphylls
96
New cards
monilophytes
these plants are all part of which group?
* equisetum
* psilotum
* ferns
* equisetum
* psilotum
* ferns
97
New cards
seed plants
these are all synapomorphies of which group?
* integument (the outer layer(s) of the ovule and develop into a seed coat as the ovule matures following fertilization)
* ovule
* seeds
* pollen
* pollen with pollen tube
* bifacial vasular cambium
* heterospory
* integument (the outer layer(s) of the ovule and develop into a seed coat as the ovule matures following fertilization)
* ovule
* seeds
* pollen
* pollen with pollen tube
* bifacial vasular cambium
* heterospory
98
New cards
gymnosperms
these are all plants in which group
* cycad
* ginko
* gnetophytes
* conifers
* cycad
* ginko
* gnetophytes
* conifers
99
New cards
gnetophytes
which plant evolved to have vessel elements on the plant phylogeny **before** they appeared as a synapomorphy of a plant group?
100
New cards
angiosperms
these are all synapomorphies of which group?
* endosperm
* double fertilization
* carpel
* fruit
* vessel elements
* endosperm
* double fertilization
* carpel
* fruit
* vessel elements