Chapter 9b: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
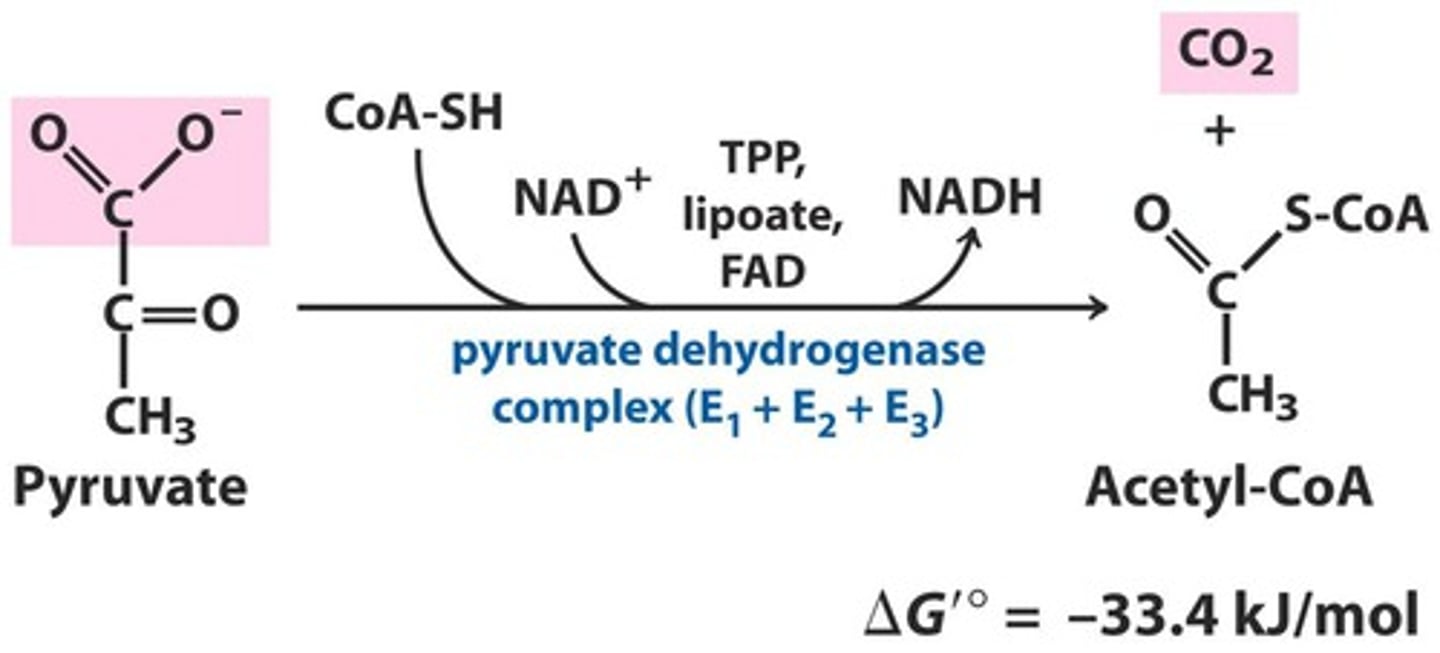
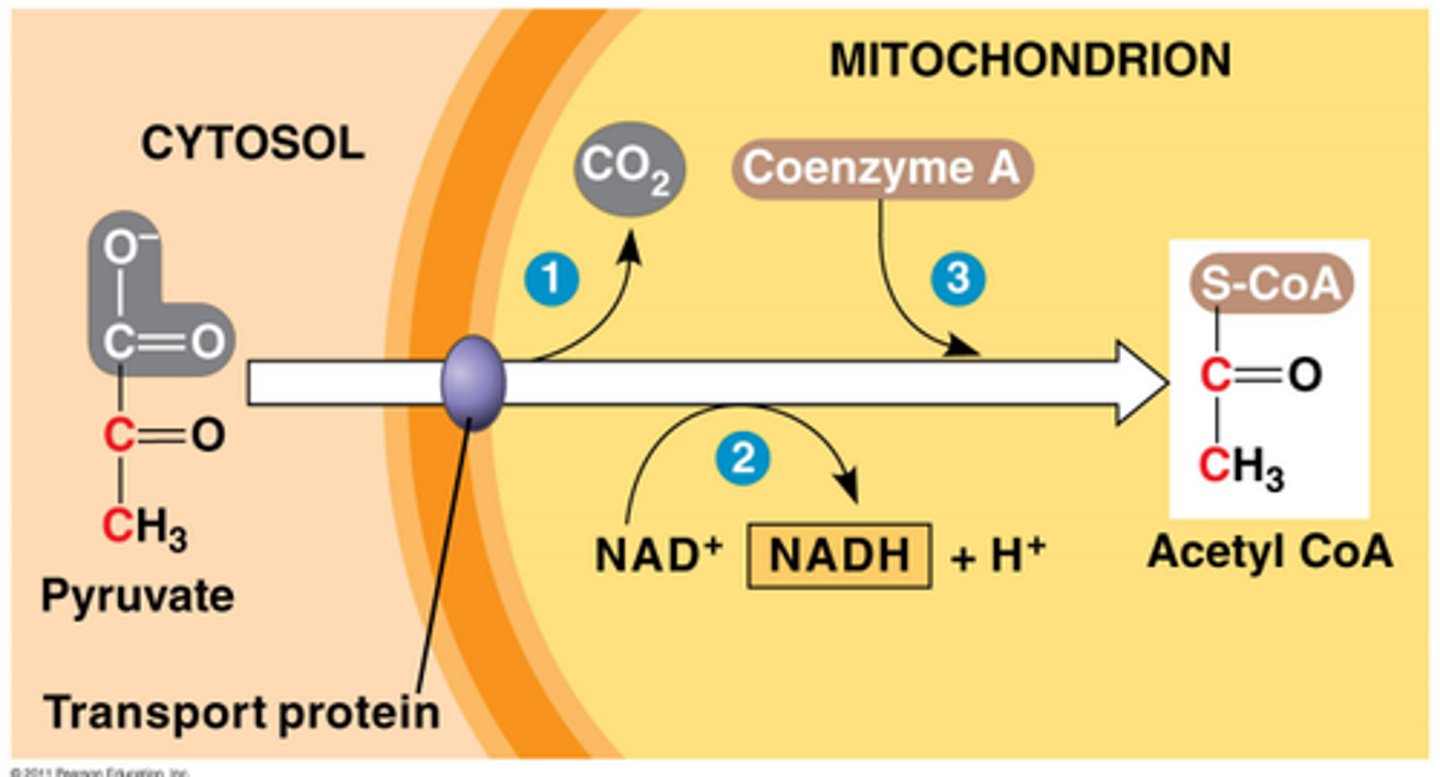
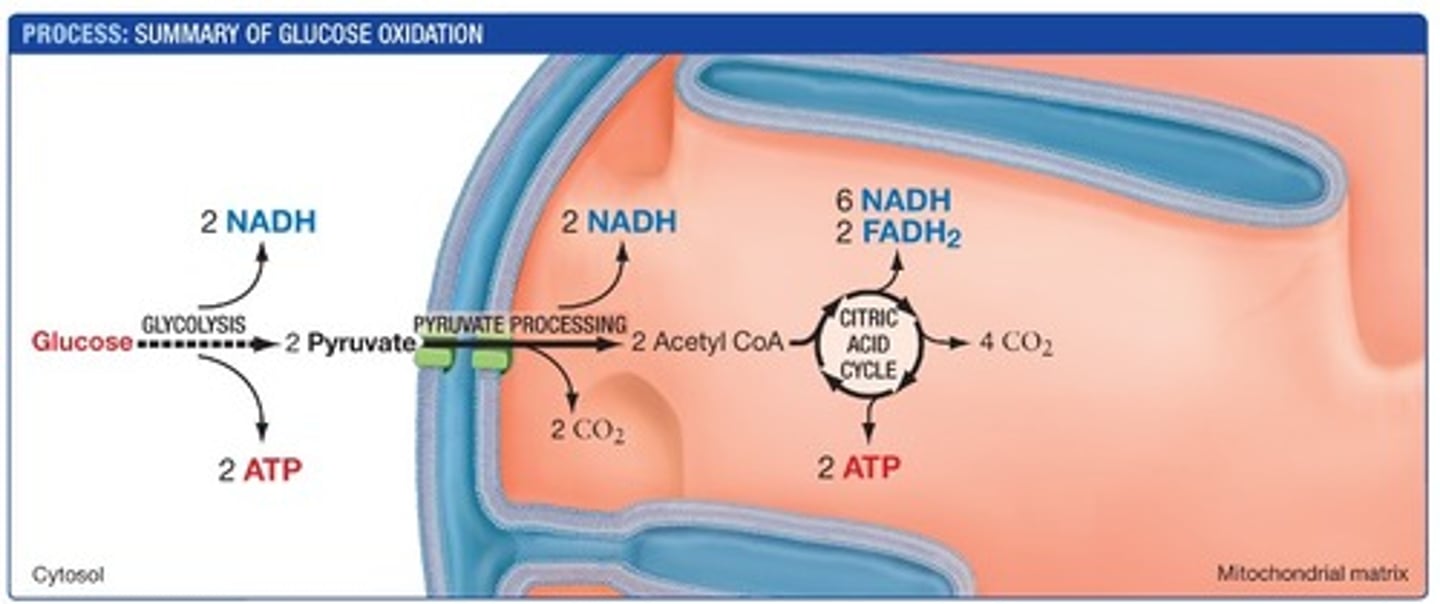
pyruvate processing turns...
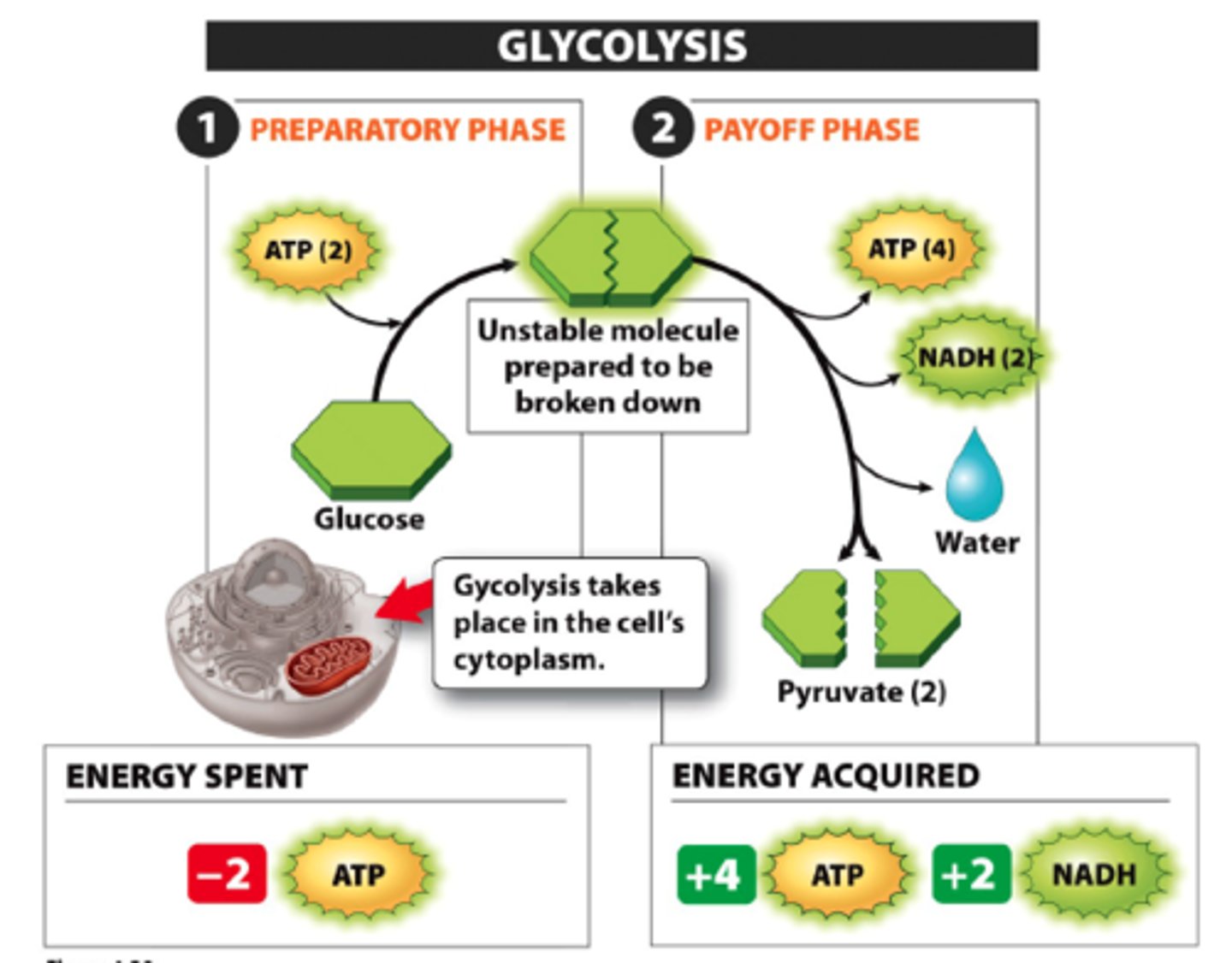
-2nd process of glycolysis
-turns pyruvate in acetyl CoA
-some electrons go to NADH
-electrons lost in pyruvate form product of CO2
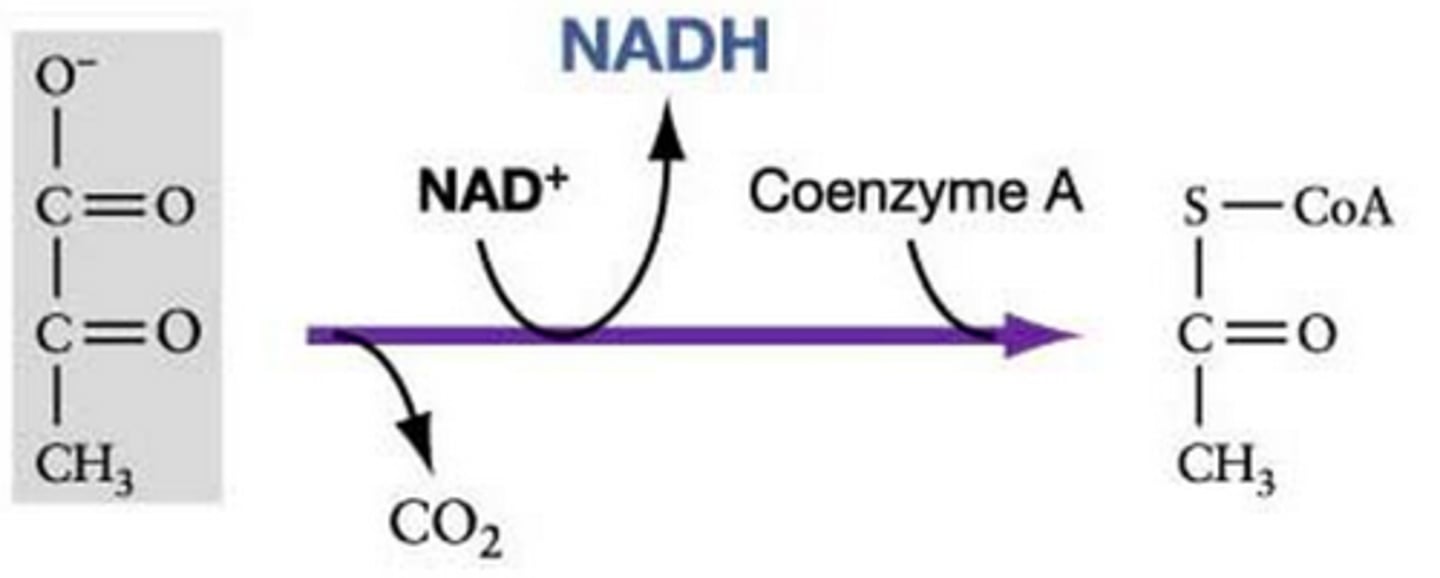
pyruvate processing
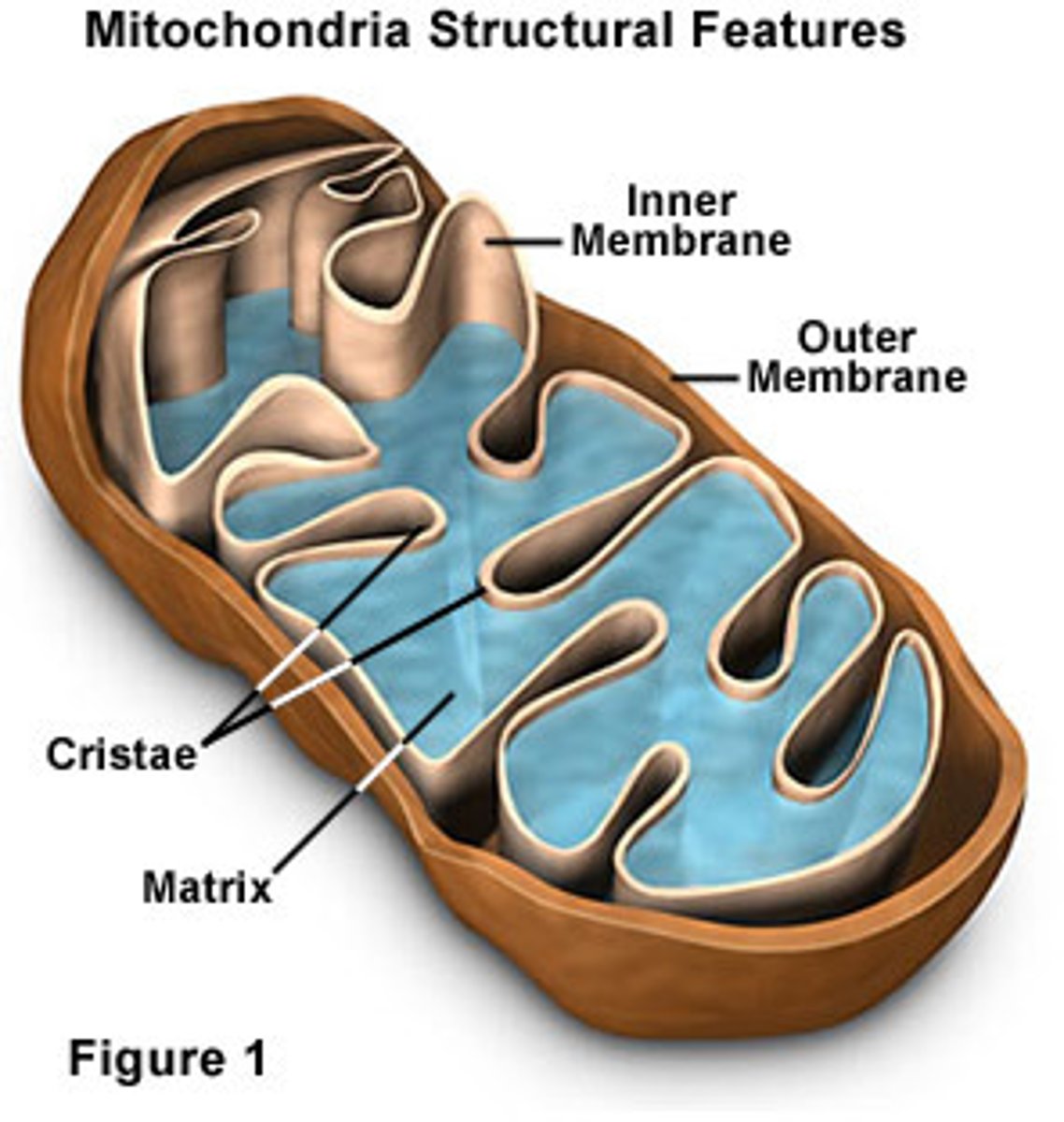
matrix of mitochondria
pyruvate dehydrogenase
-enzyme complex where pyruvate processing occurs
-located in mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotes
-located in cytosol of prokaryotes
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
-catalyzes oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
-energy is captured in NAD+ and in the thioester bond formed with Coenzyme A
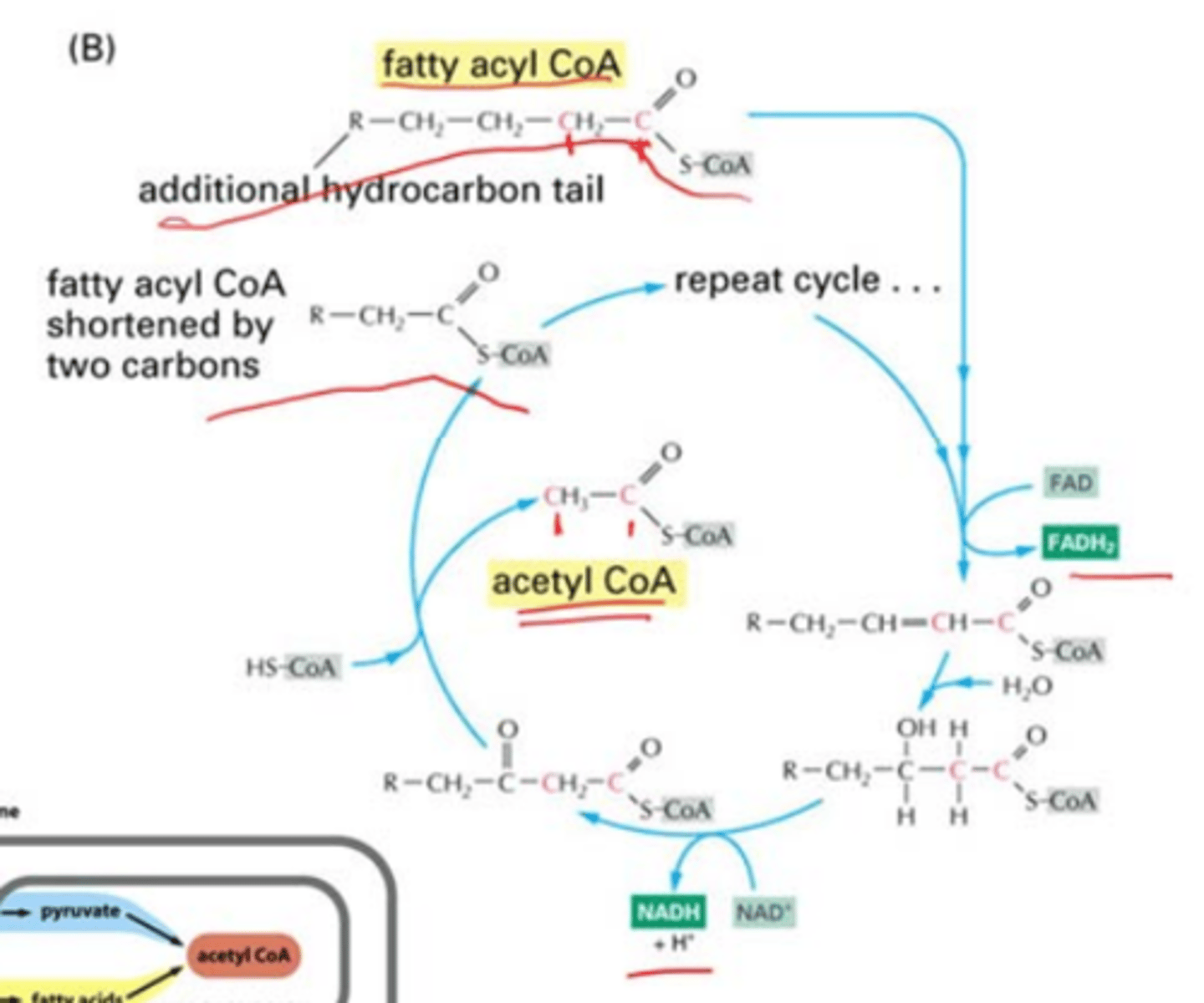
beta oxidation
-reaction that converts fatty acids to acetyl CoA to enter the citric acid cycle by continuously breaking off carbons
-each cycle yields 1 NADH2, 1 NAD+, and acetyl CoA
final electron acceptor is ETC
oxygen
citric acid cycle
-metabolic breakdown of glucose molecules to carbon dioxide
-occurs within the matrix
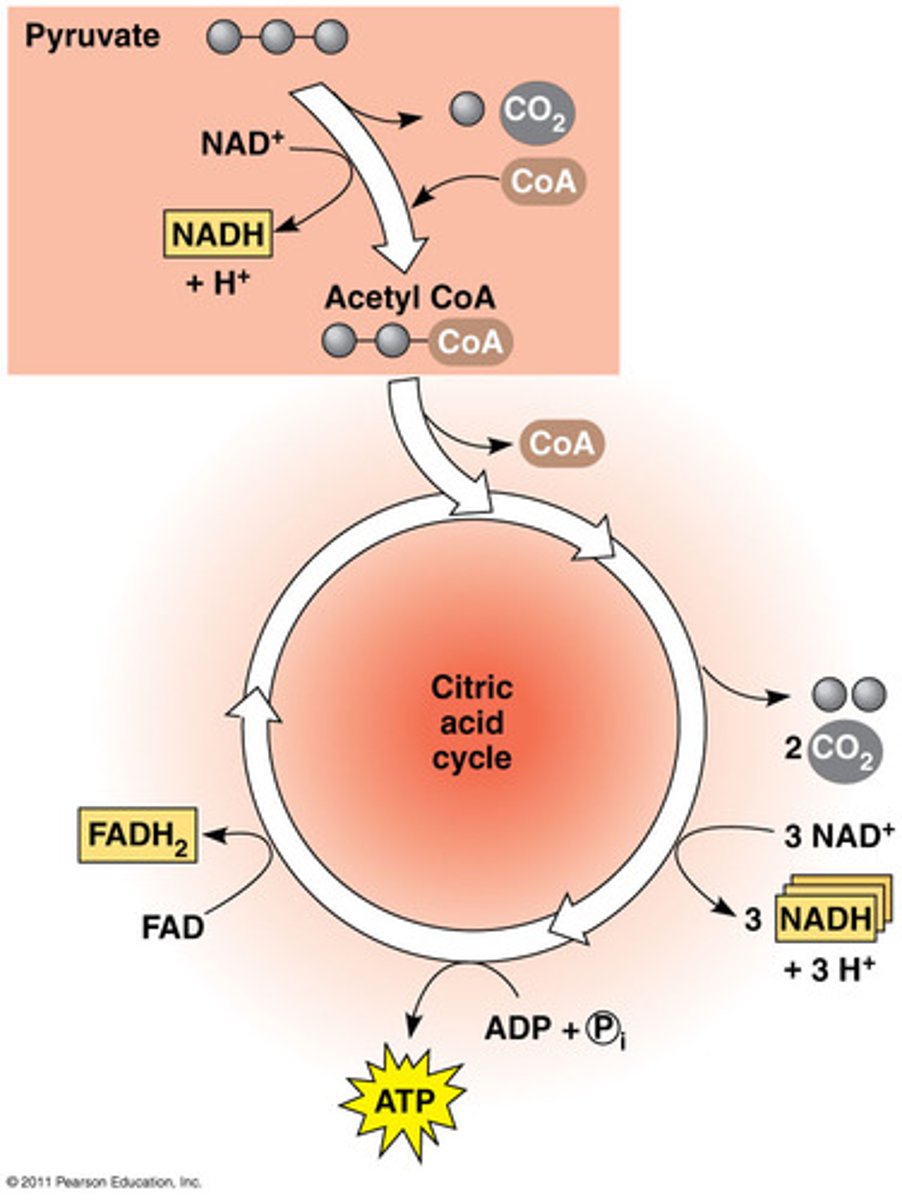
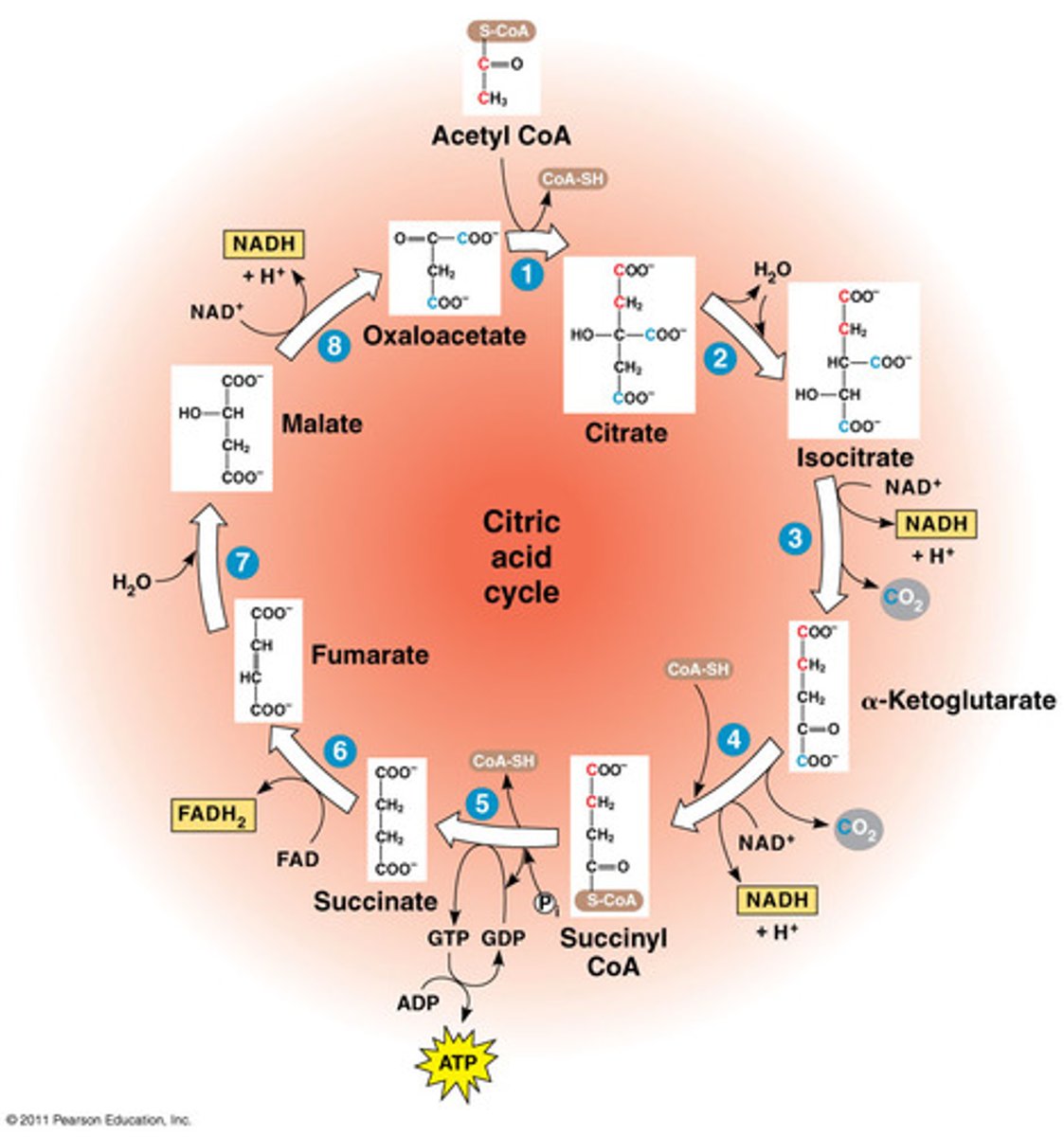
in each citric acid cycle
-there are 5 dehydrogenase reactions
-1 substrate level phosphorylation
-2 molecules of acetyl CoA produce 3 NADH, 2 CO2, 1 NADH2, and 1 GTP
for each molecule of glucose oxidized...
-6 CO2
-4 ATP
-10 NADH and FADH2
free energy
is reduced as glucose is oxidized
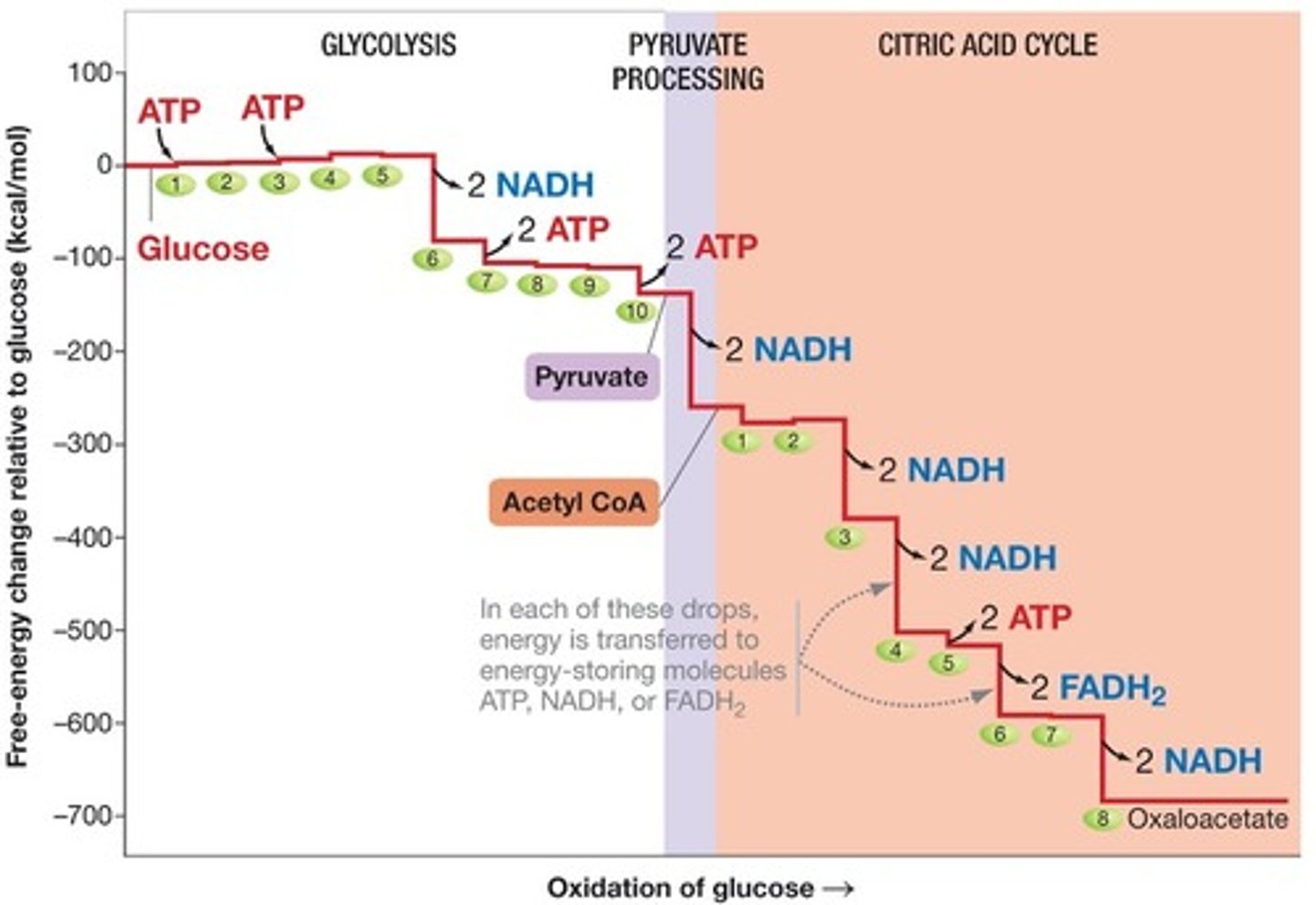
molecules that carry most energy ranked
1.) NADH
2.) FADH2
3.) ATP
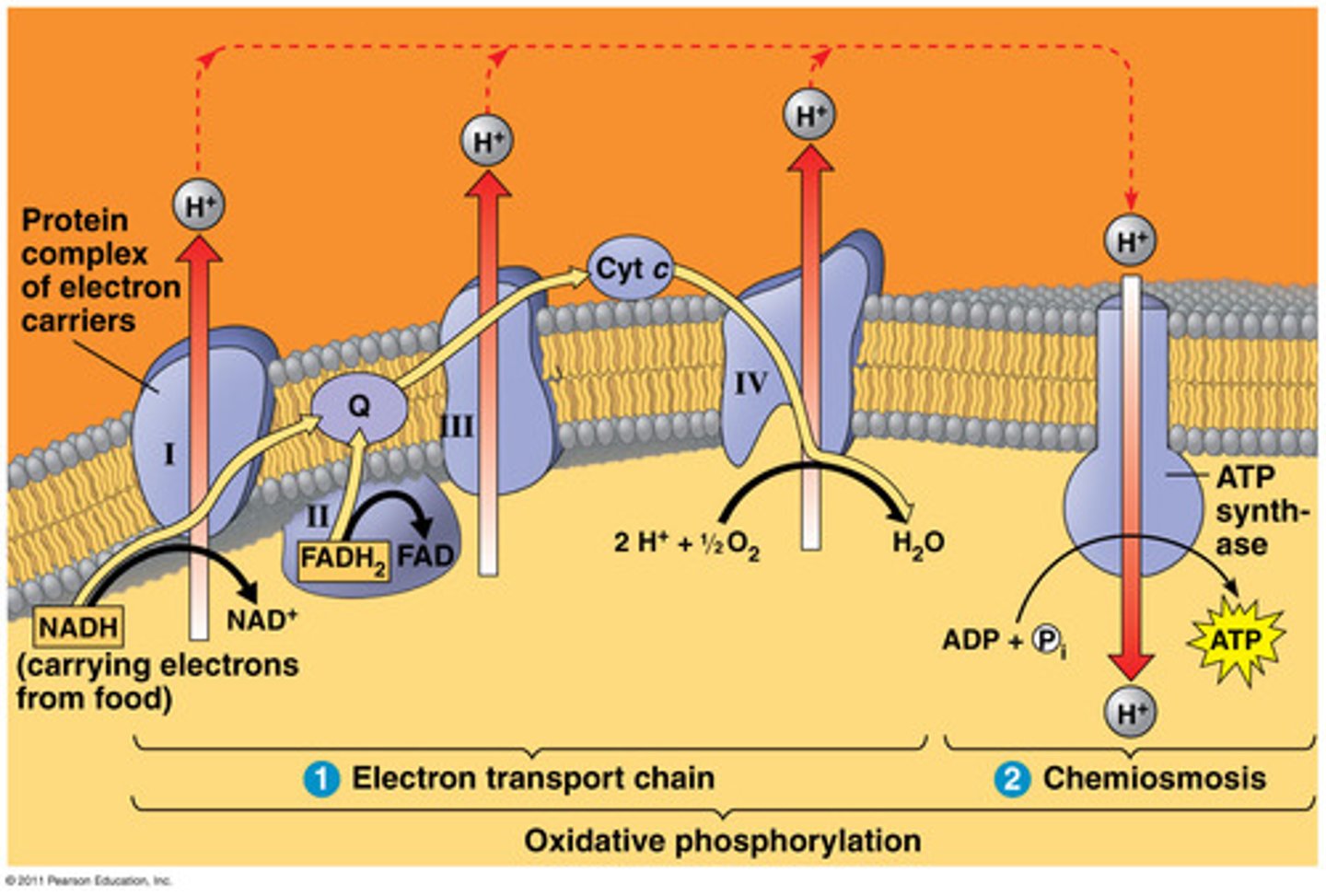
mitochondrial electron transport chain
high-energy electrons allow H+ to be pumped across the mitochondrial inner membrane from the matrix into the inter-membrane space until finally accepted by oxygen to produce water. CANT HAPPEN WITHOUT OXYGEN
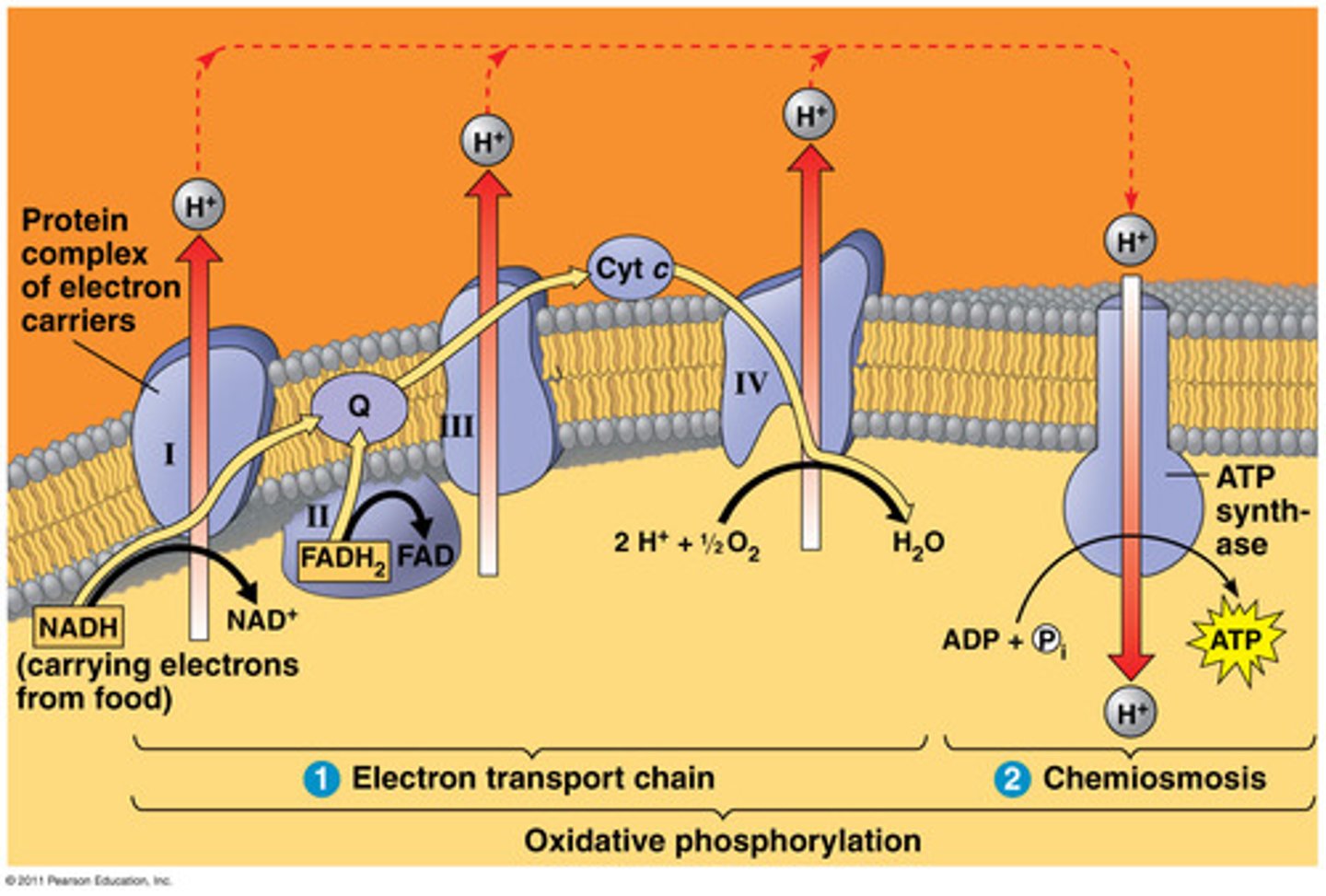
ATP synthase
-energy released by H+ flow (down gradient) is used to make ATP
-process is Chemiosmosis
-ATP production is dependent on the proton motive force generated by the electrochemical gradient
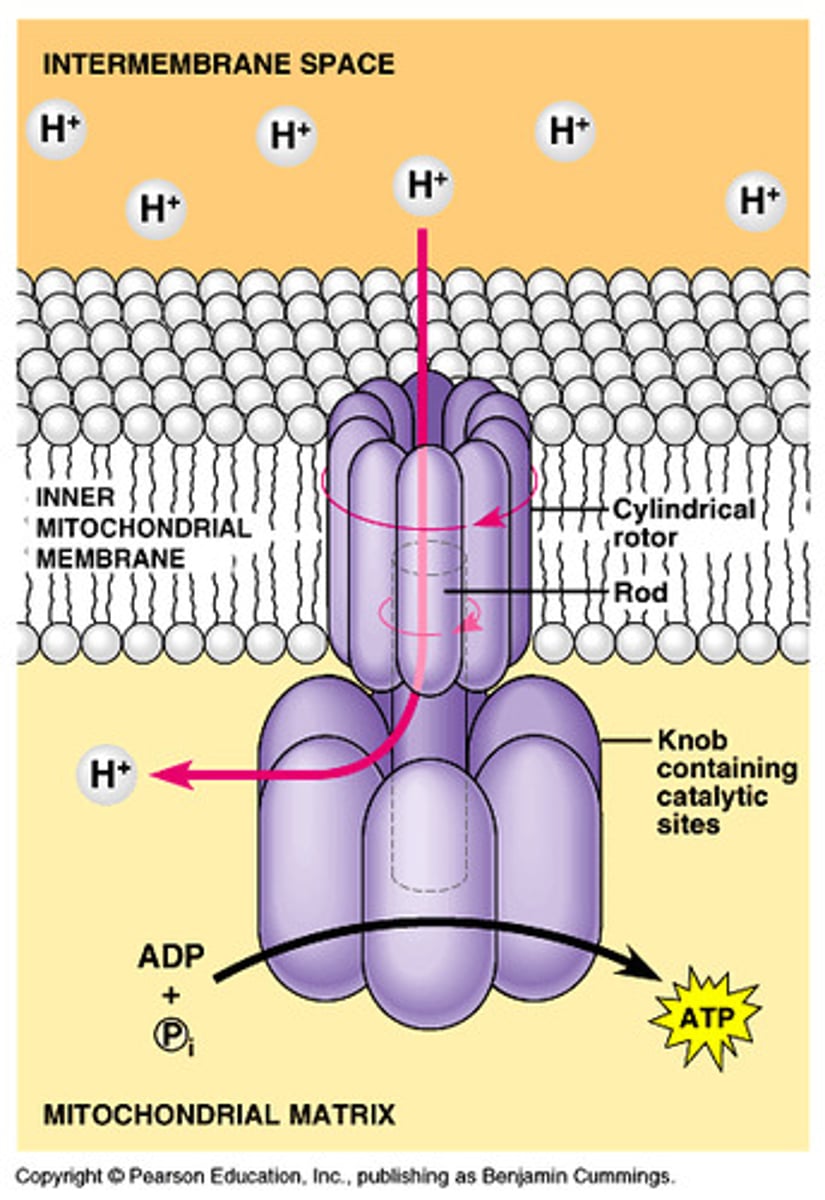
most energy made in...
oxidative phosphorylation (ETC and ATP synthase)
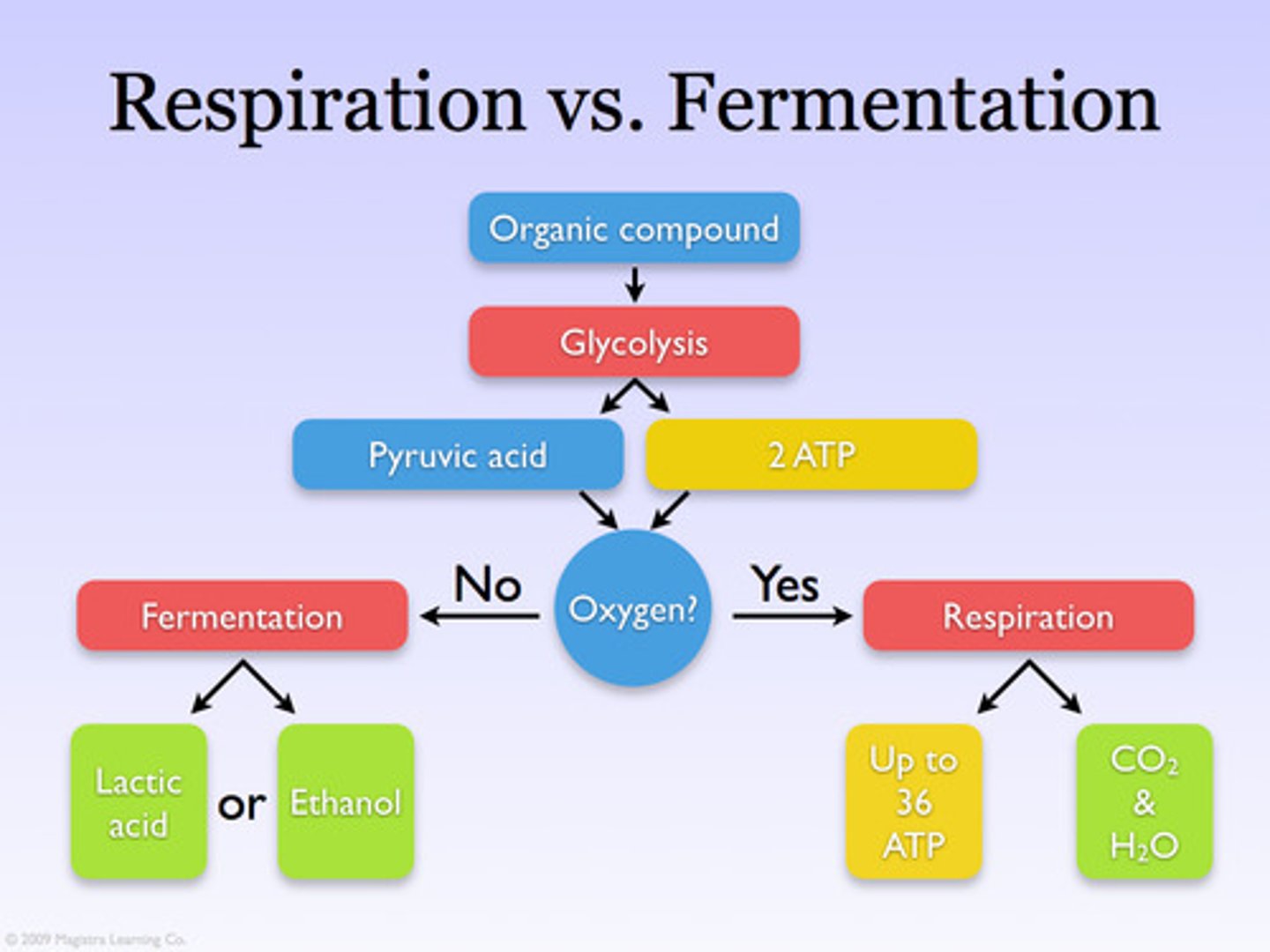
fermentation
-process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose without an ETC
-oxidizes NADH to NAD+ to continue glycolysis when no oxygen is available
-that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol(yeast) or lactic acid(animals)
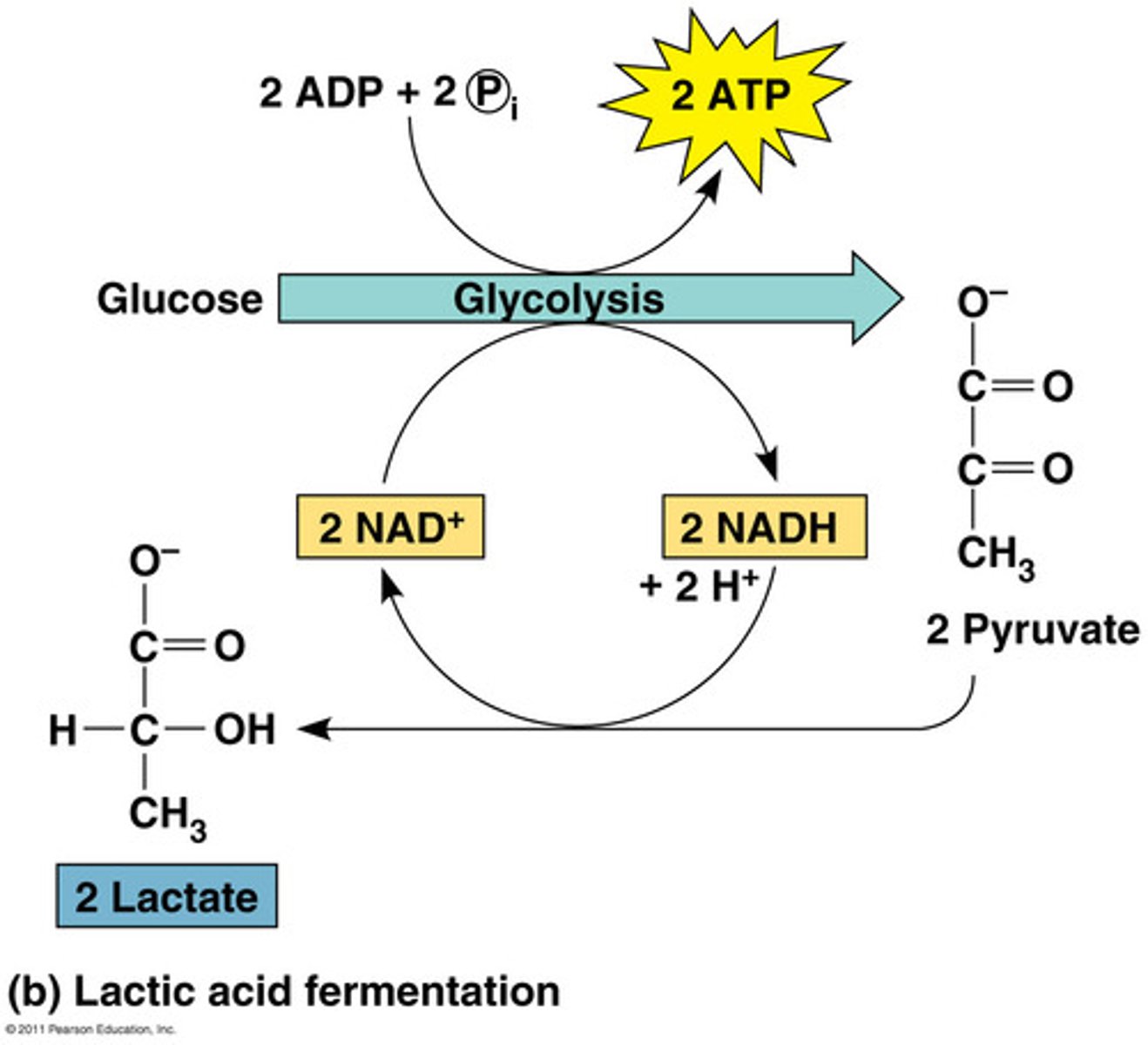
fermentation vs cellular respiration
-fermentation is less efficient than cellular respiration
-only 2 ATP produced in fermentation vs 30