RadPatho GI System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Fistula
Abnormal connection between two hollow organs.
Atresia
abnormal closure of an orifice or passage.
Esophageal atresia
Rare congenital anomaly in which the esophagus fails to develop past some point, resulting in discontinuation of the esophagus
caused by a defect in cell differentiation of the trachea and esophagus during the fourth to sixth week of embryonic development.
symptoms are visible soon after birth and include excessive salivation, choking, gagging, dyspnea, and cyanosis.
Tracheoesophageal fistula
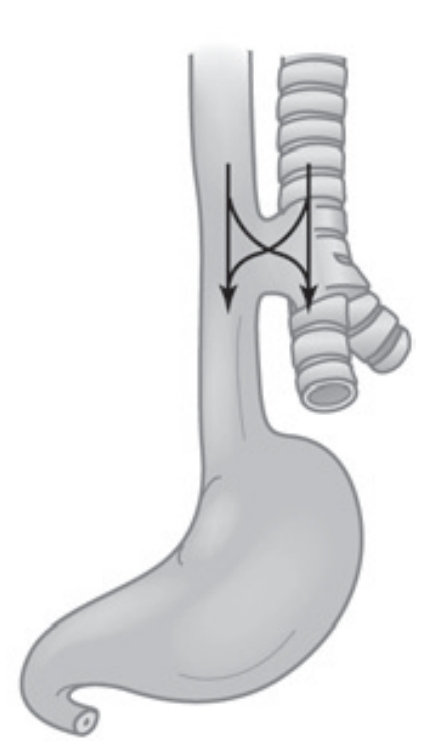
Is coincident with atresia. This consists of an atresia at the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra with a fistula—an abnormal tubelike passage from one structure to another—to the trachea.
Such a condition is incompatible with life for more than 2 to 3 days, but the prognosis is good if the infant is handled appropriately before surgery to prevent aspiration.
Isolated Esophageal Atresia
Esophageal Atresia with proximal Tracheoesophageal Fistula
Esophageal Atresia with distal Tracheoesophageal Fistula
Esophageal Atresia with dual Tracheoesophageal Fistula
H-type Tracheoesophageal Fistula (no Esophageal Atresia)
Five types of Congenital Atresia:
Isolated Esophageal Atresia
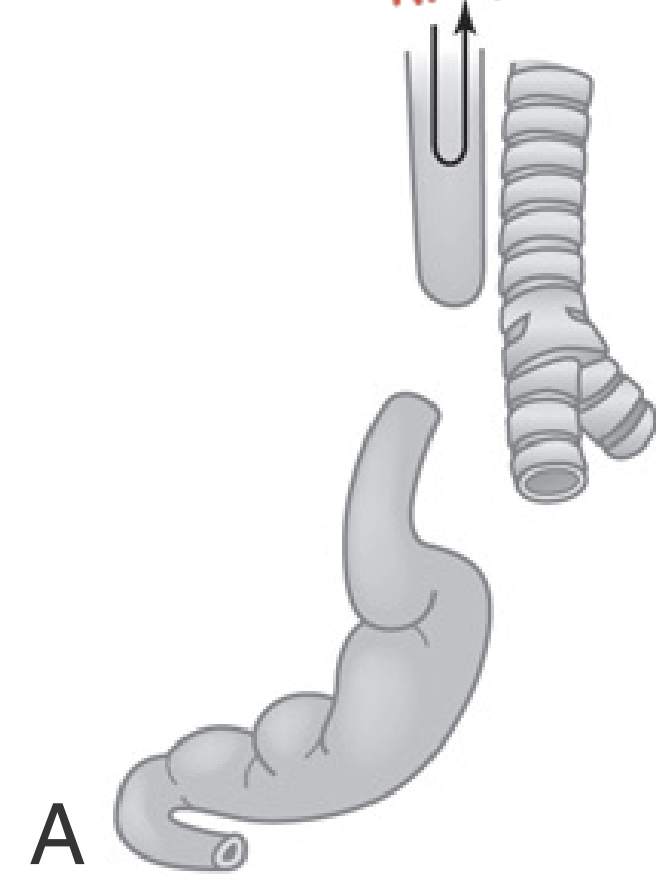
Esophageal Atresia with Proximal Tracheoesophageal Fistula
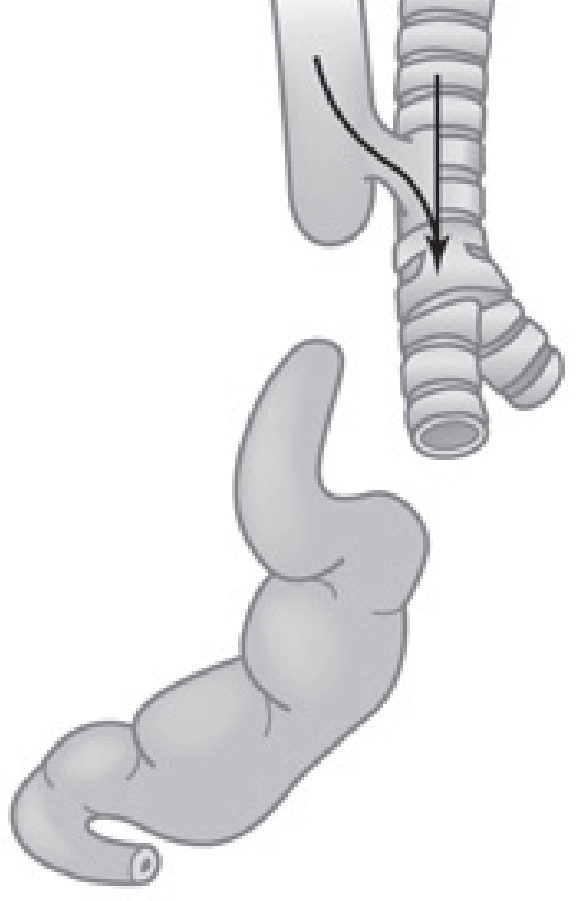
Esophageal Atresia with Distal Tracheoesophageal Fistula
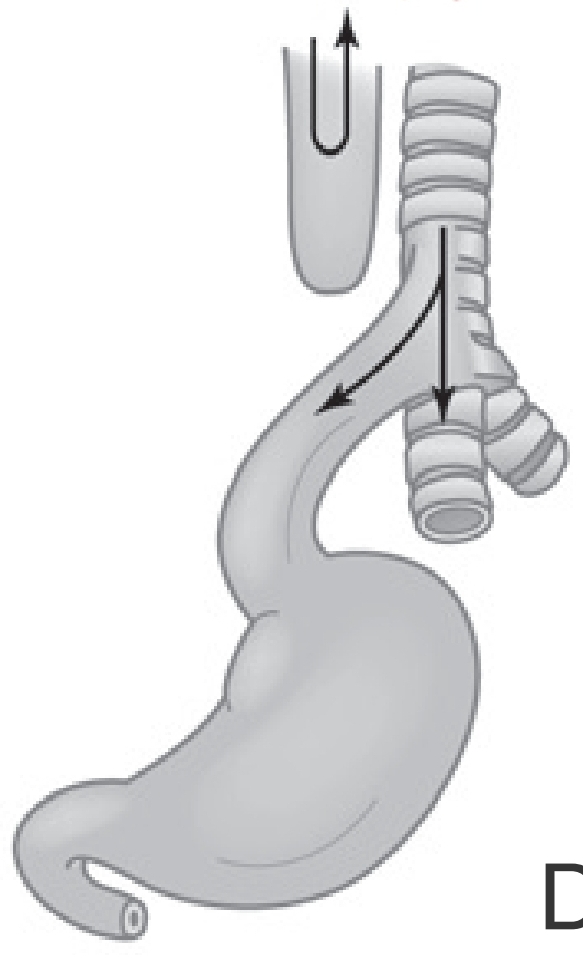
Esophageal Atresia with Dual Tracheoesophageal Fistula
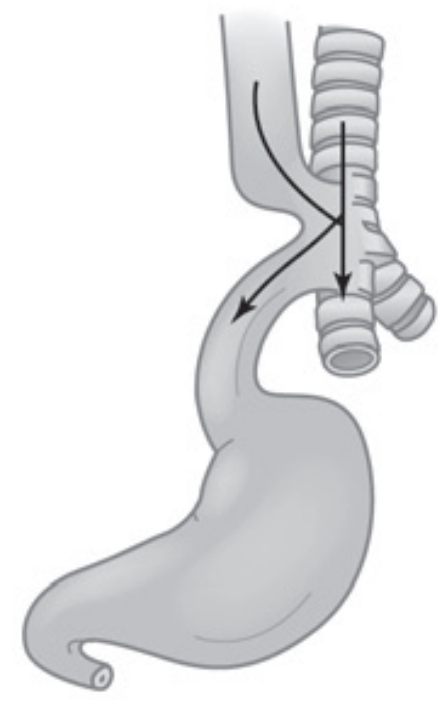
H-type Tracheoesophageal Fistula (no Esophageal Atresia)
Imperforate anus or Anal agenesis
Is a congenital disorder in which anal opening to the exterior is absent.
A fistula may be present
between the colon and the perineum or the urethra in boys;
between the colon and the vagina in girls.
Demonstrated with a cross-table lateral rectum projection with the patient lying prone or by performing a fistulogram.
It is corrected surgically shortly after birth and may require a temporary colostomy
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
results from an incompetent cardiac sphincter, which allows the backward flow of gastric acid and contents into the esophagus.