Fetal Development (via drew_biegner4)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the stages of prenatal growth?
- germinal period: 0-2 weeks (cells multiply here)
- embryonic period: 2-8 weeks (systems start to form)
- Fetal period: early is 3-6 months and later is 7-9 months (everything matures and begins to function)
What occurs in the germinal period and what is the general timing of it?
- rapid cell division occurs
- Occurs 8-9 days after conception -> implantation to uterus
What are the 3 layers of tissue?
- Endoderm: central nerves
- Mesoderm: bones and the muscles
- Ectoderm: skin
How does the CNS develop?
- in the embryonic period it goes from a primitive streak, to a neural plate, and it then should have a tube fusion at about 28 days
What is the big deal for pre-natal vitamins?
- folic acid, and that helps to promote neural development and the neural tube closing
What occurs in hat embryonic period in 2-8 weeks?
-
What occurs in the feral period?

If you are born <26 weeks what is the risk?
- you are at a higher risk for neurodevelopmental disability
What occurs in the germinal period?
Weeks 0-2
- There is rapid cell division
- Days 8-9 after the implantation to the uterus this is most clear
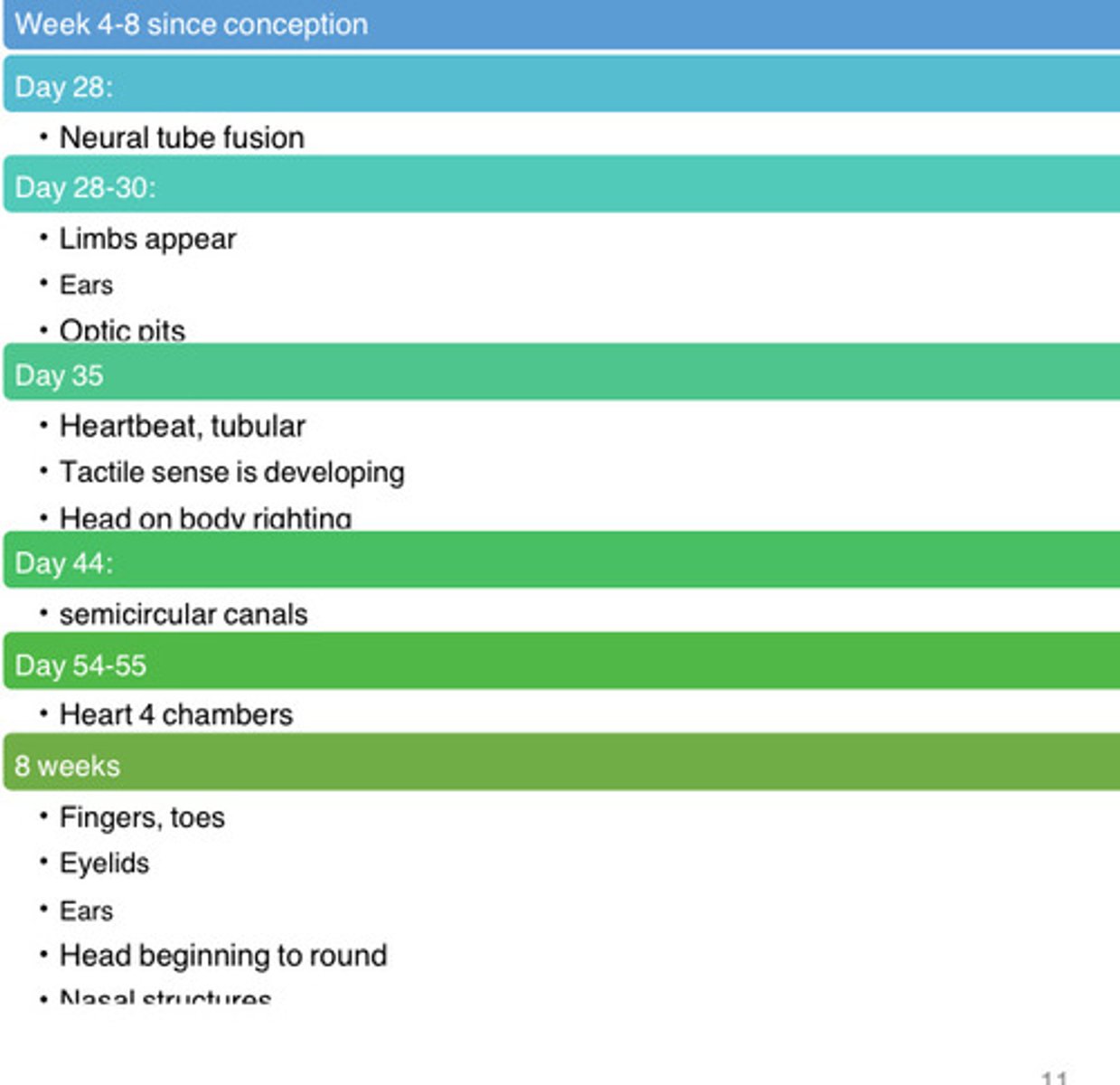
What occurs in the embryonic period? Specifically at day 28, 28-30, 35, 44, 54-55, and at 8 weeks
This is weeks 3-8
- Day 28 there is neural tube fusion
- days 28-30 the limbs appear, ears appear, and optic pits appear
- day 35 there is a heartbeat formation, tactile sense develops, and head on body righting
- Day 44 there is semicircular canal formation
- Day 54-55 there is 4 heart chambers
- at 8 weeks there are fingers, toes, eyelids, ears, and head begins to round
What occurs at week 9?
External genitalia
What occurs at weeks 9-12, 11-13, 13-15, 13-16?
- 9-12 - limb bud grows
- 11-13 - taste bus
- 13-15 - nasal plugs disappear, olfactory nerve grows
- 13-16 - ossification centers appear
- 14: slow eye movement
- 16: eyes and nose move to midline
What occurs at 14 weeks? 16?
- 14: slow eye movement
- 16: eyes and nose move to midline
What occurs at weeks 20-22? At week 23?
- ears are formed, hearing begins, skin develops, surfactant begins to develop
- week 23 is when startle develops
What occurs at 24-28 weeks?
- eyelids separate and blink
- fingernails and toenails appear
What does the 26 week mark in a pregnancy?
- Any baby born prior to 26 weeks risks neurodevelopmental disability
What development occurs at 26 weeks?
- eye lids open
- rapid eye maturation
- rooting reflex
What occurs in weeks 26-28, then 26-29?
- taste is developed, facial movements to bitter
- gyri developments
- pulmonary developments
What occurs in the development from weeks 30-34?
- pupillary reflex and increased survival rate
What occurs from week 35-38?
- grasp
- orient to light
- head and abdomen are same size
- awake visual alertness
What are the 3 trimesters?
FIRST: 1-3mo (week 1-12); SECOND: 4-6mo (weeks 13-27); THIRD: 7-9mo (weeks 28-40)
What is the critical periods of womb development?
- a specific time during development when a particular event has its greatest consequences
- begins and ends abruptly
- if proper stimuli does not occur, development is altered
- Every different part of the body has different critical and sensitive periods, see the attached picture. Red is critical, yellow is sensitive
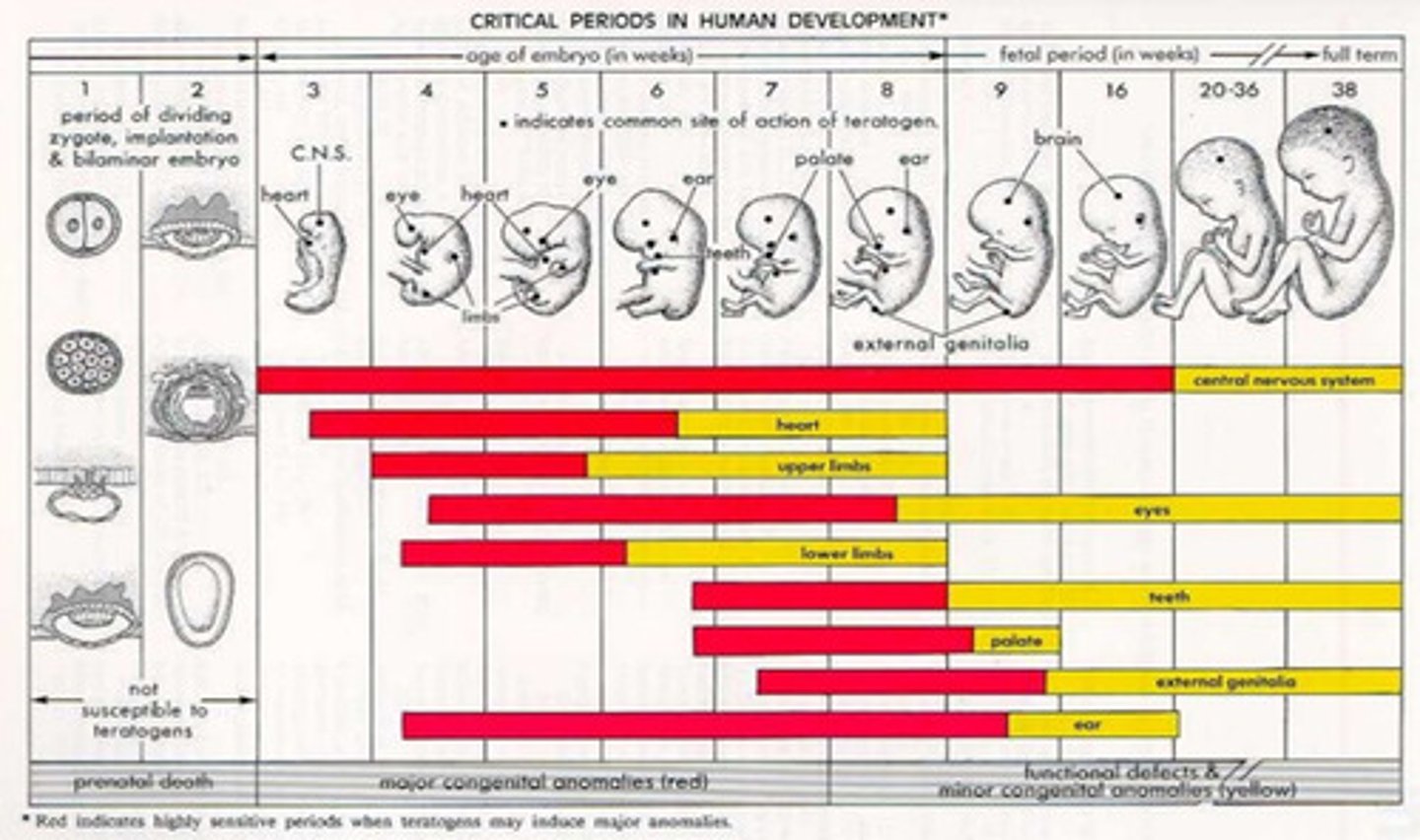
What is the sensitive period of womb development?
- begins and ends gradually
- period of maximal sensitivity
- can still learn after, but not as efficient
What is the critical period for heart?
- week 5 (from conception) is the heart beat
- The first functioning organ in tubular form is the heart
At what weeks can permature babies survive?
- about 21 weeks. Surfactant is made at 21 weeks and that is the vital piece
What is the critical period for the lung?
- Week 21 the surfactant begins to build
- Weeks 26-29 are where the lungs are developed enough to breath
- Week 32: alveoli developed for better gas exchange
What are the critical periods for neural development?
- The primitive streak has its critical period at week 3
- The neural plate and neural tube fusion occurs at week 4
- The gyri forms through week 28
When are their significant developments in bones?
- Day 28-30 there are limb bud appearings
- Day 54-55 or week 9-12 the fingers and toes appear
- Weeks 13-16 the ossification begins
What is the order of development of senses (KNOW THIS!)?
- touch
- vestibular (early proprioception and flip turns)
- smell
- taste
- hearing
- sight
What is the fetal movement in the first trimester?
- hands to face
- jaw movements
- they bend and stretch
- breathing occurs
- UE movements to reach
When can moms start to feel movement?
- 16-18 weeks
What is the fetal movements in the second trimester?
- hiccups, startles, stretches, UE and LE movement, mouths, trunk movements
What is the fetal movement in the third trimester?
- decreased movement overall, face movements increase 26-28 weeks and sleep cycles start
What should we know about primitive reflexes?
- most begin in utero - however the ultimate purpose is not fully understood
- These reflexes are used to evaluate neural system
—— The clinical findings that would warrant further investigation includes no reflexes, weak reflexes, asymmetrical reflexes, or strong reflexes
What can go wrong to impact fetal development?
- teratogens
- heredity
- maternal factors like nutrition, healthcare, exercise
- oxygen deprivation
- low birth weight
- pre-term birth
- post-term birth
What is the difference in postural control between full term and pre-term infants?
- full term: general activity is good with spontaneous kicking/flailing, reflexes are developed and brisk, baby assumes physiological flexion
- Preterm: general activity is poor/diminished, autonomic reflexes are sluggish (suck/swallow), and the baby may assume an extended posture due to low tone
What is low body weight?
- <5# or 2500gms
What is very low body weight?
- <3.3# or 1500gms
What is excessively low body weight?
- <2.2#, 1000gms
What is SGA, LGA, IUGA?
- small for gestational age
- large for gestational age
- intra uterinal growth restriction