Ch 7 Corruption and Ethics in Global Business
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Ethics
The branch of philosophy that addresses the values pertaining to human behavior, with regard to the "rightness" and "wrongness" of actions and to the "goodness" and "badness" of the intent and results of such actions.
Integrity
Adherence to moral and ethical principles; soundness of moral character; honesty. As a practical matter, a person of integrity knows what is right and has the courage to do it.
Imperative principle
Do what is right.
Utilitarian principle
Do what produces the greatest good.
Generalization argument
Do what is right, but filter the action by consideration of the consequences.
Basic Steps in Ethical Decision Making
Define all the facts and circumstances, including who, what, where, when, and how. Identify the people affected by the situation and their rights and obligations. Identify the alternative decisions and consequences. Make the decision: determine the right thing to do and then do it.
BBB Code of Business Practices
A set of guidelines that include building trust, advertising honestly, telling the truth, being transparent, honoring promises, being responsive, safeguarding privacy, and embodying integrity.
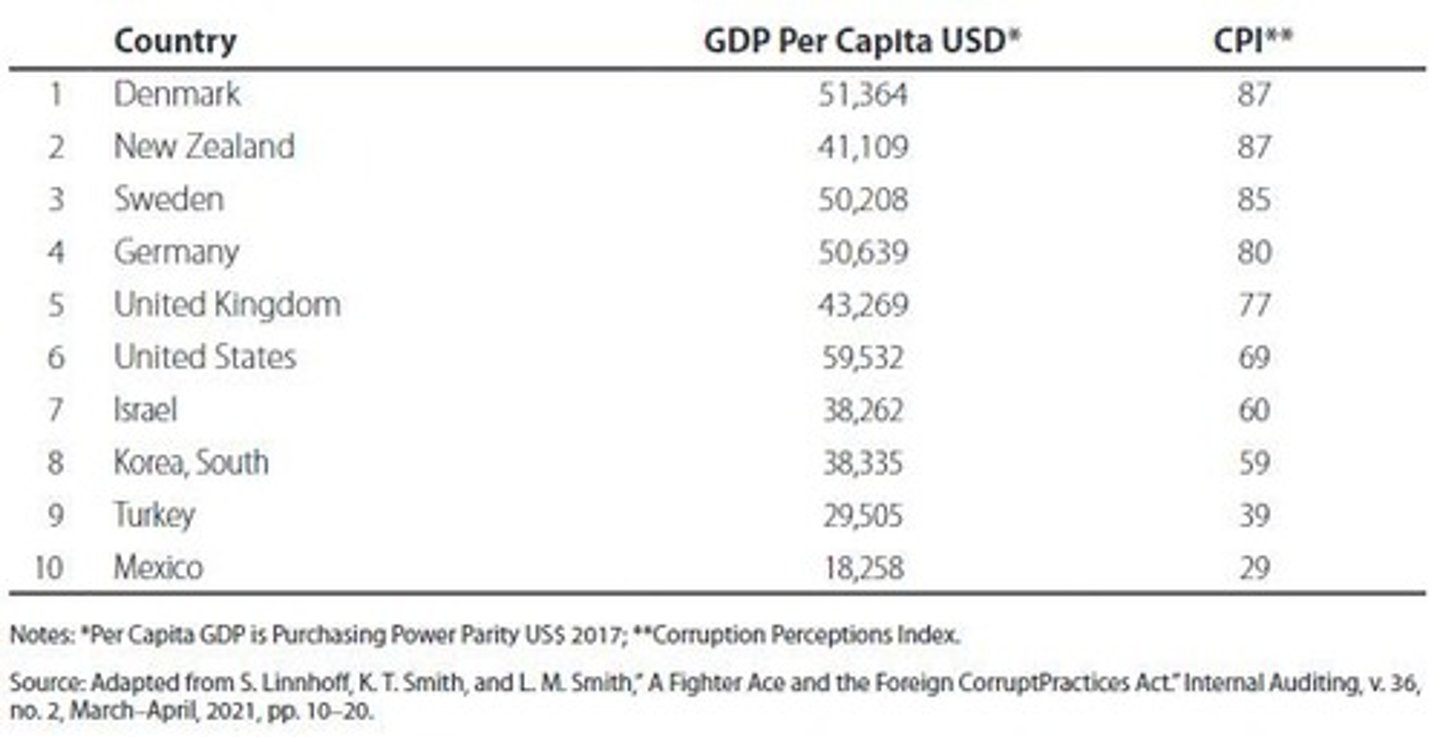
Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI)
Published each year by Transparency International, providing metrics to the potential corruption risk for most of the world's countries.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
A company's obligations to society, including the welfare of people and places affected by company activities.
CSR Mandates
A company should try to provide quality products or services, provide an appropriate return on investment to the company's stockholders, treat its employees with dignity and respect, take care of the environment, meet its legal obligations, and deal fairly with suppliers, lenders, and other business parties.
Ethics in Business and Society
For ethical business activity to occur, mutual trust, fair dealings, and honest communication are essential.
Unethical behavior
Destroys fair investment markets, such as using inside information.
Commonly-shared positive ethical values
Values regarding respect for individuals, their lives, their property, and their freedoms promote individual integrity and doing the 'right thing.'
Making an ethical choice
Follow legal rules, apply the formal ethical policies of your organization, and use your moral intuition.
The principle of consistency
Considering what would be the consequences if everyone made the same choice that you are about to make.
The principle of respect
Choosing the alternative that treats people with the greatest respect.
Enron
A major global provider of electricity, natural gas, pulp and paper, and communications services that used innovative and misleading accounting to avoid disclosing unprofitable operations.
Mark to market accounting
An accounting practice used by Enron to avoid disclosing unprofitable operations.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
A federal securities law for financial accounting and reporting transparency, passed in response to the Enron scandal.
WorldCom
A company that used fraudulent accounting methods to manipulate earnings and present a false image of growth.
Line costs
Costs that WorldCom underreported as assets rather than expensing them.
Vivendi
A French-based multinational corporation that used fraudulent accounting methods to hide financial problems.
Vivendi's CEO fine
The CEO was required to resign and pay a fine of $1 million after the fraud was discovered.
Parmalat
An Italian-based multinational corporation that used risky derivatives to disguise losses and collapsed into bankruptcy.
Teapot Dome scandal
Resulted from the secret leasing of Teapot Dome oil reserves to a businessman who paid Secretary of the Interior Albert Fall.
Ponzi scheme
A fraud in which money from later investors is used to provide returns to earlier investors.
Charles Ponzi
The individual who first perpetrated the Ponzi scheme during the 1920s.
Five fundamentals of ethics education
Personal integrity, responsibility of business in society, ethical decision making, ethical leadership, and corporate governance.
Internal Controls
A system of rules and procedures designed to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial and accounting information.
Preventive Controls
Controls that include hiring competent and ethical employees, having written policies and procedures, providing for the physical security of firm assets, and keeping adequate documents and records.
Feedback Controls
Controls that include production quality control and internal auditing.
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) of 1997
Applies to U.S. firms and to foreign firms that engage in business in the United States, consisting of an anti-bribery provision and a requirement to maintain an adequate internal control system over financial books and records.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) of 2002
Increased the prison sentence for fraud to 25 years and established 20-year sentences for destroying, altering, or fabricating records in federal investigations, or any scheme to defraud shareholders.
Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Certification
Requires that the CEO and Chief Financial Officer of a publicly traded corporation must certify that its financial statements accurately present the firm's financial condition and results of the firm's operations.
Basic Threats to Computer Security
Natural disasters, dishonest employees, disgruntled employees, persons external to the organization, accidental errors and omissions.
Cybercrime
A growing problem facing businesses, including cyber terrorism, costing a company in multiple ways, including lost business and harm done to physical and virtual assets.
Success Measurement
Many people think of fame and fortune when they measure success, but inner peace and soul-deep satisfaction come from living a life based upon integrity and noble character.
Truett Cathy Quote
A good name is more desirable than great riches; to be esteemed is better than silver or gold.
Corporate Financial Scandals
Events that have led to new regulatory measures and highlight the importance of ethics in business.
Ethics
The principles that govern a person's or group's behavior, particularly in business contexts.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
The function that describes how businesses can operate ethically and contribute to societal goals.
Integrity
The quality of being honest and having strong moral principles.
Noble Character
The quality of being honorable and having high moral standards.
Fame and Fortune
Common measures of success that many people pursue but do not guarantee true satisfaction.
Honor
A concept that is considered more valuable than honors, as expressed by President Lincoln.
Accidental Errors
Mistakes that occur unintentionally, which internal controls aim to prevent.
Intentional Misrepresentations
Deliberate inaccuracies or frauds that internal controls seek to identify and prevent.
Financial Impropriety
Unethical or illegal financial practices that internal controls help to prevent.
Ethics in Business
The study of what is right and wrong in business contexts and how ethical behavior can be promoted.
Living an Honorable Life
The idea that a life based on integrity and ethical principles is more satisfying than one focused on wealth and fame.
Charles Schwab
President of the world's largest independent steel company who died in bankruptcy.
Samuel Insull
President of the world's largest utility company who died virtually penniless.
Howard Hopson
President of the largest gas firm who was insane at the time of his death.
Ethics
Guidelines by which people relate to the world, including how they conduct business, treat others, and care about the environment.
Integrity
Adherence to moral and ethical principles, soundness of moral character, and honesty.
Ethical Decision-Making Steps
1. Define all the facts and circumstances. 2. Identify the people affected. 3. Determine the alternative decisions and consequences. 4. Make the decision, by determining the right action and carrying out the right action.
Trust in Business
Essential for business activity to occur; without it, business would grind to a halt.
Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI)
A measurement of the potential corruption risk per country, published by Transparency International.
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)
Violations of laws such as the FCPA are more likely in countries with high corruption risk.
Economic Progress and Ethics
Ethics and economic progress are tightly intertwined; ethical values are crucial for sustainable economic activity.
Corporate Social Responsibility
The function of businesses to consider the societal impacts of their actions.
Financial Scandals
Events in corporate history that highlight failures in ethics and governance.
Teaching Ethics
Methods and practices for imparting ethical principles to individuals.
Internal Controls
Systems that facilitate ethical behavior and help prevent financial impropriety.
Public Confidence
Trust in products and services that is encouraged by ethical business conduct.
Professional Responsibilities
Ethical guidelines provided by business and accounting organizations to their members.
Deterioration of Ethical Values
When a society's ethical values decline, it may lead to increased reliance on government for regulation.
Sustainable Economic Activity
Economic activity that can be maintained over the long term, reliant on ethical practices.
Government's Role
Limited ability to maintain societal order when ethical values are collapsing.
Long-term Trust
Trust that depends upon ethical business practices for a company's success.
Risk assessment
Should be thorough and focused upon operations in high-risk countries, without ignoring low-risk countries.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Refers to a company's obligations to society, including the welfare of a wide range of stakeholders: people and places affected by company activities.
Quality product or service
One of the obligations of CSR, requiring companies to provide a quality product or service to customers.
Return on investment
An obligation of CSR to provide an appropriate return on investment to shareholders.
Dignity and respect
CSR mandates that companies treat employees with dignity and respect.
Environmental care
CSR includes the obligation to take care of the environment.
Legal obligations
Companies must meet legal obligations as part of their CSR.
Fair dealings
CSR requires companies to fairly deal with suppliers, lenders, and other business parties.
Ethical choice
Following legal rules is a starting point for making an ethical choice.
Formal policies
A second way to resolve an ethical question is to apply the formal policies of the company or professional organization.
Informal guidelines
Following informal guidelines such as moral intuition is a third way to make an ethical choice.
Principle of consistency
To apply this principle, ask: 'What if everyone did it?'
Principle of respect
One must make a choice that treats people with the greatest respect.
Corporate ethics code
Many companies have established a corporate ethics code to help employees do the right thing in difficult circumstances.
Walmart Canada's Environmental Stewardship
An example used to discuss the impact of good corporate social responsibility on the reputation and business success of a company.
Corporate financial scandals
Recent scandals have often led to investors' loss of confidence in the stock market and in the reliability of corporate financial reports.
Enron scandal
Caused people to question the reliability of the financial reporting practices of publicly traded corporations and led to the Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002.
Mark to market accounting
An accounting practice that updates the value of an asset to its current market levels.
WorldCom scandal
From 1999 to 2002, manipulated earnings by using fraudulent accounting methods, presenting a false image of economic growth.
French-based multinational corporation scandal
Cooked its books to make its financial performance appear better than it was for the purpose of making acquisitions.
Italian-based multinational corporation scandal
Used derivatives for financing to disguise the extent of the company's financial liabilities and losses.
Notorious fraudster
Sometimes the name of the person committing the fraud becomes so notorious that it identifies that type of fraud.
Ponzi scheme
A type of fraud where returns to earlier investors are paid using the capital from newer investors.
Charles Ponzi
An infamous fraudster who tricked thousands into investing in a postage stamp speculation scheme during the 1920s.
40% return in three months
The guaranteed return promised by Charles Ponzi to his investors.
Bernard Madoff
A money manager who perpetrated a Ponzi scheme amounting to an estimated $65 billion between the early 1990s and 2008.
Ethics education
Academic research shows that ethics classes positively affect people's actions and ethical perspectives.
Five fundamentals of ethics education
Personal integrity, responsibility of business in society, ethical decision-making, ethical leadership, corporate governance.
Preventive controls
Internal control procedures aimed at preventing accidental errors and intentional misrepresentations.
Feedback controls
Internal control procedures that identify errors and irregularities after they occur for corrective action.