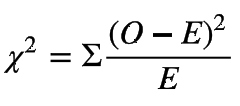Chapter 2: Mendelian Inheritance
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:02 AM on 2/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
theory of pangenesis
“seeds” are produced by all parts of the body and then collected and transmitted to the offspring at the time of conception
2
New cards
Hippocrates, seeds, all, offspring, first
theory of pangenesis:
* explanation for hereditary traits by Greek physician, _____
* “_____” are produced by _____ parts of the body and then collected and transmitted to the _____ at the time of conception
* _____ attempt to explain the transmission of hereditary traits from generation to generation
* explanation for hereditary traits by Greek physician, _____
* “_____” are produced by _____ parts of the body and then collected and transmitted to the _____ at the time of conception
* _____ attempt to explain the transmission of hereditary traits from generation to generation
3
New cards
theory of preformationism
a “homunculus” unfolds and grows to adult proportions with proper nourishment
4
New cards
homunculus
diminutive fully formed human body, historically believed to inhabit a germ cell (an egg or a sperm) and to have the capacity to increase in size, giving rise to an adult human
5
New cards
homunculus, spermists, ovists
theory of preformationism:
* a “_____” unfolds and grows to adult proportions with proper nourishment
* _____ and _____
* a “_____” unfolds and grows to adult proportions with proper nourishment
* _____ and _____
6
New cards
blending hypothesis of inheritance
traits can blend together generation after generation
7
New cards
intermediate, blend
theory of blending:
* first systematic studies of genetic crosses were carried out by German botanist Joseph Kolreuter from 1761 to 1766
* in cross between different strains of tobacco plants, he found that the offspring were usually _____ in appearance between two parents
* this observation led Kolreuter to conclude that both parents make equal genetic contribution to their offspring
* blending hypothesis of inheritance: the factors that dictate hereditary traits could _____ together from generation to generation
* first systematic studies of genetic crosses were carried out by German botanist Joseph Kolreuter from 1761 to 1766
* in cross between different strains of tobacco plants, he found that the offspring were usually _____ in appearance between two parents
* this observation led Kolreuter to conclude that both parents make equal genetic contribution to their offspring
* blending hypothesis of inheritance: the factors that dictate hereditary traits could _____ together from generation to generation
8
New cards
Gregor Mendel
“father of genetics”
9
New cards
Pisum sativum, varieties, crosses, hybridization
Mendel’s pea plants:
* garden pea: _____ _____
1. the species was available in several _____, which varies in height and in the appearance of their flowers, seeds, and pods
2. Structure of the plant allowed for easy and well controlled _____
* “Experiments on Plant Hybrid” 1866
* _____: mating/crossing between individuals that have different characteristics
* garden pea: _____ _____
1. the species was available in several _____, which varies in height and in the appearance of their flowers, seeds, and pods
2. Structure of the plant allowed for easy and well controlled _____
* “Experiments on Plant Hybrid” 1866
* _____: mating/crossing between individuals that have different characteristics
10
New cards
cross/hybridization
* a breeding between two distant individuals. An analysis of their offspring may be conducted to understand how traits are passed from parent to offspring.
* the breeding of two organisms of the same species with different characteristics
* the breeding of two organisms of the same species with different characteristics
11
New cards
gamete
a reproductive cell (usually haploid) that can unite with another reproductive cell to create a zygote
12
New cards
sperm cell
* a male gamete
* are small and usually travel relatively far distances to reach the female gamete
* are small and usually travel relatively far distances to reach the female gamete
13
New cards
pollen grain
the male gametophyte of flowering plants
14
New cards
anther
the structure in flowering plants in which pollen grains form
15
New cards
sperm cells, pollen grains, anthers
_____ _____ are produced within _____ _____ that form in the _____
16
New cards
egg cell
* a female gamete
* is usually very large and nonmotile
* is usually very large and nonmotile
17
New cards
ovule
the structure in flowering plants where the female gametophyte is produced
18
New cards
ovary
in plants, the structure in which the ovules develop
19
New cards
egg cells, ovules, ovaries
_____ _____ are produced within _____ that form in the _____
20
New cards
stigma
the structure in flowering plants on which the pollen grain lands, stimulating the growth of the pollen tube so that sperm cells can reach the egg cells
21
New cards
self-fertilization
fertilization that involves the union of male and female gametes derived from the same parent
22
New cards
cross-fertilization
a cross in which the male and female gametes come from separate individuals
23
New cards
anthers, pollen, pollen, stigma, anthers
How Mendel cross-fertilized pea plants:
* Mendel was able to pry open immature flowers and remove the _____ before they produced pollen
* therefore, these flowers could not self-fertilize
* he then obtained _____ from another plant by gently touching its mature anthers with a paintbrush
* Mendel applied this _____ to the _____ of the flower that already had its _____ removed
* Mendel was able to pry open immature flowers and remove the _____ before they produced pollen
* therefore, these flowers could not self-fertilize
* he then obtained _____ from another plant by gently touching its mature anthers with a paintbrush
* Mendel applied this _____ to the _____ of the flower that already had its _____ removed
24
New cards
character
in genetics, a general characteristic such as eye color
25
New cards
trait/variant
characteristics of an organism; also specific properties of a character, such as tall and dwarf pea plants
26
New cards
true-breeding line
strain of a particular species that continues to produce the same trait after several generations of self-fertilization (in plants) or inbreeding
27
New cards
single-factor cross
a cross in which an experimenter is following the outcome of only a single character
28
New cards
monohybrid
a individual produced from a single-factor cross in which the parents had different variants for a single character
29
New cards
2 variants, 1 trait
monohybrid cross
* crossing _____ _____ of _____ _____
* crossing _____ _____ of _____ _____
30
New cards
parental generation
in a genetic cross, the first generation in the experiment. In Mendel’s studies, the parental generation was true-breeding with regard to particular traits
31
New cards
first, true-breeding, homozygous
parental generation:
* _____ generation in the experiment
* in Mendel’s studies, the parental generation was _____ with regard to particular traits (_____)
* _____ generation in the experiment
* in Mendel’s studies, the parental generation was _____ with regard to particular traits (_____)
32
New cards
F1 generation
the offspring produced from a cross of a parental generation
33
New cards
F2 generation
the offspring produced from a cross or self-fertilization of the F1 generation
34
New cards
dominant
describes an allele that determines the phenotype in the heterozygous condition
35
New cards
recessive
a trait or gene that is masked by the presence of a dominant trait or gene
36
New cards
particulate theory of inheritance
a theory proposed by Mendel. It states that traits are inherited as discrete units that remain unchanged as they are passed from parent to offspring.
37
New cards
two, two, identical, different, dominant, recessive, randomly
particulate theory of inheritance:
* _____ discrete hereditary factors - one from each parent
* the _____ factors can be _____ or _____
* one factor is _____ (seen) and the other is _____ (not seen)
* paired factors segregate _____
* Mendel’s Law of Segregation
* _____ discrete hereditary factors - one from each parent
* the _____ factors can be _____ or _____
* one factor is _____ (seen) and the other is _____ (not seen)
* paired factors segregate _____
* Mendel’s Law of Segregation
38
New cards
gene
a unit of heredity that may influence the outcome of a trait in an organism. At the molecular level, a gene is a segment of DNA that contains the information to make a functional product, either RNA or a polypeptide.
39
New cards
allele
an alternative form of a specific gene
40
New cards
Mendel’s law of segregation
the two copies of a gene segregate (or separate) from each other during transmission from parent to offspring
41
New cards
homozygous
describes a diploid individual that has two identical alleles of a particular gene
42
New cards
heterozygous
describes a diploid individual that has different versions (i.e., two different alleles) of the same gene
43
New cards
genotype
the genetic composition of an individual, especially in terms of the alleles for particular genes
44
New cards
phenotype
the observable traits of an organism
45
New cards
Punnett square
a diagrammatic method in which the gametes that two parents can produce are aligned next to a square grid as a way to predict the types of offspring the parents will produce and in what proportions
46
New cards
two-factor cross
a cross in which an experimenter follows the outcome of two different characters
47
New cards
2 variants, 2 traits
dihybrid cross:
* crossing plants with _____ _____ of _____ _____
* crossing plants with _____ _____ of _____ _____
48
New cards
traits linked, traits independent
two possible results from a two-factor cross
49
New cards
traits linked
the two genes always stay associated with each other
50
New cards
traits independent
the two different genes randomly segregate into haploid cells
51
New cards
RrYy, RY, ry
trait linked:
* P generation seeds: RRYY x rryy
* F1 generation seeds: _____
* Haploid gametes: 1/2 _____, 1/2 _____
* P generation seeds: RRYY x rryy
* F1 generation seeds: _____
* Haploid gametes: 1/2 _____, 1/2 _____
52
New cards
RrYr, RY, Ry, rY, ry
traits independent:
* P generation seeds: RRYY x rryy
* F1 generation seeds: _____
* Haploid gametes: 1/4 _____, 1/4 _____, 1/4 _____, 1/4 _____
* P generation seeds: RRYY x rryy
* F1 generation seeds: _____
* Haploid gametes: 1/4 _____, 1/4 _____, 1/4 _____, 1/4 _____
53
New cards
2, 2, 3/4, 1/4, parental phenotypes
traits linked:
* Punnett square will be _____ x _____
* offspring:
* _____ round yellow
* _____ wrinkled green
* _____ _____: all phenotypes are similar to the parents
* Punnett square will be _____ x _____
* offspring:
* _____ round yellow
* _____ wrinkled green
* _____ _____: all phenotypes are similar to the parents
54
New cards
4, 4, 9/16, 3/16, 3/16, 1/16, non parental phenotypes
traits independent:
* Punnett square will be _____ x _____
* offspring:
* _____ round yellow
* _____ round green
* _____ wrinkled yellow
* _____ wrinkled green
* _____ _____: see phenotypes different from the parents
* Punnett square will be _____ x _____
* offspring:
* _____ round yellow
* _____ round green
* _____ wrinkled yellow
* _____ wrinkled green
* _____ _____: see phenotypes different from the parents
55
New cards
Mendel’s law of independent assortment
two different genes will randomly assort their alleles during gamete formation
56
New cards
segregation
monohybrid cross → principle of _____
57
New cards
independent assortment
dihybrid cross → principle of _____
58
New cards
pedigrees
charts representing family relationships
59
New cards
female
\

60
New cards
male

61
New cards
deceased individual
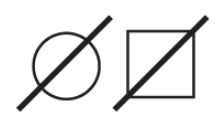
62
New cards
unaffected individual

63
New cards
affected individual

64
New cards
heterozygote

65
New cards
25%, 100%, skipping generation
autosomal recessive patten:
* 2 normal heterozygous individuals → _____ recessive offspring
* 2 affected individuals (homozygous recessive) -> _____ recessive offspring
* _____ _____
* 2 normal heterozygous individuals → _____ recessive offspring
* 2 affected individuals (homozygous recessive) -> _____ recessive offspring
* _____ _____
66
New cards
one
dominant pattern:
* affected individuals will inherit gene from _____ affected parent
* affected individuals will inherit gene from _____ affected parent
67
New cards
males
sex linked:
* affects on sex more often than the other
* more common in _____
* affects on sex more often than the other
* more common in _____
68
New cards
probability
the chance that an outcome will occur in the future
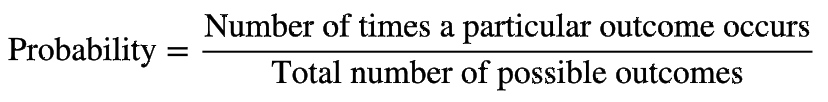
69
New cards
chance, size, large, small
probability:
* the _____ that an outcome will occur in the future
* the accuracy of the prediction depends to a great extent on the _____ of the sample
* random sampling error:
* _____ for small sample sizes
* _____ for large sample sizes
* the _____ that an outcome will occur in the future
* the accuracy of the prediction depends to a great extent on the _____ of the sample
* random sampling error:
* _____ for small sample sizes
* _____ for large sample sizes
70
New cards
sum rule
the probability that one of two or more mutually exclusive events will occur is equal to the sum of the individual probabilities of the events
71
New cards
product rule
the probability that two or more independent events will occur is equal to the product of their individual probabilities
72
New cards
binomial expansion
represents all of the possibilities for a given set of unordered events
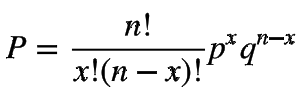
73
New cards
chi square test
a commonly used statistical method for determining the goodness of fit