november 6 lecture
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
name of lecture
Neuroendocrine control of the HPG axis
Core principles of this lecture (7)
• Pulsatile release of GnRH is critical for its function
• Pulse frequency differentially regulates LH and FSH production and secretion
• Normal pulsatile and surge patterns of GnRH release — essential for reproductive function — require kisspeptin signaling
• Kiss neurosecretory cells mediate positive feedback effects of estradiol on GnRH secretion
• KNDy neurons regulate negative feedback to GnRH neurosecretory cells
• The induction of puberty in humans is poorly understood but requires a reduction in the expression of MKRN3
• Stress and low body weight reduce GnRH release and reduce fertility
Reproduction occurs only if sufficient — are present
resources
Primary regulator of gonadotropin secretion is
GNRH
half life of gnrh
under 5 mins
how many peptides in GNRH?
10 (decapeptide)
is gnrh conserved in mammalian species?
yes
— is central to Gnrh’s regulation of the gonadotrope cells
Pulsatile release
Pulsatile release of gnrh is coordinated by —
a neural pacemaker – GnRH pulse generator
GnRH decapeptide forms a —-like shape to interact with its receptor
horseshoe
what happens when gnrh is continuous?
lh and fsh levels drop
GnRH pulse — and — change during the menstrual cycle
frequency and amplitude
t or f
GnRH is not measurable in the systemic circulation
t
how do we measure gnrh?
each pulse in GnRH evokes a pulse of LH; thus, LH pulsatility is often used as an indicator of GnRH pulsatility
when are gnrh pulses the most freqeunt?
right around ovulation
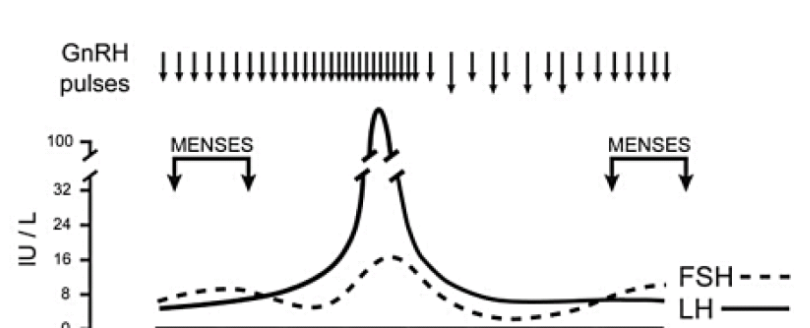
—- pulse frequency of gnrh favors LH Beta gene expression
rAPID
— pulse frequency of gnrh favors FSH Beta gene expression
slow
when grnh pulse is low, when gnrh binds to its receptor, which signalling pathway is set off?
G alpha-s pathway
what does the G alpha-s pathway entail?
adenylate cyclase
cAMP
PKA
CREB
creb TF for FSH
when gnrh pulse is high, and gnrh binds to receptor, what pathway gets set off?
G alpha-q pathway
what happens in the Gaq pathway?
PLC
PIP2 makes (DAG+IP3) and PKC
IP3 releases calcium from ER
PKC induces MEK
MEK induces ERK ½
turns on ELK1
transcribes ERG1
ERG1 increases LH transcription
where is Gnrh released?
the hypothalamic hypophyseal portal system
most amino acids in nature are L or D?
L
when the GNRH molecule is in the horseshoe shape to bind with its receptor, what would happen if you did D-amino acid substitution for all the L-amino acids?
stabilizes the horseshoe conformation
increases binding affinity
enhance the activity of GNRH
why would it be important to know about this D-amino acid substitution?
because that’s one way you can make an agonist drug, it makes it stronger
what are 2 reasons we cant measure GNRH in the blood?
it never gets into full circulation, it only goes through hypophyseal portal system
half life is less than 5 mins
in the follicular phase describe the appearance of LH peaks (whihc are a proxy for GNRH pulses)
relatively low amplitude but frequent
near ovulation describe the appearance of LH peaks (whihc are a proxy for GNRH pulses)
largest amplittude and frequency
in the luteal phase describe the appearance of LH peaks (whihc are a proxy for GNRH pulses)
high amplitude but lower frequency
Two components can change LH/FSH ratio
amplitude of pulse
frequency of pulse
where is activin released from?
cells in the pituitary
is activin a protein?
yes
where does activin bind to?
receptors on the gonadotrope cells
when activin binds to the receptor on the gonadotrope cell membrane, what happens?
apparently it triggers FSh and GNRH secretion??? idk how it can trigger GNRH release?
okay I think her main point is that it locally triggers FSH release
When you have rapid pulses, you also get the production of a locally produced protein called —
follistatin
both— and — block the activity of activin in different ways
inhibin and follistatin
where does inhibin come from?
released by sertoli/granulosa cells following FSh stimulation
how does follistatin inhibit activin?
it acts like a fake receptor kind of, it just like envelops activin and stops it from binding to its receptor
how does inhibin inhibit activin?
it binds to the type 2 receptor for activin but does not activate it, so the receptor is clogged up and then activin cant bind
Which statement correctly describes the role of follistatin in regulating FSH secretion?
A. Follistatin binds to GnRH and prevents its release from the hypothalamus.
B. Follistatin binds to activin and prevents it from binding to its receptor.
C. Follistatin stimulates activin to enhance FSH secretion during slow GnRH pulses.
D. Follistatin acts as an activin receptor antagonist by triggering intracellular signaling.
B. Follistatin binds to activin and prevents it from binding to its receptor.
whats the name of the kiss peptin receptor
GPR54
where is the kiss receptor expressed?
GNRH neurons
LOF mutations in GPR54 lead to —
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
what is hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
the pituitary gland or hypothalamus fails to produce enough gonadotropins (LH & FSH), leading to low sex hormone (testosterone/estrogen) production by the gonads (testes/ovaries), resulting in delayed puberty, infertility, low libido