BTEC applied science Unit 5 Physics
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is Hooke's Law?
When a spring stretches, the extension of the spring is proportional to the force stretching it, provided the elastic limit of the spring is not exceeded.
Equation for Hooke's law
F=K x e
What do the letters stand for in the hookes law equation
F= Force in newtons (N)
K=Spring constant in newtons per meter (N/m)
e= Extension in meters (m)
When deforming materials, what is the point called where it will no longer return to its original shape
Elastic limit
A spring with 10,000 n/m extends 10cm, how much force was applied?
F=Ke
F=10,000 x 0.1
F=1,000N
Steps for working out a maths question in Physics.
1 Write out the equation
2. Substitute
3.Calculate
4.Units
What is the difference between heat anf temperature
Temperature - Kinetic energy of particles (Vibrating)
Heat- is energy (J)
What is specific heat capacity
Specific heat capacity is the amount of energy needed to change the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1 degree celcius without changing state.
Units do q=mC∆T
Q= Energy in JM= mass in kilograms C=Specific heat capacity∆T= Change in temperature ( degrees C)
How do you work out gradient
change in y/change in x
What is Power?
the rate at which work is done
Power( W)=
Energy transfer (J)/Time (S)
Efficiency
The efficiency of an energy transfer is the proportion of the input energy that becomes useful output energy.
Efficiency=
Useful energy output / total energy input
terminal velocity
When a object falls it must move the fluid around it. This causes an upwards drag force which acts against the movement of the object.
What is Bernoulli's principle?
As the flow rate of a fluid increases the pressure at right angle to thee flow decreases.
Types of energy
mechanical energy, electrical energy,chemical energy,nuclear energy,thermal energy
Types of energy pathways
EM-radiation Electric current Mechanical waves
How do you transfer kelvin in to Celsius
-273
How do you transfer celsius to kelvin ?
+273
Springs in series
Springs arranged one after an other
Double the extension
each string will extend the same amount as they are both under the same amount of weight.
Springs in parallel
the weight is distributed evenly between parallel springs
tensile strength
A measure of how much stress from pulling, or tension, a material can withstand before breaking.
Equation for tensile stress
Stress= Force (N) / Area (M2)
Example question- A 10g log pen dangles from a human hair of diameter 10 micrometers. What is the stress?
Force+ 0.01 x 10= 0.1 N
Area = Pi x R2
Pi x (5X10 -6)= 7.85 x 10 -13M
Stress =Force/ Area
0.1/7.85 x 10 -3
=1.27 x 10 power of 11 Pa
Stain =
Change in length/ original length
Young's Modulus
stress ( Pa)/strain (Unitless)
Work done =
force x distance
What does the area between the lines on a load and extension graph of rubber show ?
Area between curves shows energy loss to thermal - count the squares.
Fatigue
By repeatedly loading and unloading a material we can microscopic defets. Continuing to load and unload the material makes these defects larger. This makes the material brittle and it will fracture .
Creep
All materials have particles moving with a distribution (Temperature ) . of energies.
What affects how fast a fluid flows down an incline?
Friction,
Temperature,
Material of the surface ,
gradient,
Viscosity of the fluid,
Depth of fluid
The Lower the viscosity the ....
Less friction there is between each layer
The deeper the fluid the greater the....
Number of joints between layer to slide past each other
What is vaminar flow
Vaminar flow is when the fluid stays in neat layers and moves along
What happens if there is an object in the way of the laminar flow ?
Turbulence occurs
What happens if fluid tries to flow too quickly
The frictional force between the laminar can cause the fluid at that point to move up or down .
Terminal velocity
When an object falls it must move the fluid around it . This causes an upwards drag force which acts against the movement of the object.
Bernoulli's Principle
as the velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases
Efficiency
The efficiency of an energy transfer is the proportion of the input energy that becomes useful out put energy
Efficiency=
Useful output / total input
What is the difference between heat and temperature?
Temperature- Kinetic energy of particles ( Vibrating )
Heat- Is energy
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1oC
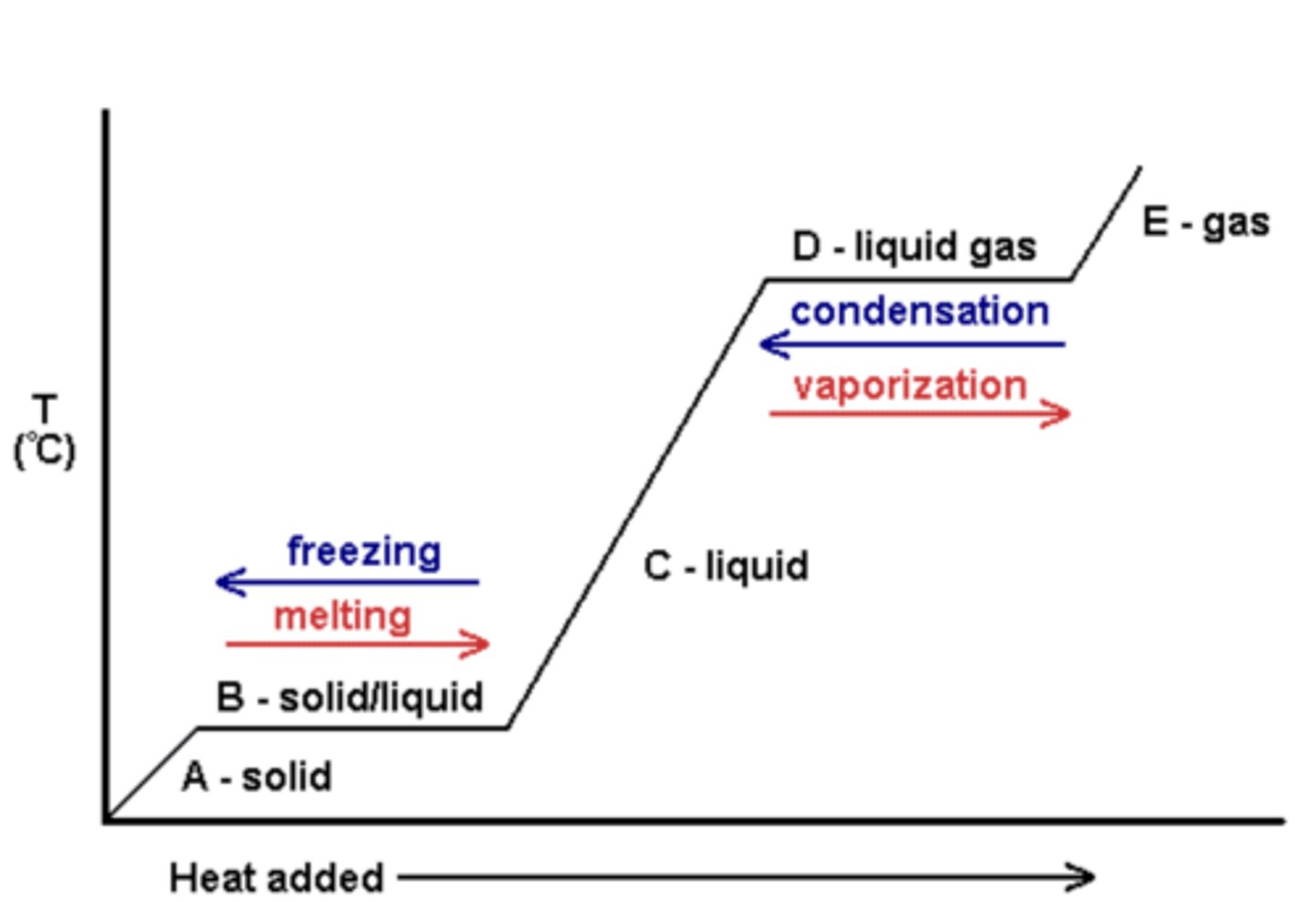
cooling curve graph