AP Psychology - Methods
4.8(5)
Card Sorting
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:09 AM on 4/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
Hindsight Bias
The tendency for someone to think they knew a conclusion from research before it was released, even though they did not.
2
New cards
Applied Research
Research to solve practical problems that have real-world applications.
3
New cards
Basic Research
Research into areas that are of interest to psychologists but that do not have real world applications.
4
New cards
Hypothesis
An assertion that there is a relationship between two variables that someone makes as a prelude to performing research.
5
New cards
Can you prove a hypothesis?
No, you cannot prove a hypothesis. Research can only support a hypothesis, but it is impossible to fully assert that a hypothesis is true. If you are doing spaced repetition or learning, note that this is a question.
6
New cards
Independent Variable
The variable that is changed or modified.
7
New cards
Dependent Variable
The variable that changes as a result of changes to the independent variable,
8
New cards
Theory
A claim that is backed by evidence from research (although admittedly some examples of this in psychology lack research).
9
New cards
Operational Definition
A definition of something in terms of how it will be used in the procedure and how it will be measured.
10
New cards
Validity
How well the research measures what the researcher set up to measure.
11
New cards
Reliability
How consistent the results are, even when done by different researchers (with the same procedure)
12
New cards
Participants
Subjects in research.
13
New cards
Sampling
The process wherein participants are selected.
14
New cards
Sample
The group of participants
15
New cards
Population
Anyone who __**could**__ be selected to be in the sample for the study.
16
New cards
Representative Sample
A sample that is representative of the population the participants were selected from.
17
New cards
Random Sampling or Random Selection
The process of selecting participants wherein everyone in a population has an equal chance of being selected.
18
New cards
Stratified Sampling
The process of selecting participants in which participants are randomly selected, but the number of people of different demographics are standardized to prevent inequality. For example, if a population is 1/3 White, 1/3 Black, and 1/3 Asian, then a study of that population with participants picked this way should have 1/3 of the participants be of each demographic, and the participants selected randomly for each demographic.
19
New cards
Laboratory Experiments
Experiments conducted in a lab.
20
New cards
Field Experiments
Experiments conducted in the actual world, in uncontrolled environments.
21
New cards
Experiment
One type of research that determines cause-and-effect relationships.
22
New cards
Confounding Variables
Any factors that may affect the dependent variable that are not the independent variable.
23
New cards
Participant-Relevant Confounding Variables
Variables that affect the assignment of participants. For example, if someone picks their group, they may pick their group based on their personality, and if the researcher picks their group, they may either have biases or they may unconsciously assign people to certain groups based on things like when they arrived or where they were waiting for the research to start.
24
New cards
Situation-Relevant Confounding Variables
Variables that impact the situations different groups are put in. Participants should be put in equivalent situations except for their independent variable to minimize this.
25
New cards
Assignment
The process of putting participants into groups.
26
New cards
Random Assignment
A type of assignment in which each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group.
27
New cards
Controls
Ways that researchers minimize the impact of confounding variables.
28
New cards
Group Matching
A process of assignment in which you divide people into groups and then randomly assign them roles. For example, you could create two different groups based on gender before assigning people to groups.
29
New cards
Experimenter Bias
The __**unconscious**__ tendency for a researcher to treat members of the control and experimental groups differently to prove their hypothesis.
30
New cards
Double-Blind Procedure
When neither the researcher nor participants can affect the study, most frequently done by not telling the participants of their group and having someone else who doesn’t know their groups interact with the participants.
31
New cards
Single-Blind Procedure
When only the participants are unaware of their group.
32
New cards
Response Bias
When a person asks biased questions because of expectations.
33
New cards
Participant Bias
A participant in a study unconsciously behaving the way the researcher expects them to.
34
New cards
Social Desirability
A response bias wherein people give answers that reflect well upon them.
35
New cards
Experimental Group
The group receiving the independent variable.
36
New cards
Control Group
The group that does not receive the independent variable and is compared with the group that does.
37
New cards
Hawthorne Effect
An effect wherein people behave differently when they know they are being studied.
38
New cards
Placebo Method
A method of studying where both groups are lead to believe they’re the experimental group to account for any psychosomatic responses.
39
New cards
Counterbalancing
A method of research in which all groups are both the experimental and control groups, removing confounding variables.
40
New cards
Positive correlations
The presence of when thing predicts the presence of another.
41
New cards
Negative correlations
The presence of one thing predicts the absence of another.
42
New cards
Quasi-Experimental (Ex Post Factor) Study
A study where most aspects are controlled, but some are left as confounding variables.
43
New cards
Survey Method
A method of research using surveys where there is neither an independent nor a dependent variable and instead asks people questions to determine a relationship between two variables.
44
New cards
Response Rate
The rate at which people respond to requests to fill in surveys. This is usually quite low.
45
New cards
Naturalistic Observation
A method of research in which someone watches behavior without interacting or changing variables.
46
New cards
Case Study Method
A method of studying where a specific person or group of people (with a condition) are studied over a long period of time to get a full picture of their development over time.
47
New cards
Descriptive Statistics
Statistics that describe a type of data.
48
New cards
Frequency Distribution
A distribution of a statistic showing its varying levels of frequency in a population. This is frequently used to make graphs, one example being bell curves.
49
New cards
Mean
A measure of central tendency that is usually referred to as the average of a data set, found by adding all of the values together and dividing the sum by the number of values.
50
New cards
Median
The central value in a distribution, found by counting to the middle value of a data set in chronological or descending order.
51
New cards
Mode
The value that appears most frequently in a distribution.
52
New cards
Extremes Scores or Outliers
A value or set of values that is significantly different from other values in the distribution. This can affect the mean and skew distributions.
53
New cards
Positive Skew
Distribution created when there are very high outliers.
54
New cards
Negative Skew
Distribution created when there are very low outliers.
55
New cards
Range
The distance between the highest and lowest values in the distribution.
56
New cards
Standard Deviation
Average deviation of the mean.
57
New cards
Variance
Average squared deviation of the mean.
58
New cards
*Z* Score
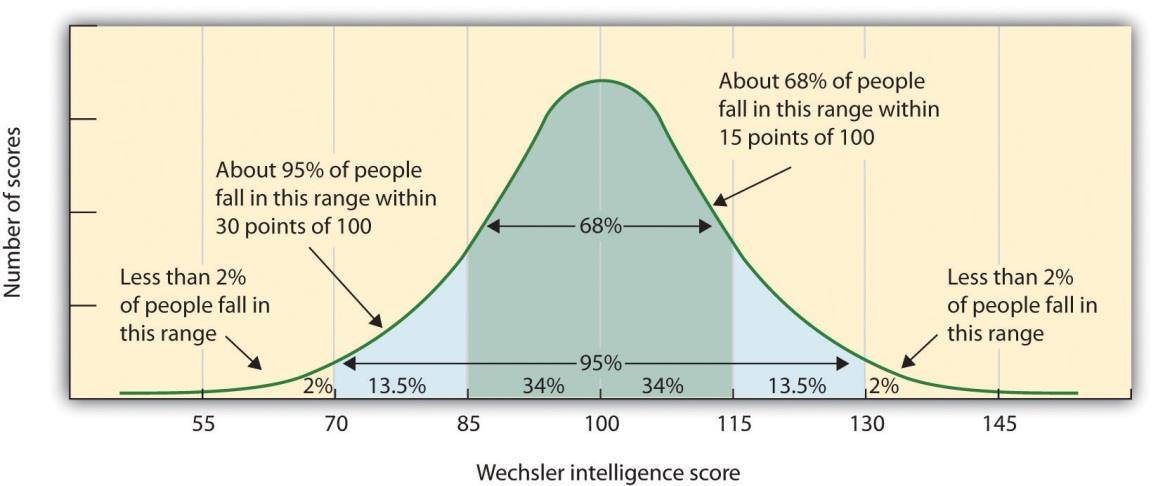
A measure of distance from the mean in standard deviation. For example, if someone got 115 on an IQ test, the would have a measure of 1, because 115 is 1 standard deviation away from the mean.
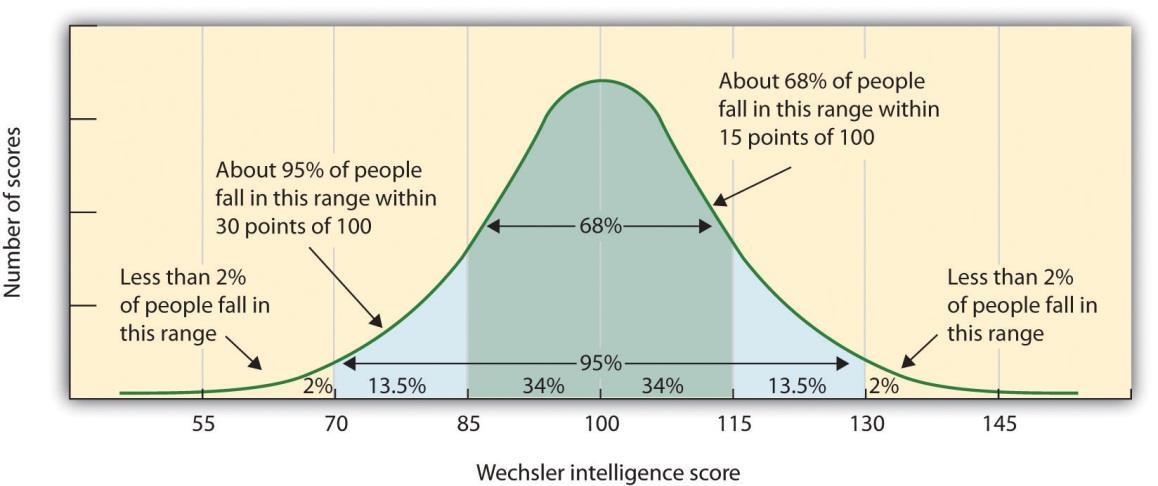
59
New cards
\~Normal Curve
A bell curve that is symmetrical and has \~68% of people in the first standard deviation, \~95% of people in the second, and \~99% of people in the third. One example is an IQ bell curve.
60
New cards
Correlation Coefficient
The measure of a strength of a correlation, that can range from -1 to +1. -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, +1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, and 0 indicates no correlation.
61
New cards
Scatter Plot
A chart that graphs pairs of values and depicts a correlation (or lack thereof).
62
New cards
Line of Best Fit/Regression Line
A (linear) line that depicts the general trend shown in a scatter plot to the best extent possible.
63
New cards
Inferential Statistics
Statistics that determine how applicable findings are to the general population.
64
New cards
Sampling Error
The extent to which a sample differs from the population.
65
New cards
*p* value
The probability that the difference between the control and experimental groups is due to chance (and no/minimal other factors).
66
New cards
Statistical Insignificance
A label giving to data that has a high probability of being caused by chance and not differences between the groups studied. This label is applicable when the *p* value of a study is higher than 0.05.
67
New cards
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
An institution of the American Psychological Association that determines if a study has ethical violations before research is started.
68
New cards
Coercion
When someone is forced in some way to participate in a study. This is an ethical violation according to the APA.
69
New cards
Informed Consent
Researchers must make sure the participant is aware of the study they are participating in. They can be decieved slightly if necessary for the study, but they cannot be deceived to an extent high enough to cause trauma, and the information given must be similar to the contents of the actual study. A lack of this is an ethical violation according to the APA.
70
New cards
Anonymity
A researcher should maintain privacy for the participants to prevent their data in the study from being connected to their name (to the best extent possible). A lack of this is an ethical violation according to the APA.
71
New cards
Confidentiality
If a researcher is unable to provide anonymity, they should do this, which leaves the source of data in a study indeterminate. A lack of this and a lack of anonymity is an ethical violation.
72
New cards
Risk
Participants should not be placed at significant mental or physical risk. Too much of this is an ethical violation according to the APA.
73
New cards
Debriefing
After the study, participants should be both informed of the study and given a way to access the researcher for findings. A lack of this is an ethical violation according to the APA.