Neuroscience
1/367
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
368 Terms
Which of the following is NOT a function of the nervous system?
A) Sensory function
B) Integrative function
C) Motor function
D) All are functions of the nervous system
E) None are functions of the nervous system
All are functions of the nervous system
Which of the following types of cells display the property of electrical excitability?
A) Muscle cells
B) Neurons
C) endocrine cells
D) liver cells
E) Both muscle and neurons
Both muscle and neurons
Which of following organelles is a common site of protein synthesis in neurons?
A) mitochondria
B) nucleus
C) Nissl body
D) Golgi apparatus
E) nucleolus
Nissl body
Which of following organelles is a common site of protein synthesis in neurons?
A) mitochondria
B) nucleus
C) rough endoplasmic reticulum
D) Golgi apparatus
E) nucleolus
rough endoplasmic reticulum
With respect to neurons, the term “nerve fiber” refers to
A) an axon.
B) a dendrite
C) a Nissl body.
D) both axons and dendrites.
E) all of these choices
an axon.
This type of neuron has one dendrite and one axon emerging from the cell body.
A) Multipolar neuron
B) Bipolar neuron
C) Unipolar neuron
D) Purkinje cell
E) Renshaw cell
Bipolar neuron
This type of nervous tissue contains neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminals, and neuroglial cells.
A) Gray matter
B) White matter
C) Nissl bodies
D) Ganglia
E) Nuclei
Gray matter
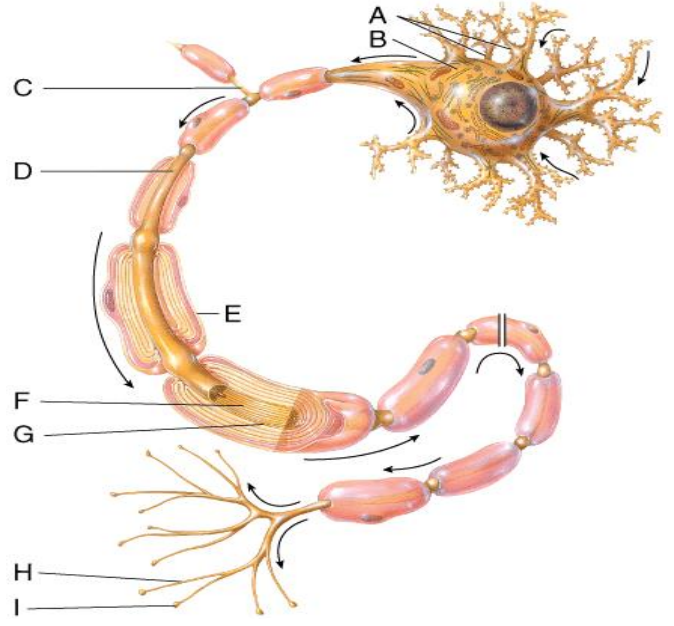
This part of the neuron contains the nucleus and Nissl bodies.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) E
E) Both A and B
B
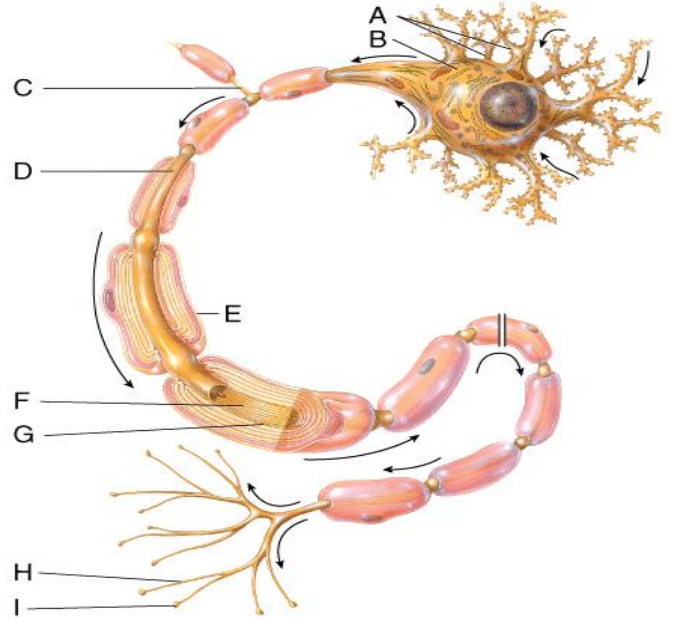
This part of a neuron contains the nucleus and cytoplasm of the Schwann's cell that has formed a myelin sheath around the axon.
A) C
B) D
C) E
D) F
E) G
C) E
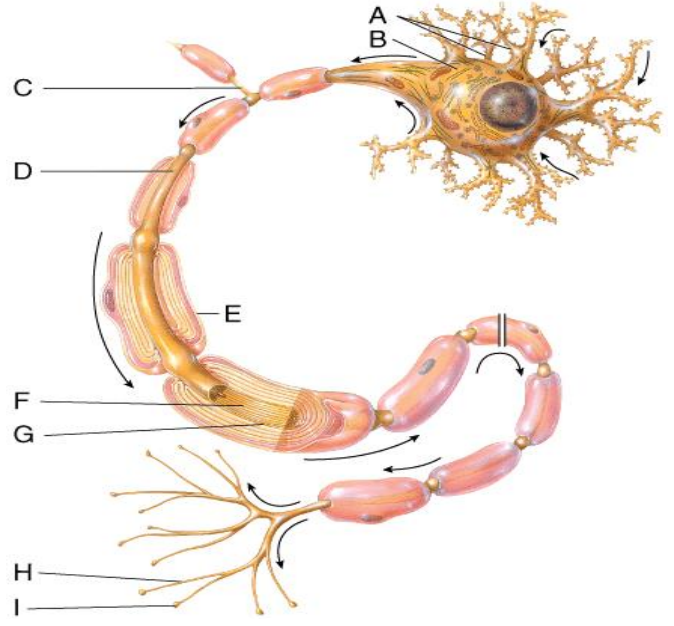
In the diagram, where is the axon collateral?
A) C
B) D
C) F
D) H
E) I
A) C
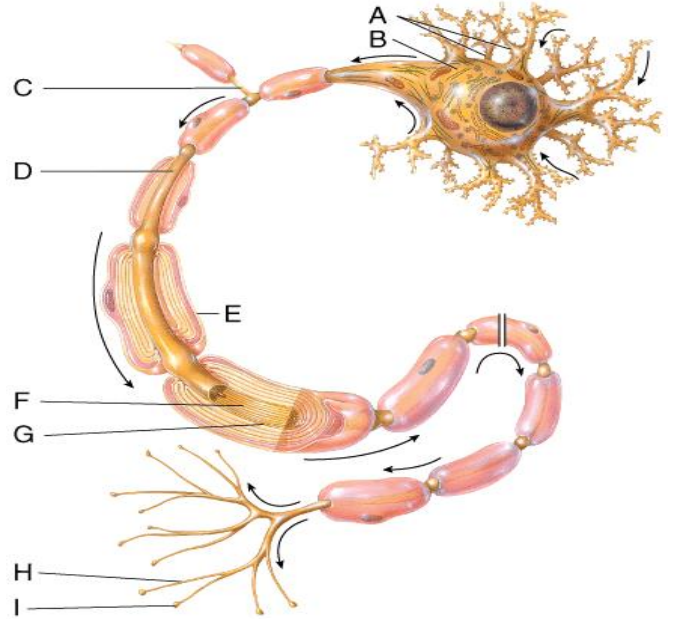
In the diagram, where are axon terminals?
A) H & I
B) G
C) H
D) I
E) A
A) H & I
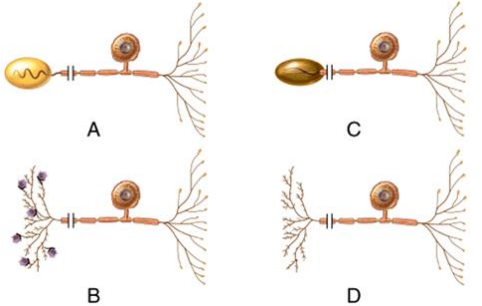
Which of the neurons is considered to be a bipolar neuron?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) All of the neurons.
E) None of the neurons
D) All of the neurons.
Neurons comprise two types of processes: axons and dendrites. What is the major difference between the two? Choose the correct option.
A) Dendrites are of uniform diameter throughout while axons taper to a point.
B) Dendrites receive incoming signals from other neurons while axons carry the output of the neurons.
C) A cell body gives rise to a single dendrite and multiple axons.
D) Dendrites travel long distances while axons taper to a point.
E) Dendrites send information to other neurons
Dendrites receive incoming signals from other neurons while axons carry the output of the neurons.
A scientist looks through a microscope at the structure of the neuron. The scientist notices a layer of molecules separating the neuron's intracellular space from the extracellular space. What is this part of the neuron known as?
A) Organelle
B) Soma
C) Neuronal membrane
D) Nuclear envelope
E) Ion channels
Neuronal membrane
What do you understand by the term “translation”?
A) Assembling a piece of mRNA
B) Assembling proteins from amino acids
C) Removal of introns and specific exons
D) The “reading” of DNA
E) The reading of genes
Assembling proteins from amino acids
What is the most important function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
A) RNA splicing
B) Post-translational protein processing
C) Site of protein synthesis
D) Cellular respiration
E) protein packaging
Site of protein synthesis
Identify an important difference between the cytoplasm of the axon and that of the axon terminal.
A) Protein content of the membrane differs from the soma
B) Occurrence of protein synthesis
C) Presence of ribosomes
D) Large numbers of mitochondria
E) Small numbers of mitochondria
Large numbers of mitochondria
What is the function of a neurotransmitter receptor in the dendritic membrane?
A) Release synaptic vesicles
B) Detect neurotransmitters
C) Destroy extra neurotransmitter left in the synaptic cleft
D) Form gap junctions
E) Activate the cell
Detect neurotransmitters
Which of the following is the largest of the cytoskeletal elements?
A) Microfilament
B) Neurofilament
C) Microtubule
D) Tubulin
E) Nissle bodies
Microtubule
What is retrograde axoplasmic transport?
A) Movement of material from axon terminal to soma
B) Movement of material from soma to axon terminal
C) Movement of material within the synaptic terminal
D) Movement of material among axon collaterals
E) None of the above
Movement of material from axon terminal to soma
What is the site where the axon begins?
A) Soma
B) Axon hillock
C) Axon collateral
D) Axon terminal
E) myelin sheeth
Axon hillock
The watery fluid inside a neuron is called:
A) Cytoplasm
B) Synaptic cleft
C) Synaptic terminal
D) Cytosol
E) Plasma
Cytosol
The part of the neuron containing all the neuronal contents apart from the nucleus is called the:
A) Cytoplasm
B) Cytosol
C) Neurofilaments
D) Soma
E) Actin filaments
Cytoplasm
This organelle is the major site of mRNA Transcription:
A) Mitochondria
B) Nucleus
C) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
D) Ribosome
E) Golgi
Nucleus
This organelle is the major site for protein synthesis:
A) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
B) mitochondria
C) Nucleus
D) Lysosome
E) Golgi
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
This organelle is important for preparing/ proteins for delivery to different cell regions
A) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
B) Ribosome
C) Nucleus
D) Lysosome
E) Golgi
Golgi
This organelle is part of the Cytoskeleton of neurons
A) Microfilaments
B) Ribosome
C) Nucleus
D) Lysosome
E) Golgi
Microfilaments
Which of the following are CNS glia
Select one or more:
a. Astrocyte
b. Satellite Glial Cell
c. Schwann Cells
d. Oligodendrocyte
e. Microglia
Astrocyte
Oligodendrocyte
Microglia
Which of the following is true of the blood-brain barrier?
Select one or more:
a. it makes the CNS 'immune privileged'
b. it is formed by endothelial cells
c. it prevent alcohol from entering the brain
d. it transports glucose into the brain
it makes the CNS 'immune privileged'
it is formed by endothelial cells,
it transports glucose into the brain,
Which of these are functions of glia?
Select one or more:
a. immune functions
b. regulation of extracellular potassium
c. injury responses
d. uptake of glutamate
e. myelination
immune functions
regulation of extracellular potassium
injury responses
uptake of glutamate
myelination
How does myelin increase speed of conduction in nerves
Select one or more:
a. contains glutamate receptors
b. makes the neuronal membrane more excitable
c. provides energy for axons
d. contains potassium channels
e. provides electrical insulation
provides electrical insulation
Which of the following are true concerning injury in the CNS and PNS
Select one or more:
a. Regeneration in the CNS fails because the glial scar inhibits regeneration
b. Schwann cells inhibit regeneration in the PNS
c. The CNS regenerates readily following injury
d. Schwann cells promote regeneration in the PNS
e. astrocytes respond by forming a glial scar in the CNS
Regeneration in the CNS fails because the glial scar inhibits regeneration
Schwann cells promote regeneration in the PNS
astrocytes respond by forming a glial scar in the CNS
Faster communication and synchronization are two advantages of
A) chemical synapses
B) electrical synapses
C) ligand-gated channels
D) voltage-gated channels
E) mechanically-gated channels
electrical synapses
An excitatory neurotransmitter _________ the postsynaptic membrane.
A) depolarizes
B) repolarizes
C) hyperpolarizes
D) does not affect the polarity of
E) moves across channels in
depolarizes
Diffusion, enzymatic degradation, and uptake by cells are all ways to
A) remove a neurotransmitter
B) stop a spatial summation
C) continue a temporal summation
D) inhibit a presynaptic potential
E) excite a presynaptic potential
remove a neurotransmitter
Which of the following neurotransmitters are used in virtually all of the inhibitory synapses?
A) gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and acetylcholine
B) gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine
C) epinephrine and norepinephrine
D) serotonin and melatonin
E) glutamate and aspartate
gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine
A neurotransmitter that binds to an ionotropic receptor that contains a chloride channel would be classified as an
A) inhibitory neurotransmitter and would produce an EPSP in the postsynaptic neuron.
B) inhibitory neurotransmitter and would produce an IPSP in the postsynaptic neuron.
C) excitatory neurotransmitter and would produce an EPSP in the postsynaptic neuron.
D) excitatory neurotransmitter and would produce an IPSP in the postsynaptic neuron.
E) excitatory neuropeptide and would hyperpolarize the postsynaptic neuron.
inhibitory neurotransmitter and would produce an IPSP in the postsynaptic neuron.
What are second messengers?
A) Molecules that activate additional enzymes in the cytosol
B) Voltage-gated ion channels
C) Peptide neurotransmitters
D) Special proteins that span a 3-nm gap between two cell membranes
E) Receptors
Molecules that activate additional enzymes in the cytosol
How are released neurotransmitters cleared from the synaptic cleft?
A) Enzymatic destruction and diffusion
B) Exocytosis
C) Endocytosis
D) Enzymatic destruction and diffusion; Exocytosis; Endocytosis
E) None of the above
Enzymatic destruction and diffusion; Exocytosis; Endocytosis
What is the effect of activating G-protein-coupled neurotransmitter receptors A
) Activate effector proteins such as ion channels
B) Activate enzymes that generate intracellular second messengers
C) Activate effector proteins such as ion channels or those that generate intracellular second messengers
D) Neither does it activate effector proteins such as ion channels nor those that generate intracellular second messengers
E) Neuronal inhibition
Activate effector proteins such as ion channels or those that generate intracellular second messengers D) Neither does
Where is ChAT produced?
A) Axon terminal
B) Soma
C) Synaptic vesicles
D) Postsynaptic membrane
E) Dendrites
Soma
Which of the following is a glutamate receptor subtype?
A) NMDA receptor
B) AMPA receptor
C) Kainate receptor
D) NMDA receptor, AMPA receptor, and kainate receptor
E) Nicotinic
NMDA receptor, AMPA receptor, and kainate receptor
Which of the following mediate most of the synaptic inhibition in the CNS?
A) GABA and glycine
B) Glutamate and glycine
C) GABA and glutamate
D) Glycine and glycerine
E) Serotonin
GABA and glycine
What are vesicular transporters? What is their role?
A) Enzymes that synthesize neurotransmitters from metabolic precursors; responsible for concentrating neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft
B) Synthesizing enzymes for both amino acid and amine neurotransmitters; responsible for concentrating neurotransmitters inside the vesicle
C) Special proteins embedded in the vesicle membrane; responsible for synthesizing neurotransmitters
D) Special proteins embedded in the vesicle membrane; responsible for concentrating neurotransmitters inside the vesicle
E) None of the above
Special proteins embedded in the vesicle membrane; responsible for concentrating neurotransmitters inside the vesicle
Which chemical structure unifies catecholaminergic neurons?
A) Adrenaline
B) Dopamine
C) Catechol
D) Norepinephrine
E) Amine chain
Catechol
The following is an amino acid neurotransmitter
A) dopamine
B) serotonin
C) glutamate
D) noradrenaline
E) acetylcholine
glutamate
NMDA are a sub-class of the following receptors
A) GABA
B) Glycine
C) glutamate
D) histamine
E) cholinergic receptors
glutamate
The vesicular glutamate transporter moves glutamate into
A) glia
B) synapses
C) neurons
D) synaptic vesicles
E) axons
synaptic vesicles
Which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain?
A) Glutamate
B) GABA
C) Acetylcholine
D) Dopamine
E) Noradrenaline
GABA
Which of the following enable ions to cross the cell membrane?
A) Nicotinic Acetyl Choline receptor
B) AMPA receptor
C) GABA-A Receptor
D) all of the above
E) None of the above
all of the above
Which of the following is a G-protein coupled receptor?
A) GABA-B receptor
B) AMPA Receptor
C) Insulin-Like Growth Factor
D) NMDA receptor
E) Nicotinic ACh Receptor
GABA-B receptor
Which of the following neurotransmitters is synthesized by neurons of the locus coeruleus
A) acetylcholine
B) dopamine
C) glutamine
D) GABA
E) noradrenaline
noradrenaline
The activation of which of the following receptors results in neuronal excitation?
A) NMDA receptors
B) GABA-A receptor
C) GABA-B receptors
D) Muscarinic 2 receptors
E) all of the above
NMDA receptors
Which of the following can be an effect of activation of a G-protein coupled receptor?
A) Stimulation of cAMP
B) Inhibition of cAMP
C) Activation of phospholipase C
D) Activation of potassium channels
E) all of the above
all of the above
What is the principal neurotransmitter produced by neurons of the substantia nigra?
A) dopamine
B) noradrenaline
C) glutamate
D) GABA
E) serotonin
dopamine
The following drug binds to the benzodiazepine site of GABA-A receptors and enhances their function.
A) GABA
B) Muscimol
C) Flunitrazepam
D) Flumazenil
E) All of the above
Flunitrazepam
The following drug binds to the benzodiazepine site of GABA-A receptors and inhibits their function.
A) GABA
B) Muscimol
C) Flunitrazepam
D) Flumazenil
E) All of the above
Flumazenil
The following drug activates D2 receptors
A) Bromocriptine
B) Haloperidol
C) Clozapine
D) Raclopride
E) Quinpirole
Bromocriptine
This drug is an Alpha1 adrenergic receptor agonist
A) Clonidine
B) Prazosin
C) Phenylephrine
D) Propranolol
E) Terbutaline
Phenylephrine
This drug is a Beta adrenergic receptor antagonist
A) Clonidine
B) Prazosin
C) Phenylephrine
D) Propranolol
E) Terbutaline
Propranolol
This drug is an Alpha2 adrenergic receptor agonist A) Clonidine B) Prazosin C) Phenylephrine D) Propranolol E) Terbutaline
Clonidine
This drug is a muscarinic receptor agonist
A) atropine
B) pirenzepine
C) carbachol
D) adrenaline
E) dopamine
carbachol
This drug is a muscarinic receptor antagonist
A) atropine
B) pirenzepine
C) carbachol
D) adrenaline
E) dopamine
atropine
This drug is a 5HT1a receptor agonist
A) metoclopramide
B) ondansetron
C) fluoxetine
D) ketanserin
E) buspirone
buspirone
Which of the following is true of the resting membrane potential (RMP)
Select one or more:
a. it is generated by the sodium-potassium pump
b. it is around +30 mV in neurons
c. it is the difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane
d. only neurons have a RMP
e. it depends strongly on potassium
it is the difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane,
it depends strongly on potassium
Which of the following is true of the sodium-potassium pump?
Select one or more:
a. it pumps sodium out of the cell
b. it generates the action potential
c. it is only found in neurons
d. it needs ATP as energy to fuel the pump
e. it pumps potassium into the cell
it pumps sodium out of the cell
it needs ATP as energy to fuel the pump
it pumps potassium into the cell
Which of the following are true of the action potential
Select one or more:
a. the AP is only generated when the RMP depolarizes to a threshold
b. voltage-gated sodium channels are opened at threshold
c. once the threshold is reached, there is an all-or-nothing AP
d. at the peak of the AP, the membrane potential becomes +30 mV or so, known as the overshoot zero
e. opening of voltage-gated sodium channels results in depolarization and the rising phase of the action potential
the AP is only generated when the RMP depolarizes to a threshold
voltage-gated sodium channels are opened at threshold
once the threshold is reached, there is an all-or-nothing AP
at the peak of the AP, the membrane potential becomes +30 mV or so, known as the overshoot zero
opening of voltage-gated sodium channels results in depolarization and the rising phase of the action potential
Which of the following is a G-protein coupled receptor
Select one or more:
a. opioid mu receptor
b. GABA-A receptors
c. metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR)
d. AMPA-type glutamate receptor
e. GABA-B receptors
opioid mu receptor
GABA-A receptors
metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR)
Which of the following are intracellular second messengers
Select one or more:
a. cAMP
b. DAG
c. calcium
d. adenylyl cyclase
e. IP3
cAMP
DAG
calcium
adenylyl cyclase
IP3
Which of the following can be an effect of GPCR activation
Select one or more:
a. inhibition of calcium channels
b. activation of phospholipase C (PLC)
c. stimulation of cAMP
d. inhibition of cAMP
e. activation of potassium channels
inhibition of calcium channels
activation of phospholipase C (PLC)
stimulation of cAMP
inhibition of cAMP
activation of potassium channels
GPCR that have unknown ligands and/or functions are known as -
Select one or more:
a. unknown
b. unspecified
c. orphan
d. indefinite
e. rogue
orphan
The following brain region controls homeostatic functions such as body temperature
A. the cerebellum
B. the brain stem
C. the hypothalamus
D. the basal ganglia
E. the cerebral cortex
the hypothalamus
Which neurotransmitter is synthesized and released by the pedunculopontine nucleus?
A. Serotonin
B. Acetylcholine
C. Norepinephrine
D. Serotonin, acetylcholine, and norepinephrine
E. glutamate
Acetylcholine
This region of the brain functions as a relay station for information entering the cerebrum
A. the midbrain
B. the hypothalamus
C. the pons
D. the medulla
E. the thalamus
the thalamus
The drug carbamazepine is commonly used to treat which disorder
A. schizophrenia
B. Alzheimer's disease
C. depression
D. anxiety
E. epilepsy
epilepsy
The limbic system is important for the processing of which types of information
A. motor
B. body temperature
C. emotion
D. sensory
E. auditory
emotion
A common type of disabling senile dementia that affects about 11% of the population over 65 and results in loss of reasoning and ability to care for oneself, is called
A. agnosia.
B. prosopagnosia.
C. Alzheimer disease.
D. transient ischemic attack syndrome.
E. amylotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Alzheimer disease.
This drug is useful in treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
A. Reserpine
B. Granisetron
C. methylphenidate
D. amphetamine
E. Risperidone
methylphenidate
Which neurotransmitter is synthesized by neurons of the locus coeruleus?
A. acetylcholine
B. dopamine
C. glutamine
D. GABA
E. noradrenaline
noradrenaline
Catecholamines are derived from:
A. acetylcholine
B. epinephrine
C. tyrosine
D. tryptophan
E. serotonin
tyrosine
The following part of the brain is involved in executive function
A. the brainstem
B. the spinal cord
C. the prefrontal cortex
D. the thalamus
E. the locus coeruleus
the prefrontal cortex
Which of the following is a nucleus found in the midbrain that releases serotonin?
A. Substantia nigra
B. Locus Coeruleus
C. Dorsal Raphe
D. Cerebral peduncle
E. Apneustic area
Dorsal Raphe
Pyramidal neurons are mainly found in the
A. cerebellum
B. cortex
C. the spinal cord
D. the thalamus
E. the brainstem
cortex
The activity of the dopamine transporter located in presynaptic nerve terminals is enhanced by
A. haloperidol
B. amphetamine
C. levodopa
D. odansetron
E. bromocriptine
amphetamine
This drug blocks 5HT3 receptors
A. odansetron
B. clozapine
C. buspirone
D. sumatriptan
E. fluoxetine
odansetron
This drug blocks dopamine 2 receptors
A. bromocritine
B. L-DOPA
C. haloperidol
D. all of the above
E. none of the above
haloperidol
The reticular activating system is located within which brain region
A. the thalamus
B. the cerebrum
C. the hypothalamus
D. the spinal cord
E. the midbrain
the midbrain
Sumatriptan is an agonist at which receptors
A. noradrenergic
B. serotonergic
C. dopaminergic
D. glutamatergic
E. GABAergic
serotonergic
Which of the following brain structures consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain?
A. Brain stem
B. Cerebrum
C. Cerebellum
D. Diencephalon
E. Dura mater
Brain stem
The drug Venlafaxine ...
A. increases the synaptic levels of noradrenaline
B. increases the synaptic levels of dopamine
C. increases the synaptic levels of serotonin
D. increases the synaptic levels of noradrenaline and dopamine
E. increases the synaptic levels of noradrenaline and serotonin
increases the synaptic levels of noradrenaline and serotonin
The decussation of the pyramids occurs in the following brain region
A. the medulla oblongata
B. the cerebellum
C. the raphe
D. the basal ganglia
E. the cortex
the medulla oblongata
The basal ganglia DO NOT include the
A. globus pallidus
B. caudate nucleus
C. putamen
D. striatum
E. locus coeruleus
locus coeruleus
This is the main neurotransmitter implicated in schizophrenia
A. glutamate
B. GABA
C. acetylcholine
D. noradrenaline
E. dopamine
dopamine
The Purkinje neuron is found in the following brain region
A. the cerebellum
B. the thalamus
C. the cortex
D. the brainstem
E. the locus coeruleus
the cerebellum
This drug activates 5HT1A receptors
A. clozapine
B. sumatriptan
C. fluoxetine
D. buspirone
E. odansetron
buspirone
Which of the following brain neurotransmitter systems is particularly important for regulating arousal?
A. noradrenaline
B. dopamine
C. GABA
D. glutamate
E. glycine
noradrenaline
What is the principal neurotransmitter produced by neurons of the substantia nigra?
A. dopamine
B. noradrenaline
C. glutamate
D. GABA
E. serotonin
dopamine
Interneurons located within the cortex generally release which neurotransmitter?
A. glutamate
B. noradrenaline
C. serotonin
D. GABA
E. acetylcholine
GABA
Modafinil
A. can be used to treat dementia
B. can be used to treat depression
C. can be used to treat epilepsy
D. can be used to treat narcolepsy
E. is not useful, clinically to treat any brain disorders
can be used to treat narcolepsy
The following drug can be used to treat vomiting:
A. Ondansetron
B. Fenfluramine
C. Fluoxetine
D. Buspirone
E. Carbamazepine
Ondansetron