3.2 Demand, Supply, & Gov Policies
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Consumer Surplus
= WTP (value of buyers) - P (amount paid by buyers)
= buyers’ gains from participating in the market
Producer Surplus
= P (amount received by sellers) - (cost to sellers)
= sellers’ gains from participating in the market
Total Surplus
CS + PS
= total net gains from trade in a market
= (value to buyers) - (cost to sellers)
Efficiency means
The goods are consumed by the buyers who value them most highly
The goods are produced by the producers with the lowest costs
Raising or lowering the quantity of a good would not increase total surplus
Economic Efficiency
A market outcome in which the marginal benefit to consumers of the last unit produced is equal to its marginal cost of production and in which the total surplus is at a maximum.
Government Policies
such as price controls - legal restrictions on a market price may go- or taxes alter the private market outcome.
Price Ceiling
a legal maximum price sellers are allowed to charge for a good or service (usually set BELOW the equilibrium)
Ex. rent control
Price Floor
a legal minimum price that buyers are required to pay for a good or service (usually set ABOVE the equilibrium)
Ex. minimum wage
Taxes
The government can make buyers or sellers pay a specific amount on each unit
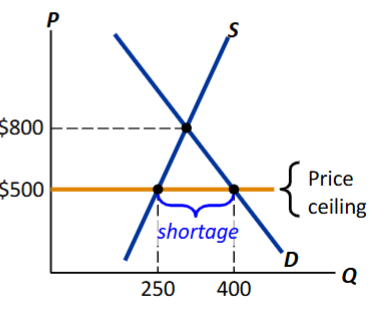
Price Ceilings Example
The equilibrium price ($800) is above the ceiling and therefore, illegal
The ceiling is a binding constraint on the price, causing a shortage
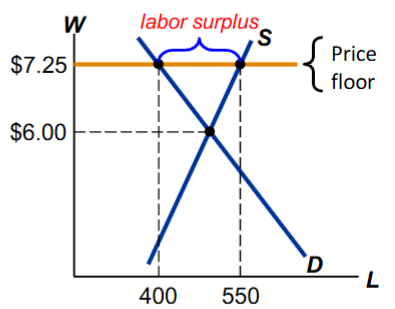
Price Floor Example
The equilibrium wage ($6) is below the floor and therefore illegal.
The floor is a binding constraint on the wage, causing a surplus = unemployment
Deadweight loss
is the loss in total surplus that occurs
Whenever an action or a policy reduces the quantity transacted below the efficient market equilibrium
quantity
excise tax
a tax charged on each unit of a good or service that is sold
When the tax is levied on sellers, When the tax is levied on buyers
analyze the effects of the excise tax, and we’ll graph two scenarios:
incidence of tax
a measure of who really pays it.
Tax on Buyers
Pb = Ps + Tax
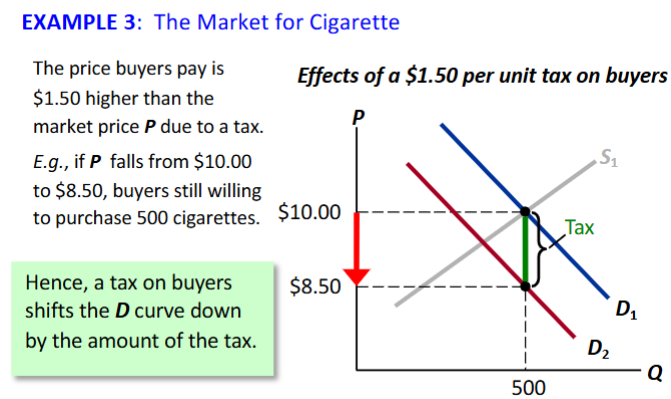
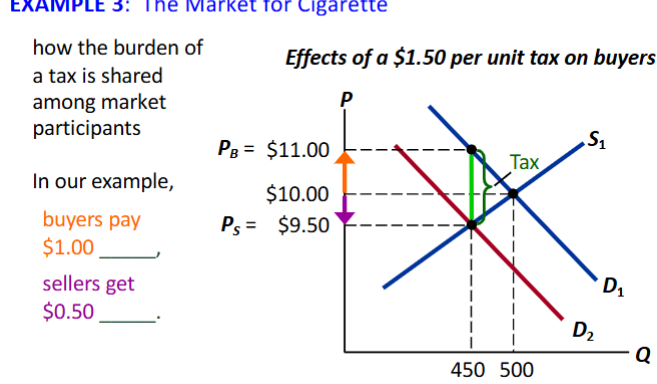
Incidence of tax
Buyers pay $1 more, sellers get $.50
Those with the smallest deadweight loss
Which goods or services should gov’t tax to raise the revenue it needs?