Cell Theory and Plant Cell Structure
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
All life forms are made up of cells (Schleiden & Schwann) ○ Can exist on its own
The cell is the basic unit of life (Schleiden & Schwann) ○ Simplest form of life
Cells come from pre-existing cells (Virchow) ○ Evolves through reproduction (cycle)
What are the three basic tenets of the cell theory?
Hans and Zacharias Janssen
Who first invented the compound microscope in 1595.?
Robert Hooke
Who coined the term “cell” after observing a cork under the microscope in 1665?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Who made his own microscope in 1668 and is known as the Father of Microscopy and Microbiology?
Theodore Schwann & Matthais Schleiden
Who found that animals were composed of cells?
Rudolf Virchow
Who concluded that cells can only come from preexisting cells in 1855?
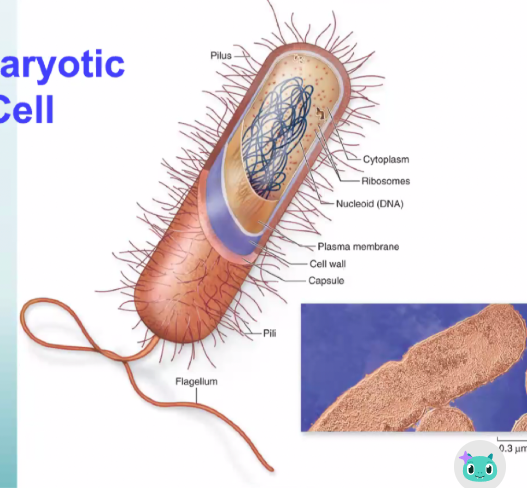
Prokaryotic Cells
Single-celled organisms without nuclei and membrane-bound organelles.
examples: bacteria and archaea
Eukaryotic Cells
Multicellular organisms with organized compartments, membrane-bound organelles, and membrane-bound nucleus. Possess a cytoskeleton for support and to maintain cellular structure
examples: Protists, fungi, plants, and animals
Endosymbiotic Hypothesis
This hypothesis claims that eukaryotes arose from a symbiotic relationship between various prokaryotes
Cell Structure
All cells share genetic material and plasma membrane.
Cell Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer acting as a selective barrier.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures for protein synthesis.
Cellulosic Cell Wall
Provides structure and support in plant cells.
Surrounds growing cells, meristematic cells, and cells in succulent tissues
Primary Cell Wall
First layer surrounding growing plant cells; produced after mitosis
Secondary Cell Wall
Inner layer, thickens plant cells for sturdiness; pushes the primary cell outward
More common in MORE STURDY parts of the plant (wood, cork)
has 3 layers
Middle Lamella
Cements primary walls of adjacent plant cells.
Plasmodesma
Cytoplasmic thread allowing communication between plant cells.
Lipid Rafts
Specialized membrane domains for cellular functions.
made up of Lipid bilayer, cholesterols, and sphingolipids
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes heterogeneous nature of cell membranes.
Soluble Fiber
Dissolves in water, lowers cholesterol levels.
Insoluble Fiber
Speeds digestion, reduces colon cancer risk.
Cytoplasm
Semifluid matrix containing organelles and cytosol.'
gel-like fluid inside the cell. It is the medium for chemical reaction
Plastids
Organelles involved in storage and pigment synthesis.
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis, contains chlorophyll and DNA.
Genetic material (in a nucleoid or nucleus)
Cytoplasm (semifluid matrix)
Plasma membrane (phospholipid bilayer)
Ribosome (protein synthesis)
What are the common cell structures among all cells?
Prokaryotic
What kind of cell is this?
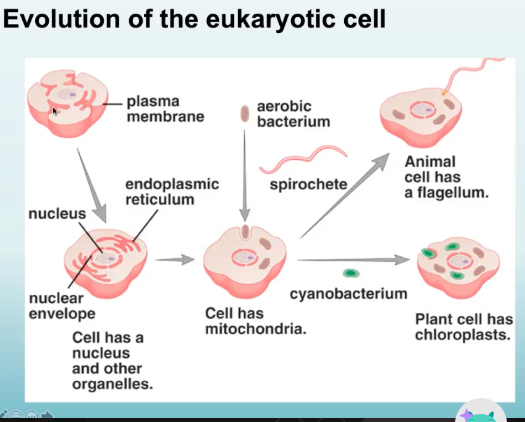
From the prokaryotic cell, it may have swallowed another prokaryotic cell. This prokaryotic cell now becomes part of the mother prokaryotic cell.
If the mother prokaryotic cell swallowed an organism with chlorophyll pigments that can undergo photosynthesis
As it accumulates, these parts have evolved into specialized parts within the mother cell.
Aerobic bacterium now has become a mitochondria
Bacterium with chlorophyll now has become the chloroplastid
The nuclear material inside now has developed its own membrane around it
There developed subunits or organelles with specific functions within the cell. It now has become more complicated and in turn, into a EUKARYOTIC CELL
Describe the endosymbiotic hypothesis
Mitochondria; chloroplasts
In the endosymbiotic hypothesis,
Heterotrophic bacteria became_______
Cyanobacteria became_________
The mitochondria and chloroplasts
Similar to bacteria in both size and structure
Bounded by a double membrane (outer membrane is the engulfing vesicle, the inner from the prokaryote)
Each contain a circular DNA and divide by splitting
Have their own ribosomes and produce some proteins, like prokaryotes
Pieces of evidence for the endosymbiotic hypothesis
Centriole and the lysosome are present in only animal cells, not plant cells
What are unique to animal cells?
Cell walls, chloroplastids, large central vacuole
What structures found in plant cells but not in animal cells?
lysosomes
Break down materials
Central vacuole
What is the equivalent of lysosomes in plant cells?
Cellulose, hemicellulose (alkali-soluble portion of the cell wall), pectin (water soluble), and glycoprotein
What are cell walls (primary wall) composed of?
lignin
An aromatic polymer that rigidifies secondary cell walls
pectin
Cementing substance made up of calcium and magnesium pectates
Pectin
Primary wall
Secondary wall (S1)
Secondary wall (S2)
Secondary wall (S3)
Describe the sequence from the outside to the inside of the cell wall
The roughness of the older cell wall
What makes the cementing substance stick together?
It loses its stability
What happens if the hemicellulose, lignin, proteins etc are dissolved in the secondary wall?
An extra cellular layer between two cells that keep them together
What is mid lamella/middle lamella?
30-35%
All higher plants except the grass family have walls of ______ pectin
10%
How much pectin does the grass family contain?
Fiber
__________ is an undigestible complex carbohydrate found in plants

Describe soluble fibers

Describe insoluble fibers
Thin areas on the secondary cell walls of plants. They look like depressions on the walls. Also, they aid in the transport of minerals and water between the cells
What are pits?
External
Cytoplasm is __________ to the endomembrane system
Eukaryotic cells are full of membrane-enclosed compartments
Separates incompatible chemical and physical conditions
Proteins can be both synthesized and hydrolyzed within a single cell
What is compartmentalization?
cytosol
It is found in the cytoplasm, where the cytosol acts as the liquid portion composed of water, enzymes, precursors, and intermediate by-products where all the organelles are suspended in
Stroma
What are the chloroplast constituents?
Proplastids
Specialized for dividing to form new plastid and are usually found in meristematic cells
Etioplasts
These plastids develpo in the absence of light. This does not need photosynthesis
Amyoplasts
These are specialized for storage that contain a large amount of starch. It also does not contain chlorophyll
Chromoplasts
Contains red, orange, or yellow carotenoid pigments that are water-insoluble
Elaioplasts
Contains oil droplets and usually found in fruits or seeds
proteinoplast
Plastids that contain proteins
Proplast
Etioplast
Amyloplast
What are the different leucoplasts (colorless)?
Non-raft lipids: portions with lipid and proteins
Raft: clustering of specific lipids and proteins that move along the surface
Non-raft vs raft lipids
No, because lipids with those proteins change positions around the cell membrane
Are lipid rafts stable?
Glycolipids
Carbohydrates attached to the phospholipid bilayer are called
Glycoproteins
Carbohydrates attached to membrane proteins are called