BIO LAB : Diffusion and Osmosis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is diffusion?
The movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
What is osmosis?
The movement of water across a membrane from areas of high free water concentration to areas of low free water concentration across the membrane
What are cells surrounded by?
Plasma
What are the components of a cell membrane?
Semi permeable
Composed of phospholipids
Passive and Active Transport
Simple and Facilitated Diffusion
What are the parts of phospholipids?
Hydrophilic Head (attracted to water)
Hydrophobic Tail (repelled by water)
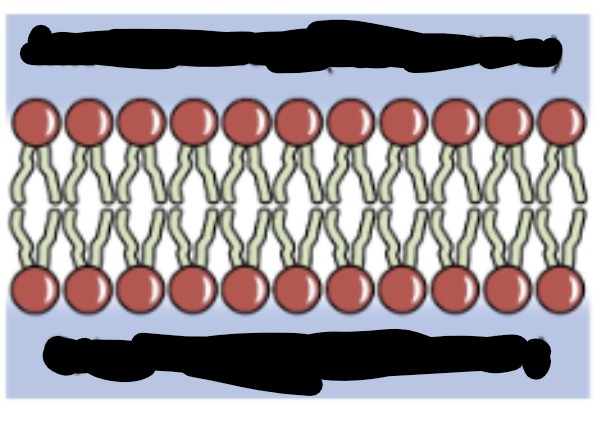
From Top to bottom
Interstitial Fluid (extracellular)
Cytosolic Fluid (Intracellular)
What is passive transport?
Type of transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes from high to low concentration
What is active transport?
Type of movement that requires ATP to move substances across the membrane from low to high concentration
What is simple diffusion?
Passive movement across a semipermeable membrane from a high to low concentration without assistance or energy
What is facilitated diffusion
Passive transport that uses membrane proteins to move molecules across a membrane from high to low concentration
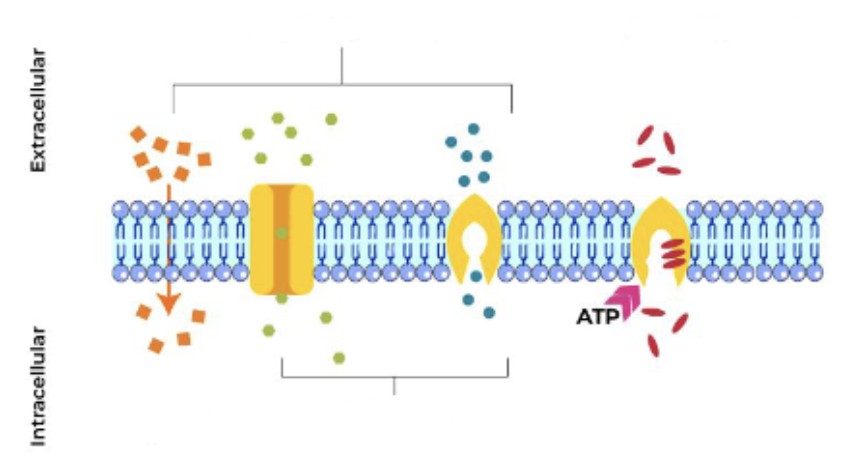
From top to Bottom
Passive and Active Transport
Simple Diffusion and Facilitated Diffusion
Dialysis Tubing have microscope holes that allow what?
For small molecules to pass through but not large molecules (separates molecules based on size)
What is hemodialysis?
Using dialysis membrane to clean blood and remove harmful substances
What is peritoneal dialysis?
Uses dialysis fluid to remove harmful substances inside the body
What is hypotonic, isotonic, and hypotonic solutions?
Hypotonic: Cell fills up with an excessive amount of water
Isotonic: Cell fills up and loses normal amount of water
Hypertonic: Cell loses an excessive amount of water
What is water intoxication?
When a person consumes excessive amounts of water causing the body’s electrolyte balance to be disrupted
What is the part of the paramecium that appears and disappears under the microscope?
Contractile Vacuoles (regulate osmotic pressure)
What happens during plasmolysis?
Happens during a hypertonic solution and is when the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall as the cell loses water
Which parts of the heart carry oxygenated blood?
Lungs, Pulmonary Vein, Aorta
Which parts of the heart carry deoxygenated blood?
Pulmonary artery, Vena Cava, Heart
What is the cardiac cycle composed of?
Contraction of the atria
Relaxation of the atria
Contraction of the ventricles
Relaxation of the ventricles
What happens during systemic circulation?
Left side propels fresh oxygenated blood from the lungs through the left atria to the left ventricle then throughout the whole body
What happens during pulmonary circulation?
Deoxygenated blood is received in the right atrium though the vena cavas then pushed to the right ventricle though the pulmonary trunk then to the pulmonary arteries then back to the lungs