quantum mechanics part 1
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
what is the wavelength?
the distance between two wave crests or troughs
what is the frequency?
the number of wave crests that pass over the origin every second
what is black body radiation?
the light radiated by an object when it’s hot
what is emitted when light is shone on a metal surface?
what is expected to happen (energy)? what actually happens?
how was this resolved?
electrons
energy of electrons should depend on intensity of incident light. instead, electrons are emitted above a certain frequency of UV
resolved by considering light as photons
what is the equation for kinetic energy of ejected electron?
m is mass
v is speed
Φ is work function of material (energy to remove electron from surface)
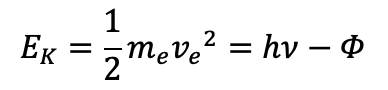
how does the atomic spectrum of hydrogen hint at quantisation?
when heat or electrical energy is applied, it emits an atomic spectrum with discrete wavelengths
only certain frequencies are emitted
different for each element
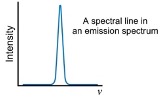
emission spectrum
appearance
where are transitions to and from?
what does spectral line look like?
bright lines against dark background
transitions are from higher to lower energy levels
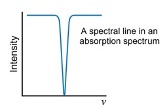
absorption spectrum
appearance
where are transitions to and from?
what does spectral line look like?
dark line against bright background
transitions are from low to high energy levels
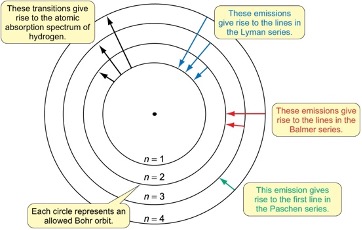
what are Paschen series transitions?
Transitions to n=3
what are Balmer series transitions?
transitions to n=2
what are Lyman series transitions?
transitions to n=1
what is the equation for frequency of light in Hz for hydrogen?
RH is the Rydberg constant (=3.29×1015 Hz )
n1, n2 are integers representing ELs
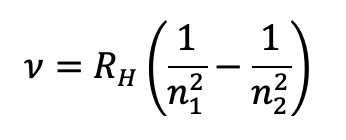
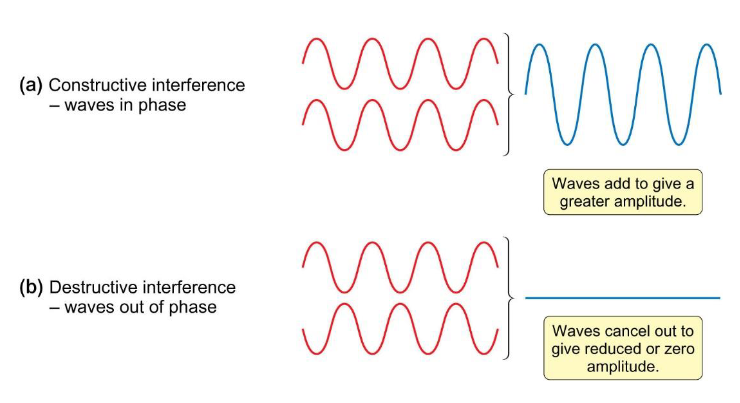
what is the difference between constructive and destructive interference of waves?
constructive = in phase
destructive = out of phase
how does amplitude change with constructive and destructive interference?
constructive = waves add to give greater amplitude
destructive = cancel out to give reduced/zero amplitude
what was Bohr’s model of the atom?
electrons move around the nucleus in a fixed orbit
why do macroscopic objects not show perceptible wave like properties?
the de Broglie wavelength is too small
diagram of particle moving in circle
show r, m, v and centripetal force
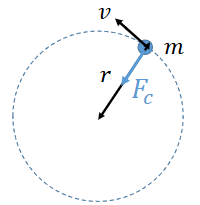
how to calculate angular momentum?
L=mvr
r is radius of orbit
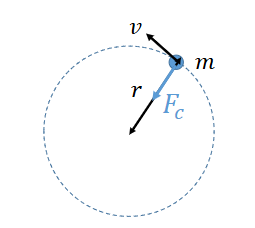
how to calculate centripetal force?
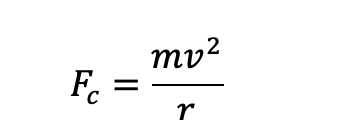
why is there an electrostatic force pulling electron into centre of orbit?
nucleus has protons and is positively charged
attraction between electrons and protons pulling into nucleus
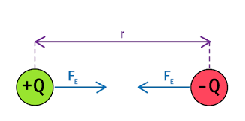
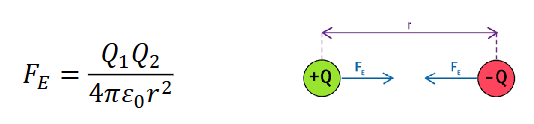
how to calculate electrostatic force?
Q1 and Q2 are point charges
ε0 is constant, permittivity of free space
what does quantisation mean?
there are discrete levels of energies in an atom, rather than continuous spectrum
what happens if wave is out of phase as it travels in orbit?
starts to destructively interfere and you won’t have a wave anymore
what is the condition of constructive interference of electron wave as it travels around the nucleus?
you need exact number of wavelengths going around the circumference so it starts to overlap
2πr = n𝜆 (circumference)
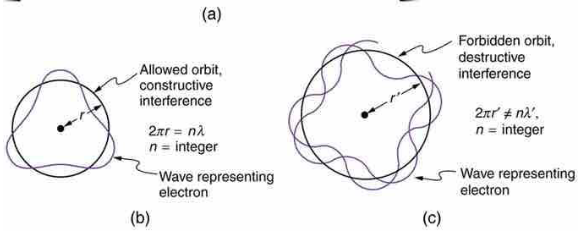
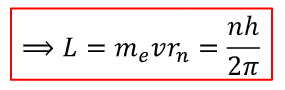
how is this derived?
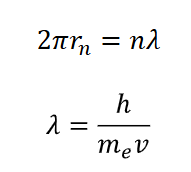
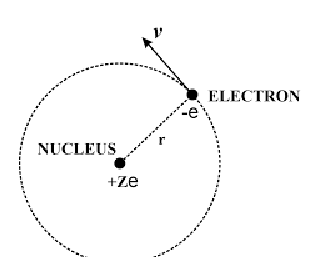
what is e? what is Z? what is v?
v is velocity of electron
e is charge (-e for electron and +e for protons in nucleus)
Z is number of protons (atomic number)
for an electron in orbit around the nucleus, what is centripetal force equal to?
electrostatic force
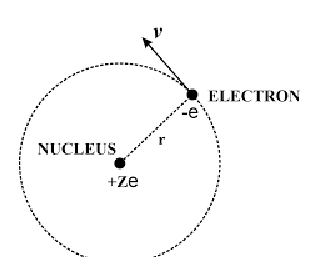
using the fact electrostatic and centripetal forces are equal
find equation for rn
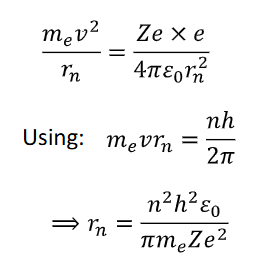
how to find potential energy of electron in orbit?
E = force x distance (rn)
= electrostatic force x rn
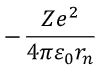
how to find energy of electron?
kinetic energy + potential energy
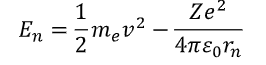
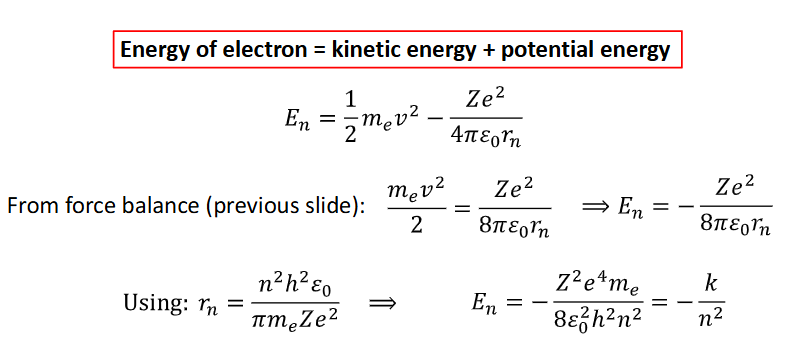
use expression for rn and the energy of electron to find equation for En
equation for frequency using rydberg constant
how to modify if calculating other than H?
multiply by Z2
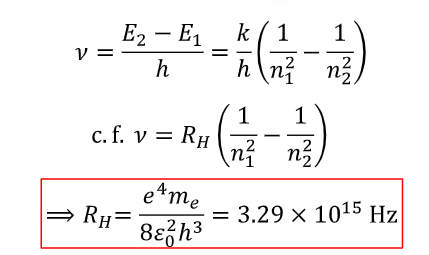
what were the problems with Bohr’s model?
· He couldn’t explain the quantisation condition for angular momentum. (only certain orbits allowed)
· Classically, an orbiting charged particle would emit electromagnetic radiation, lose energy and fall into the nucleus.
· While the model could explain the atomic spectrum of hydrogen, it couldn’t predict the spectra of other atoms.
what is the time independent Schrödinger equation?
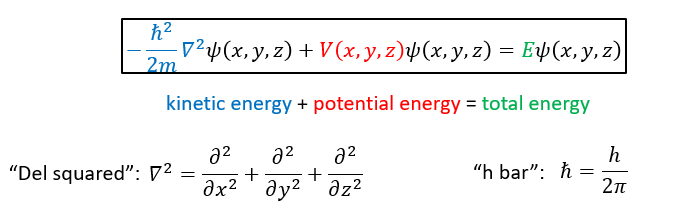
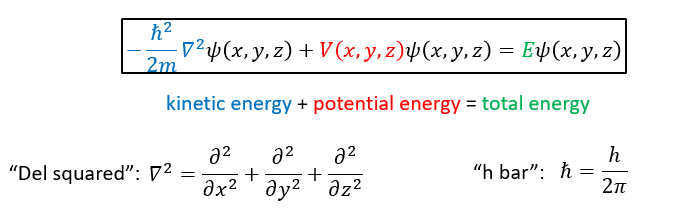
what do the differentials in the Schrodinger equation show?
how wavefunction changes with distance from the nucleus
e.g. d2/dx2 describes how ψ changes along x axis with constant y and x
what type of problems are solved with the schrodinger equation?
in the case of atoms?
two body problems
this is a nucleus and singular electron in the case of atoms
what is kinetic energy
what is potential energy
kinetic = energy of motion
potential = dependent on position
what is the wavefunction ψ (psi) - what does it contain info about
is it directly measurable?
contains info on the properties and behaviour of a particle but is not directly measurable
what is ψ2 proportional to?
what does it mean if ψ2 is high?
the probability of finding the particle in a small volume dV
if ψ2 is high, the probability of finding the electron is high
what is ψ2 for electrons?
electron density
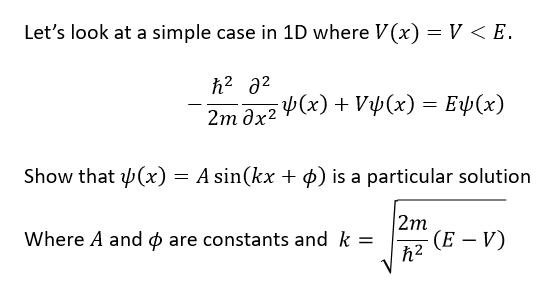
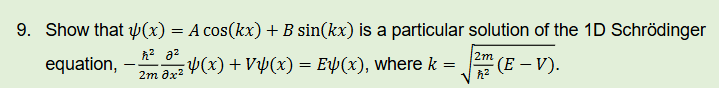
how does schrodinger equation agree with Rydberg and Bohr for hydrogen?
matches predictions that energy depends on principle quantum number
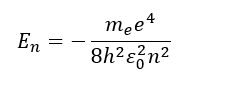
what is the Heisenberg uncertainty principle?

what does l describe
orbital angular quantum number
how many nodes - ie which orbital it is
what are the values of l for s, p, and d orbitals
s: l = 0
p: l = 1
d: l = 2
for n = 1, n = 2, n =3, what are the values of l?
n = 1 : l = 0
n = 2 : l = 0, 1
n = 3: l = 0, 1, 2 (s,p,d)
what does ml describe
magnetic quantum number
the direction of the orbital
for l = 0, l = 1, l =2
what are the values of ml?
l = 0 (s orbital), ml = 0
l = 1 (p orbital), ml = -1, 0, 1
l = 2 (d orbital), ml = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2
why would you want to calculate wavefunction as a function of spherical coordinates rather than polar?
atoms are spherical
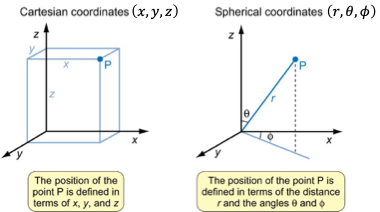
how to calculate x,y,z using polar coordinates?
x=r sinθ cosϕ
y=r sinθ sinϕ
z=r cosθ
what is the hydrogen wavefunction equation using polar coordinates?
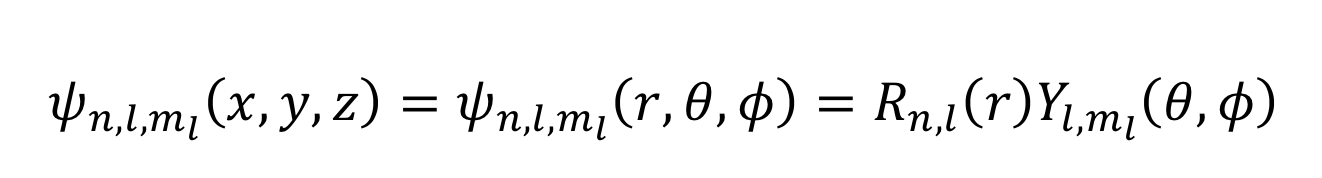
what is the radial wavefunction dependent on?
what does it describe?
n and l
contains info about how wavefunction changes as distance from nuclei increases
what does the angular wavefunction depend on?
what does it describe?
l and ml
contains info about the shape of orbital
how many nodes does
s orbital
p orbital
d orbital
f orbital have?
s is n-1
p is n-2
d is n-3
f is n-4
why is the s orbital spherically symmetric?
no angular dependence
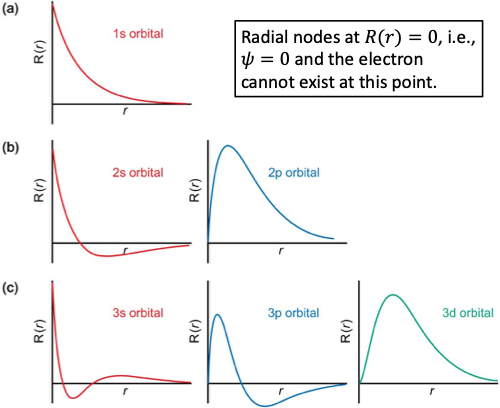
which orbitals are not zero at the nucleus (radial nodes)?
s orbitals
what are the radial nodes graph shapes for n =1,2,3?
where is the highest probability for the electron in radial distribution functions?
the maximum value is most probable distance
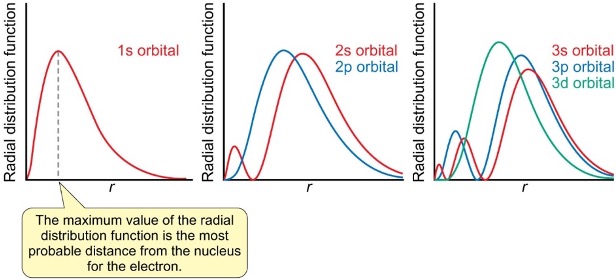
what is the radial distribution function?
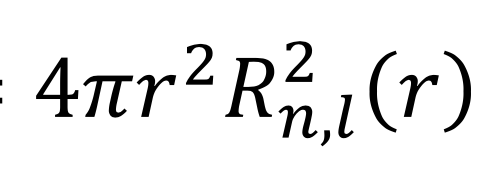
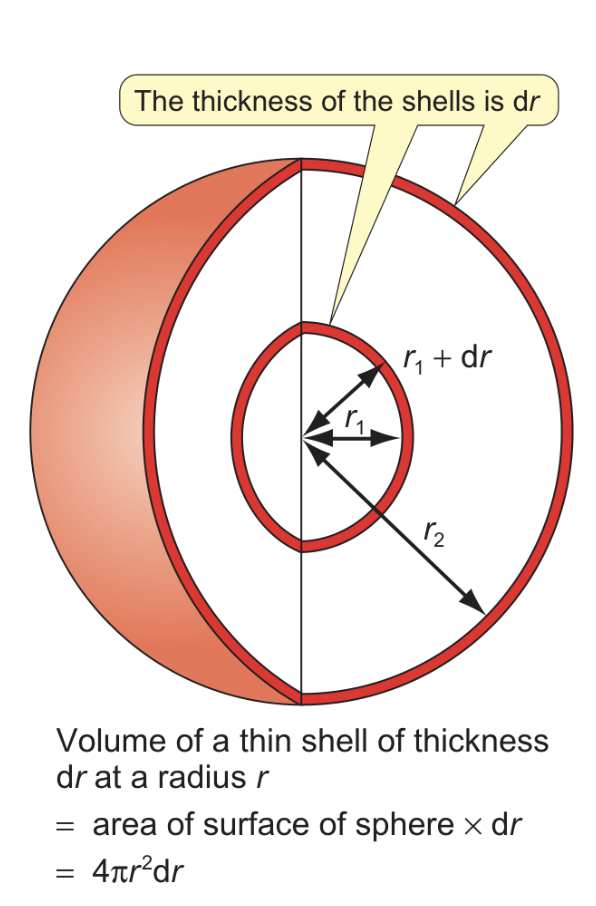
how does the radial distribution function change with increasing shells?
using sphere with radius r and shell thickness dr
volume is greater for larger sphere since r is larger
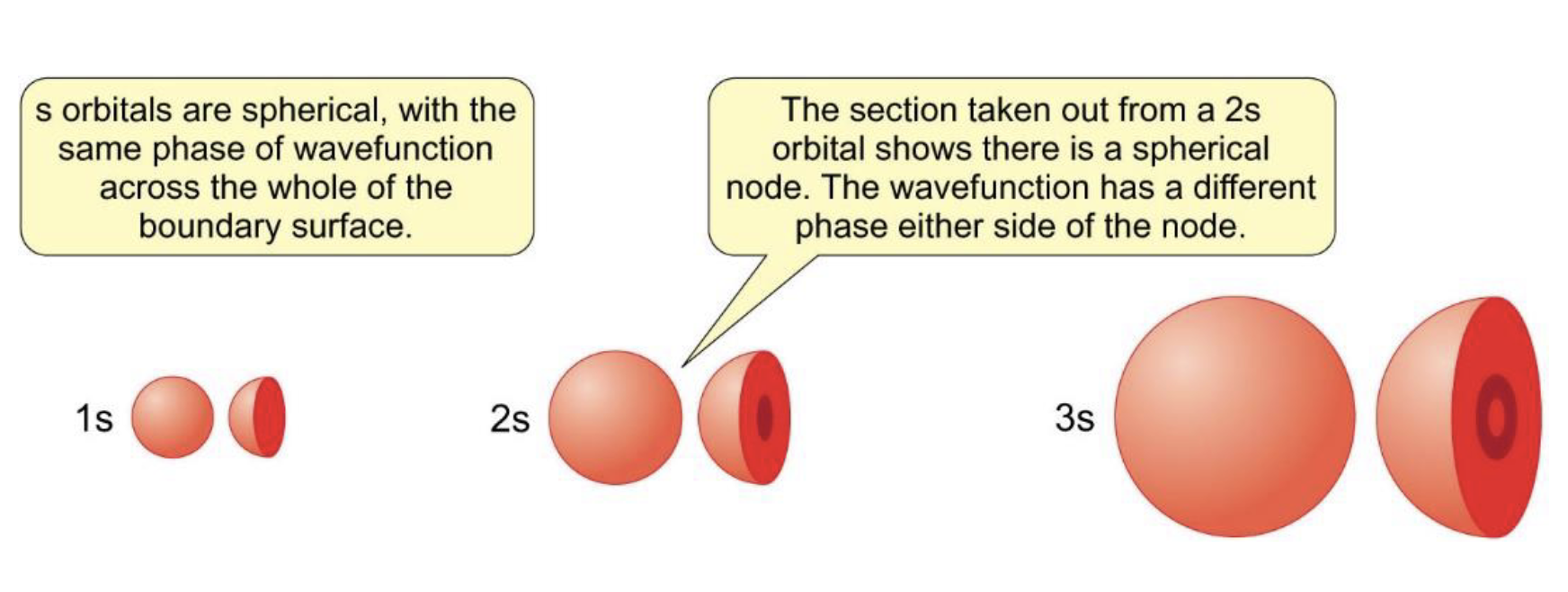
how does shape of s orbital change as n increases from 1 to 3?
radial nodes increases
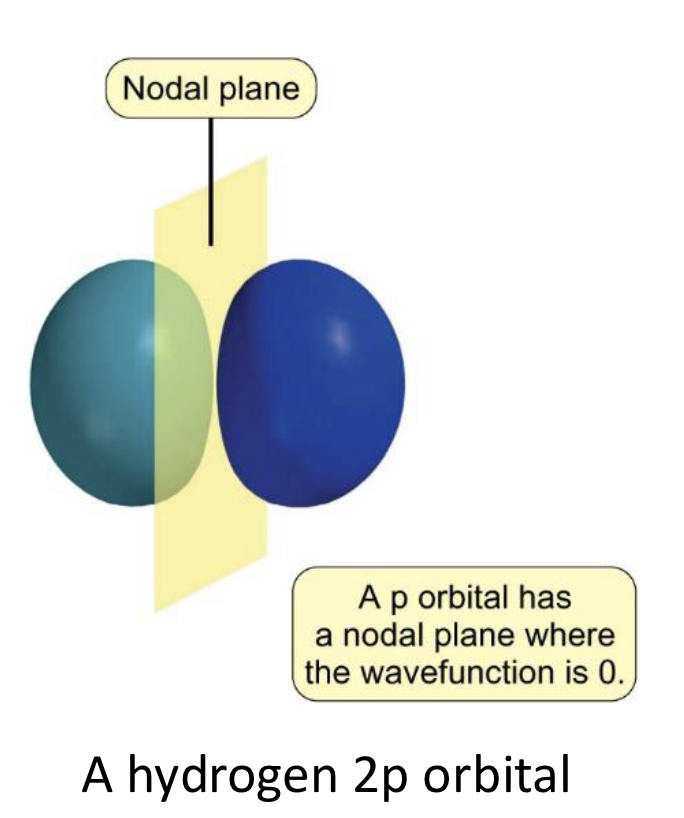
what does p orbital have when wavefunction is zero?
nodal plane
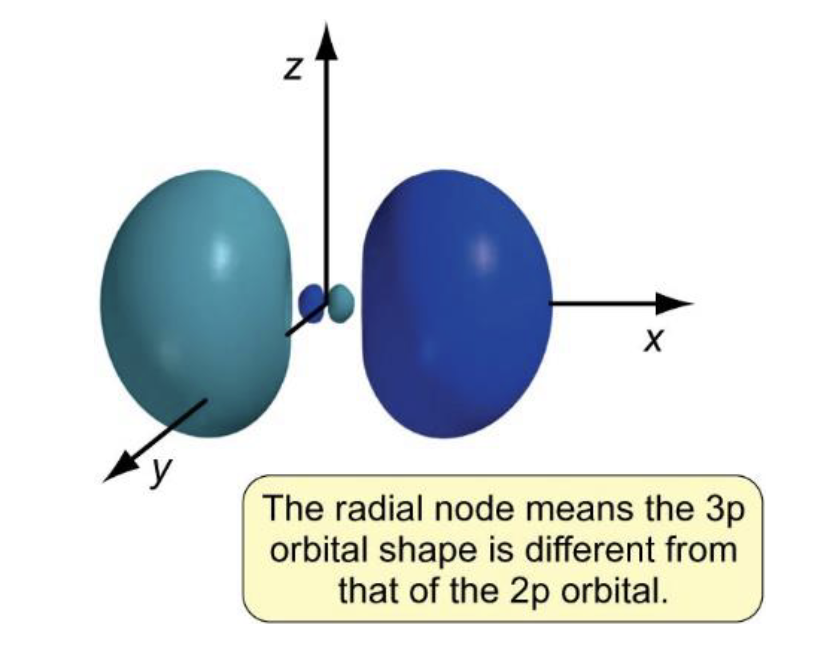
how does shape of p orbital change from n = 2 to n = 3?
how does nodal plane change for dz2 and dx2-y2?
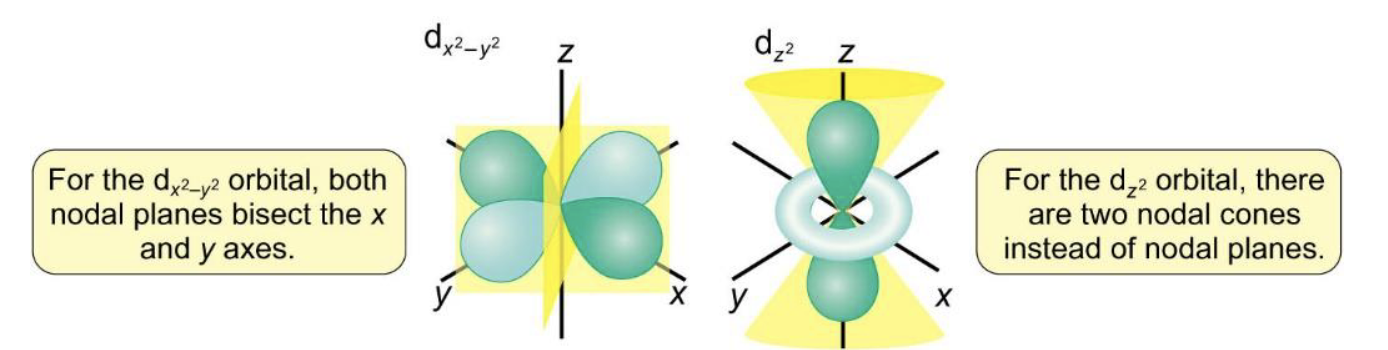
how is Schrödinger equation resolved for multi electron atoms?

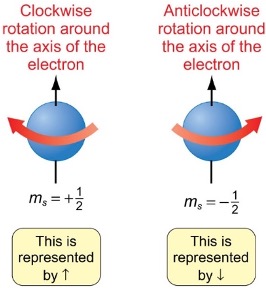
what is the spin quantum number?
which way is clockwise/anticlockwise?
represents the direction of spin, ms = ± ½
what is the Aufbau principle?
Lowest energy levels are filled first
what do the energy levels for multi-electron atoms depend on?
principle quantum number n (which EL)
orbital angular quantum number l (which orbital)
for hydrogen, what do energy levels depend on?
what does this explain?
energy levels depend only on n
energy levels are degenerate for different values of l and ml for given value of n
this is why Bohr model worked for hydrogen
what is Pauli exclusion principle?
no two electrons in same region of space can have the same 4 quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms)
this means 2 electrons per orbital (ms = ± 1/2)
what happens to electrons with same quantum numbers when electron orbitals overlap?
electrons in different atoms with same quantum numbers repel
what are the different types of energy stored?
electronic, vibration, rotation, translation
why can the different forms of energy stored in a molecule be treated independently?
electronic transitions are much faster than bond vibrational motion, faster than rotations, faster than translational motion
in particle in a box, what is the potential energy inside the box?
0
in particle in a box, what is the potential energy outside the box?
∞
what are the boundary conditions?
𝜓 (𝑥) = 0
x = 0, l
what is the wavefunction at the edge of the box?
how does this affect quantisation?
0
the particle cannot exist in regions of space where 𝜓 (𝑥) = 0, so confinement leads to quantisation of energy levels
what is the energy inside the box?
all energy is kinetic
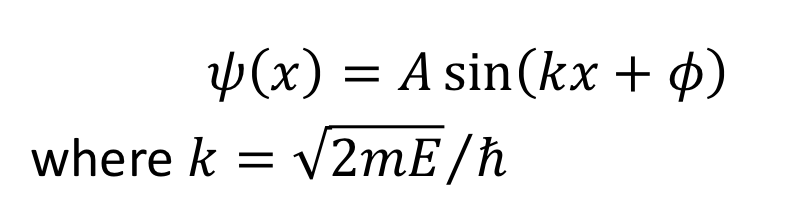
for this solution, what is the wavefunction when x = 0 ?
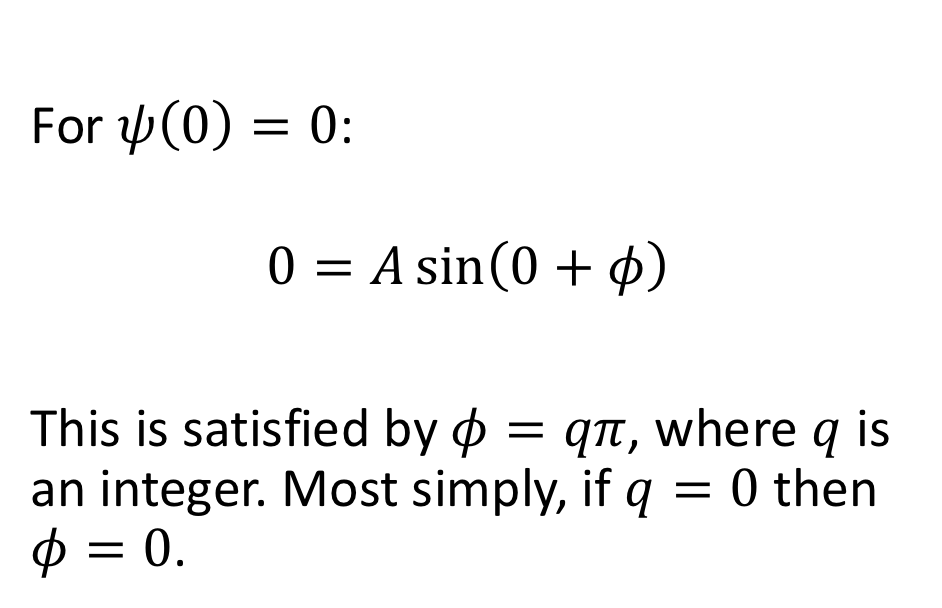
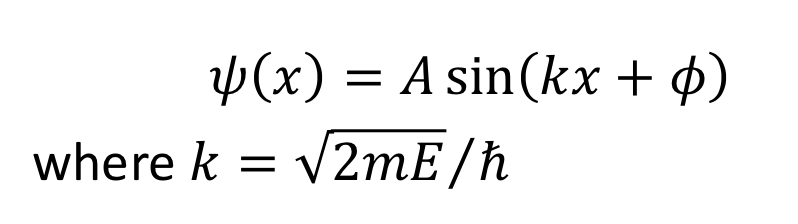
for this solution, what is the wavefunction when x = l ?
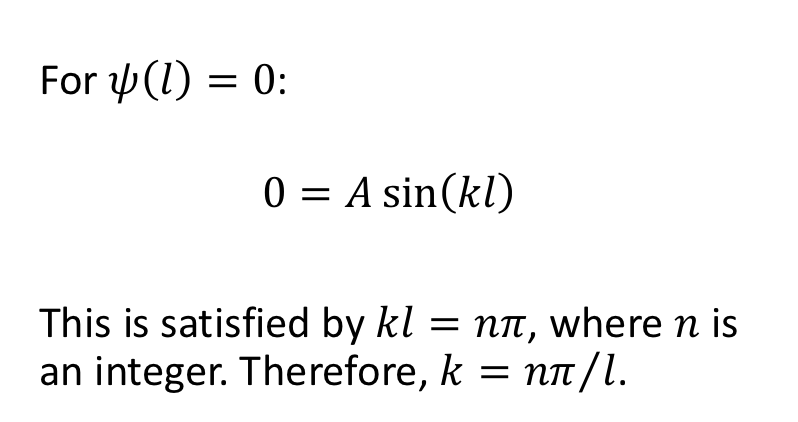
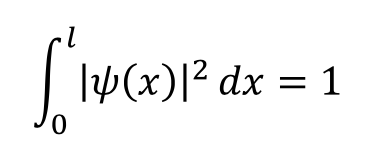
using this normalisation of the wavefunction, calculate A
(use formula for x = l)
n is translational quantum number
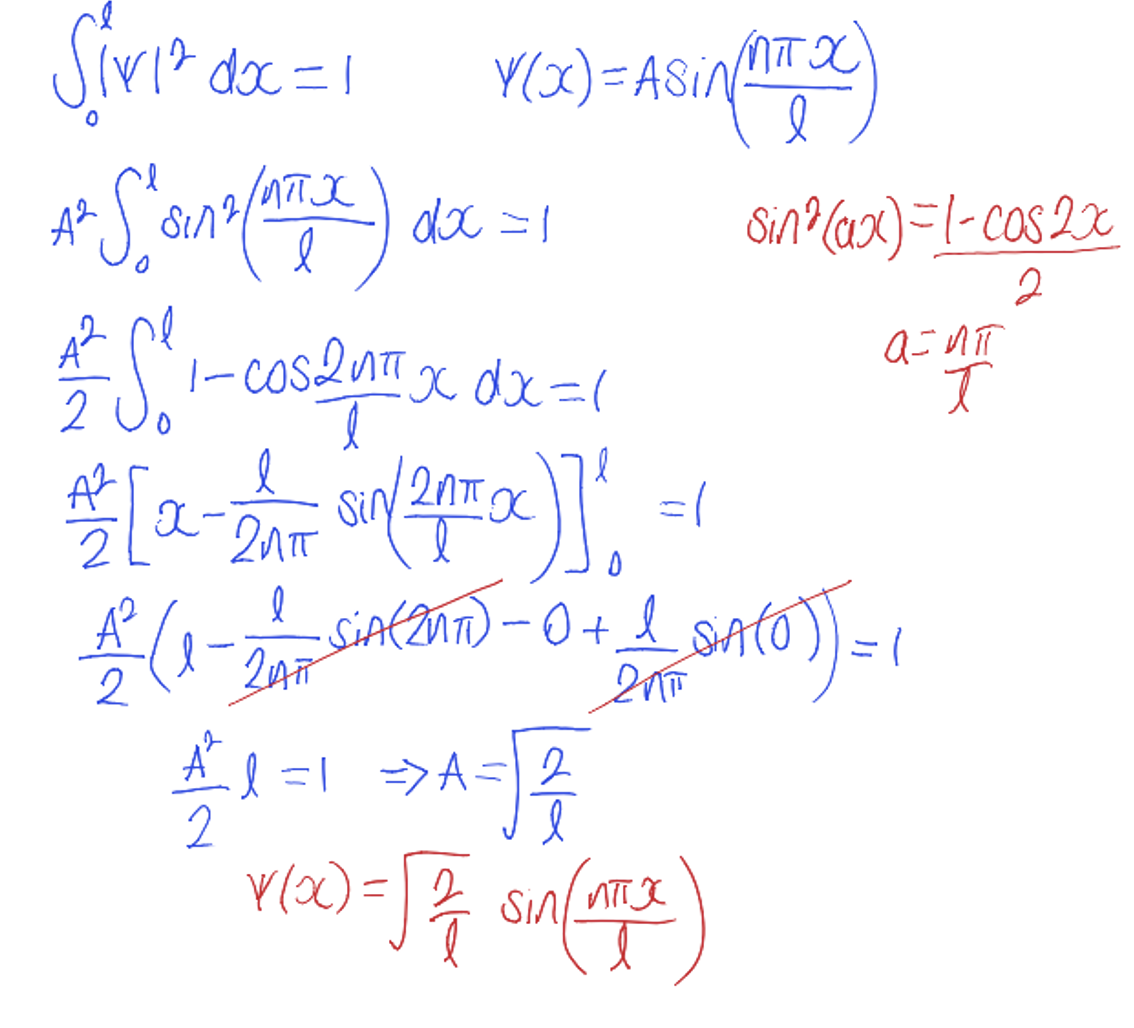
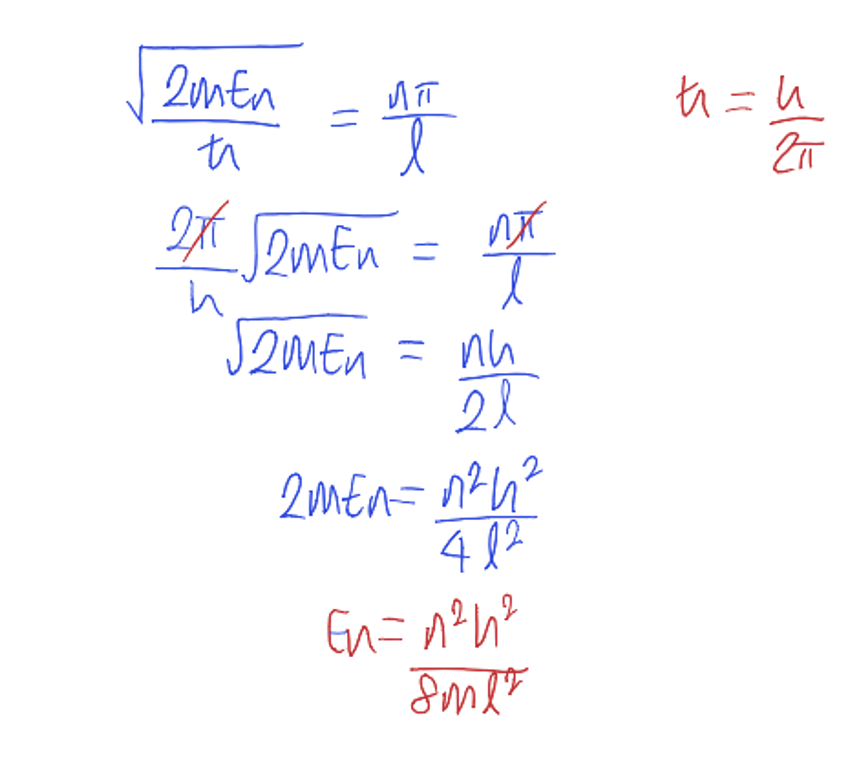
using the equation for k, calculate En
how does increasing quantum dot particle size affect wavelength and ΔE?
increases emission wavelength and decreases gaps between ELs
why can transitions between translational energy levels be treated as a continuum?
transitions are such small ΔE gaps that they are too small to measure