1. Main Features of Earthquakes & Volcanoes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
How does a volcano form?
A volcano forms when magma erupts onto the Earth’s surface, as lava, through a vent in the Earth’s crust.
How is the magnitude of a volcanic eruption measured?
Through the Volcanic explosivity Index (VEI)
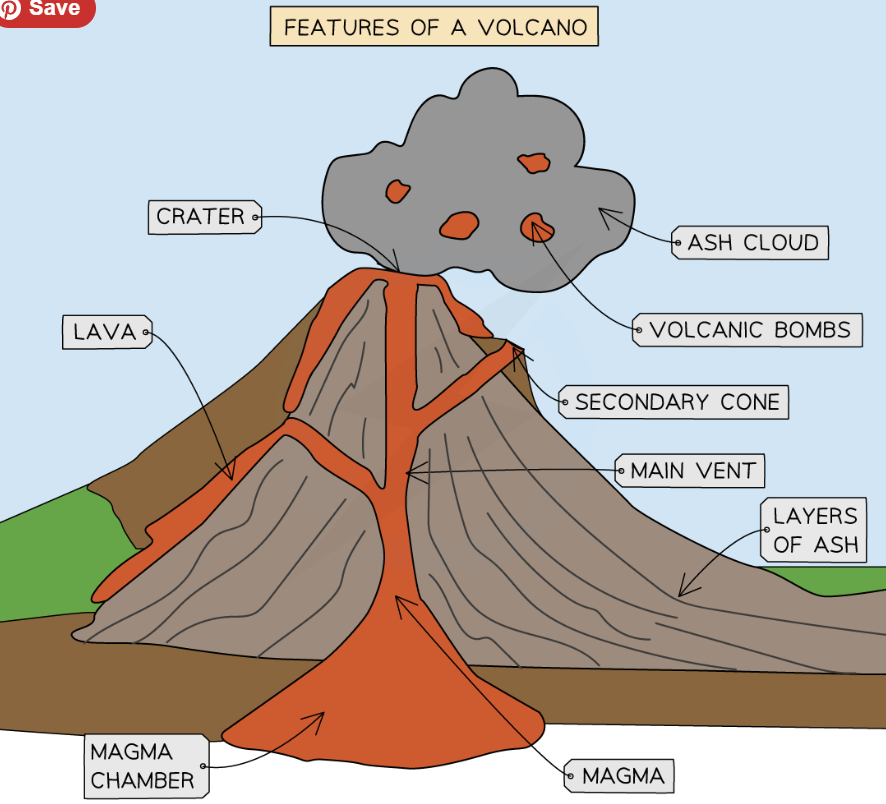
What are the most common features of a Volcanoe?
Crater
Secondary cone
Main Vent
Lava
Volcanic bombs
Ash cloud
Layers of Ash
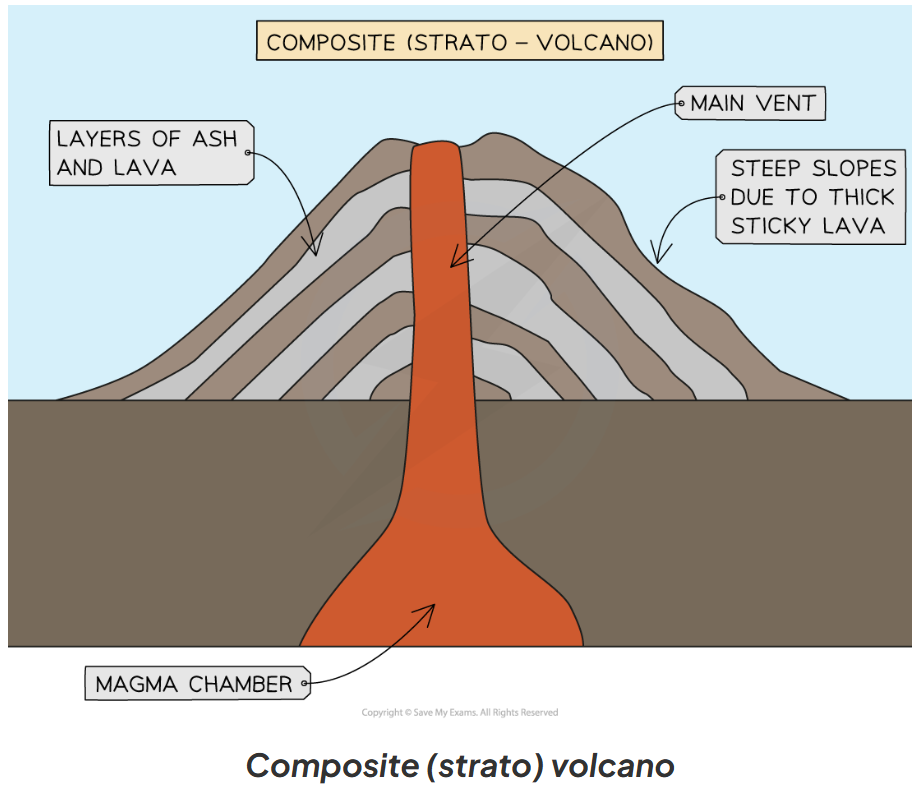
How is a Composite Volcano formed and what are its features?
A composite volcano, also known as a strato-volcano, forms on a convergent (destructive) plate boundary. (going against)
A composite volcano has:
steep-sides
sticky (vicious) lava
more explosive eruptions
alternating layers of ash and lava
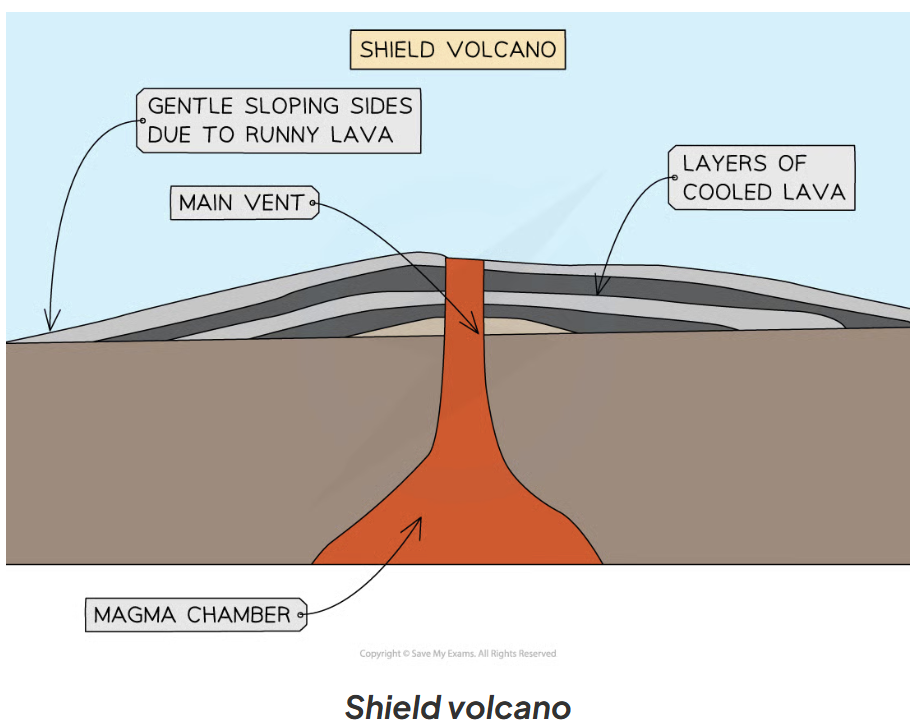
How is a Shield Volcano formed and what are its features?
A Shield Volcano is formed by divergent (constructive) plate boundaries or hot spots.
A shield volcano has:
gently sloping sides
runny/thin lava
less explosive-gentle eruptions
frequent eruptions
What are the three stages a Volcano might be in?
Active; when the volcano has recently erupted and is likely to erupt again
Dormant; when it has not erupted for many years, but there is evidence of a magma reservoir
Extinct; when it does not show evidence of eruption in history times and there is no evidence of a magma reservoir.
What are the features of a Volcanic eruption?
The features of a Volcanic eruption may involve Lava, Ash, Pyroclastic flow, Lahars, Earthquakes and Volcanic bombs
Explain in what shape lava can come as
Lava can come as thin or runny or thick and slow moving.
Explain what Ash is
Ash is pulverised solid lava, which measures less than 2mm in diameter. It is ejected into the atmosphere and can travel thousands of kilometers
Explain what Pyroclastic flow is
Pyroclastic flow is fast-moving, very hot clouds of poisonous gases mixed with ash.
*It can move up to 700km/h
Explain when a Lahar occurs
A Lahar occurs when volcanoes erupt and snow and ice on the peak melts.
→ So that means when snow and ice is present on the top of the volcano and it erupts, it forms a lahar.
The melted water combines with the ash and it creates a fast-moving mudflow or lahars.
What are earthquakes caused by
Earthquakes are caused by magma rising to the surface through the vents in the volcano, therefore, it increases pressure on the earth’s crust, leading to earth tremors.
Define an Earthquake? (2 marks)
An earthquake is the sudden, violent shaking of the ground, which is the result of building pressure when tectonic plates move.
Define epicentre point
The epicentre is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus.
Define focus point
The focus is the point at which the earthquake starts below the Earth’s surface.
Define magnitude
The magnitude is the amount of energy released by the earthquake.
How is magnitude measured?
On the Moment Magnitude Scale → Richter Scale
What is used to measure the damage caused by an earthquake?
The Mercalli Scale
Where do earthquakes usually happen?
Near plate boundaries:
constructive (divergent) → away from each other
destructive (convergent) → towards each other
collision → towards each other but are continental plates
conservative (transform) → slide past each other horizontally
At which plate boundary is the earthquake most powerful?
At a destructive (convergent) plate boundary
At which plate boundary is the earthquake least powerful?
At the constructive (divergent) plate boundary.
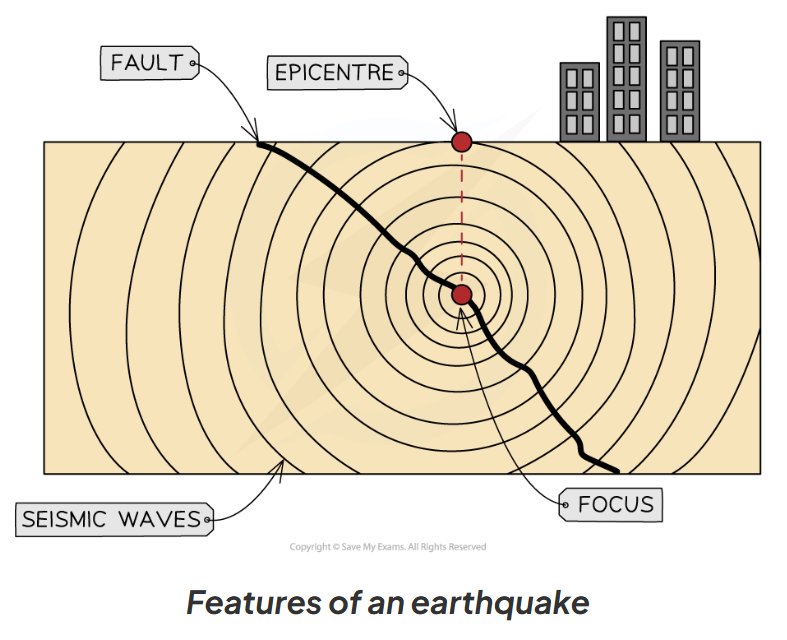
Describe the sequence of an earthquake and define the focus and epicentre.
Plates can get stuck as they move.
Pressure builds as the plates continue trying to move.
Plates jolt free, releasing energy.
Focus: the point inside the Earth where the earthquake starts.
Epicentre: the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus.
Energy spreads through the crust as waves → the earthquake is felt.