cholinergics and histamanergics (dont think i spelled either right)
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
![<p><strong><em>Anticholinergic: Contraindications</em></strong><br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Increased angle closure pressure</p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> obstruction (e.g. prostatic hyperplasia)<br></p><ul><li><p>Prevents contraction </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> obstruction<br></p><ul><li><p>Slows motility </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Delays gastric emptying</p></li><li><p>increase ulcer symptoms </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Worsens symptoms </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/34e2975f-ad99-4c43-9286-c6b7225934db.png)
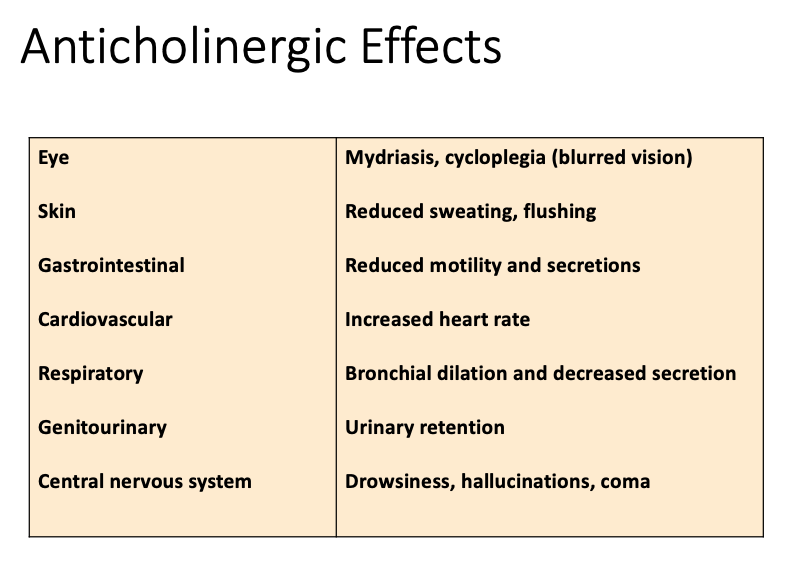
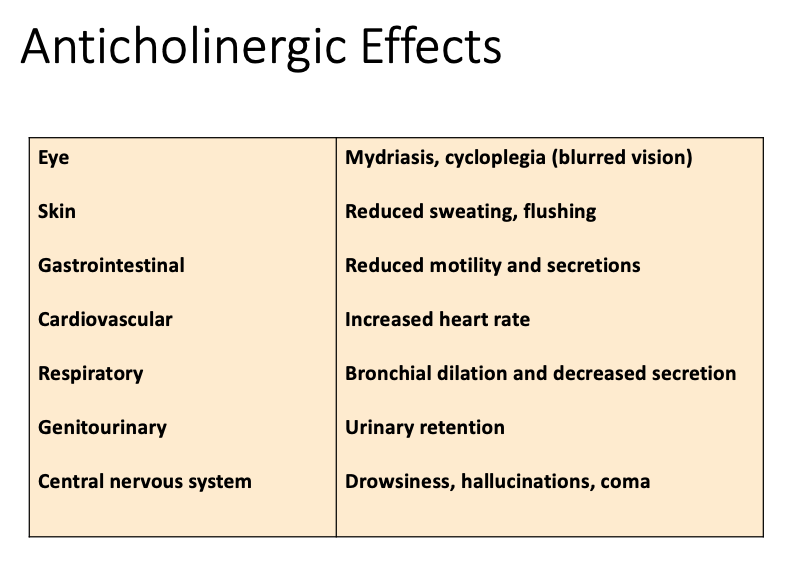
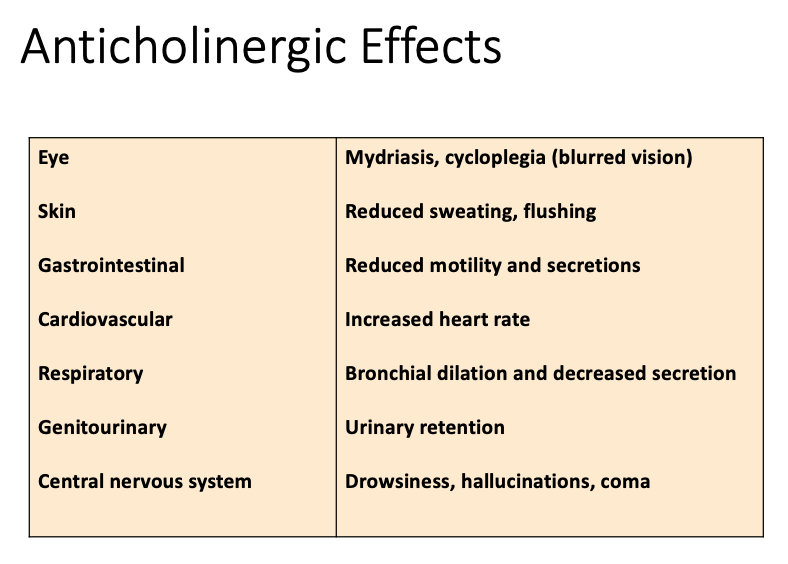
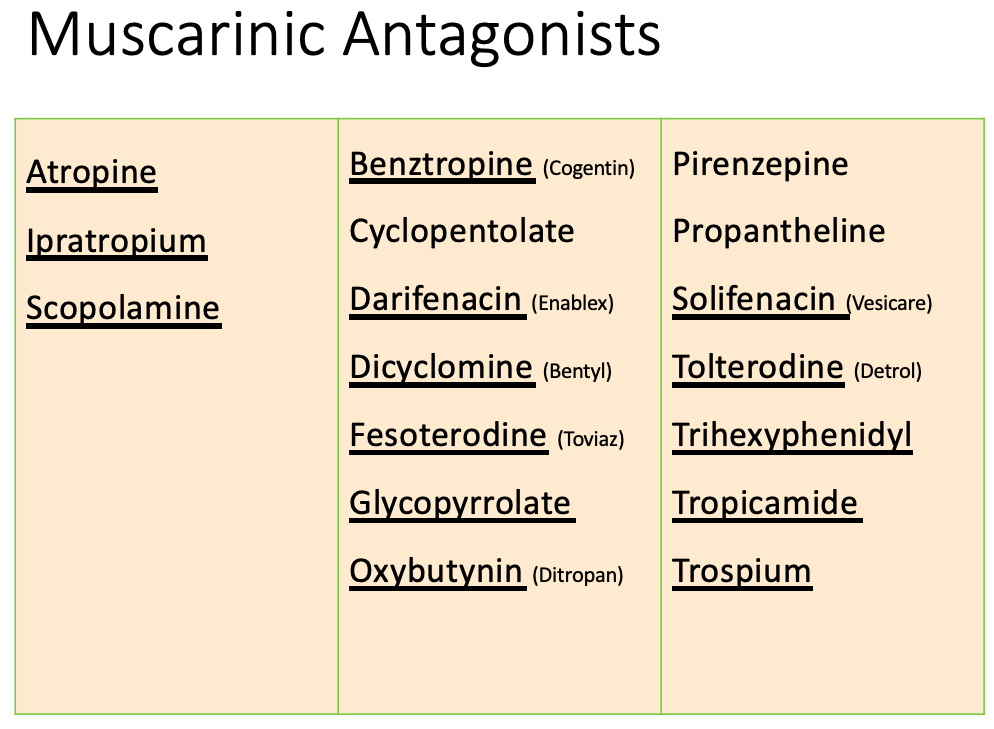
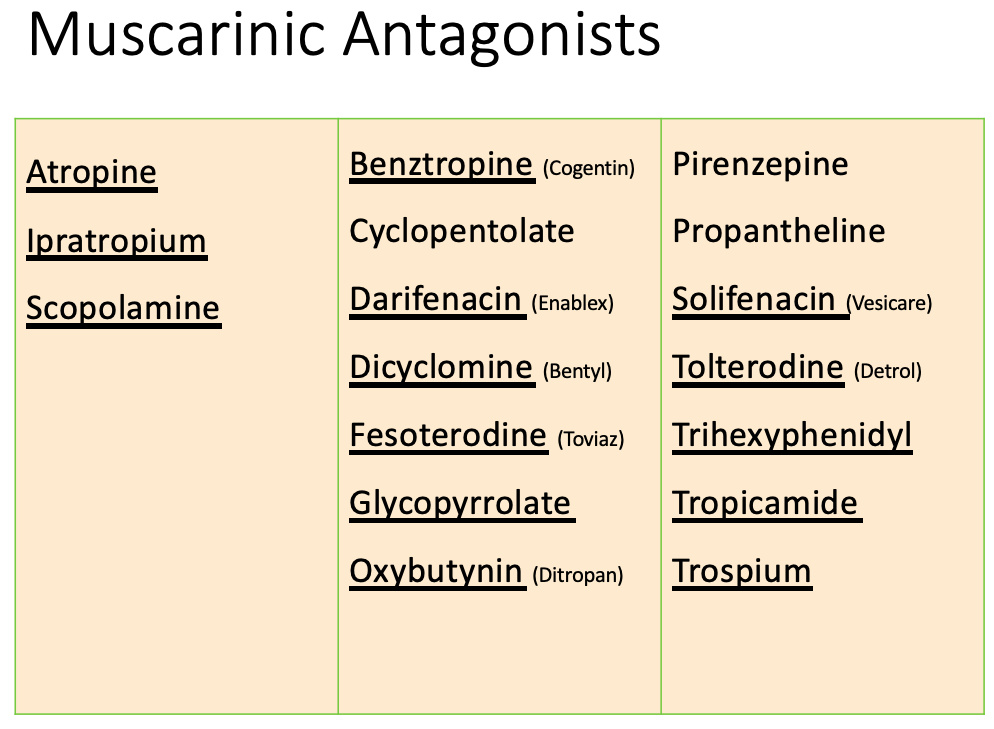
Anticholinergic: Contraindications
[...]
Increased angle closure pressure
[...] obstruction (e.g. prostatic hyperplasia)
Prevents contraction
[...] obstruction
Slows motility
[...]
Delays gastric emptying
increase ulcer symptoms
[...]
Worsens symptoms
Glaucoma, especially angle-closure glaucoma
Urinary Tract
GI
Peptic ulcer disease
Myasthenia Gravis
Effects of Histamine on Organ Systems
CV
H1→ [...] BP, flushing, sense of warmth, headache, edema
H2→ [...] HR
dec
inc
[...]
MOA:
Blocks neural pathways from vestibular apparatus in the inner ear to the emetic center in the brainstem
More significant CNS effects than atropine at therapeutic doses (crosses BBB more easily)
Drowsiness, amnesia, fatigue, dreamless sleep, euphoria
Clinical uses:
Motion sickness (transdermal)
must be used prophylactically for best results
Postoperative (IM,IV)→for nausea and vomiting
Scopolamine
![<p><span>Scopolamine</span></p><ul><li><p>MOA:</p><ul><li><p><strong><em>Blocks neural pathways from vestibular apparatus</em></strong> in the inner ear to the emetic center in the brainstem </p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[More or less]</strong></span> significant CNS effects than atropine at therapeutic doses (<span><strong>[why?]</strong></span>)<br></p><ul><li><p>Drowsiness, amnesia, fatigue, dreamless sleep, euphoria </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Clinical uses:<br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong><em>Motion sicknes</em>s</strong></span> (transdermal)</p><ul><li><p>must be used prophylactically for best results</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Postoperative (IM,IV)→for nausea and vomiting </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8076e86f-4156-441d-9d6d-bcfb48078821.jpg)
Scopolamine
MOA:
Blocks neural pathways from vestibular apparatus in the inner ear to the emetic center in the brainstem
[More or less] significant CNS effects than atropine at therapeutic doses ([why?])
Drowsiness, amnesia, fatigue, dreamless sleep, euphoria
Clinical uses:
Motion sickness (transdermal)
must be used prophylactically for best results
Postoperative (IM,IV)→for nausea and vomiting
More
crosses BBB more easily
Motion sickness can also be treated by 1st generation H1 antagonist --> Diphenydramine
Scopolamine
MOA:
Blocks neural pathways from vestibular apparatus in the inner ear to the emetic center in the brainstem
More significant CNS effects than atropine at therapeutic doses (crosses BBB more easily)
Drowsiness, amnesia, fatigue, dreamless sleep, euphoria
Clinical uses:
[...] (transdermal)
must be used prophylactically for best results
Postoperative (IM,IV)→for nausea and vomiting
Motion sickness
Histamine poisoning from [...]
Normal concentration is less than 0.1 mg/100 g of fish
FDA considers toxic > 50 mg/100 g of fish
Poorly preserved fish (often tuna, sardines, mackerel)
Gram negative bacteria thrive
Histidine in the fish muscle gets converted to histamine by bacterial enzymes
Scombroid Syndrome
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p><ul><li><p>blurred vision </p></li><li><p><span>Anticholinergic</span> effect </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d3ec5049-78f2-4ccb-8bed-de7971442701.png)
[...]
blurred vision
Anticholinergic effect
cycloplegia
cyclopes has blurred vision
![<p><span>cycloplegia</span> </p><ul><li><p>blurred vision </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[cholinergic or anticholinergic]</strong></span> effect </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f757058f-5d36-48b5-91e2-1d21a1f1632e.png)
cycloplegia
blurred vision
[cholinergic or anticholinergic] effect
Anticholinergic
cyclopes has blurred vision
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Unique antihistamine because it has <strong>anti-serotonergic activity</strong></p></li><li><p>No longer used for allergies</p></li><li><p>Off-label use for <strong>treating decreased appetite</strong> secondary to chronic disease </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a17f4fb9-c69d-432e-a176-0ce5ede2bddb.jpg)
[...]
Unique antihistamine because it has anti-serotonergic activity
No longer used for allergies
Off-label use for treating decreased appetite secondary to chronic disease
Cyproheptadine
[H1 or H2] antagonists
Allergy
cold medicine
sleep aids
motion sickness
antiemetic, etc.
H1
1st and 2nd generation H1 antagonists
[H1 or H2] antagonists
Indications:
Peptic ulcer disease
GERD
Ulcer prophylaxis
Heartburn
Drugs
Famotidine
Cimetidine
Ranitidine
H2
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>dilation of the pupil of the eye</p></li><li><p><span>Anticholinergic</span> effect </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a0628e46-b2c3-40c1-b079-ae05bc607136.png)
[...]
dilation of the pupil of the eye
Anticholinergic effect
Mydriasis
Mydriasis = dilation
![<p><span>Mydriasis</span></p><ul><li><p>dilation of the pupil of the eye</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[cholinergic or anticholinergic]</strong></span> effect </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e4e75e87-148a-4a2c-8ee1-ae1d58acdd66.png)
Mydriasis
dilation of the pupil of the eye
[cholinergic or anticholinergic] effect
Anticholinergic
Mydriasis = dilation
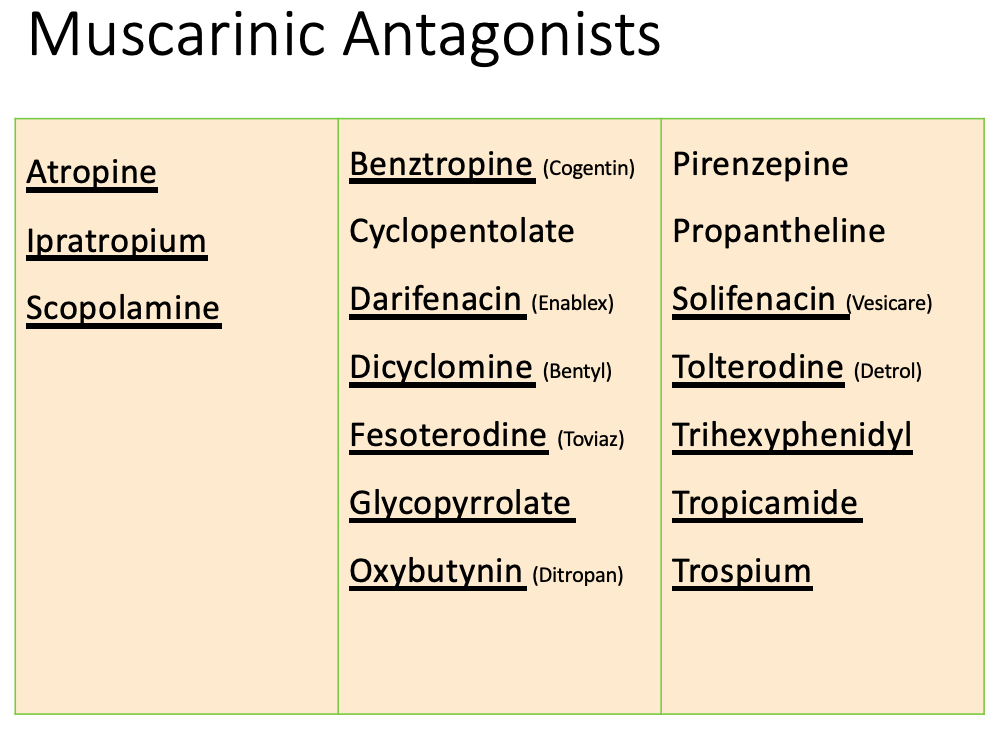
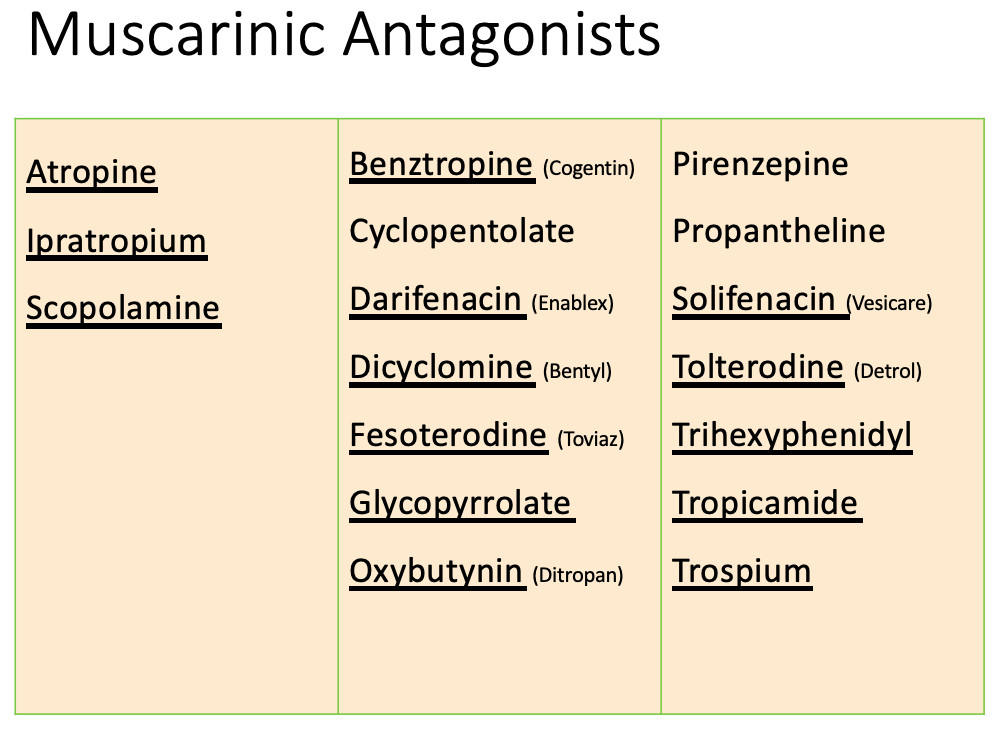
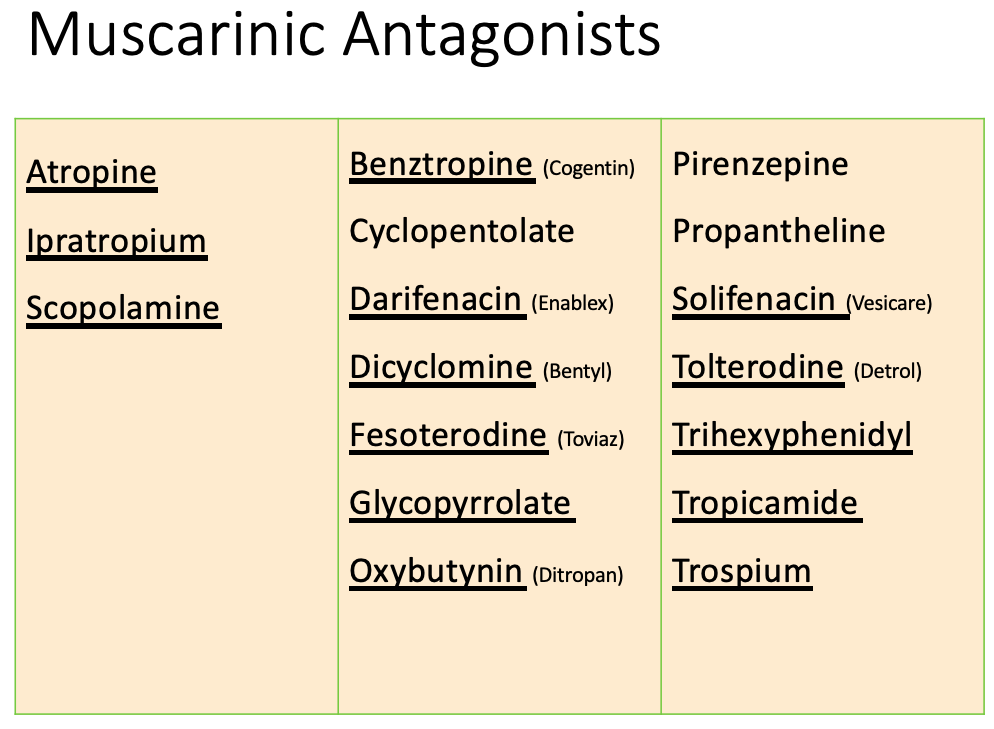
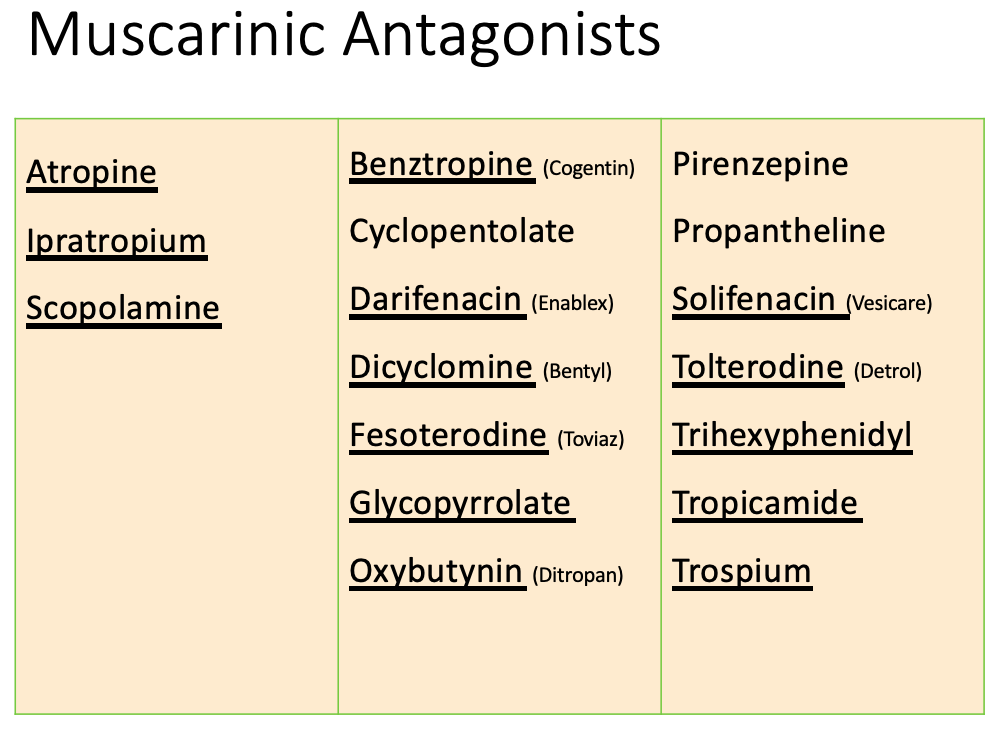
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Ophthalmology
MOA:
causes mydriasis and cycloplegia
Indication:
ophthalmoscopic examination of retina
Drugs
[...]
[...]
[...]
Homatropine
Atropine
Tropicamide
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p>Cholinergic Poisoning<br></p><ul><li><p>Drugs</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9a9a7a68-41e5-43d9-b6d3-3925438c6d73.png)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Cholinergic Poisoning
Drugs
[...]
[...]
Atropine
Pralidoxime (2-PAM)
Sketchy -- paralidoxime (closes lid on toxic spray)
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p>Bardycardia </p><ul><li><p>Atropine </p><ul><li><p>MOA: blocks <span><strong>[which]</strong></span> receptors on the SA nodal pacemaker cells</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f4bcdc95-c056-4e48-b138-41a8cbc88780.png)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Bardycardia
Atropine
MOA: blocks [which] receptors on the SA nodal pacemaker cells
M2
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[What's the indication?]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>Ipratropium</strong></span> (metered dose inhaler, nebulizer)</p><ul><li><p>Inhaled so <span>there is minimal systemic absorption</span></p></li><li><p>Blocks ACh in the bronchial smooth muscles→broncho<span>dilation</span></p></li><li><p>Adverse effects: </p><ul><li><p>xerostomia</p></li><li><p>cough</p></li><li><p>blurred vision</p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Others: </p><ul><li><p><strong>tiotropium</strong></p></li><li><p>aclidinium</p></li><li><p>umeclidinium </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8eede63d-5e21-4a69-97d9-159807586429.jpg)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
[What's the indication?]
Ipratropium (metered dose inhaler, nebulizer)
Inhaled so there is minimal systemic absorption
Blocks ACh in the bronchial smooth muscles→bronchodilation
Adverse effects:
xerostomia
cough
blurred vision
Others:
tiotropium
aclidinium
umeclidinium
COPD/asthma
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p><span>COPD/asthma</span><br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> (metered dose inhaler, nebulizer)</p><ul><li><p>Inhaled so <span>there is minimal systemic absorption</span></p></li><li><p>Blocks ACh in the bronchial smooth muscles→broncho<span>dilation</span></p></li><li><p>Adverse effects: </p><ul><li><p>xerostomia</p></li><li><p>cough</p></li><li><p>blurred vision</p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Others: </p><ul><li><p><strong>tiotropium</strong></p></li><li><p>aclidinium</p></li><li><p>umeclidinium </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/80ff3a8f-9748-4714-8d5f-f42dd889e64f.jpg)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
COPD/asthma
[...] (metered dose inhaler, nebulizer)
Inhaled so there is minimal systemic absorption
Blocks ACh in the bronchial smooth muscles→bronchodilation
Adverse effects:
xerostomia
cough
blurred vision
Others:
tiotropium
aclidinium
umeclidinium
Ipratropium
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p><span>COPD/asthma</span><br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>Ipratropium</strong></span> (metered dose inhaler, nebulizer)</p><ul><li><p>Inhaled so <span><strong>[how much systemic absorption is there]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Blocks ACh in the bronchial smooth muscles→broncho<span><strong>[dilation or constriction]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Adverse effects: </p><ul><li><p>xerostomia</p></li><li><p>cough</p></li><li><p>blurred vision</p></li></ul></li></ul></li><li><p>Others: </p><ul><li><p><strong>tiotropium</strong></p></li><li><p>aclidinium</p></li><li><p>umeclidinium </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/abcfd85a-1c97-462e-a77c-30faf649c8fe.jpg)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
COPD/asthma
Ipratropium (metered dose inhaler, nebulizer)
Inhaled so [how much systemic absorption is there]
Blocks ACh in the bronchial smooth muscles→broncho[dilation or constriction]
Adverse effects:
xerostomia
cough
blurred vision
Others:
tiotropium
aclidinium
umeclidinium
there is minimal systemic absorption
dilation
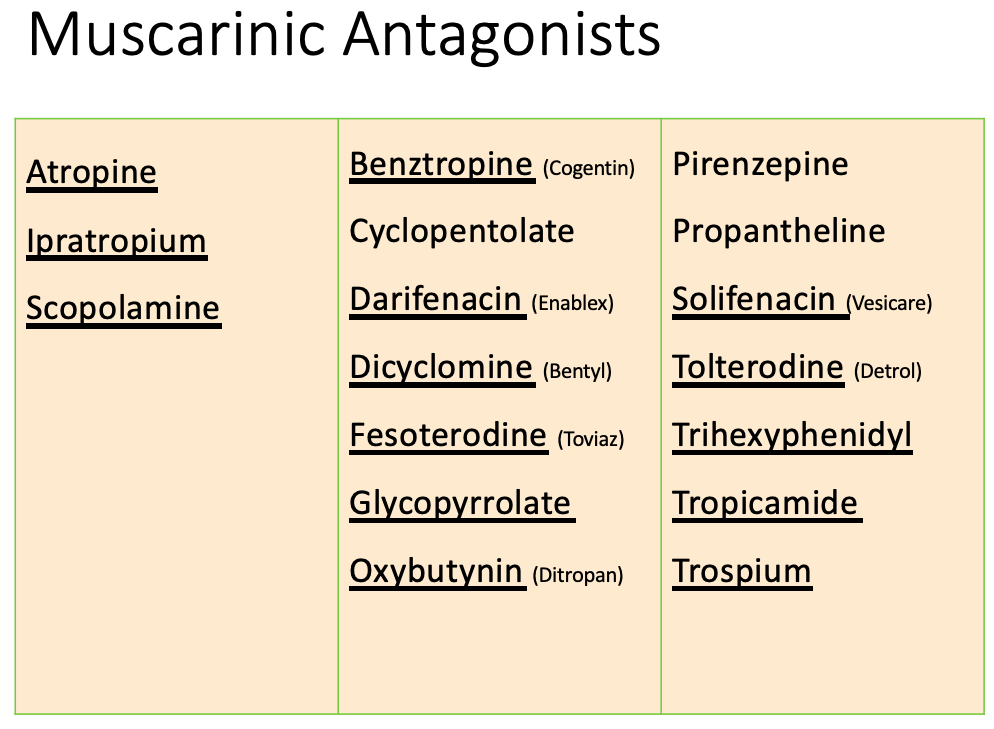
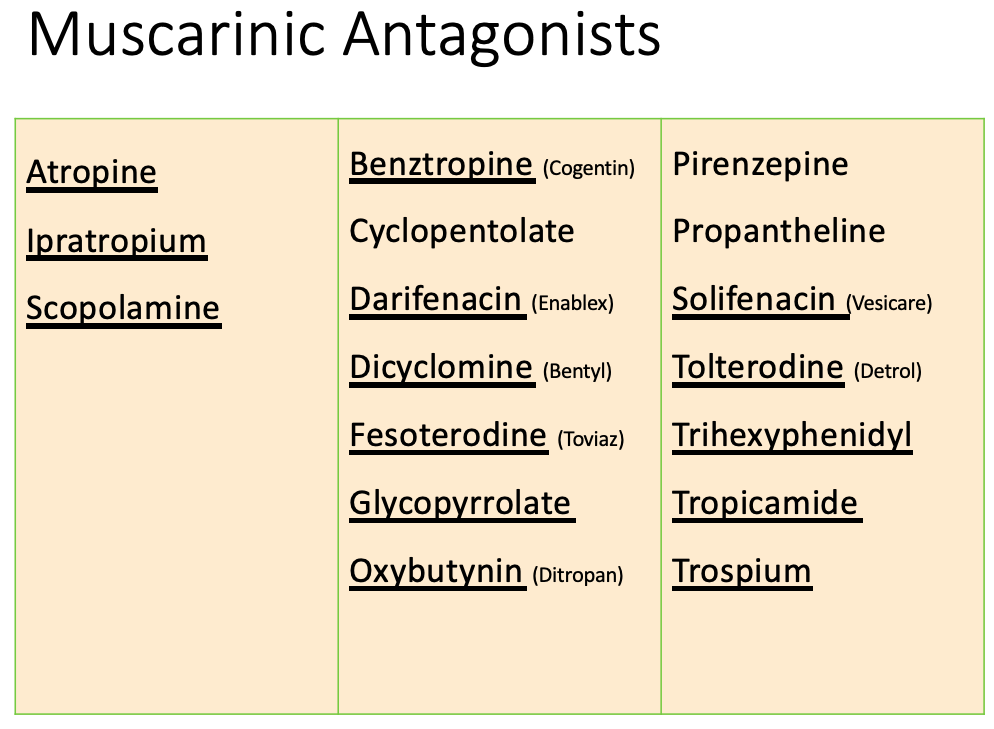
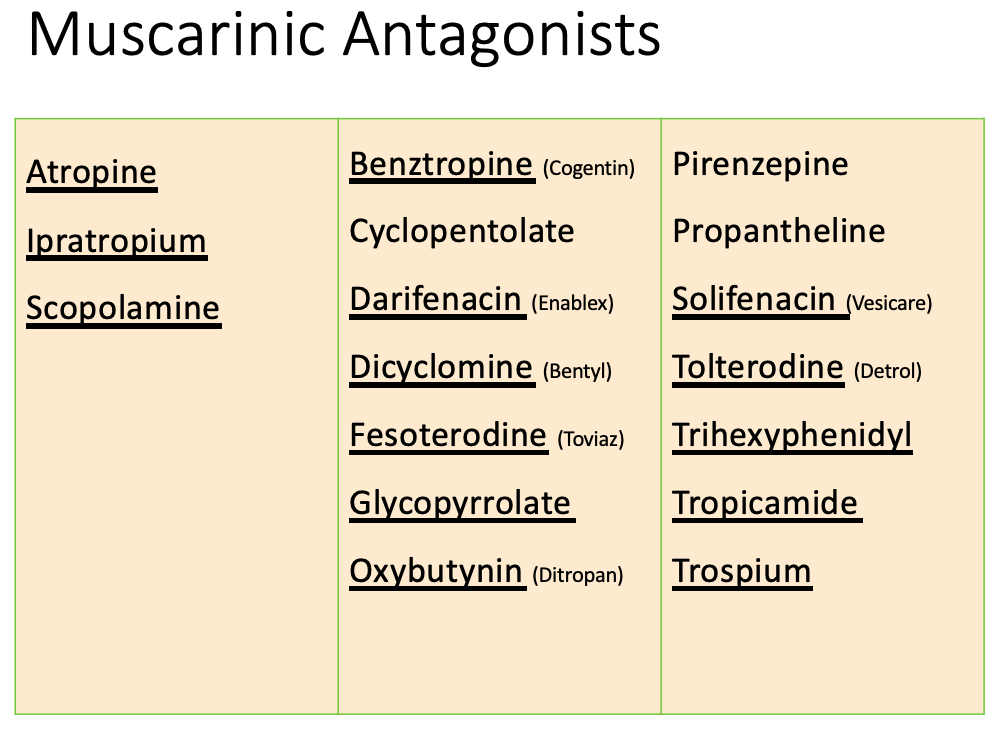
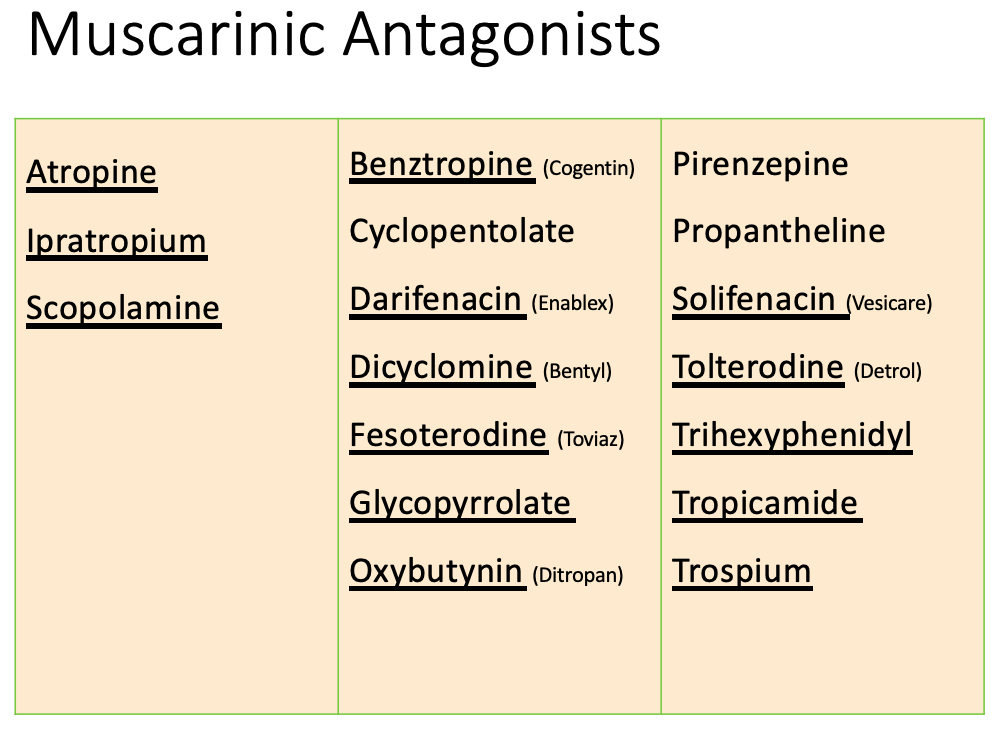
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
[Indication?]
Drugs:
Oxybutynin
tolterodine
trospium
solifenacin
darifenacin
fesoterodine
MOA:
somewhat targets M3 receptors in bladder to relieve spasms
Oral, IV, patch
1/5 the anticholinergic activity of atropine
4 to 10x the antispasmodic activity of atropine
No effects at skeletal muscle or autonomic ganglia
Adverse effects:
dizziness, drowsiness, xerostomia, constipation
Overactive bladder
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Overactive bladder
Drugs:
Oxybutynin
tolterodine
trospium
solifenacin
darifenacin
fesoterodine
MOA:
somewhat targets [...] receptors in bladder to relieve spasms
Oral, IV, patch
1/5 the [...] activity of atropine
4 to 10x the [...] activity of atropine
No effects at skeletal muscle or autonomic ganglia
Adverse effects:
dizziness, drowsiness, xerostomia, constipation
M3
anticholinergic
antispasmodic
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Overactive bladder
Drugs:
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
MOA:
somewhat targets M3 receptors in bladder to relieve spasms
Oral, IV, patch
1/5 the anticholinergic activity of atropine
4 to 10x the antispasmodic activity of atropine
No effects at skeletal muscle or autonomic ganglia
Adverse effects:
dizziness, drowsiness, xerostomia, constipation
Oxybutynin
tolterodine
trospium
solifenacin
darifenacin
fesoterodine
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p>Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) <br></p><ul><li><p>Drugs </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>MOA: </p><ul><li><p>spasmolytic effects on the smooth muscle of GI tract </p></li><li><p><span>decreases</span> peristalsis </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3d391bb1-f761-4301-a073-46d1fa03b0af.png)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Drugs
[...]
[...]
MOA:
spasmolytic effects on the smooth muscle of GI tract
decreases peristalsis
Dicyclomine
Hyoscyamine
Just because I'm dying or high, doesn't mean I will poop
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p>Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) <br></p><ul><li><p>Drugs </p><ul><li><p><span>Dicyclo<u>mine</u></span> </p></li><li><p><span>Hyoscya<u>mine</u></span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>MOA: </p><ul><li><p>spasmolytic effects on the smooth muscle of GI tract </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[increases or decreases]</strong></span> peristalsis </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4c48f0e0-809a-471b-8cd9-2f21d160cbe2.png)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Drugs
Dicyclomine
Hyoscyamine
MOA:
spasmolytic effects on the smooth muscle of GI tract
[increases or decreases] peristalsis
decreases
Just because I'm dying or high, doesn't mean I will poop
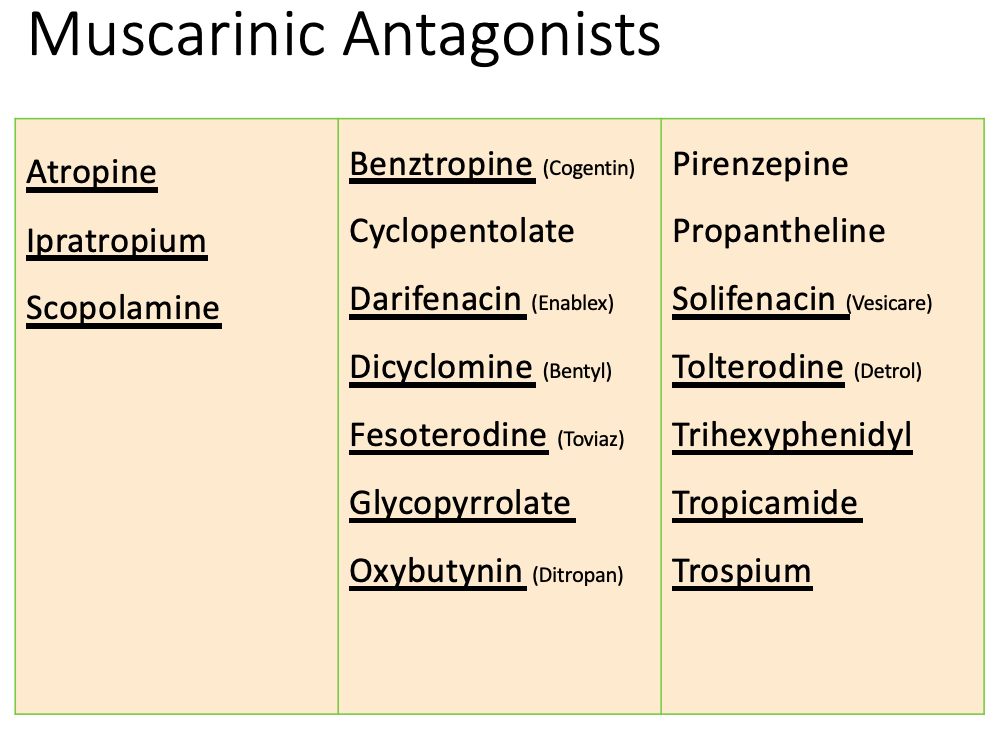
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p>Parkinsons <br></p><ul><li><p>Drugs </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul></li><li><p>MOA: antagonizes ACh </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/eb4ddf6d-587b-4cd5-8415-f5b8727ba2c1.png)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Parkinsons
Drugs
[...]
[...]
MOA: antagonizes ACh
Benztropine
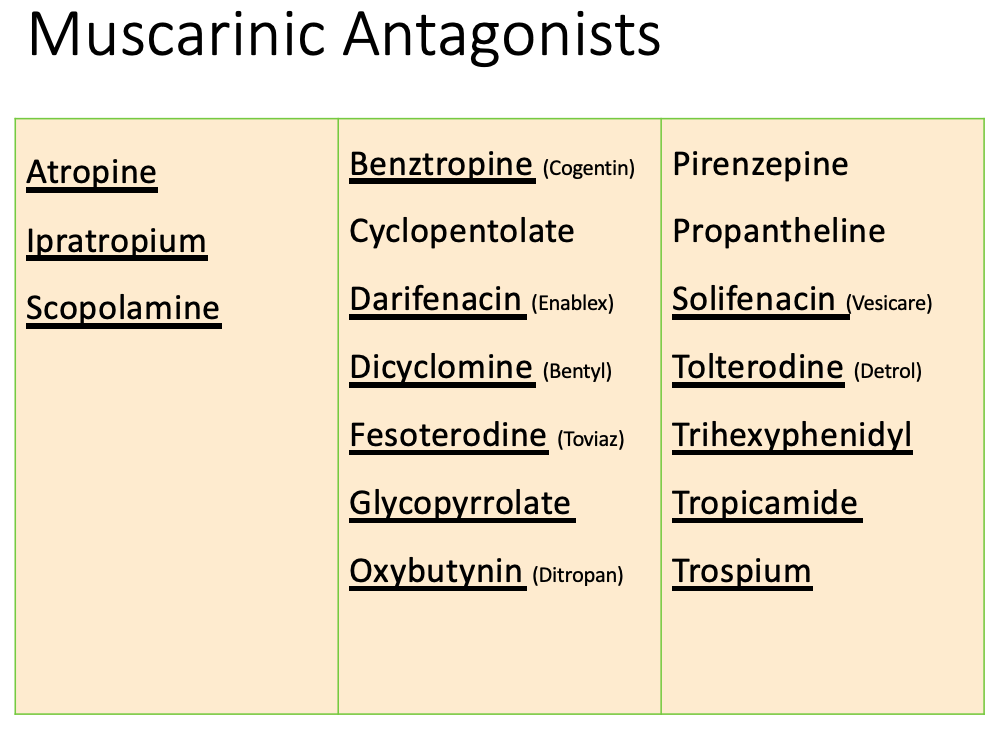
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p><span>Reduction of Secretions/Drooling</span> <br></p><ul><li><p>Drugs </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>MOA: </p><ul><li><p>anticholinergic effects inhibits salivation and secretion</p></li><li><p>causes bronchodilation </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/15620538-558a-448c-8118-0719e14bdd92.png)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
Reduction of Secretions/Drooling
Drugs
[...]
[...]
MOA:
anticholinergic effects inhibits salivation and secretion
causes bronchodilation
Glycopyrrolate
Atropine
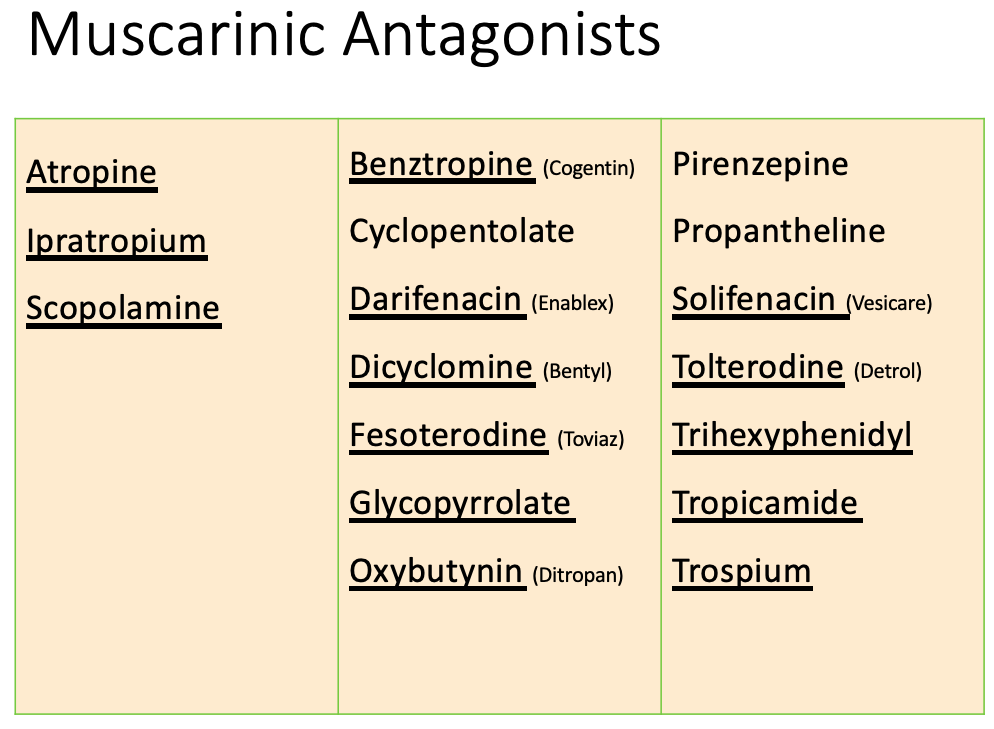
![<p>Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Indication?]</strong></span> <br></p><ul><li><p>Drugs </p><ul><li><p><span>Glycopyrrolate</span> </p></li><li><p><span>Atropine</span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>MOA: </p><ul><li><p>anticholinergic effects inhibits salivation and secretion</p></li><li><p>causes bronchodilation </p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/304e3921-231a-4135-a60e-16dd0cc50c8e.png)
Anticholinergics: therapeutic uses
[Indication?]
Drugs
Glycopyrrolate
Atropine
MOA:
anticholinergic effects inhibits salivation and secretion
causes bronchodilation
Reduction of Secretions/Drooling
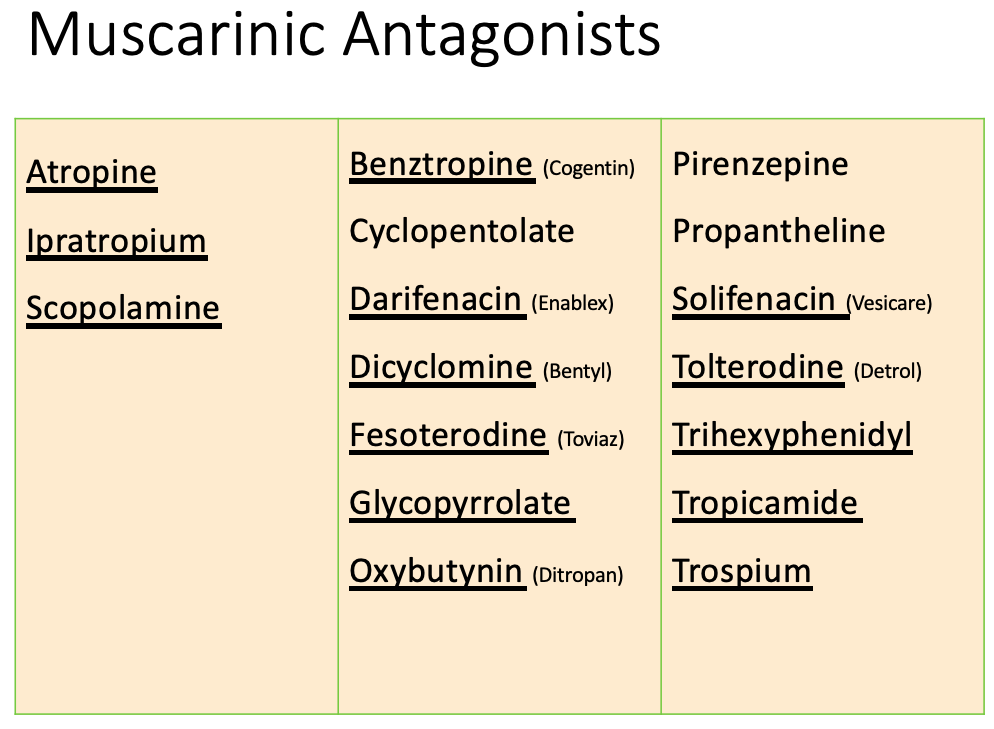
![<p>Cholinergic Clinical Uses: Neuromuscular junction</p><ul><li><p>Myasthenia gravis<br></p><ul><li><p>Edrophonium is used as a diagnostic agent; not available in the US</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> and <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> are used for long-term therapy </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/71ceafe5-18d8-4c9f-abad-3054d449d26b.jpg)
Cholinergic Clinical Uses: Neuromuscular junction
Myasthenia gravis
Edrophonium is used as a diagnostic agent; not available in the US
[...] and [...] are used for long-term therapy
Pyridostigmine and neostigmine
H1 antagonists clinical use: Generalized Anxiety
[...]
in adjunct with organic disease states in which anxiety is manifested
Hydroxyzine
Histamine
Mediator of allergic and inflammatory rxns with some role in anaphylactic rxns
Causes
Local vaso[dilation or contraction]
release of [...] and [...]
Chemotactic response via:
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes
dilation
C-reactive protein and antibodies
Histamine binds to various receptors throughout the body
4 histamine receptors
H1
smooth muscle, endothelium, brain
[Important in?]
H2
gastric mucosa, cardiac muscle, mast cells, brain
[important in?]
H3
presynaptic brain, myenteric plexus
part of GI nervous system (NT control)
H4
CD4+ T cells, eosinophils, neutrophils
immune response regulation
acute allergic response
gastric acid secretion
Histamine Receptor Antagonists
Physiological antagonists
[What] causes opposite effect of histamine on smooth muscle
used in [...] treatment
Epinephrine
anaphylaxis
Histamine release
Immunologic
Release (degranulation) occurs when an antigen binds to the IgE Ab on the cell
Type I allergic reaction (e.g. hay fever and acute urticaria)
Chemical and mechanical
Direct injury to mast cells
Causes release of histamine
Ex: [...]: causes direct interaction with mast cells and causes a reaction
morphine
Histamine
Functions as a NT and neuromodulator
Location
[...]
[...]
Mast cells
Basophils
Mast cell histamine
Stored in granules in a bound inactive form
Most abundant at sites of [...]
Nose
mouth
feet
blood vessels
internal body surfaces
potential tissue injury
Non-mast cell histamine
Brain:
neuroendocrine control
CV regulation
thermal and body weight regulation
sleep and arousal
Fundal cells of the stomach
histamine release [stimulates or inhibits] acid production
stimulates
![<p><span>Toxicity of H1 antagonists </span><br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[What type of]</strong></span> effects<br></p><ul><li><p>Sedation </p></li><li><p>Dry mouth</p></li><li><p>Blurred vision </p></li><li><p>Urine retention </p></li><li><p>GI upset, nausea, constipation </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Caution in <span><strong>[...]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Sedation more pronounced with combined with alcohol and other CNS depressants </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Excitation and convulsion in children </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> hypotension (e.g. promethazine)</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dddddc29-1c0c-4175-9123-6613743657e0.jpg)
Toxicity of H1 antagonists
[What type of] effects
Sedation
Dry mouth
Blurred vision
Urine retention
GI upset, nausea, constipation
Caution in [...]
Sedation more pronounced with combined with alcohol and other CNS depressants
Excitation and convulsion in children
[...] hypotension (e.g. promethazine)
Anti-ACh
elderly
Postural
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> disease is <strong><u>characterized by cholinergic deficiency</u></strong> in the cortex and basal forebrain </p><ul><li><p>Contributes to cognitive deficits</p></li><li><p><span>Donepezil</span>, <span>galantamine</span> and <span>rivastigmine</span><br></p><ul><li><p><span>Inhibit acetylcholinesterase</span></p></li><li><p>Work primarily in the CNS</p></li><li><p><strong><em><u>Increase the ACh in the CNS for synaptic transmission </u></em></strong></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b4058151-9011-4120-8150-75d996cc1b59.jpg)
[...] disease is characterized by cholinergic deficiency in the cortex and basal forebrain
Contributes to cognitive deficits
Donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine
Inhibit acetylcholinesterase
Work primarily in the CNS
Increase the ACh in the CNS for synaptic transmission
Alzheimer’s
![<p><span>Alzheimer’s</span> disease is <strong><u>characterized by cholinergic deficiency</u></strong> in the cortex and basal forebrain </p><ul><li><p>Contributes to cognitive deficits</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span>, <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> and <span><strong>[...]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p><span>Inhibit acetylcholinesterase</span></p></li><li><p>Work primarily in the CNS</p></li><li><p><strong><em><u>Increase the ACh in the CNS for synaptic transmission </u></em></strong></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3c890599-6344-442e-aaa7-6e4ad1f30c9f.jpg)
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by cholinergic deficiency in the cortex and basal forebrain
Contributes to cognitive deficits
[...], [...] and [...]
Inhibit acetylcholinesterase
Work primarily in the CNS
Increase the ACh in the CNS for synaptic transmission
Donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine
![<p><span>Alzheimer’s</span> disease is <strong><u>characterized by cholinergic deficiency</u></strong> in the cortex and basal forebrain </p><ul><li><p>Contributes to cognitive deficits</p></li><li><p><span>Donepezil</span>, <span>galantamine</span> and <span>rivastigmine</span><br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[MOA?]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Work primarily in the CNS</p></li><li><p><strong><em><u>Increase the ACh in the CNS for synaptic transmission </u></em></strong></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bab226f4-724b-4b44-bff4-582b6df39524.jpg)
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by cholinergic deficiency in the cortex and basal forebrain
Contributes to cognitive deficits
Donepezil, galantamine and rivastigmine
[MOA?]
Work primarily in the CNS
Increase the ACh in the CNS for synaptic transmission
Inhibit acetylcholinesterase
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Cardiovascular
[increase or decrease] peripheral vascular resistance and [speeds up or slow downs] HR
Agents are not used clinically for these purposes
Adverse effects:
[increased or decreased] inotropy, chronotropy, CO, and vascular resistance
Decrease
slows
decreased
![<p>Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Genitourinary </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>treats urinary retention, neurogenic bladder</p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>post-op bladder distension/urinary retention </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dd48ce67-d848-4ec8-bb66-d5c7761e72a9.jpg)
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Genitourinary
[...]
treats urinary retention, neurogenic bladder
[...]
post-op bladder distension/urinary retention
Bethanechol
Neostigmine

![<p>Cholinergic Organ System Effects: GI</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Increased or decreased]</strong></span> motility, secretion </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[Contracts or relaxes]</strong></span> sphincters</p></li><li><p><span>Neostigmine</span> and <span>Bethanechol</span>: </p><ul><li><p>post-op ileus</p></li><li><p>atony of the urinary bladder</p></li></ul></li><li><p><span>Pilocarpine</span> and <span>Cevimeline</span></p><ul><li><p>dry mouth due to Sjӧgren’s </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5a3377be-06df-40c7-9e46-769c4611adf5.jpg)
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: GI
[Increased or decreased] motility, secretion
[Contracts or relaxes] sphincters
Neostigmine and Bethanechol:
post-op ileus
atony of the urinary bladder
Pilocarpine and Cevimeline
dry mouth due to Sjӧgren’s
Increased
Relaxes
Postoperative ileus (POI) may be defined as the impairment of gastrointestinal (GI) motility after intra-abdominal or nonabdominal surgery

![<p>Cholinergic Organ System Effects: GI</p><ul><li><p><span>Increased</span> motility, secretion </p></li><li><p><span>Relaxes</span> sphincters</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> and <span><strong>[...]</strong></span>: </p><ul><li><p>post-op ileus</p></li><li><p>atony of the urinary bladder</p></li></ul></li><li><p><span>Pilocarpine</span> and <span>Cevimeline</span></p><ul><li><p>dry mouth due to Sjӧgren’s </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/90c60a45-6f01-43d4-8953-f9393911574a.jpg)
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: GI
Increased motility, secretion
Relaxes sphincters
[...] and [...]:
post-op ileus
atony of the urinary bladder
Pilocarpine and Cevimeline
dry mouth due to Sjӧgren’s
Neostigmine and Bethanechol
Postoperative ileus (POI) may be defined as the impairment of gastrointestinal (GI) motility after intra-abdominal or nonabdominal surgery

![<p>Cholinergic Organ System Effects: GI</p><ul><li><p><span>Increased</span> motility, secretion </p></li><li><p><span>Relaxes</span> sphincters</p></li><li><p><span>Neostigmine</span> and <span>Bethanechol</span>: </p><ul><li><p>post-op ileus</p></li><li><p>atony of the urinary bladder</p></li></ul></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> and <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>dry mouth due to Sjӧgren’s </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e228323b-1bce-4460-b778-ef0abfc55d03.jpg)
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: GI
Increased motility, secretion
Relaxes sphincters
Neostigmine and Bethanechol:
post-op ileus
atony of the urinary bladder
[...] and [...]
dry mouth due to Sjӧgren’s
Pilocarpine and Cevimeline
Postoperative ileus (POI) may be defined as the impairment of gastrointestinal (GI) motility after intra-abdominal or nonabdominal surgery
![<p>Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Respiratory</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[contraction or dilation]</strong></span> of smooth muscle of the bronchial tree </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[stimulates or inhibits]</strong></span> secretion</p></li><li><p>Avoid in asthma patients <br></p><ul><li><p><span>Methacholine</span> is occasionally used for bronchial challenge test to help diagnose asthma </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/042af389-bfe2-45ba-a3a8-a8ac5128ef39.jpg)
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Respiratory
[contraction or dilation] of smooth muscle of the bronchial tree
[stimulates or inhibits] secretion
Avoid in asthma patients
Methacholine is occasionally used for bronchial challenge test to help diagnose asthma
Contraction
Stimulates
![<p>Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Respiratory</p><ul><li><p><span>Contraction</span> of smooth muscle of the bronchial tree </p></li><li><p><span>Stimulates</span> secretion</p></li><li><p>Avoid in asthma patients <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> is occasionally used for bronchial challenge test to help diagnose asthma </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b29e7588-f7fe-4608-b5f2-3dcf08055d33.jpg)
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Respiratory
Contraction of smooth muscle of the bronchial tree
Stimulates secretion
Avoid in asthma patients
[...] is occasionally used for bronchial challenge test to help diagnose asthma
Methacholine
![<p><span><strong>[cholinergic or anticholinergic]</strong> effects</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/62bf19ff-46d3-430a-ad35-c9cf8e5cd239.png)
[cholinergic or anticholinergic] effects
Anticholinergic
![<p><span>Acetylcholine binds to the <strong>[nicotinic or muscarinic]</strong> receptors in the ganglia </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a9ecfc75-18f9-4437-bb4a-91642f91931e.png)
Acetylcholine binds to the [nicotinic or muscarinic] receptors in the ganglia
nicotinic
ACh is released via [...] dependent exocytosis
Blocked by Botulinum Toxin
calcium
ACh is released via calcium dependent exocytosis
Blocked by [...]
Botulinum Toxin
ACh synthesized from acetyal coenzyme A and choline
Via [which enzyme?]
ChAT (choline acetyltransferase)
![<p><span>All autonomic ganglia have <strong>[Nicotinic or Muscarinic]</strong> receptors</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bd710f48-6672-4492-b538-e06bf4826944.png)
All autonomic ganglia have [Nicotinic or Muscarinic] receptors
nicotinic
![<p><span>All receptors at the neuromuscular junction are <strong>[nicotinic or muscarinic]</strong> receptors</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7f2141fe-21b3-4b4f-9bb9-50a757da7600.png)
All receptors at the neuromuscular junction are [nicotinic or muscarinic] receptors
nicotinic
![<p><span>All</span><strong><u> target organs</u></strong><span> of the parasympathetic nervous system have <strong>[nicotinic or muscarinic]</strong> receptors</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fb9820f4-4368-4b70-913e-ff72131284cc.png)
All target organs of the parasympathetic nervous system have [nicotinic or muscarinic] receptors
muscarinic
![<p>Almost all efferent fibers leaving the CNS are cholinergic. Why? </p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2a321589-251f-4ff8-860b-4470f523a70f.png)
Almost all efferent fibers leaving the CNS are cholinergic. Why?
[...]
Because preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine
Almost all efferent fibers leaving the CNS are [...]
cholinergic
Atropine
[What type of] antagonist at the muscarinic receptors
Increasing ACh can overcome atropine
Clinical Uses
Bradycardia
Salivation/secretion
Ophtalmology
Muscarine-containing mushroom poisoning
Organophosphate poisoning
Competitive
![<p><span>Atropine </span></p><ul><li><p><span>Competitive</span> antagonist at the muscarinic receptors<br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[How can the effects of atropine be overcome?]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>Clinical Uses<br></p><ul><li><p>Bradycardia</p></li><li><p>Salivation/secretion</p></li><li><p>Ophtalmology </p></li><li><p>Muscarine-containing mushroom poisoning</p></li><li><p>Organophosphate poisoning</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fbdb0baa-4320-4715-8f65-05f46166ab98.png)
Atropine
Competitive antagonist at the muscarinic receptors
[How can the effects of atropine be overcome?]
Clinical Uses
Bradycardia
Salivation/secretion
Ophtalmology
Muscarine-containing mushroom poisoning
Organophosphate poisoning
Increasing ACh can overcome atropine
![<p><span>Atropine Effects </span></p><ul><li><p>Eye<br></p><ul><li><p>Clinical use → <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a38054f4-bac2-4719-99dd-79e8453cbada.png)
Atropine Effects
Eye
Clinical use → [...]
ophthalmologic procedures
Causes unopposed sympathetic dilator activity and mydriasis by blocking cholinergic responses on the pupillary sphincter muscle of the iris
Dilation results in photophobia
Because the lens is fixed for far vision, objects up close appear blurred
Clinical use → ophthalmologic procedures
![<p><span>Cholinergic Clinical Uses: Neuromuscular Junction</span></p><ul><li><p>Reversal of neuromuscular blockade<br></p><ul><li><p>NMBs block the nicotinic ACh receptor inducing paralysis </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> and <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> are used after surgery to reverse neuromuscular blockade </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/358bedab-2dc9-490b-aa94-71bc56388f98.jpg)
Cholinergic Clinical Uses: Neuromuscular Junction
Reversal of neuromuscular blockade
NMBs block the nicotinic ACh receptor inducing paralysis
[...] and [...] are used after surgery to reverse neuromuscular blockade
Neostigmine and pyridostigmine
![<p><span>Cholinergic drugs mimic Ach (<strong>[aka?]</strong>)</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d24ab9d3-8119-4677-a478-d31a0ae509bd.png)
Cholinergic drugs mimic Ach ([aka?])
cholinomimetics
![<p>Cholinergic Drugs</p><ul><li><p>Direct-acting <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[how does it work?]</strong></span> </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Indirect-acting <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[how does it work?]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/825a0a9b-abc8-4f03-98e8-4370d4b5cb50.png)
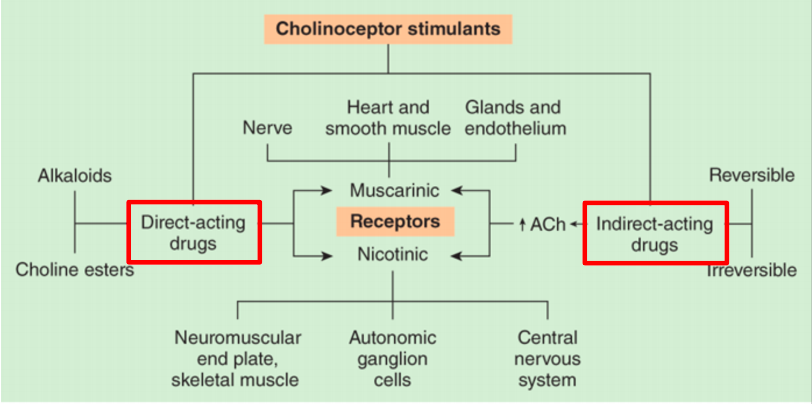
Cholinergic Drugs
Direct-acting
[how does it work?]
Indirect-acting
[how does it work?]
Directly act on ACh receptors
Increases ACh through inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Eye
Direct/indirect agents were used in past to treat glaucoma
[...]
treats acute angle-closure glaucoma
can lead to blindness
MOA
contraction of iris and ciliary muscles→aqueous humor outflow
Carbachol
used if Pilocarpine is not effective
Pilocarpine
pile of carp -- pilocarpine
Cholinergic Organ System Effects: Eye
Direct/indirect agents were used in past to treat glaucoma
Pilocarpine
treats acute angle-closure glaucoma
can lead to blindness
MOA
contraction of iris and ciliary muscles→aqueous humor outflow
[...]
used if Pilocarpine is not effective
Carbachol
pile of carp -- pilocarpine
Cholinergic Response
Cardiovascular
[Increase or Decrease] HR and BP
Decrease
Cholinergic Response
GI
[increases or decreases] motility
[relaxes or contracts] sphincters
[stimulates or inhibits] secretion
Increases
relaxes
stimulates
Cholinergic Response
Glands
[Increase or decrease] secretions (tears/sweat/salivary)
Increase
Cholinergic Response
GU
[Relaxes or contracts] sphincters
[Relaxes or contracts] bladder wall
Relaxes
Contracts
Cholinergic Response
Respiratory
Bronchial [constriction or dilation]
[increase or decrease] secretions
constriction
Increase
Cholinergic Response
Eye -- [contraction or dilation]
Miosis (contraction of the pupil)
![<p><span>Direct </span></p><ul><li><p>Esters <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Is it structurally related?]</strong></span> to ACh</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Alkaloids <br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Is it structurally related?]</strong></span> to ACh</p></li><li><p>So <span><strong>[is it metabolized]</strong></span> by acetylcholinesterases</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e0c48a2f-b21a-4e8e-9bbc-c26f036599b1.png)
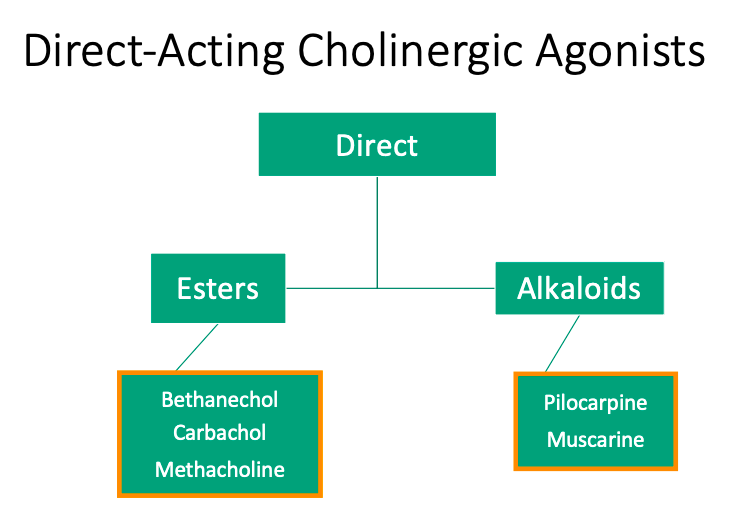
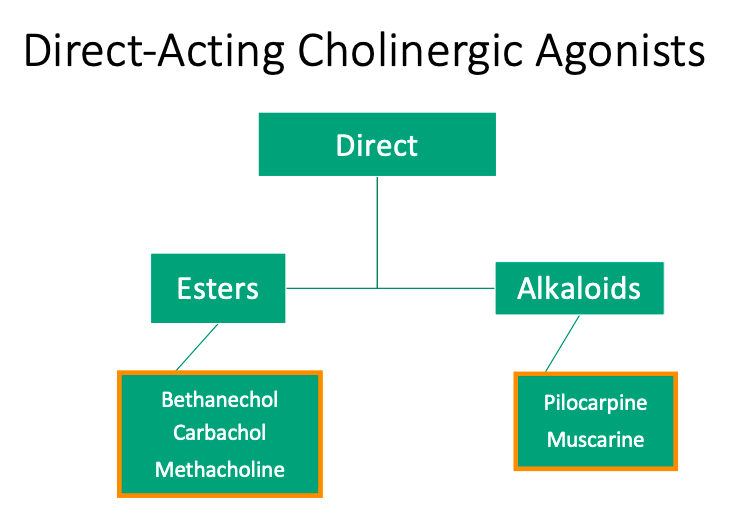
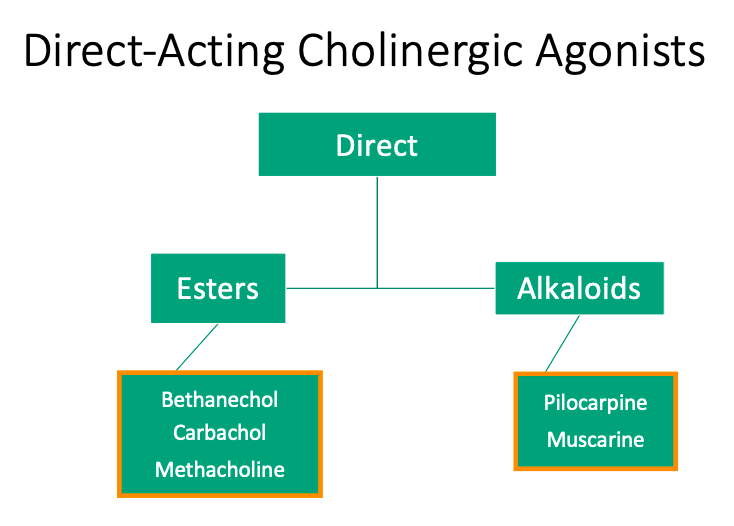
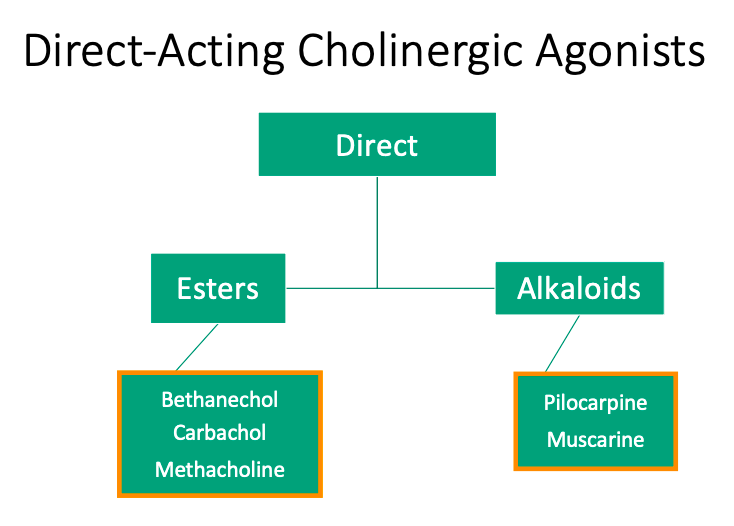
Direct
Esters
[Is it structurally related?] to ACh
Alkaloids
[Is it structurally related?] to ACh
So [is it metabolized] by acetylcholinesterases
Structurally related
Not structurally related
not metabolized
![<p><span>Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems</span></p><ul><li><p>Heart<br></p><ul><li><p>High doses cause <span><strong>[tachycardia or bradycardia]</strong></span> by blocking M2 receptors on the SA nodal pacemaker, thereby antagonizing parasympathetic tone of the heart</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Clinical use</p><ul><li><p>acute symptomatic <span><strong>[tachycardia or bradycardia]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>cholinergic poisoning </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/17c9dbc1-7889-4af3-8101-dfedd9811b40.png)
Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems
Heart
High doses cause [tachycardia or bradycardia] by blocking M2 receptors on the SA nodal pacemaker, thereby antagonizing parasympathetic tone of the heart
Clinical use
acute symptomatic [tachycardia or bradycardia]
cholinergic poisoning
tachycardia
bradycardia
![<p><span>Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems </span></p><ul><li><p>Respiratory<br></p><ul><li><p>Promotes broncho<span><strong>[dilation or constriction]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[increases or decreases]</strong></span> secretion</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/658dcf74-7a1f-4137-a7b8-63bc3286ac91.png)
Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems
Respiratory
Promotes broncho[dilation or constriction]
[increases or decreases] secretion
dilation
decreases
Inhibits bronchoconstriction caused by histamine, bradykinin, etc.
![<p><span>Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems</span></p><ul><li><p>GU</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Constricts or Relaxes]</strong></span> smooth muscle of ureters and bladder wall </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/99f7f24c-fc05-4579-a096-7aeb1d17efcc.png)
Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems
GU
[Constricts or Relaxes] smooth muscle of ureters and bladder wall
Relaxes
![<p><span>Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems</span></p><ul><li><p>GI<br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[increased or decreases]</strong></span> tone and motility by blocking the muscarinic receptors in the GI</p><ul><li><p>Gastric emptying time is <span><strong>[prolonged or shortened]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/278dfe5e-552a-4626-b003-5871be0f9b7f.png)
Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems
GI
[increased or decreases] tone and motility by blocking the muscarinic receptors in the GI
Gastric emptying time is [prolonged or shortened]
Decreases
prolonged
![<p><span>Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems</span></p><ul><li><p>GI<br></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[stimulates or inhibits]</strong></span> salivary secretions causing <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>can make swallowing difficult</p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/79561fcd-7ac0-4cd1-8794-83a8ec81d326.png)
Effects of Atropine on Organ Systems
GI
[stimulates or inhibits] salivary secretions causing [...]
can make swallowing difficult
Inhibits
xerostomia
Clinical use
used during pre-anesthesia to inhibit salivation
Effects of Histamine on Organ Systems
Bronchiolar smooth muscle
H1 → broncho[dilation or constriction]
constriction
Effects of Histamine on Organ Systems
GI
H1→ [contraction or dilation] of intestinal smooth muscle
H2→ [increased or decreased] secretion of acid from parietal cells
contraction
increased
Effects of Histamine on Organ Systems
Skin
[...]
Nervous system
H1 → [...]
GU
Histamine induced contractions cause [...]
wheel and flare
pain and itching
abortion
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Allergic reactions
[which drug?]
Combined with EPI in anaphylaxis reactions
Allergic rhinitis, urticaria, hay fever→ 2nd generation agents preferred for these
[...]
for Pruritus
MOA:
antagonizes histamine effects on smooth muscle, blood vessels, immune cells
Also blocks muscarinic receptors
1st generation much more potent than 2nd generation to block these receptors
Hydroxyzine
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Allergic reactions
Diphenhydramine
Combined with EPI in anaphylaxis reactions
Allergic rhinitis, urticaria, hay fever→ [1st or 2nd] generation agents preferred for these
Hydroxyzine
for Pruritus
MOA:
antagonizes histamine effects on smooth muscle, blood vessels, immune cells
Also blocks muscarinic receptors
1st generation much more potent than 2nd generation to block these receptors
2nd
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Allergic reactions
Diphenhydramine
Combined with EPI in anaphylaxis reactions
Allergic rhinitis, urticaria, hay fever→ 2nd generation agents preferred for these
Hydroxyzine
for Pruritus
MOA:
antagonizes histamine effects on smooth muscle, blood vessels, immune cells
Also blocks [...]
1st generation much more potent than 2nd generation to block these receptors
muscarinic receptors
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Allergic reactions
Diphenhydramine
Combined with EPI in anaphylaxis reactions
Allergic rhinitis, urticaria, hay fever→ 2nd generation agents preferred for these
Hydroxyzine
for Pruritus
MOA:
antagonizes histamine effects on smooth muscle, blood vessels, immune cells
Also blocks muscarinic receptors
[1st or 2nd more potent?] to block these receptors
1st generation much more potent than 2nd generation
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Nausea and vomiting
[...]
Combined with vitamin B6
Preferred in pregnancy
Doxylamine (PO)
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Nausea and vomiting
Doxylamine (PO)
Combined with [...]
Preferred in pregnancy
vitamin B6
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Sleep Aids
[...]
[...]
Doxylamine
Diphenhydramine
H1 antagonists : clinical use
[...] and [...]
Diphenhydramine
dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
promethazine
meclizine
MOA:
Antimuscarinic effects
suppresses vestibular end-organ receptors
inhibits activation of central cholinergic pathway
Motion sickness and Vestibular Disturbances
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Motion sickness and Vestibular Disturbances
Diphenhydramine
dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
promethazine
meclizine
MOA:
[What type of] effects
suppresses vestibular end-organ receptors
inhibits activation of central cholinergic pathway
Antimuscarinic
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Motion sickness and Vestibular Disturbances
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
MOA:
Antimuscarinic effects
suppresses vestibular end-organ receptors
inhibits activation of central cholinergic pathway
Diphenhydramine
dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
promethazine
meclizine
![<p>H1 antagonists : clinical use </p><ul><li><p><span>Motion sickness</span> and <span>Vestibular Disturbances</span> <br></p><ul><li><p><span>Diphenhydramine</span></p></li><li><p><span>dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)</span></p></li><li><p><span>promethazine</span></p></li><li><p><span>meclizine</span></p></li><li><p>MOA:</p><ul><li><p><span>Antimuscarinic</span> effects </p><ul><li><p>suppresses <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>inhibits <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0459c517-cf33-4d70-be42-cb510b13815e.jpg)
H1 antagonists : clinical use
Motion sickness and Vestibular Disturbances
Diphenhydramine
dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
promethazine
meclizine
MOA:
Antimuscarinic effects
suppresses [...]
inhibits [...]
vestibular end-organ receptors
activation of central cholinergic pathway
Dragonfly men prompted me close in
![<p><span>Indirect </span></p><ul><li><p>Effects are like cholinomimetic agonists (direct-acting) </p></li><li><p>Bind to and inhibit acetylcholinesterase <br></p><ul><li><p>Increases ACh levels at <span><strong>[which receptors?]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a0cbbf77-a042-4887-984b-73ceb05d8c31.png)
Indirect
Effects are like cholinomimetic agonists (direct-acting)
Bind to and inhibit acetylcholinesterase
Increases ACh levels at [which receptors?]
both muscarinic and nicotinic cholinoceptors
![<p>Indirect </p><ul><li><p>Reversible <br></p><ul><li><p>Alcohols and carbamates </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[Shorter or longer]</strong></span> duration of action (compared to the irreversible agents) </p></li><li><p>Minutes to hours </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Irreversible <br></p><ul><li><p><strong>Nerve gases and insecticides (organophosphates) </strong></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[Shorter or longer]</strong></span> duration of action due to covalent bonds between phosphorus-enzyme complex</p></li><li><p>Some compounds last >100 hours </p></li><li><p><span>Crosses BBB due to to lipophilicity</span> </p></li><li><p>Reversal agents: atropine</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6d729103-7bda-4034-b93a-bf08dfd2ab21.png)
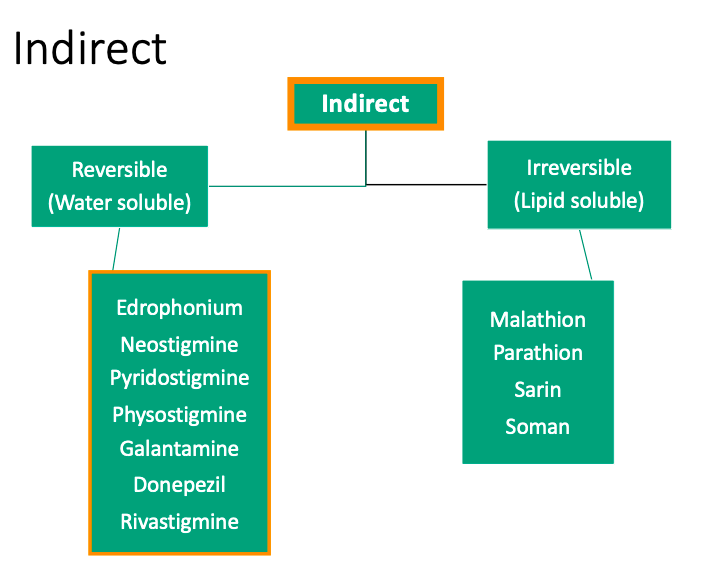
Indirect
Reversible
Alcohols and carbamates
[Shorter or longer] duration of action (compared to the irreversible agents)
Minutes to hours
Irreversible
Nerve gases and insecticides (organophosphates)
[Shorter or longer] duration of action due to covalent bonds between phosphorus-enzyme complex
Some compounds last >100 hours
Crosses BBB due to to lipophilicity
Reversal agents: atropine
Long
![<p>Indirect </p><ul><li><p>Reversible <br></p><ul><li><p>Alcohols and carbamates </p></li><li><p><span>Shorter</span> duration of action (compared to the irreversible agents) </p></li><li><p>Minutes to hours </p></li></ul></li><li><p>Irreversible <br></p><ul><li><p><strong>Nerve gases and insecticides (organophosphates) </strong></p></li><li><p><span>Long</span> duration of action due to covalent bonds between phosphorus-enzyme complex</p></li><li><p>Some compounds last >100 hours </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[Why can it cross the BBB?]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>Reversal agents: atropine</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1a2eb347-1e8a-47a7-8c62-97b6295ca75c.png)
Indirect
Reversible
Alcohols and carbamates
Shorter duration of action (compared to the irreversible agents)
Minutes to hours
Irreversible
Nerve gases and insecticides (organophosphates)
Long duration of action due to covalent bonds between phosphorus-enzyme complex
Some compounds last >100 hours
[Why can it cross the BBB?]
Reversal agents: atropine
Crosses BBB due to to lipophilicity
![<p><span>Why is Physostigmine only reserved for emergency cases??</span></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1c81ce79-7561-4ba8-bed2-eb1ebac4f67a.png)
Why is Physostigmine only reserved for emergency cases??
[...]
Physostigmine has a tertiary amine that makes it different from the pyridostigmine and neostigmine which allows it to cross the BBB
[...] is the major neurotransmitter stored in vesicles
Acetylcholine (Ach
Synthesized from actyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) and choline pre-ganglionic nerve terminal
Released in response to an action potential
Calcium-dependent exocytosis
Ach binds to the nicotinic receptors on the postganglionic cell
[...] hydrolyzes Ach
Found in high concentrations around neuronal membranes
Acetylcholinesterase
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong> denotes receptors that respond to Ach (muscarinic and nicotinic)</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e83bf3c8-f689-4407-b5b8-813c266ce748.png)
[...] denotes receptors that respond to Ach (muscarinic and nicotinic)
Cholinoceptor
[...]
contraction of the pupil
Miosis
![<p><span><strong>[Nicotinic or Muscarinic]</strong></span> acetylcholine receptors</p><ul><li><p>Cardiac and smooth muscle</p></li><li><p>Gland cells</p></li><li><p>Nerve terminals</p></li><li><p>Sweat glands </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ff7dc465-9868-4c38-9e21-e4e2e2778c78.png)
[Nicotinic or Muscarinic] acetylcholine receptors
Cardiac and smooth muscle
Gland cells
Nerve terminals
Sweat glands
Muscarinic