Chapter 13 Reactions at the alpha-Carbon of carbonyl compounds
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
13.1 The acidity of an alpha hydrogen
The alpha hydrogen of a ketone or an aldehyde is ______ (more/less) acidic than the alpha hydrogen of an ester
more
13.1 The acidity of an alpha hydrogen
The pKa value for dissociation of a proton from the alpha carbon of an aldehyde or a ketone ranges from ______, and the pKa value for dissociation of a proton attached to the alpha carbon of an ester is about ___
16-20, 25
13.1 The acidity of an alpha hydrogen
Notice that although the alpha hydrogen is more acidic that most other carbon-bound hydrogens, it is _____ (more/less) acidic than a hydrogen of water
less
13.1 The acidity of an alpha hydrogen
A hydrogen bonded to an alpha carbon is more acidic than hydrogens bonded to other sp3 carbons because the base formed when a proton is removed from an alpha carbon is relatively stable. As we know, the more stable the base, the _____ (weaker/stronger) its conjugate acid
stronger
13.1 The acidity of an alpha hydrogen
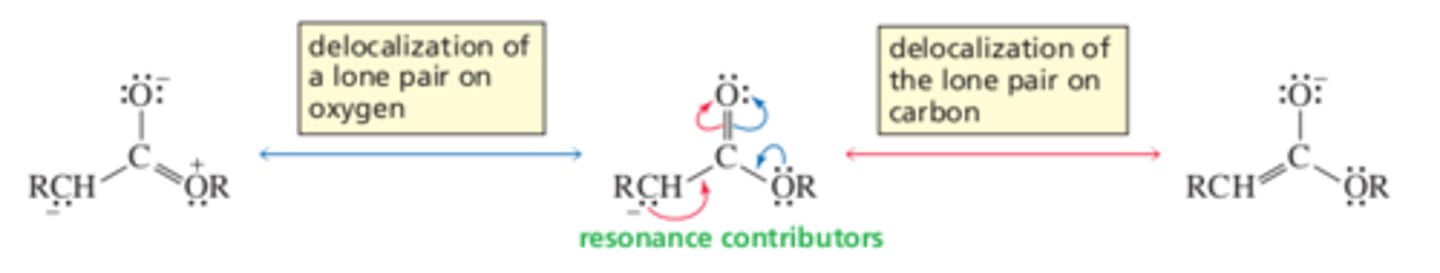
Why are aldehydes and ketones more acidic than esters?
The electrons left behind when a proton is removed from the alpha carbon of an ester are not as readily delocalized onto the carbonyl ______ as they would be in an aldehyde or a ketone.
oxygen
13.2 Keto-Enol Tautomers
Keto-enol tautomers differ in the location of a double bond and a _____
hydrogen
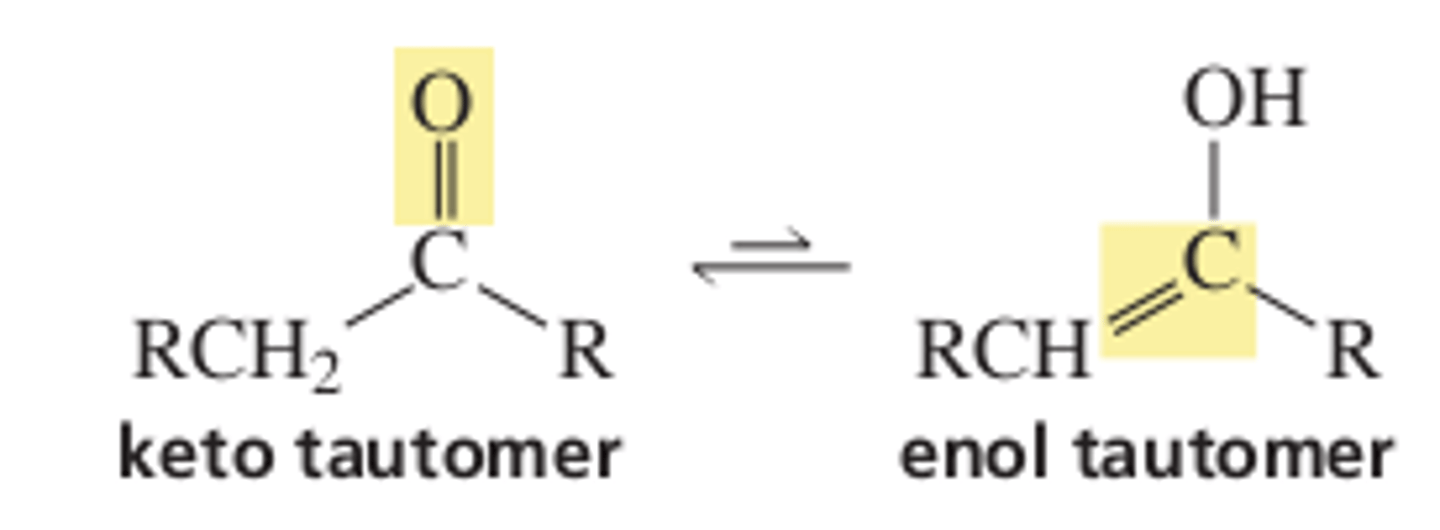
13.2 Keto-Enol Tautomers
For most ketones, which tautomer is less stable?
enol
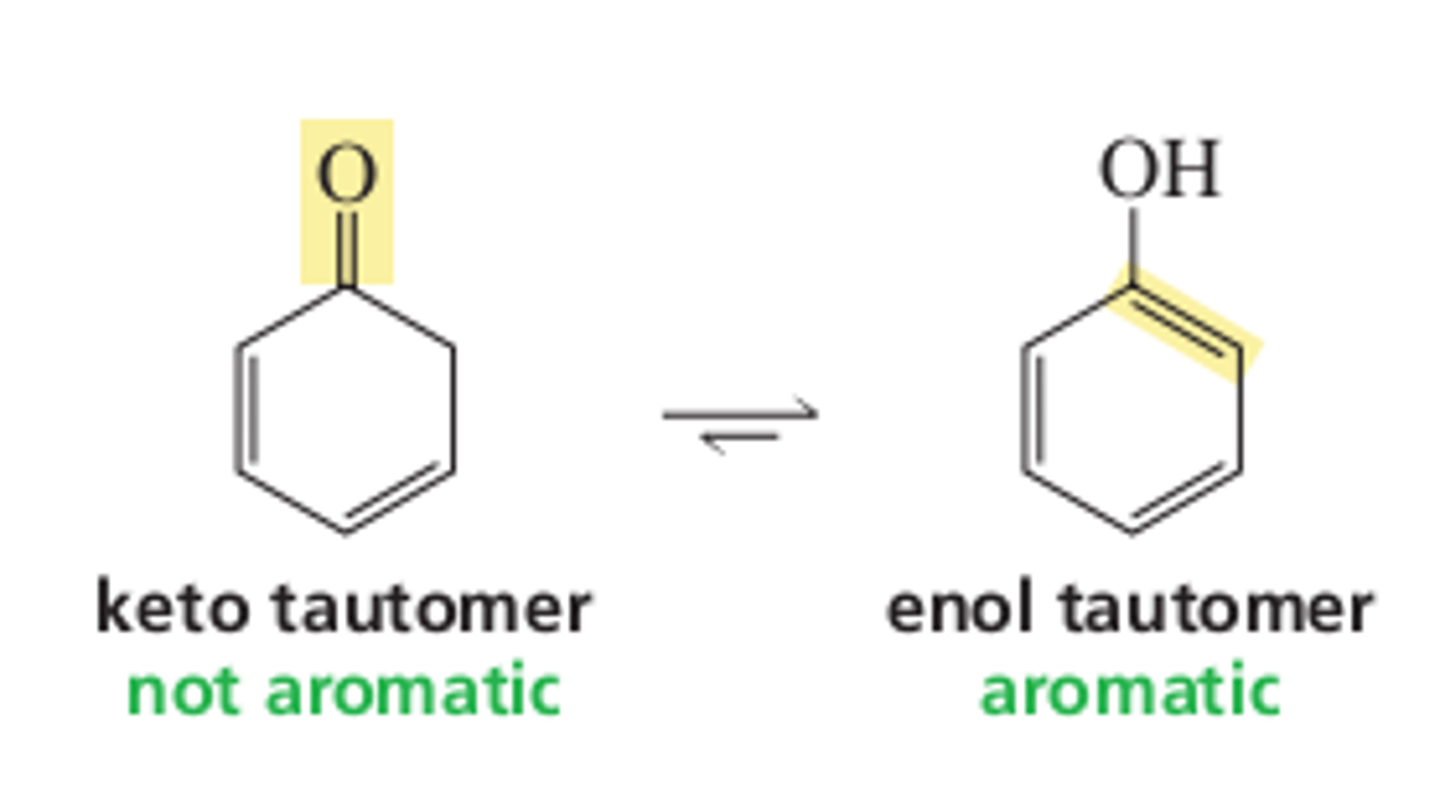
13.2 Keto-Enol Tautomers
Phenol is unique in that its enol tautomer is more stable than its keto tautomer. What characteristic is responsible for the stability?
aromaticity
13.3 Keto-Enol Interconversion
Mechanism for Base catalyzed keto-enol interconversion
(Hydroxide ion removes proton from the alpha carbon of the keto tautomer, forming an anion called an enolate ion. The enolate ion has 2 resonance contributors. Protonating the oxygen forms the enol tautomer)
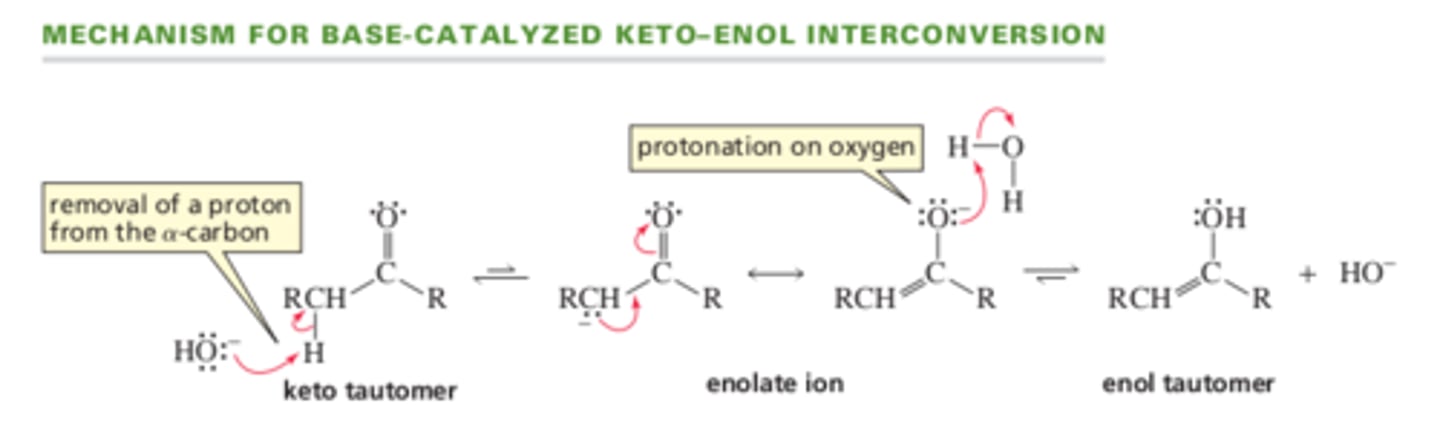
13.3 Keto-Enol Interconversion
Mechanism for acid catalyzed keto-enol interconversion
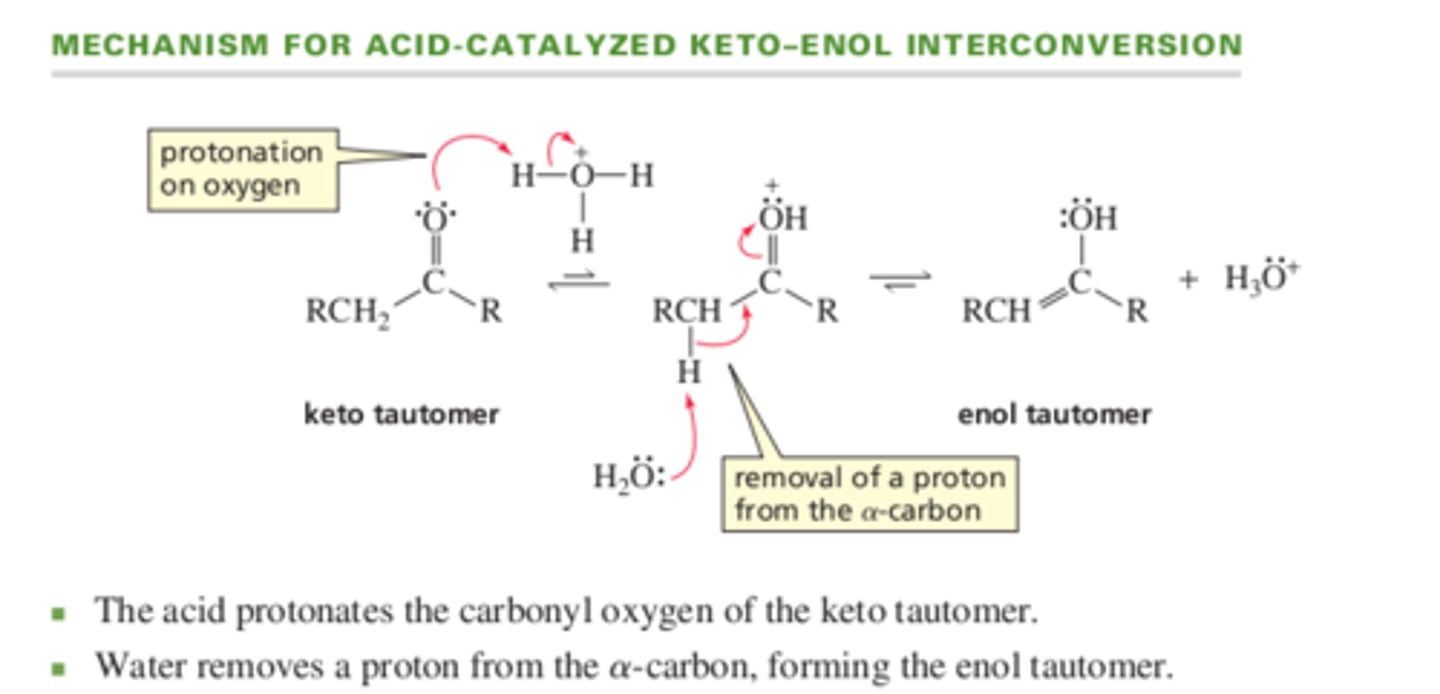
13.4 Alkylation of Enolate Ions
13.3 Keto-Enol Interconversion
The steps are reversed in the base and acid catalyzed interconversions.
Acid or base catalyzed reaction?
Step 1: The base removes a proton from the alpha-carbon
Step 2. The oxygen is protonated
base
13.3 Keto-Enol Interconversion
Acid or base catalyzed reaction?
Step 1: the oxygen is protonated
Step 2: proton is removed from the alpha carbon
acid
13.4 Alkylation of Enolate Ions
Alkylation of the alpha carbon of a carbonyl compound is an important reaction because it gives us another way to form a ______ bond
carbon-carbon
13.4 Alkylation of Enolate Ions
Alkylation is carried out by first removing a ______ from the alpha carbon with a base and then adding the appropriate alkyl halide
proton
13.4 Alkylation of Enolate Ions
Alkylation is an _______ reaction, so it works best with primary alkyl halides and methyl halides
SN2
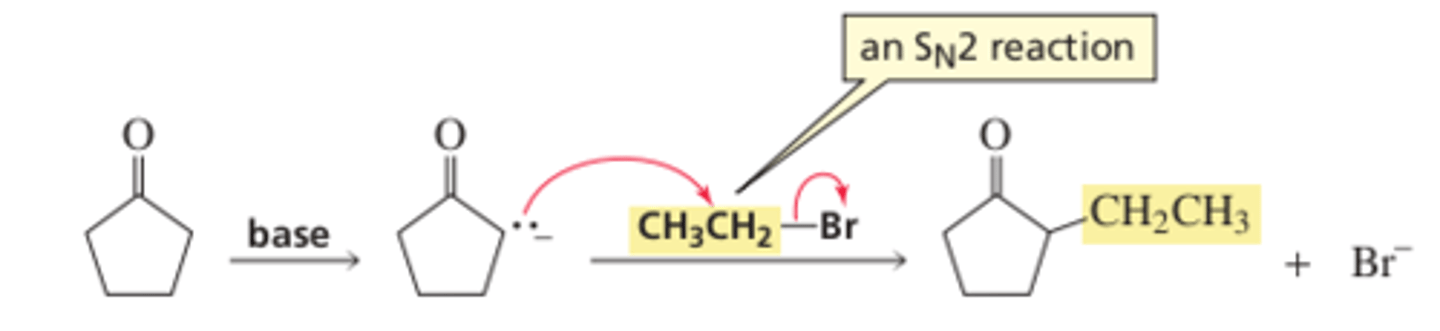
13.4 Alkylation of Enolate Ions
If the ketones is unsymmetrical and has hydrogens on both alpha carbons, ____ monoalkylated products can be obtained because either alpha carbon can be alkylated
2
13.4 Alkylation of Enolate Ions
The kinetic product is the faster formed product. The thermodynamic product is the _____ (more/less) stable product
more
13.5 An Aldol Addition forms beta-hydroxyaldehydes or beta-hydroxyketones
We have just seen that a proton can be removed from the alpha-carbon of an aldehyde or a ketone, converting the alpha carbon into a _____
nucleophile
13.5 An Aldol Addition forms beta-hydroxyaldehydes or beta-hydroxyketones
An aldol addition. One molecule of a carbonyl compound, after a proton is removed from an alpha carbon, reacts as a _______ and adds to the ______ carbonyl carbon of a 2nd molecule of the carbonyl compound
nucleophile, electrophilic
13.5 An Aldol Addition forms beta-hydroxyaldehydes or beta-hydroxyketones
An aldol addition is a reaction between 2 molecules of a/n _______ or 2 molecules of a/n ____
aldehyde, ketone
13.5 An Aldol Addition forms beta-hydroxyaldehydes or beta-hydroxyketones
Aldol addition: This reaction forms a new C-C bond that connects the alpha carbon of one molecule and the Carbon that was originally the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule
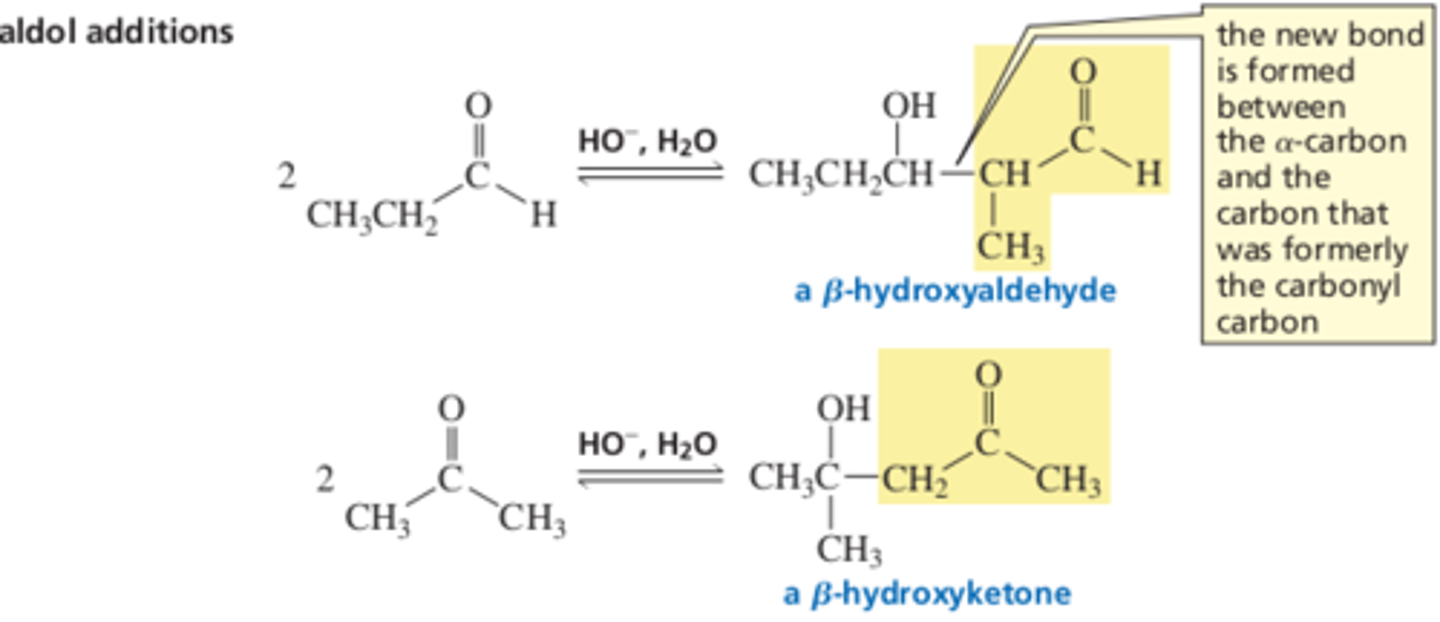
13.5 An Aldol Addition forms beta-hydroxyaldehydes or beta-hydroxyketones
Mechanism for Aldol Addition screenshot
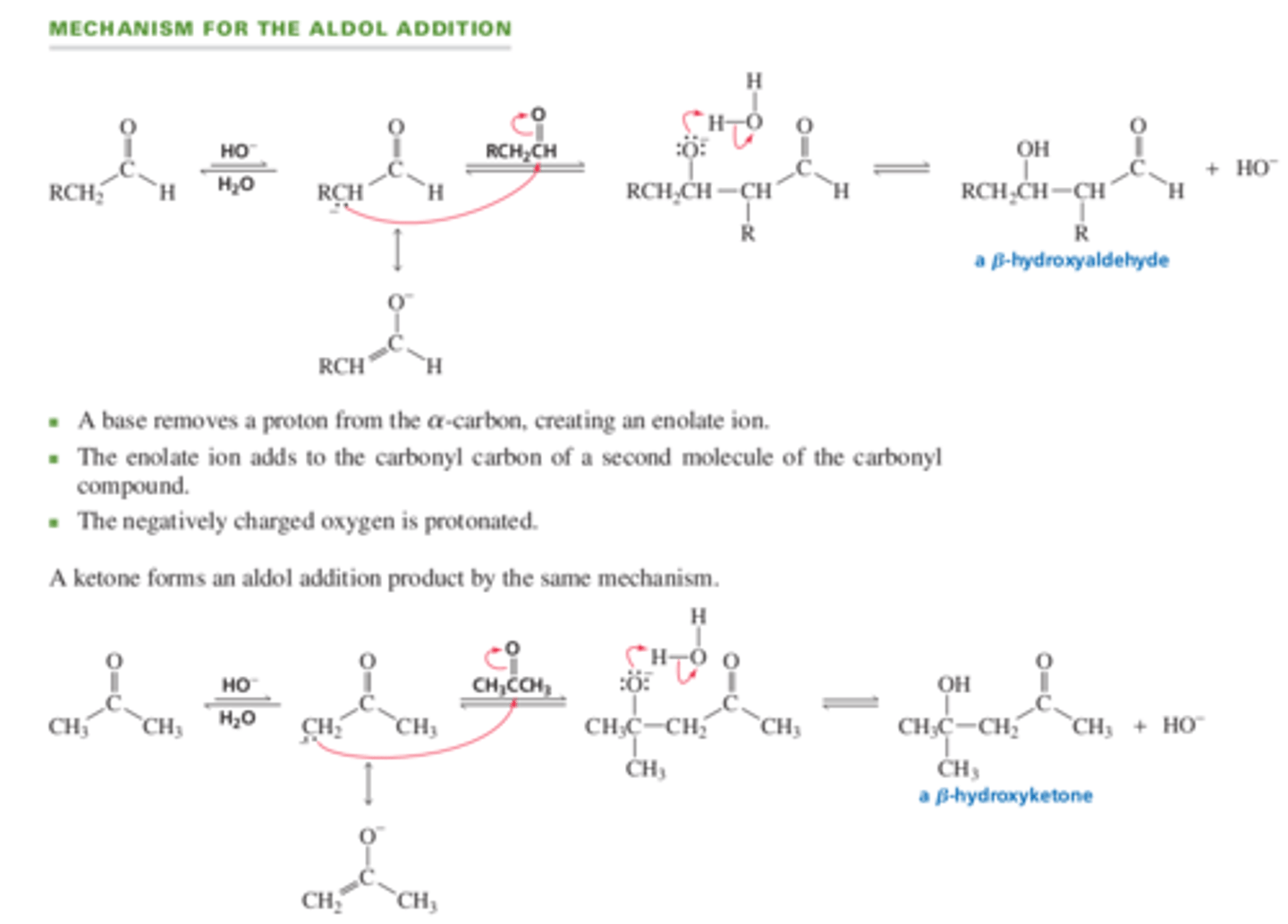
13.5 An Aldol Addition forms beta-hydroxyaldehydes or beta-hydroxyketones
The aldol addition is what kind of reaction?
nucleophilic addition
13.5 An Aldol Addition forms beta-hydroxyaldehydes or beta-hydroxyketones
Because an aldol addition is _______, when the product of an aldol addition (beta hydroxyaldehyde or beta-hydroxyketone)is heated with a hydroxide ion and water, the aldehyde or ketone that formed the aldol addition product can be regenerated
reversible
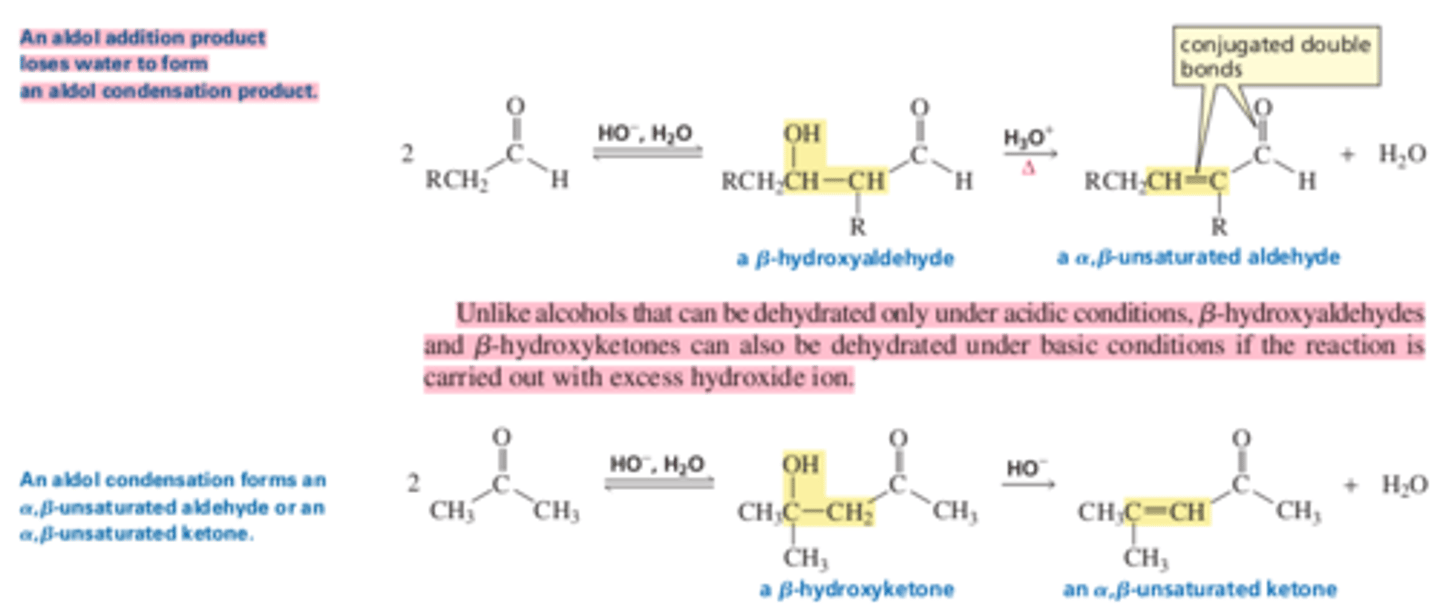
13.6 The Dehydration of Aldol Addition Products Forms alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones
Remember that alcohols dehydrate when heated with _____
acid
13.6 The Dehydration of Aldol Addition Products Forms alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones
The Beta-hydroxyaldehyde and Beta-hydroxyketone products of aldol addition reactions are easier to dehydrate than many other alcohols, because the double bond formed when the compound is dehydrated is _________ with a carbonyl group.
This characteristic increases the stability of the product and thus makes it easier to form
conjugation
13.6 The Dehydration of Aldol Addition Products Forms alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones
An aldol addition product loses _______ to form an aldol condensation product
water
13.6 The Dehydration of Aldol Addition Products Forms alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones
Unlike alcohols that can only be dehydrated under acidic conditions, Beta-hydroxyaldehydes and beta-hydroxyketones can be dehydrated under ______ conditions if the rxn is carried out with excess hydroxide ion
basic
13.6 The Dehydration of Aldol Addition Products Forms alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones
Reaction screenshot
13.8 A Claisen Condensation forms a β-Keto Ester
When 2 molecules of an ______ undergo a condensation reaction, it is called a Claisen condensation
esters
13.8 A Claisen Condensation forms a β-Keto Ester
Mechanism for Claisen Condition
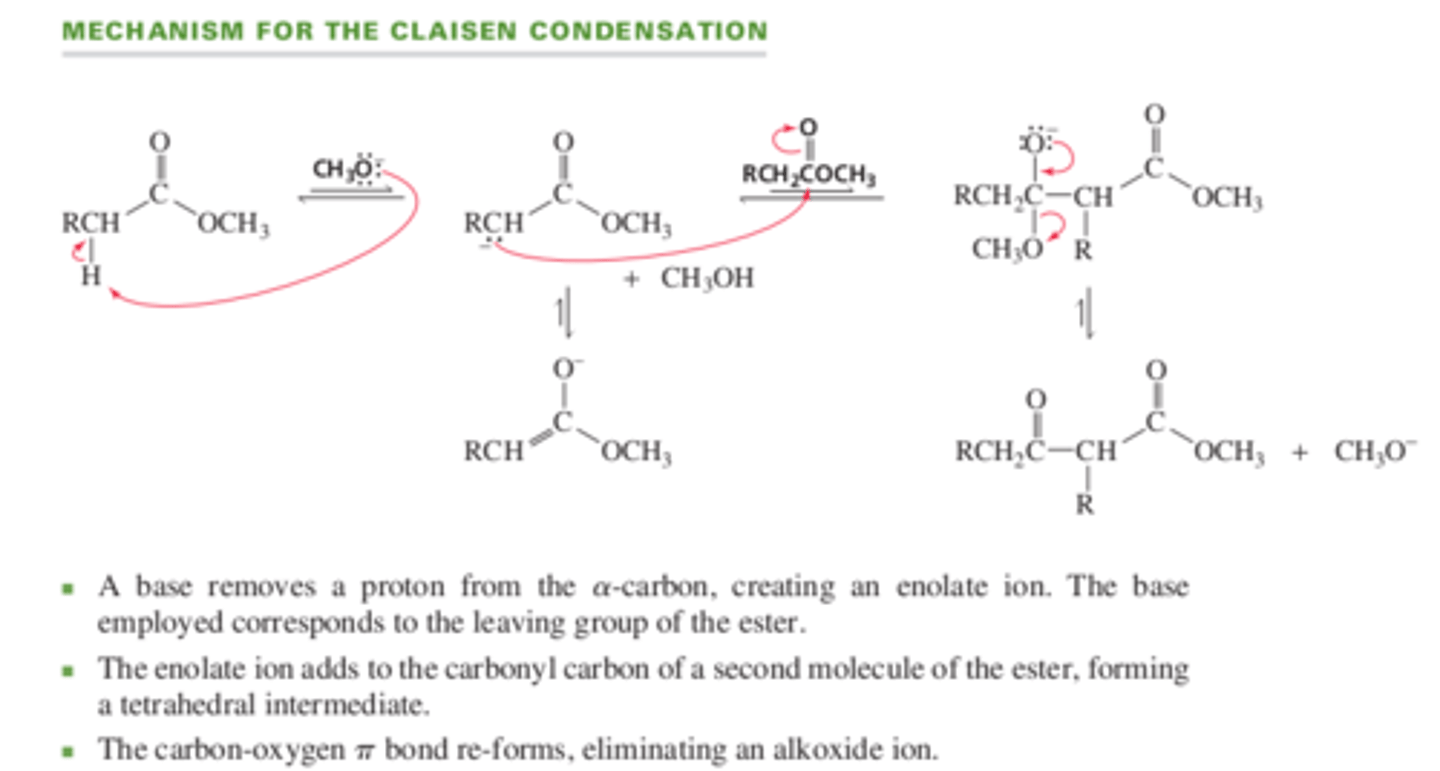
13.8 A Claisen Condensation forms a β-Keto Ester
The Claisen condensation is what kind of reaction?
nucleophilic acyl substitution
13.8 A Claisen Condensation forms a β-Keto Ester
In the Claisen condensation, the negatively charged oxygen re-forms the carbon-oxygen pi bond and eliminates the -OR group. In the aldol addition, the negatively charged oxygen obtains a _____ from the solvent
proton
13.8 A Claisen Condensation forms a β-Keto Ester
What kind of reaction is the Claisen condensation reaction?
What kind of reaction is the aldol addition?
nucleophilic acyl substitution, nucleophilic addition
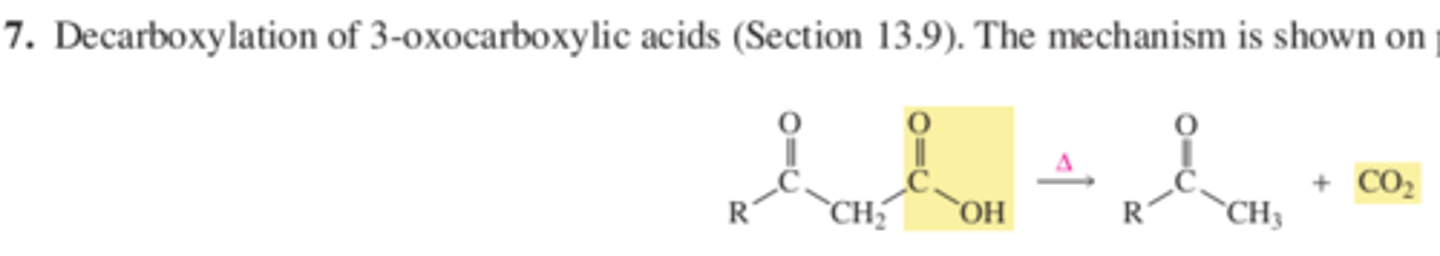
13.9 CO2 can be removed from a carboxylic acid with a carbonyl group at the 3 position
Decarboxylation is the loss of CO2 from a molecule and can occur if the CO2 group is attached the carbonyl group. What characteristic of carbanion is responsible for this phenomenon?
poor leaving group (strong base)
13.9 CO2 can be removed from a carboxylic acid with a carbonyl group at the 3 position
In summary, carboxylic acids with a carbonyl group at the 3 position lose CO2 when they are heated.
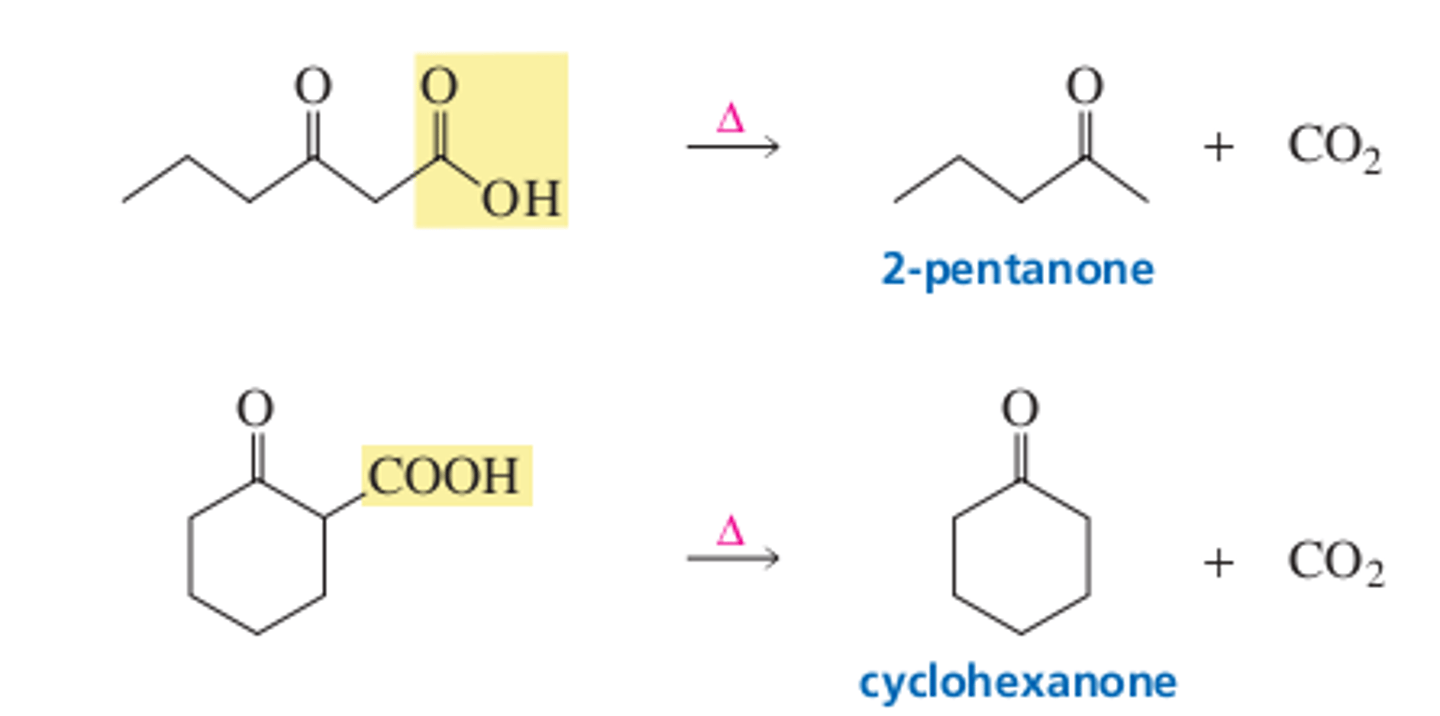
Summary points
A hydrogen bonded to an α-carbon of an aldehyde, ketone, or ester is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a _______ (weak/strong) base
strong
Summary points
Aldehydes and ketones (pKa 16-20) are _____ (more/less) acidic than esters (pKa 25). A hydrogen bonded to an α carbon flanked by 2 carbonyl groups is even____ (more/less) acidic (pKa 9-11)
more, more
Summary points
Keto-enol interconversion can be catalyzed by acids or bases. Which tautomer is more stable, keto or enol?
keto
Summary points
What reaction?
, the enolate ion of an aldehyde or a ketone reacts with the carbonyl carbon of a second molecule of aldehyde or ketone, forming a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone. The new C-C bonds forms between the alpha carbon of one molecule and the carbon that formerly was the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule
Chap 13 Summary Reactions
Rxn 1 Keto-enol interconversion (13.3 p 465)

Chap 13 Summary Reactions
Rxn 2 Alkylating the alpha carbon of carbonyl compounds (13.4 p 467)
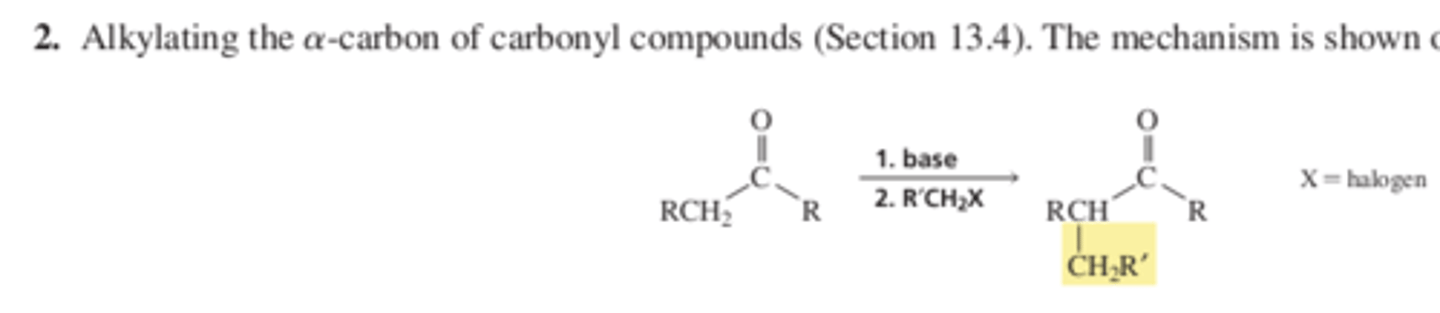
Chap 13 Summary Reactions
Rxn 3 An aldol addition of 2 aldehydes, 2 ketones, or an aldehyde and a ketone (13.5 p 469)
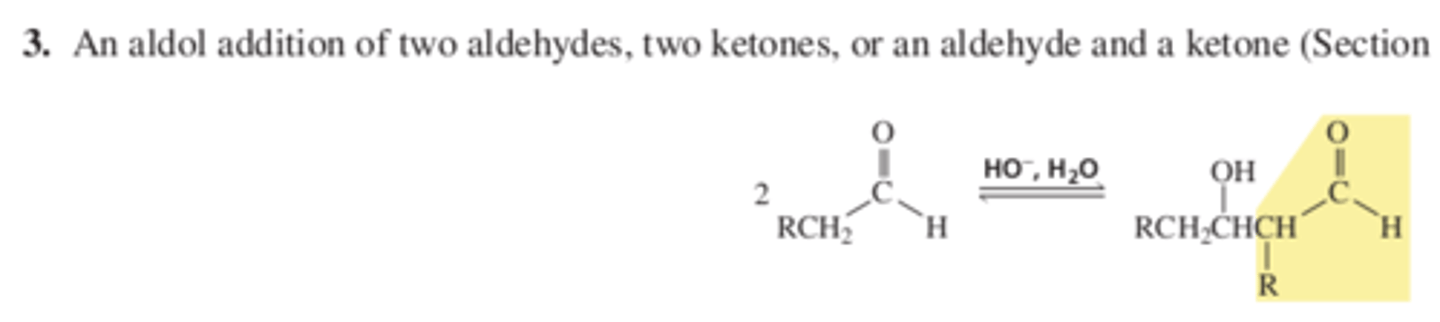
Chap 13 Summary Reactions
Rxn 4 An aldol condensation is an aldol addition followed by acid-catalyzed or base-catalyzed dehydration (13.6) p 470
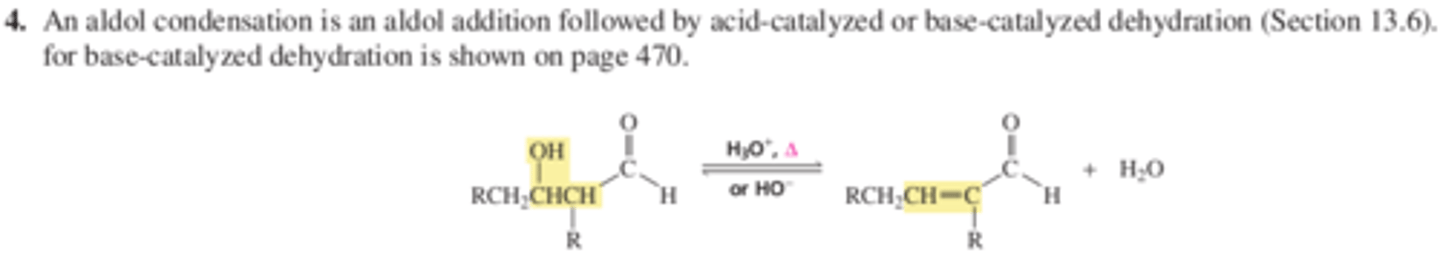
Chapter 13 Reactions
Rxn 5 Claisen condensation of 2 esters (13.8 p 473)
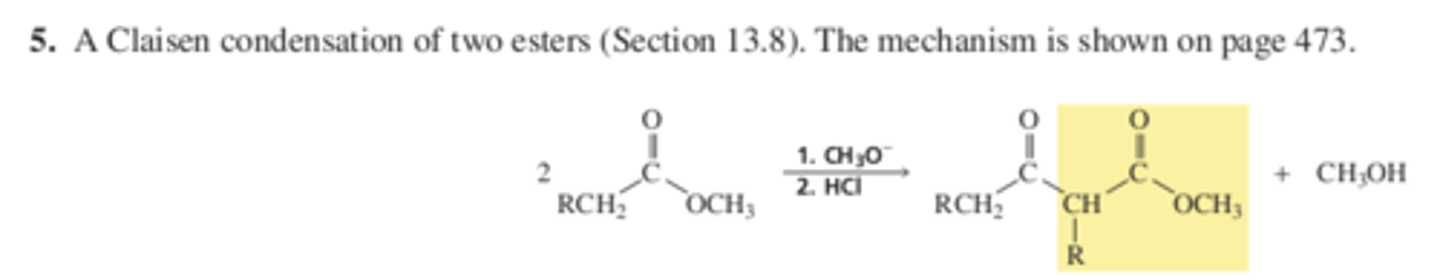
Chapter 13 Reactions
Rxn 7 Decarboxylation of 3-oxocarboxylic acids (13.9 p. 475)