General overview (electricity and circuits)
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Position, mass, and charge of a proton
Found in the nucleus, mass of 1, charge of +1
Position, mass, and charge of a neutron
Found in the nucleus, mass of 1, charge of 0
Position, mass, and charge of an electron
Found in shells orbiting the nucleus, mass of 1/2000 or negligible, charge of -1
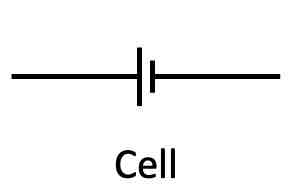
What is the circuit symbol for a cell?
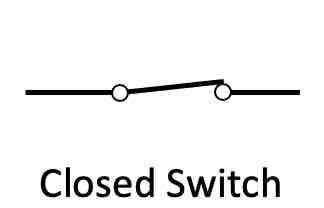
What is the circuit symbol for a closed switch?
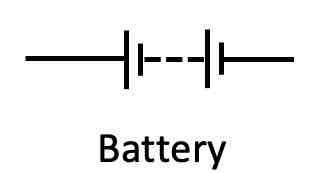
What is the circuit symbol for a battery?
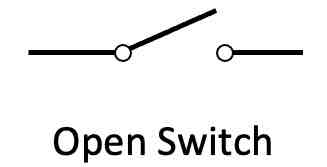
What is the circuit symbol for an open switch?
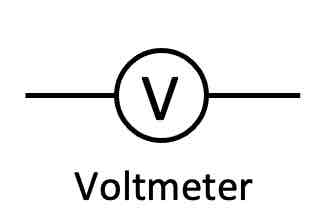
What is the circuit symbol for a voltmeter?
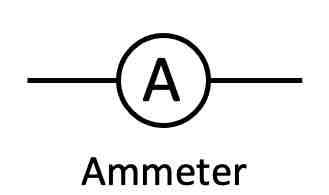
What is the circuit symbol for an ammeter?
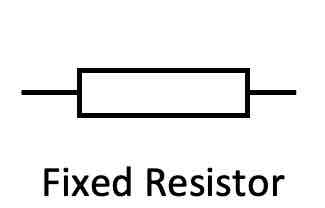
What is the circuit symbol for a resistor?
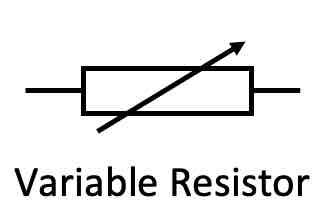
What is the circuit symbol for a variable resistor?
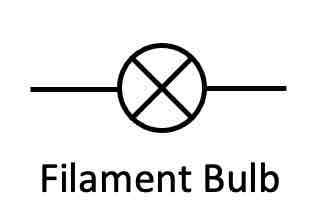
What is the circuit symbol for a lamp?
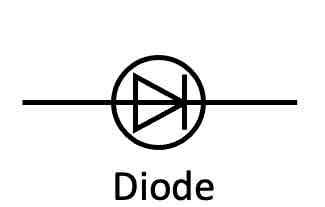
What is the circuit symbol for a diode?
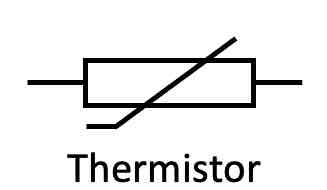
What is the circuit symbol for a thermistor?
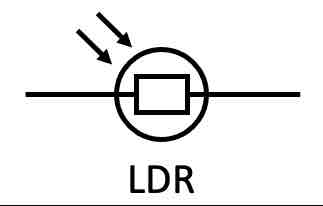
What is the circuit symbol for a LDR (light dependent resistor)?
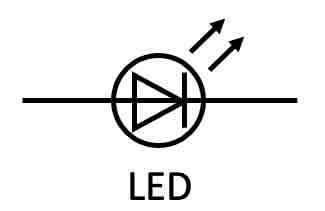
What is the circuit symbol for an LED (light emitting diode)?
What is a series circuit?
A circuit where all of the components are connected in one loop
What is a parallel circuit?
A circuit that branches into separate paths for electricity to flow through
What happens to potential difference in a series vs a parallel circuit?
Series circuit: potential difference is shared between each component
Parallel circuit: potential difference is the same across each component
What happens to current in series vs parallel circuits?
Series circuit: current is the same in every component
Parallel circuit: current splits between loops
Where are voltmeters connected in a circuit?
Using legs either side of the component, measuring before and after to find the difference
What is potential difference?
Energy transferred per unit charge passed
Measured in joules per coulomb
Formula for energy transferred
Energy transferred=charge moved x potential difference
Where are ammeters connected in a circuit?
In series, before the component being measured (its legs are connected to the circuit)
What is current?
Rate of flow of charge of electrons
Measured in amperes, or amps
Formula for charge
Charge=current x time
What happens to current at a junction?
The current is conserved
What happens when a closed circuit includes a source of potential difference?
There will be current in the circuit
How does resistance affect current?
If resistance increases, current decreases
Why does current decrease when resistance increases?
This is because more resistance makes it harder for the charge to flow through the components (temperature is increased, so the fixed ions vibrate more strongly and the delocalised electrons bump into them more frequently)
How can you change the current in a circuit?
Using a variable resistor
Formula for potential difference
Potential difference=current x resistance
What happens when two resistors are in series?
Net resistance is the sum of the two resistors (added together)
Why does net resistance increase when two resistors are in series?
This is because the charge has to push through both resistors when flowing through the circuit
What happens when two resistors are in parallel?
The two resistors will have a smaller overall resistance
Why does overall resistance decrease when two resistors are placed in parallel?
Since charge has more than one branch to take, only some charge will flow along each (as current is split at a junction), decreasing overall resistance
How is current affected by voltage in a filament lamp?
As voltage increases, current increases as long as the filament lamp is at a constant temperature. The filament lamp (as well as the wire) begins to heat up due to metal ions having more kinetic energy, causing them to vibrate more and collide with electrons as they flow through the lamp/wire.
How does current and voltage in a filament lamp link to resistance?
As voltage increases, so does current. The resistance of the filament lamp also increases, which then decreases the current in the filament lamp
How is current affected by voltage in a diode, and how does this relate to resistance?
A diode allows current to flow freely in one direction, but not at all in the other. They will not conduct electricity if the applied voltage is lower than the threshold (minimum) voltage. When the diode doesn’t conduct electricity, the resistance of the diode is considered infinite, meaning that the current cannot flow.
How is current affected by voltage in a fixed resistor, and how does this relate to resistance?
Current is directly proportional to voltage as resistance is constant
How does the resistance of an LDR vary with light intensity?
As light intensity increases (when it is very bright), the resistance of the LDR decreases. As light intensity decreases (when it is dark), the resistance of the LDR increases.
How does the resistance of a thermistor vary with change of temperature?
As temperature increases (when it becomes hotter), the resistance of the thermistor decreases
What happens when there is a current in a resistor?
There is an energy transfer, which heats the resistor
Why is energy dissipated to the surroundings due to resistance?
Electrical energy gives kinetic energy to metal ions within the lattice of the conductor. This means they move faster and collide more frequently with electrons, increasing resistance. This means work is done against the resistance in order for the charge to flow through the circuit. Some electrical energy is dissipated to the surroundings through thermal energy, and also heating the resistor.
How can you reduce unwanted energy transfers by using low resistance wires?
Low resistance wires have a smaller resistance, which means fewer collisions between the fixed ions and the delocalised electrons and less energy wasted through heating lost to the surroundings, or the components
What is the advantage of the heating effect?
It is useful for appliances where heat is the desired product (such as in hairdryers and toasters)
What are the disadvantages of the heating effect?
A loss of energy can make an appliance inefficient and wasteful. If the appliance overheats, it can catch fire - ruining the device and possibly injuring the user
What is power?
Energy transferred per second
Measured in watts
Formula for power (3)
Power=energy transferred/time
Power=current x potential difference
Power=current² x resistance
How is power transferred in a circuit related to it’s potential difference and current?
Total energy transferred is current x potential difference/time, so power is directly proportional to potential difference and current because they make up the total energy transferred.
What is AC current?
Alternating Current
Movement of charge changes direction (from a positive value to a negative value) many times per second, used in the mains supply
What is DC current?
Direct Current
Movement of charge in one direction, supplied by cells and batteries
What is the voltage of the mains supply?
230V
What is the frequency of the mains supply?
50Hz
What is the function of the live wire?
It is brown, carries 230V of potential difference, carries the AC current and 230J of energy to the appliance where it can be used
What is the function of the neutral wire?
Blue, carries 0V, and carries the electrons in the wire back to the mains where they have very little energy (as it has been used in the appliance)
What is the function of the earth wire?
Green and yellow, carries 0V, connected to metal casing. If the live wire becomes loose and touches the casing, current will flow through the earth wire and prevent electrocution
What is the function of a fuse?
When current becomes too high, the fuse wire will melt and break (as it has a set maximum current). This stops current from flowing to the appliance and prevents further damage
What is the function of a circuit breaker?
It trips if there is a large surge in current. It doesn’t need to be replaced as it can be switched to the on position again, but is easy to replace anyway
Why should fuses be connected in the live wire of a domestic circuit?
When the fuse breaks, it will break the circuit and stop current in the wire
Why is it dangerous to have a connection between the earth and the live wire?
It can result in a surge of current, causing electrical shocks
What is the relationship between power ratings and the changes in stores of energy when the appliance is in use?
Devices with higher power ratings will transfer stored energy to other types of energy at a faster rate