Simple Electric Circuits Key Terms
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
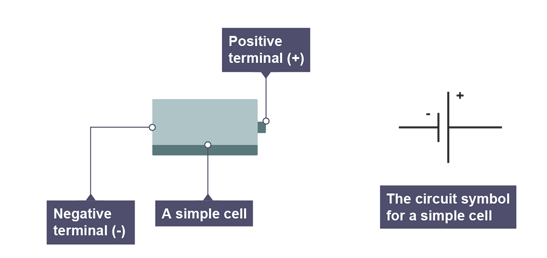
Cell (in terms of Physics)
One battery on its own is called a cell
A cell has a positive terminal and a negative terminal.
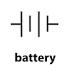
Battery
Two or more cells joined together make a battery. A battery is a source of energy which provides a push - a voltage - of energy to get the current flowing in a circuit
Circuit
Electrical current transfers energy around circuits. A closed loop through which current moves - from a power source, through a series of components, and back into the power source
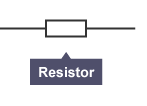
Resistor
A resistor is an electrical component that restricts the flow of electric current. Fixed-value resistors do not change their resistance, but with variable resistors it is possible to vary the resistance
Electric motor
An electric motor is a device that transfers electrical energy into rotational energy

Electrical conductor
Material that lets electric current flow through easily. Many metals, such as copper, iron and steel, are good electrical conductors
Electrical insulator
Material that does not let an electric current flow through easily e.g. the plastic coating around electrical wires prevent you from getting a shock
Electrons
A tiny particle with a negative charge. Electrons orbit the nucleus of atoms or ions in shells
Electrical current(A)
Flow of electric charge. The size of an electric current is the rate of flow of charge. Current is measured in amperes (A) using an ammeter
Coulomb (C )
The unit of electrical charge passing a point in a (direct current) circuit in 1 second when the current is 1 A
Electrical energy
Energy transferred by the movement of electrical charge.
Potential difference(V)
the amount of energy transferred or work done per unit charge. The unit is volt (V). A voltmeter is used to measure potential difference.
Series circuit
A series circuit is an electrical circuit where all components are connected in a single path, allowing the same current to flow through each component. If one component fails, the circuit is interrupted and all devices stop functioning.
parallel circuit
A parallel circuit is an electrical circuit where components are connected across the same voltage source, allowing multiple paths for current flow. If one component fails, the other components continue to operate as the current flows through multiple paths.
Fuse
A fuse is a safety device that protects electrical circuits by melting and breaking the circuit when excess current flows, preventing damage to wiring and components.
resistor
A resistor is an electrical component that resists the flow of electric current, creating a voltage drop within an electrical circuit. The resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
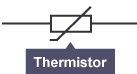
thermistor
A thermistor is a temperature-dependent resistor made from semiconductor materials, with resistance changing significantly with temperature(proportional). There are two types: NTC, which decreases in resistance as temperature rises, and PTC, which increases resistance with temperature. Commonly used in temperature sensing and control applications.
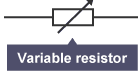
variable resistor
A variable resistor, commonly known as a potentiometer or rheostat, is an electrical component whose resistance can be adjusted manually. This adjustability allows for the precise control of current and voltage levels in a circuit.
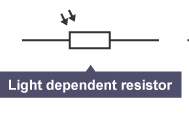
Light-dependent resistor (LDR)
The resistance of a LDR depends on light intensity.
-At low light levels, the LDR has a high resistance.
-As the light intensity increases, the resistance decreases.
A LDR can be used as a sensor in cameras or automatic lights that come on when it gets dark.
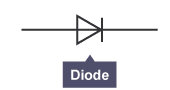
diode
A semiconductor diode allows current to flow in one direction only.
Examples of semiconducting materials include silicon and germanium.
Diodes are used to convert an alternating current into a direct current.
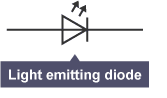
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
A light emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it, used in various lighting applications.