The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
A prominent constellation known for its large rectangle shape and bright stars.
Orion
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
A scatter graph that categorizes stars based on luminosity, absolute magnitude, color, and effective temperature.
A region on the H-R diagram where most stars, including the Sun, fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores.
Main Sequence
Stars that are less luminous than expected due to their small size, typically one-thousandth the size of main sequence stars.
White Dwarfs
Stars that are much larger and brighter than their temperature would predict, expanding to several thousand times the size of main sequence stars.
Red Giants
The final evolutionary state of stars that do not have enough mass to become neutron stars, often resulting in white dwarfs.
Stellar Remnant
A theoretical end state of a white dwarf after it has cooled and no longer emits significant light.
Black Dwarf
The stage in a star's life when it expands significantly and its core hydrogen fusion decreases due to fuel depletion.
Red Giant Phase
The actual brightness of a star, often measured in multiples of the Sun's brightness.
Luminosity
A measure of how bright a star would appear from a standard distance.
Absolute Magnitude
The brightness of a star as observed from Earth.
Apparent Magnitude
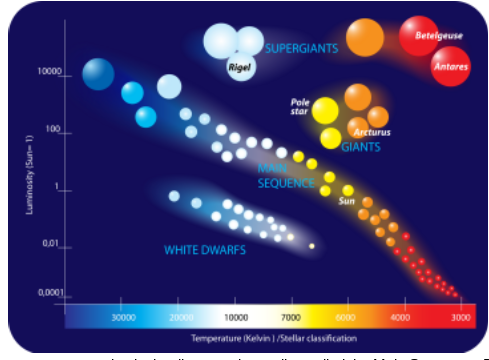
1. Which of the following is a reasonable estimate for the surface temperature of the Sun as taken from the HR diagram?
(a) 10,000 K
(b) 8,000 K
(c) 6,000 K
(d) 4,000 K
(e) 2,000 K
C
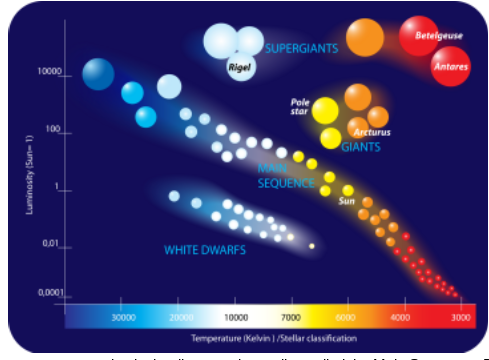
2. Would the surface temperature of white dwarfs be higher or lower than that of red giants?
higher
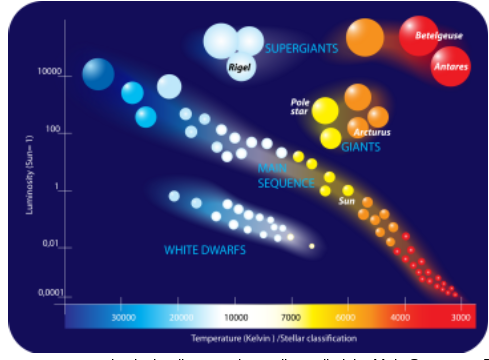
3. What is the color of the stars with the highest surface temperature?
blue
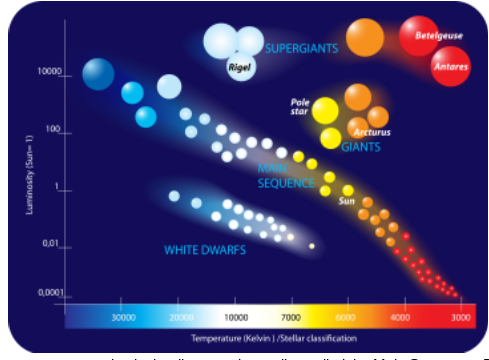
4. What is the color of the stars with the lowest surface temperature?
red
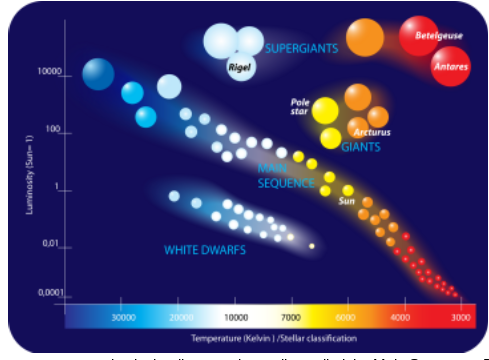
5. Most of the stars on the HR Diagram are classified as what type of stars?
main sequence stars
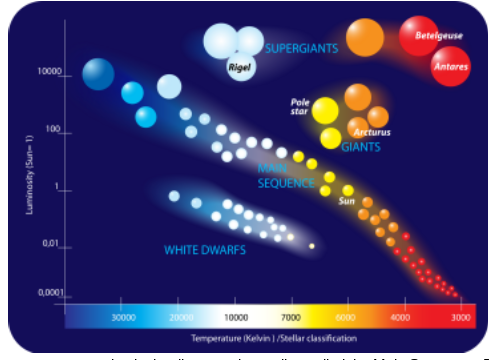
6. How is it possible for the Sun to be more luminous than a white dwarf if the Sun has a lower temperature than the white dwarf?
it is larger