Edexcel A-level Economics Theme 2
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a whole, including inflation, growth and unemployment.
Aggregate demand
The total amount of goods / services demanded in an economy at a given time at a given price level.
Aggregate supply
Total amount of goods and services supplied in the economy at a given time at given price level.
What is GDP?
Gross Domestic Product = the total value of all goods and services produced in an economy in a given time period.
What does % change in GDP show?
The rate of economic growth in an economy
Difference between real GDP and nominal GDP?
Real = adjusted for inflation. Nominal = A monetary amount not adjusted for inflation
Difference between total GDP and GDP per capita?
Total GDP = Total GDP in an economy. GDP per capita = Total GDP/Total Population
What is Gross National Income (GNI)?
The total amount of money earned by a country's people and businesses plus net overseas interest payments and dividends.
Who has the 3 biggest GDPs in the world?
1st = USA, 2nd = China, 3rd = Japan
Disadvantages of using GDP to compare economic growth? (4)
1. Inaccurate data (black markets/ tax avoiding sectors)
2. Doesn't show inequality in income distribution (Gini coefficient could help)
3. Doesn't compare quality of goods/services
4. Difficult to compare countries due to exchange rates
Benefits of economic growth on consumers (3)?
1. Higher disposable income
2. Standards of living increase
3. Price of goods may fall and quality increase.
Benefits of economic growth on firms (2)?
1. Higher revenue/profits = more investment
2. Benefits from more sales (due to higher disposable incomes)
Benefits of economic growth on the government (2)?
1. Increase in tax revenue (pay off debts/spend)
2. Wins votes
Positive impacts of economic growth on economy as a whole (2)?
1. Country wealth increases
2. Standards of living increase
Negative impacts of economic growth on an economy (4)?
1. Pollution = Transport/manufacturing
2. Unsustainable (will reach full capacity)
3. Hyper inflation due to demand driven growth
4. Potential increased inequality
Purchasing power parities
An exchange rate of one currency for another which compares how much a typical basket of goods in one country costs compared to that of another country.
How is the UK's national well-being measured?
A national well-being report (started in 2010) asks people 4 questions about satisfaction, happiness, anxiety and worthwhileness. Its updated quarterly.
How has the UK's national well-being changed from 2012-2016?
Satisfaction, happiness and worthwhile all increased (due to rising GDP and falling unemployment). Anxiety did fall but is rising again due to fears over global security.
What is the relationship between real incomes and subjective happiness?
They are positively related at low incomes (eg: if you are poor and your income rises, then your happiness will increase. However, higher incomes are not necessarily related to higher happiness levels).
Define Inflation
A sustained rise in the price level. (Erodes the purchasing power of money).
Define deflation
A persistant fall in the price level. (Money can buy more, caused by a lack of spending)
Define disinflation
When the rate of inflation decreases. (Prices are still rising just not as quickly)
Define hyper inflation
Large increases in the price level
Impacts of inflation on consumers/workers? (3)
1. Purchasing power declines (especially if inflation rises faster than wages).
2. Savings are eroded (especially if inflation rate is higher than interest rate)
3. Value of loans decreases
Impacts of inflation on Firms (4)?
1. Goods become more expensive compared to foreign competitors so exports decline.
2. Uncertainty = lack of investment etc
3. Increased revenue so potentially more profit (but costs rise too).
4. Wage increase may be below inflation (so real wage costs fall for firms).
Impacts of inflation on the government (3)?
1. Income redistribution (fixed incomes become worse off).
2. Reduced value of debt in real terms.
3. Makes people spend now before prices rise (so more tax revenue etc)
What inflation rate does the Bank of England target?
2%. (Too high would make people spend more before prices rise and hyper-inflation would occur)(Too little and disinflation could occur)
Consumer Prices Index (CPI)
A measure of the price level used across the European Union and used by the Bank of England to measure inflation against its target.
How is the Consumer Price Index (CPI) calculated?
-Calculated using a basket of 650 goods (chosen on an annual survey from 7000 households).
-Uses index based on 1996 (Prices in 1996 = 100)
-Measures percentage change based on 1996 index/
Problems with CPI (4)
1. Doesn't include housing costs
2. Basket only adjusted annually (tastes change quicker)
3. Doesn't account for quality changes
4. Surveying issues
What is the Retail Price Index (RPI)?
Similar to CPI but includes housing costs. Alternative measure of inflation but is not used and is not used for international comparison. Been used for 60 years in the UK.
What is the consumer price index including owner-occupiers' housing costs (CPIH)?
Uses a technique called 'rental equivalence' to estimate costs faced by owner-occupiers. However, doesn't have a direct measure of mortgage costs.
Causes of inflation (3)
1. Cost-push inflation
2. Demand-pull inflation
3. Growth of the money supply
Define Cost-push inflation
A cause of inflation whereby increases in in the costs of production in the economy result in increase prices. (AS falls = Price level rises)
Define demand pull inflation
Inflation caused by excess demand in an economy (AD increases pushing price level up)
How does growth of money supply lead to inflation?
When firms/consumers have greater access to money they have more to spend on the same amount of goods so prices must rise.
Define employment
The number of people in paid work
Define economically active
People who are actively seeking work
Define discouraged worker
Someone who was looking for a job but has since stopped looking (due to lack of skillset/lack of jobs).
Define unemployed
People who are economically active but are not in employment.
Define workforce
Number of people who are economically active
Define unemployment rate
The % of workforce who are seeking employment but are not employed.
Define employment rate
Number of people in work as a % of the workforce.
What are the 2 measures of employment in the UK?
1. The claimant count
2. The International Labour Organisation (ILO) and UK Labour Force Survey
Define Claimant Count
Number of people claiming the jobseekers allowance.
2 disadvantages of using claimant count
1. Some who are not actually economically active may claim jobseekers allowance.
2. Retired people may not need/want jobseekers allowance.
Describe the ILO and UK labour force survey
Labour force survey carried out by ONS surveys over 40,000 people in households. Classes people as employed (1hr+ work per week), unemployed (looking for job in past 4 weeks) or inactive (not seeking employment).
Compare claimant count and LFS
Claimant count includes people in hidden economy and fraudulent claimers.
You can't claim if your partner is in work, you study and want to work, or you are around pension age. Therefore LFS is usually higher as it does account for those people.
Why do both claimant count and LFS underestimate unemployment?
Doesn't include: sick/disabled people, people who are part time but want full time, people in training/ education who want employment.
Describe underemployment
Underemployment = Part time/ zero hour contract/ self employed people who would like to be full time employees. Also includes people who are working below their skill level (graduates working as bartenders). Not included in unemployment statistics.
Effects of an increase in inactive population (2)?
Fall in productive potential of a country.
Lower tax and lower GDP.
What is frictional unemployment?
The unemployment which exists in any economy due to people being in the process of moving from one job to another. Not serious as it is short term.
What is structural unemployment?
Long term decline of demand in an industry leading to increased unemployment. Can due to a regional closure of industry, due to a lack of demand in a sector, or due to technological changes. More serious form of unemployment.
What is seasonal unemployment?
Workers who do not work year-round because of the nature of their jobs. Eg: tourism has strong seasonal demand.
What is cyclical unemployment?
Aka: "Keynesian Demand Deficient Unemployment"
Occurs when there is a general lack of demand for goods and services in an economy (recession).
What is real wage inflexibility?
When a minimum wage means that real wages are above the market clearing level. Best shown on a Labour S+D diagram.
Impacts of migration on labour market (3)?
1. Creates more jobs due to more demand (circular flow of income)
2. Increases labour supply so lowers wages (low-skilled most affected).
3. Migrant workers may fill skill shortages in some economies.
Impacts of unemployment on consumers? (2)
1. Those who are unemployed have less to spend.
2. Less choice / lower quality
Impacts of unemployment on Firms? (3)
1. Less revenue = less profit
2. Can offer lower wages
3. Reduced pool of labour as skills become obsolete
Impacts of unemployment on workers? (3)
1. Loss of incomes for those unemployed
2. Skills become obsolete (stigma of long-term unemployment)
3. Fall in wages/ lack of security for those in jobs
Impacts of unemployment on government? (2)
1. Less tax revenue
2. Higher employment benefits to pay
Impacts of unemployment on society? (3)
1. Lower potential national output
2. Social decline (crime etc)
3. Lower living standards
What is the current account made up of?
1. Current account
2. Financial account
What does the current account measure?
Trade in goods as well as trade in services.
Current account surplus?
Where exports (of goods and services) are greater than imports.
What is the formula for AD?
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
Shows total spending in whole economy.
What is consumption (C) and what impacts it?
-Value of all goods+services purchased by consumers.
-When MPS is higher, C decreases.
-When interest rates are high, C decreases as saving is more worthwhile.
-When consumer confidence is high, C increases.
-When a country has high wealth, C increases.
What is Investment (I) and what impacts it?
-Spending by firms to increase output, efficiency and capital goods.
-Gross investment doesn't account for depreciation in -value of machinery etc, but net investment does.
-Low interest rates = high investment
-High business confidence (due to high growth levels) = high investment
-High demand for exports= increased investment
- Gov tax breaks etc = high investment
What is government spending (G) and what impacts it?
-Total spending made by a government funded by taxes and borrowing.
- Trade cycle impacts G. Eg: in a recession gov will spend more to increase AD and grow.
- Fiscal policy can change net gov spending
What impacts on net trade balance (X-M)? (6)
1. Increased real income in UK will increase imports
2. Exchanged rate: SPICED : Imports increase, exports decrease so net trade balance is negative.
3. State of world economy (Eg: the countries which the UK exports to must have a strong economy to keep trade balance positive)
4. Protectionism : Exports may decrease if someone else adds tariff or quota.
5. Non-price factors: Eg: Good quality Uk goods increases exports
6. Relative inflation: High UK inflation will increase price of UK goods making them less competitive so X falls.
What is the difference between Short and Long run AS?
Short Run - At least one factor of production is fixed
Long Run - All factors of production are variable
Factors influencing Short Run AS? (3)
A change in costs of production for firms will shift the SRAS curve. The 3 main factors are cost of raw materials, change in exchange rates, change in tax rates
How will cheaper materials, strong £ and lower tax rates impact on SRAS?
They will all lower costs of production for firms increasing SRAS shifting the curve to the right.
What are the two models for Long Run AS?
LRAS is a measure of potential output (linked to PPF)
Monetarist (Classical) LRAS curve
Keynesian LRAS curve
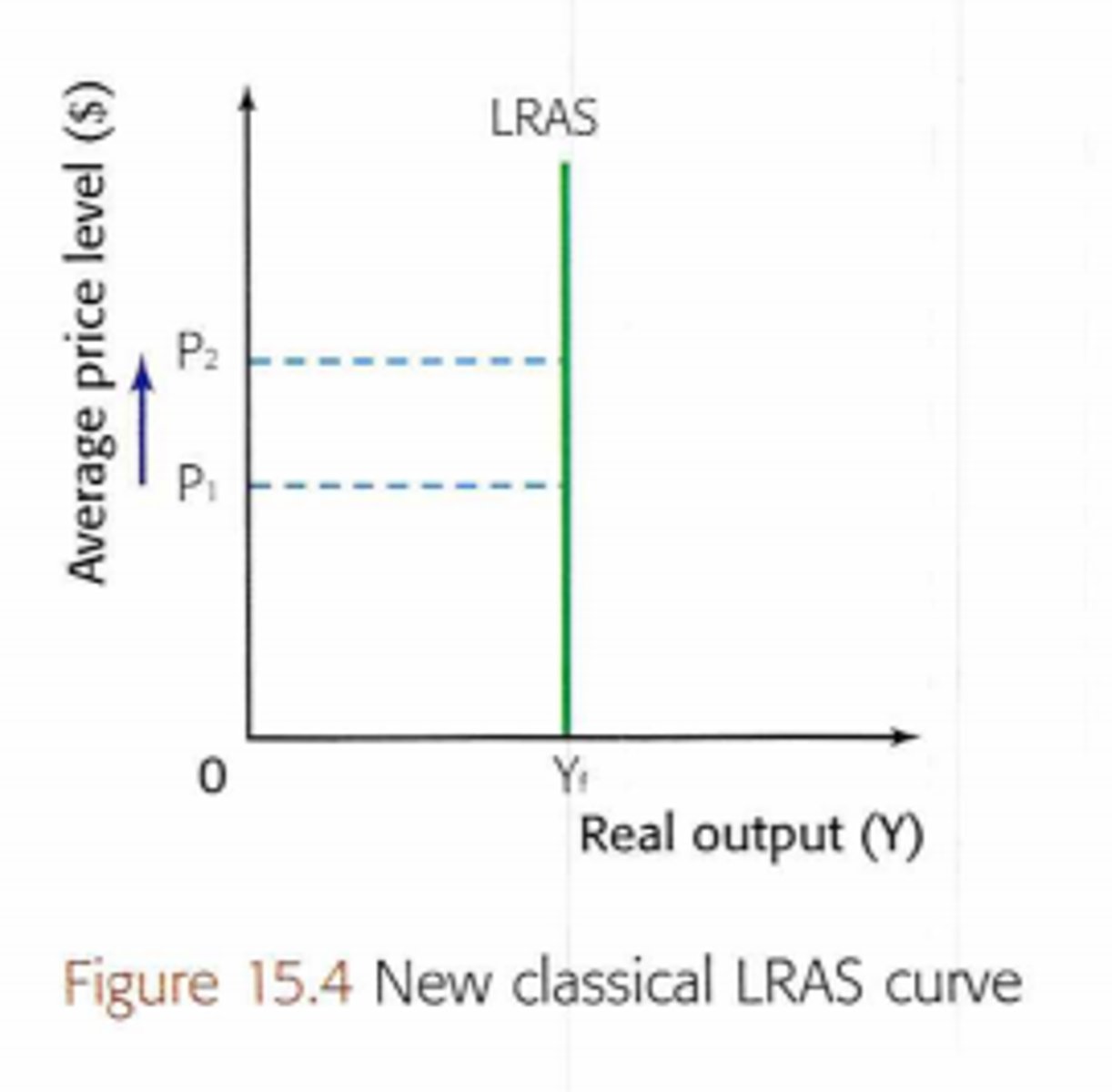
Describe Monetarist/Classical LRAS curve
Monetarist LRAS assumes an economy will always operate at full potential (Yfe) (vertical line). Therefore an increase in AD will not increase output but will just increase inflation.
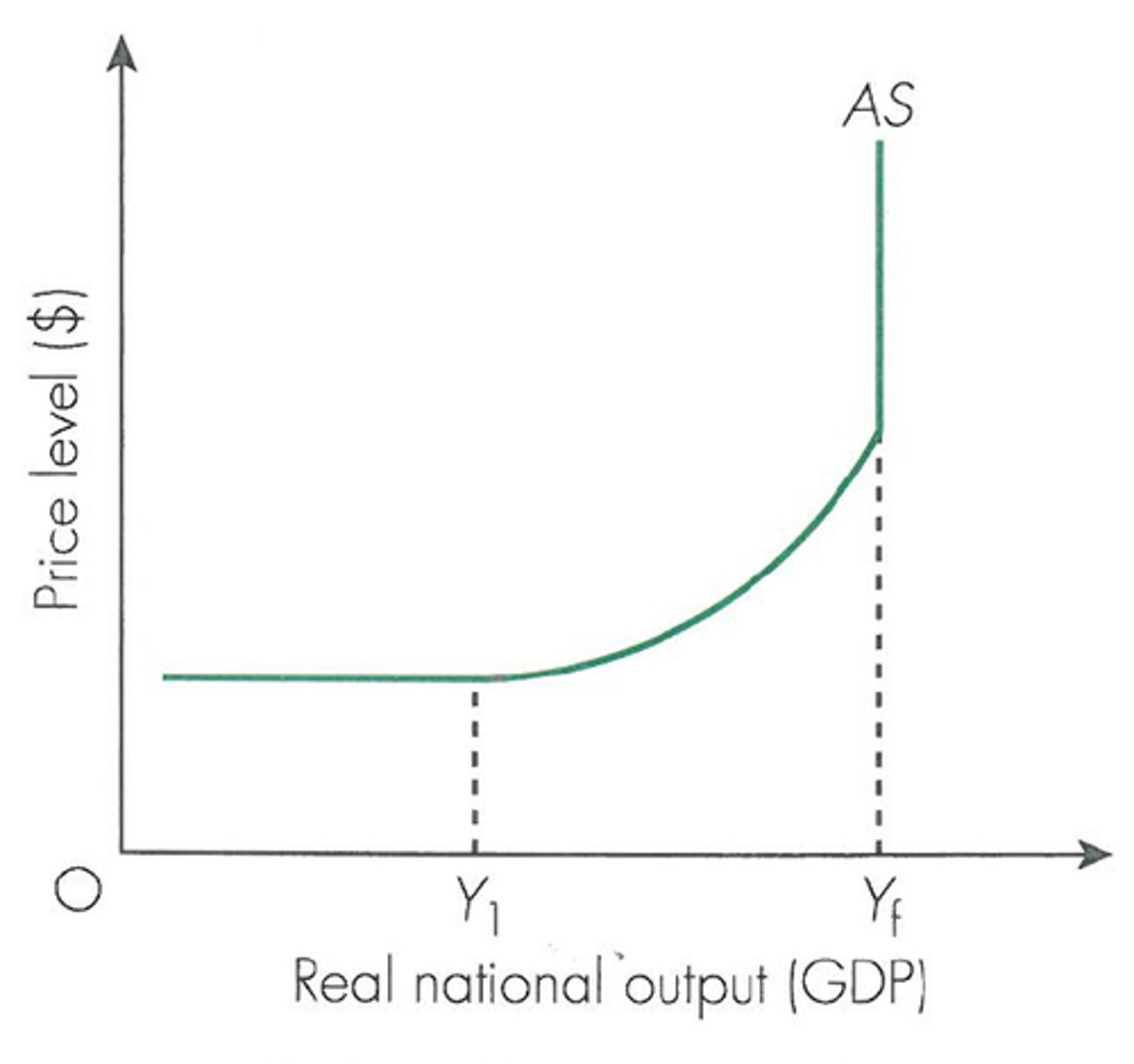
Describe Keynesian LRAS theory
Suggests that while there is a lot of spare capacity (at lower output) an increase in AD will massively increase output but only slightly increase the Price level.
However, as the economy moves closer to Yfe, an increase in AD increases output very little but results in high inflation.
State the factors influencing LRAS (6)
1. Technology
2. Changes in productivity
3. Changes in education and skills
4. Changes in government regulation
5. Demographic changes and migration
6. Competition Policy
How do technological advances impact LRAS?
Better technology speeds up production using the same amount of resources. Investment in technology will shift LRAS to the right as more can be produced so potential output increases.
What causes increased productivity and how does it impact LRAS?
Caused by increased : efficiency, skill of labour, technology.
More productive means more can be produced with the same amount of resources so LRAS is increased.
If the UK is more productive in one sector, investment into that area increases, further expanding LRAS.
How do educational and skill changes impact LRAS?
A more skilled workforce will be more employable and work more efficiently within their jobs. This will increase LRAS.
How can government policy impact LRAS?
Gov can increase size of workforce by encouraging people to go back to work.
Can offer tax breaks to research+development firms who could initiate ideas which increase productivity and LRAS.
Incentivise business start ups (lower corporation tax etc) which would increase LRAS.
High business regulation decreases LRAS as it increases costs for firms.
How do demographic changes and migration impact on LRAS?
Where immigration>emigration, population size increases so there are more workers which increases LRAS and increases productive potential (Yfe).
However, ageing population or older migrants will not increase LRAS as they do not contribute to the workforce.
How does competition policy impact LRAS?
Gov can promote competition between firms which will force each firm to increase their efficiency which will increase LRAS.
However, less competition sometimes encourages investment and innovation. (Eg: copyright laws incentivise firms to research new ideas, this will increase LRAS).
Describe the circular flow of income
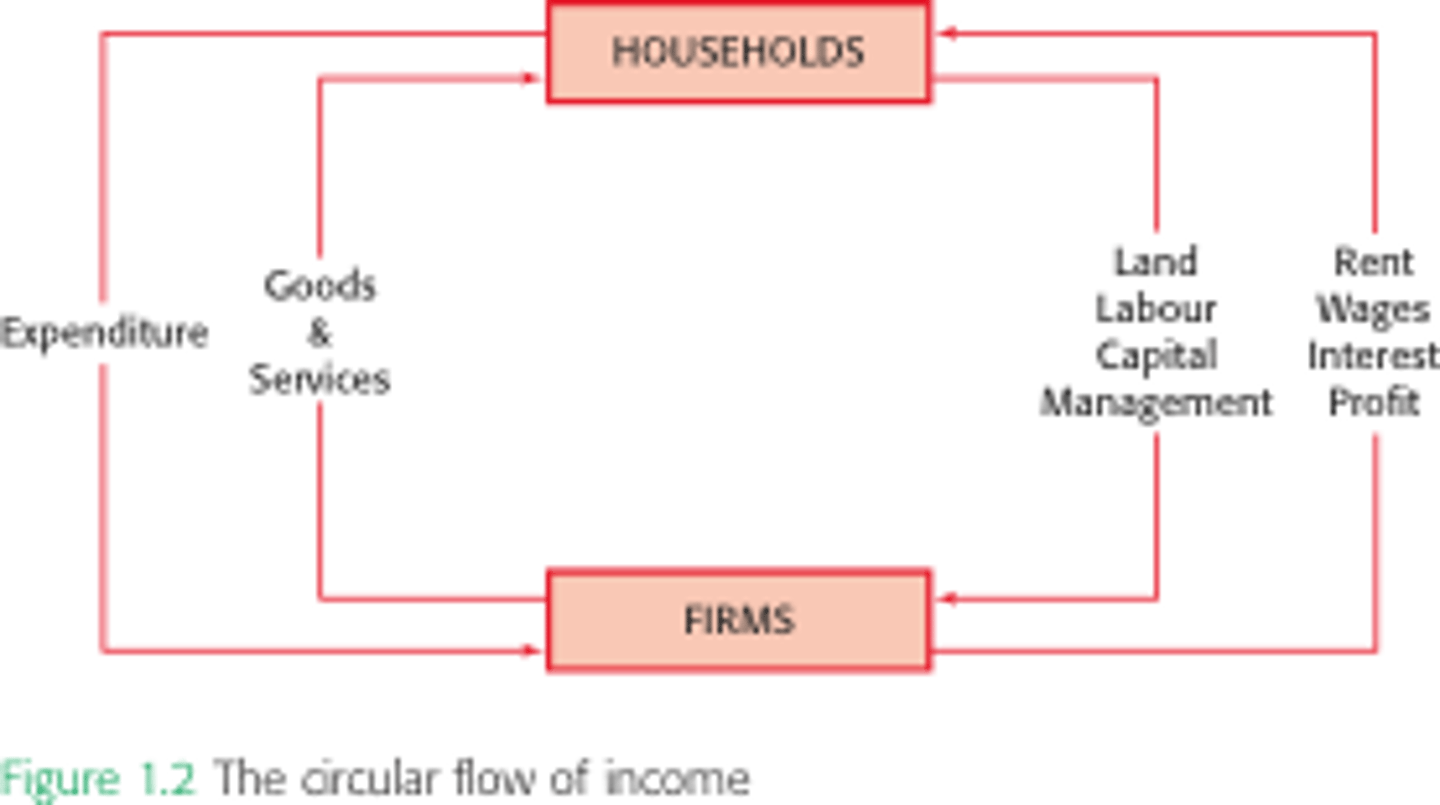
What are the injections into the circular flow of income? (3)
1. Government spending
2. Exports (puts money into economy)
3. Investment
What are the withdrawals from the circular flow of income? (3)
1. Taxation
2. Imports
3. Saving
Difference between income and wealth?
Income = Money flows whereas Wealth = Held Assets
Describe the multiplier effect
Where injection into an economy encourages more spending, sending a ripple of economic activity through the economy
What makes up MPW?
MPW = MPT + MPS + MPM
What is the multiplier equation?
Multiplier = 1/MPW
(=1/(1-MPC) as whatever isn't consumed is withdrawn
How does the multiplier work?
It means that any initial injection into the economy is multiplied and becomes greater. EG: 100bn of government spending will increase AD, but with a multiplier of 1.5, this 100bn will result in 150bn of spending which will further increase AD.
What factors influence the multiplier value?
Any factor which changes Consumption C will change MPC which will change the multiplier. EG: Interest rates decreasing = more consumption = higher multiplier
When will the multiplier be largest? Describe the impact on AD
Will be largest when MPW is lowest (ie: when MPC is highest due to (1-MPC=MPW).
This will result in a further increase in AD, greater than the initial shift after the injection.
How does spare capacity impact on the multiplier effect?
When there is little spare capacity, the multiplier will increase AD and this will increase prices more than output, so there will be little impact.
However, when there is lots of spare capacity, the rise in AD will result in a large rise in output but only a small rise in price, ie: it has a greater impact.
What are potential causes for economic growth?
Any increase in the 4 factors of production: Land, Labour, Capital or Enterprise.
Land (eg new oil resources)
Labour (size/quality of workforce)
Capital (investment will increase a country's capital)
Enterprise (Gov tax breaks etc)
Difference between potential growth and actual growth?
Potential growth = An increase in Yfe (ie: an increase in LRAS)
Actual Growth = The change in GDP.
For example, if the productive potential increases due to a shift in LRAS, then there is potential growth. When there is an increase in AD too, and there is a new output level, this is actual growth.
What is export-led growth?
Economic growth due to a rise in AD due to an increase in exports (X-M). Requires international trade.
What countries have benefitted from export-led growth?
Germany, Japan, China
Benefits of export-led growth? (3)
1. Greater GDP due to higher AD
2. Although it initially increases AD, it will force firms to invest which will increase LRAS.
3. Forces British firms to become more efficient in order to be competitive in global markets.
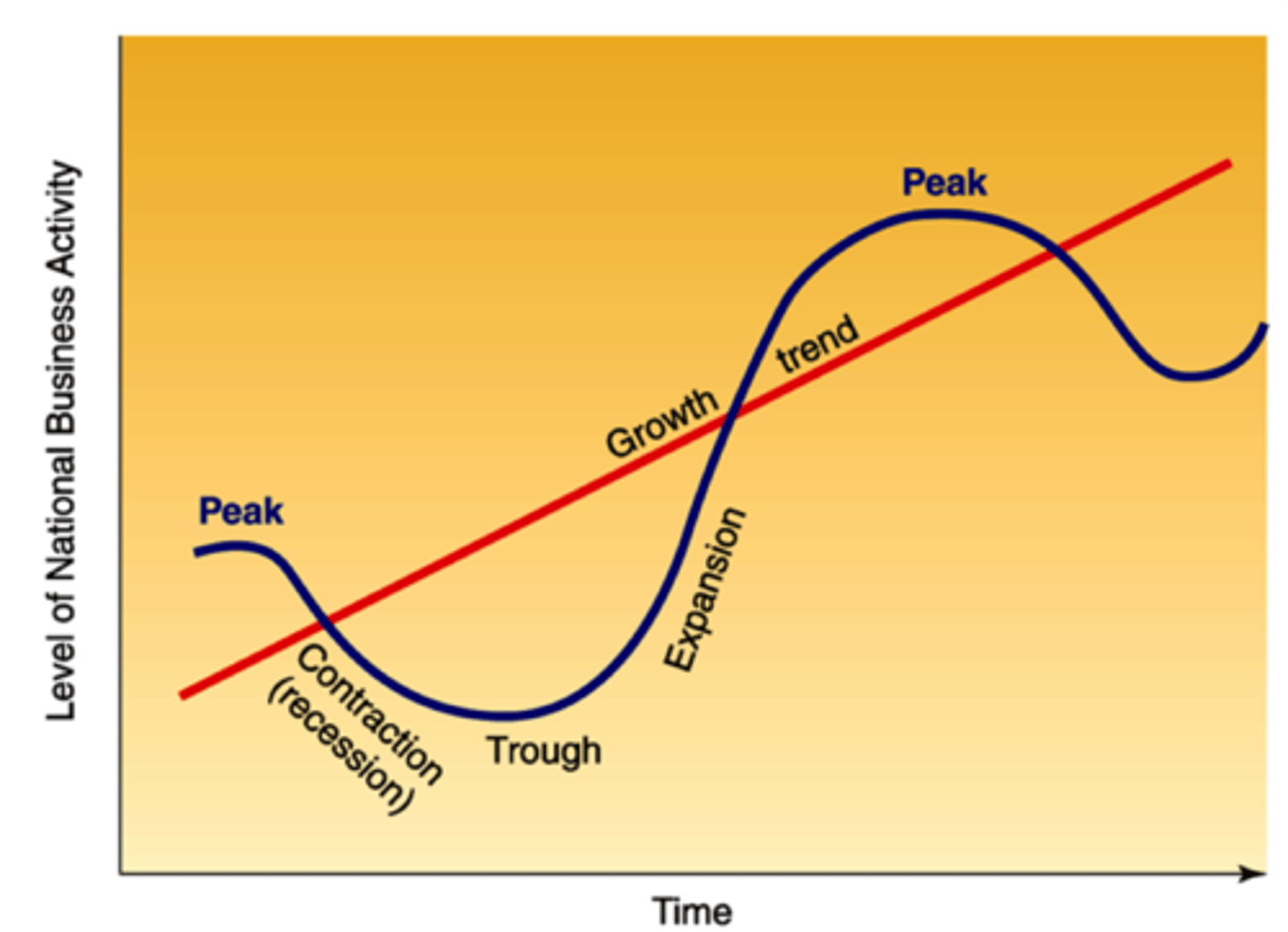
What does the business cycle show? (2 main lines)
1. Long run trend rate of growth = Trend GDP = avg sustainable rate of economic growth.
2. Actual change in GDP over a period of time