chapter 4: carbon & functional groups
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
why is carbon such a good building block
carbon is tetravalent: forms diverse complex molecules
forms covalent bonds
bonding ability allows for formation of larger interconnected molecules
its stable & doesn’t ionize easily
organic carbon molecules
associated with life — contain carbon covalently bonded to hydrogen
ex. methane, hydrocarbons, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids & nucleic acid
inorganic compounds
do not have carbon-hydrogen bonds
ex. carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, carbonates, bicarbonates, cyanide
hydrocarbons
organic molecules only made of carbon & hydrogen
backbone of many cell’s organic macromolecules
what causes molecular diversity
variation in carbon skeletons
other element’s atoms can be bonded
skeleton vary in length, straight or branched, vary in bonds, rings
importance of shape to function
3-d shape of organic molecules determines function
what is the problem presented with hydrocarbons
they are non-polar — are hydrophobic, cannot exist/function within a cell
functional group
chemical groups that replace one or more of the hydrogen atoms of the hydrocarbon skeleton
-increase the solubility of organic compounds
what are the seven functional groups
hydroxyl group (—OH)
carbonyl group (=O)
carboxyl group (—COOH)
amino group (—NH2)
sulfydryl group (—SH)
phosphate group (PO42-)
methyl group (CH3)
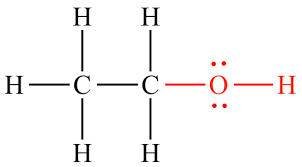
hydroxyl group
oxygen of group is bonded to carbon skeletons
carbonyl group
oxygen is double bonded to carbon atom in hydrocarbon
aldehydes: =O is at end of c-chain (ex. butanal)
ketones: =O in in c-chain (ex. butone)
carboxyl group
carbon atom at end of HC molecule is double bonded to an oxygen atom & hydroxyl group
molecules called carboxylic acids
polar, can donate H ions
amino groups
carbon in HC molecule is bonded to an N atom which is bonded to two O atoms
makes molecule basic (and polar)
can accept H ions
organic compounds with amino groups are called amines
what do amino acids have
amino & carboxyl groups
sulfydryl group
sulfur atom bonded to carbon skeleton & hydrogen atom
two groups can interact, forming disulfide bridge — stabilizes structure of proteins
phosphate group (charged)
phosphorus atom bonded to 4 oxygen, one bonded to a c & others to phosphorus — 2 are negatively charged
used to transfer energy between molecule
methyl group
adds carbon with three hydrogens bonded to it — keeps molecule non-polar
adenosine triphosphate
organic molecules — adenosine attracted to string of 3 phosphate groups — reacts with water to produce usable energy
why is carbon dioxide important
is the source of carbon for all organic molecules found in organisms
what makes something saturated
if it has its max hydrogen bonds — if double bonds are present its unsaturated
structural isomer
same molecular formula — different arrangemet
geometric isomers/cis-trans
require presence of double bond
entantiomers
mirror image — carbon bonded to four different groups/atoms — creates left & right isomer