aggregate demand and aggregate supply (macro)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Circular flow of income diagram?
what are the leakages and injections?
injections:
- gov spending
- exports
- investment
leakages:
- savings
- taxes
- imports
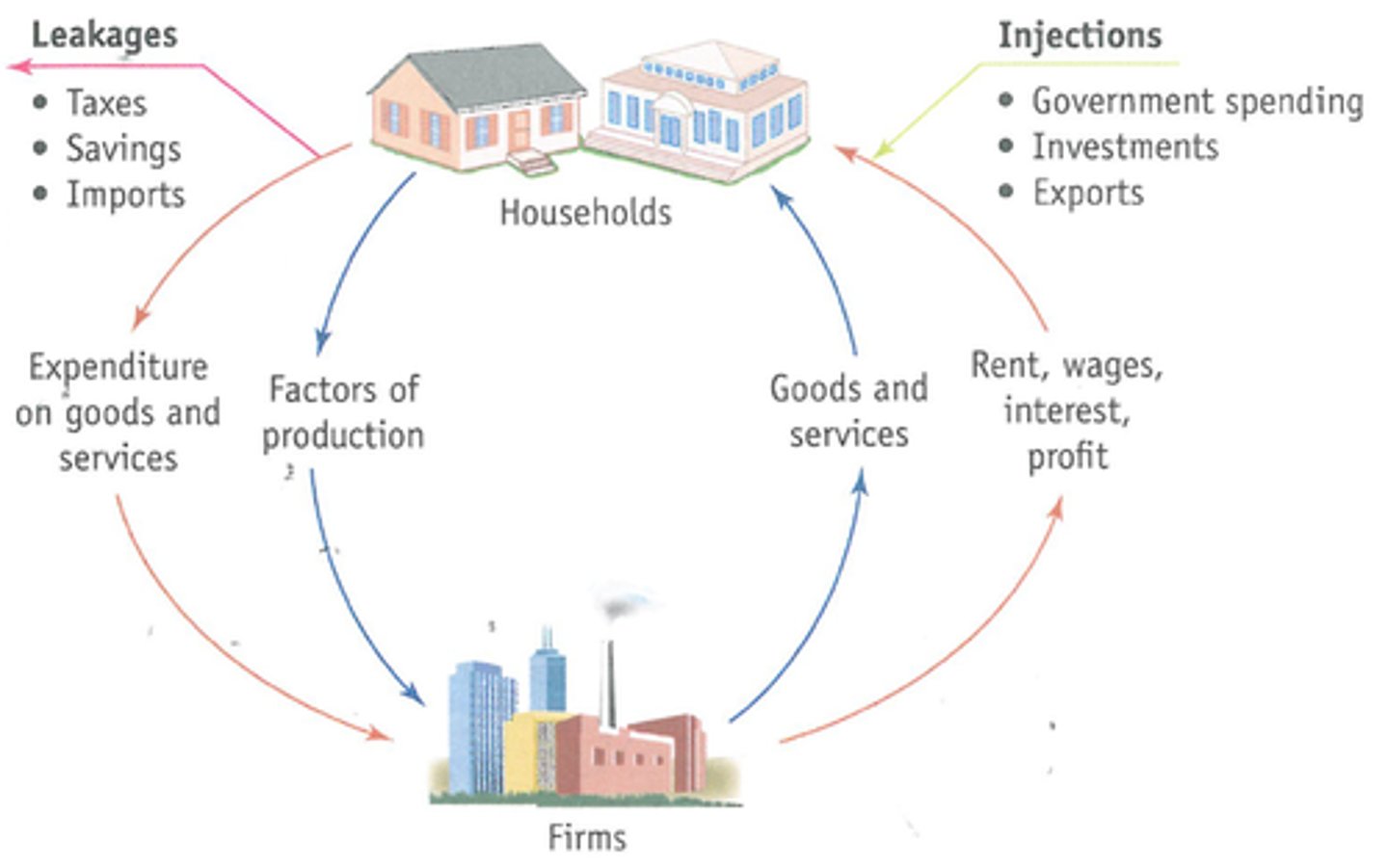
in terms of leakages and injections, when does the economy reach equilibrium?
what is the relationship between savings and investment?
what does net injections mean for national output?
- the economy reaches equilibrium when the rate of leakages = the rate of injections
- savings in an economy = investment in the economy
- net injections = expansion of national output & vice versa
what are the 3 ways of measuring GDP?
what is the equivalent for GDP?
national income = national expenditure = national output
GDP = national expenditure
formula for AD?
for consumption, where does consumer income come from?
and what influences consumption?
what percentage of AD is made up of consumption?
- AD = C + I + G + (X - M)
consumption:
- consumer income can come from wages, savings, pensions, benefits and investments such as dividend payments
- 60% of AD
influences on consumption:
- influences on consumer spending; interest rates, consumer confidence & expectations
how much of GDP is made up of capital invesment?
what influences the rate of investment?
Capital investment:
- 15% of GDP
influences on investment:
- rate of economic growth (high economic growth = more profit as higher rate of consumer spending)
- business expectations and confidence
- demand for exports (firms anticipate higher future sales)
- interest rates
- access to credit
- influence of government and regulations (coorporation tax could affect investment)
how much of GDP is made up of Gov spending ?
what are transfer payments?
are they included?
what influences the rate of gov spending ?
gov spending:
- 18% of GDP
- doesnt include transfer payments (they are simply a redistrbution of income)
infleunces of gov spending:
- economic growth (influenced by the stage of the economy in the economic cycle)
in the balance of payments, what section is made up of net trade?
what are the influences of net trade?
net trade (exports - imports):
- value of the current account on the balance of payments
- the UK has a lagre trade deficit
influences of net trade:
- real income
- exchange rates: a depreciation of the pound means imports are more expensive and exports are cheaper
- state of the world economy
what is autonomous and induced investment?
- autonomous investment refers to the investment that happens regardless of current economic conditions. this could be due to technological advancements, government projects or other long-term factors
- induced investment occurs as a response to the economy's current situation. this means firms decide to invest more based on rising income, demand or faorable interest rates.
what is the accelerator theory?
- the accelerator affect occurs when an increase in demand leads to a disproportionately larger increase in investment
what shifts SRAS?
what is the keysnian view of LRAS?
what is the neoclassical view of LRAS?
what shifts LRAS?
what is a shift in the LRAS equivalent to?
- SRAS is shifted by changes in the price of factors of production
- the keynsian view of LRAS is such that, price level is fixed until resources are fully employed (when there is no spare capacity in the economy)
- the neoclassical view of LRAS is such that, output is fixed and all factors of production are fully employed
- LRAS is shifted by changes in the quality and quantity of the factors of production or the productive efficiency of the economy which is equivalent to shifting the PPF
what is national income multiplier?
explain the multiplier effect process
what are the 2 formulas?
what is MPW made up of?
a small MPW gives a larger multiplier or a smaller?
- the national income multiplier is the ratio of the rise in national income to the initial rise in AD
- when there is an injection into the economy, it creates income for those who recieve it 'one person's spending is another person's income', this process continues in successive rounds with each round being smaller than the previous due to leakages.
- this shows that an initial increase in AD leads to an even bigger increase in national income
- formula -> k = 1/1-MPC or 1/MPW
- MPW = MPS + MPM + MPT
smaller MPW means bigger multiplier
define marginal propensity to consume (MPC)
MPC = the proportion of any additional income that is spent on consumption