biochem packets
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what type of molecule has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts?
amphipathic
List the FIVE fundamental concepts of biochemistry
Is observational & experimental science
All branches life from common ancestor
Is interdisciplinary science
life obeys laws of physics
life obeys the laws of chemistry
palmitic acid
phosphatidyl serine
cholesterol
triacylglycerol
lipids
cellulose
glucose
sucrose
fructose
starch
polysaccharide
carbohydrates
insulin
thrombin
trypsin
myoglobin
urease
antibodies
proteins
ethanol, urea, sodium ion
other
linkage for amino acid
peptide
linkage for carbohydrates
glycosidic
linkage for nucleotides
phosphodiester
Nucleus
Contains DNA; DNA is wrapped around proteins
nuclear envelope
surrounds the nucleus
nucleolus
Where rRNA is synthesized and ribosome subunits are assembled
cytoplasm
Cytosol & organelles; provides a medium for chemical reactions and supports organelles
cytoskeleton
structural framework of the cell; provides structure, shape, movement, and intracellular transport
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
makes lipids, detoxification, storage of calcium ions
lysosome
contains digestive enzymes
perixosomes
houses enzymes involved in oxidation reaction *not part of endomembrane system
golgi apparatus (cis=receiving, trans=opposite)
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids from the ER for secretion or delivery to organelles
lysosome
organelle recycling facility; digestion, waste removal
vacuole (both in animal and plant cells)
Storage organelle
the endomembrane system does not include _______ , _______ , or _______ but does include _____ ________
mitochondria
chloroplasts
peroxisomes
plasma membrane
types of noncovalent interactions (strongest → weakest)
1) h bond
2) charge charge
3) dipole dipole
4) charge induced dipole
5) dipole induced
6) van der waal
4 types of intermolecular forces
Weakest→ strongest
1) London dispersion forces (Van der Waals)
due to temporary polarity in the molecules because of unequal electron distribution
2) Dipole–dipole interactions
Due to permanent polarity in the molecules due to their structure
3) Hydrogen bonds
Very strong dipole-dipole attraction; H is attached to N, O
4) Ion–dipole interactions
Between an ion and a polar molecule ( water )
H bond donor vs H bond acceptor
Donor = gives H
Acceptor = receives H (through lone pair)
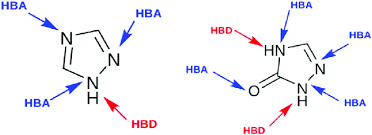
Explain where the polarity of water comes from
O more EN than H→ pulls electron density closer to O than H
Maximum number of hydrogen bonds one water molecule can have with neighboring water molecules:
4
Electrolytes dissolve readily in water because of:
Ion–dipole interactions between the ions and polar water molecules
Ionic compounds can be readily dissolved in water because the high dielectric constant of water screens and decreases the:
Electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions
micelles
spherical aggregates of amphipathic molecules
how does soap remove grease from surfaces:
form micelles around hydrophobic grease/oil
The hydrophobic tails interact with grease, and the hydrophilic heads interact with water, allowing the grease to be solubilized and washed away
The ________________ effect describes the tendency for hydrophobic molecules to aggregate by excluding water:
hydrophobic
The average charge on an amino acid below its pI will be:
positive
the net charge on an amino acid at its isoelectric point (pI) is:
Zero (neutral)
Salt bridge
attractions of oppositely charged functional groups
Many proteins interact with DNA at physiological pH because:
DNA is negatively charged (phosphate backbone), and many proteins have positively charged amino acid side chains (lysine, arginine) that bind via electrostatic interactions
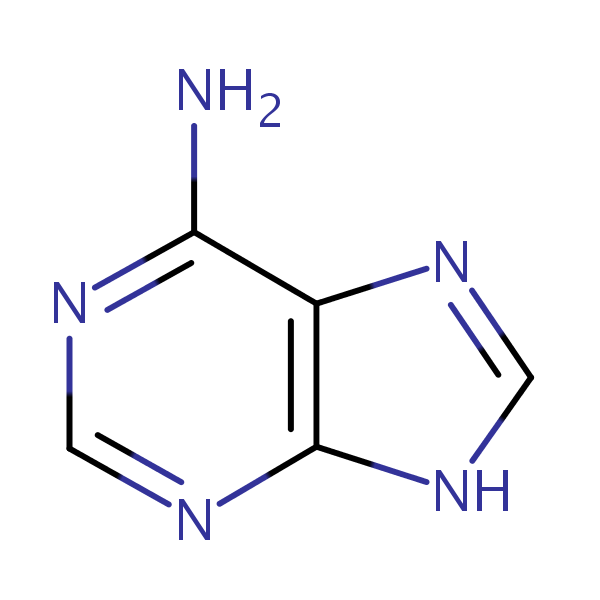
adenine
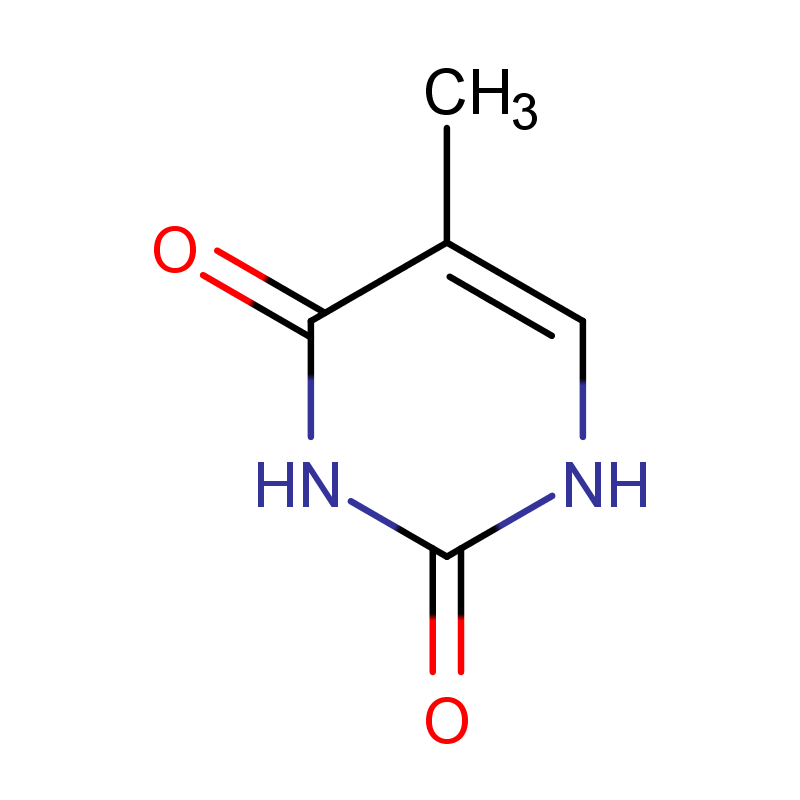
thymine
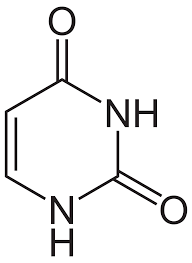
uracil
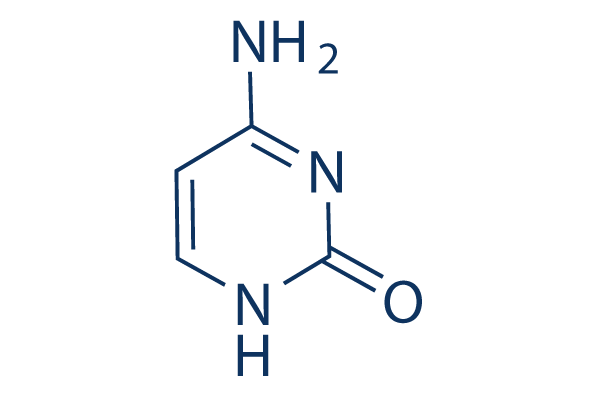
cytosine
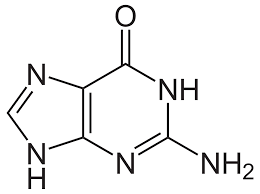
guanine
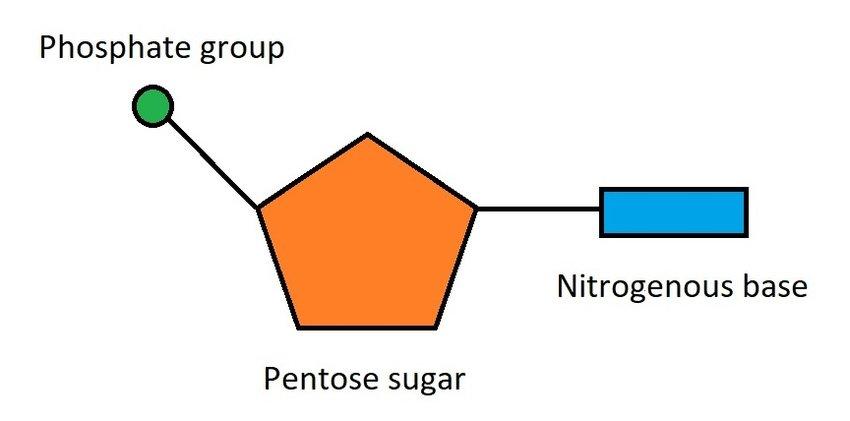
nucleotides
Charge on each repeating unit in DNA or RNA:
negative
Ions that neutralize this charge inside the cell:
Positively charged ions (cations) such as Na⁺, K⁺, Mg²⁺.
Complementary base pairing in dsDNA determines the __________ helix formation from two
____________________ strands
double, antiparallel
Purines (A, G) are larger, ____-ring structures.
Pyrimidines (T, C) are smaller, ____-ring structures.
Pairing a purine with a pyrimidine keeps the helix diameter uniform, essential for the stable double helix.
2, 1
Which of the following does NOT describe the secondary structure of DNA as proposed by
Watson and Crick?
A) The two strands of the double helix are stabilized by hydrogen-bonding between A and T and
between G and C.
B) The two strands of the double helix run in opposite directions.
C) The phosphate deoxyribose backbones of the helix are on the outside.
D) The base pairs are stacked on one other with their planes at 180o to the helix axis
D
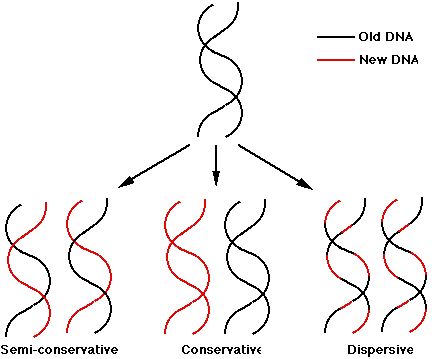
Consecutive base pairs in a dsDNA interact by ____________________________ interactions.
The nonpolar faces of the stacked bases are in the ___________ of the double helix,
_________________ from the surrounding aqueous environment, contributing to the overall
stability of the DNA structure. This is known as the hydrophobic effect.
Base stacking (van der Waals)
interior (core)
shielded
Single-stranded RNA molecules can have extensive regions of ____________ ____________ _____________
Intramolecular base pairing
The melting point, Tm, of a dsDNA is the
temperature at which the mixture contains ____%
_______ and _____% dsDNA.
The Tm is an important parameter in setting up the
temperature sequence of ____________
50% ssDNA
50%
PCR
A DNA vs B DNA
A DNA: open in center (present in low humidity, double stranded RNA, DNA-RNA hybrids), base pairs on side
B DNA: closed in center, twist angle = 36 degrees
Nucleic acids absorb strongly at UV range because their _____________ have _____________ double bonds.
nitrogenous bases, conjugated
The concentration of a dsDNA sample can be
calculated using the absorbance measured at
_______ nm, and knowing that an
A260 of 1.000 equals 50 μg/mL
260 nm
for various dsDNA fragments the Tm ________________ with increasing G C content.
Explain why
increases
More GC pairs → stronger hydrogen bonding and base stacking interactions → higher thermal stability → higher Tm.
list and describe the weak interactions that hold the dsDNA helix together
1) H bonds (a-t=2, g-c=3)
2) induced dipole: between consecutive bases
3) hydrophobic effect: bases release solvation water molecules as they stack
The phosphodiester bonds in DNA are linked between the:
3′ hydroxyl (–OH) of one deoxyribose to the 5′ phosphate (–PO₄) of the next deoxyribose.
Expression of genetic information involves first ___________ then ___________ .
transcription, translation
DNA replication inside the cell creates an __________ copy of its DNA. The process involves DNA
helicase to unwind the ____________ helix, creating a _________________ fork. Then, DNA
___________________________ (enzyme) builds 2 new DNA strands using the original strands as
_____________________
exact, double, replication, polymerase, templates
isoelectric point
pH where amino acid has no charge
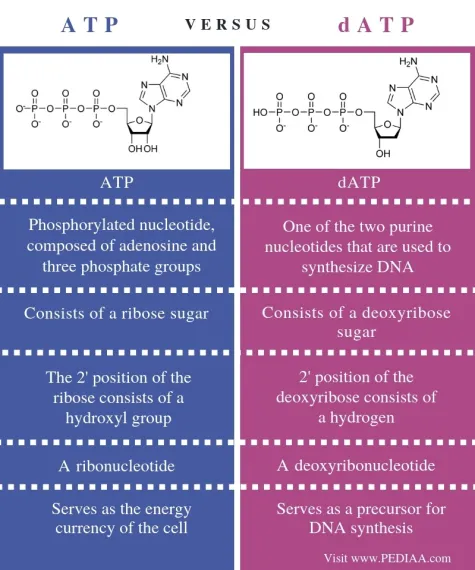
draw ATP vs DATP
primary, secondary, tertiary structure
primary: linear nucleotide sequence of a polynucleotide chain
secondary: α-helix and β-sheet formed by hydrogen bonds
tertiary: Overall 3D shape of a single protein chain
quaternary: Assembly of multiple protein chains into one functional unit
concentration of a dsDNA sample can be calculated knowing that
A260 of 1.000 equals 50 micrograms/mL
B DNA is a _______-handed helix made of ___(#) ________ strands that are held together by __________ bonds in the _____-__________ and __________-__________ base pairs.
One helical turn of B-DNA has _____ (#) base pairs that are ______ within the helix and are almost __________ to the helical axis
The diameter of the dsDNA cylinder is _____ Angstrom
The distance between consecutive base pairs is ______ Angstrom
There is a twist angle of ___ degrees between stacked base pairs
the phosphate groups are located on the _______ of the dsDNA
right-handed, 2, polynucleotide, hydrogen, A–T, G–C
10, stacked, perpendicular
20 Å, 3.4 Å, 36 degrees
outside
restriction endonucleases are useful in gene cloning because they ____ DNA at ____ and ____ sequences. Ligases _______ dna molecules by forming __________ bonds between the dna fragments
cut, specific, palindromic
join, phosphodiester
PCR is a laboratory technique used for _____________ a given sequence of _____________
amplifying, DNA
Explain the role for each component of a PCR:
___________ ___________: template containing the target sequence to be amplified
___________: single-stranded DNA sequences; provide a starting point for DNA synthesis
___________: building blocks (A, T, G, C) that DNA polymerase uses to synthesize new DNA strands
___________: maintain optimal pH and salt conditions
___________ ___________: heat-stable DNA polymerase that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding dNTPs to primers
___________: cofactor required for DNA polymerase activity; stabilizes the dNTPs and the enzyme-DNA complex
genomic DNA
primers
dNTPs
buffer
Taq Polymerase
Mg²+
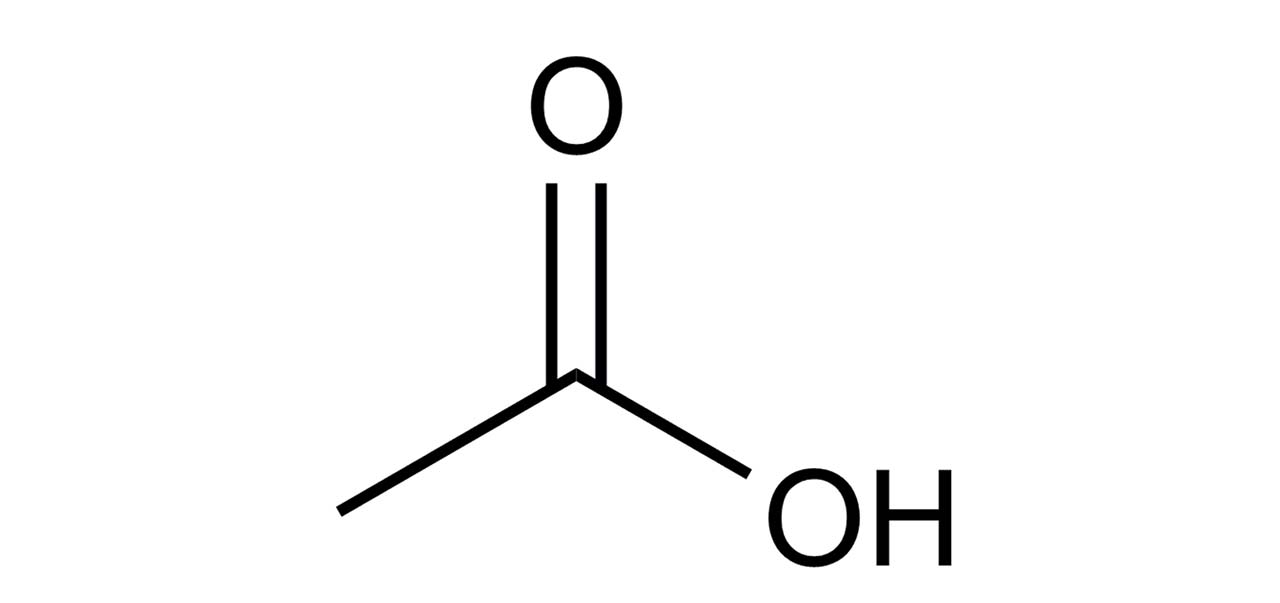
acetic acid
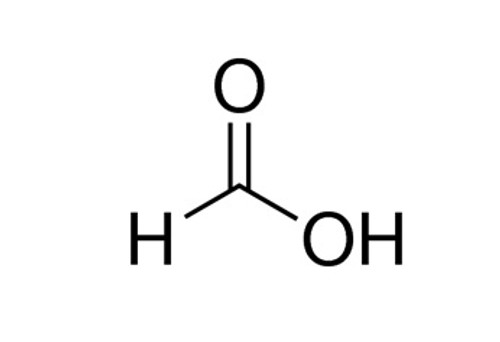
formic acid
6 strong acids
HCl
HBr
HI
HNO₃
H₂SO₄
HClO₄
8 strong bases
LiOH
NaOH
KOH
RbOH
CsOH
Ca(OH)₂
Sr(OH)₂
Ba(OH)₂
Ka equation
[H+][A-]/HA