Lecture 1 - 3
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Why Study Comp. Org. and Prog.?
Understand the detailed internals of computers; the crucial interactions between hardware and software.

risc-v
Low-level programming, very powerful, close to machine learning, direct access to computer hardware
computer
an electrical mechanism that directs processing of data and performs processing on that data in response to a program

motherboard
relay electric signals from external input devices to the CPU which processes them

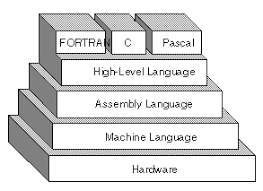
assembly language
a symbolic representation of machine instruction
machine learning
a binary representation of machine instructions
high level programming language
a language composed of words and algebraic notation that can be translated by a complier into assembly language
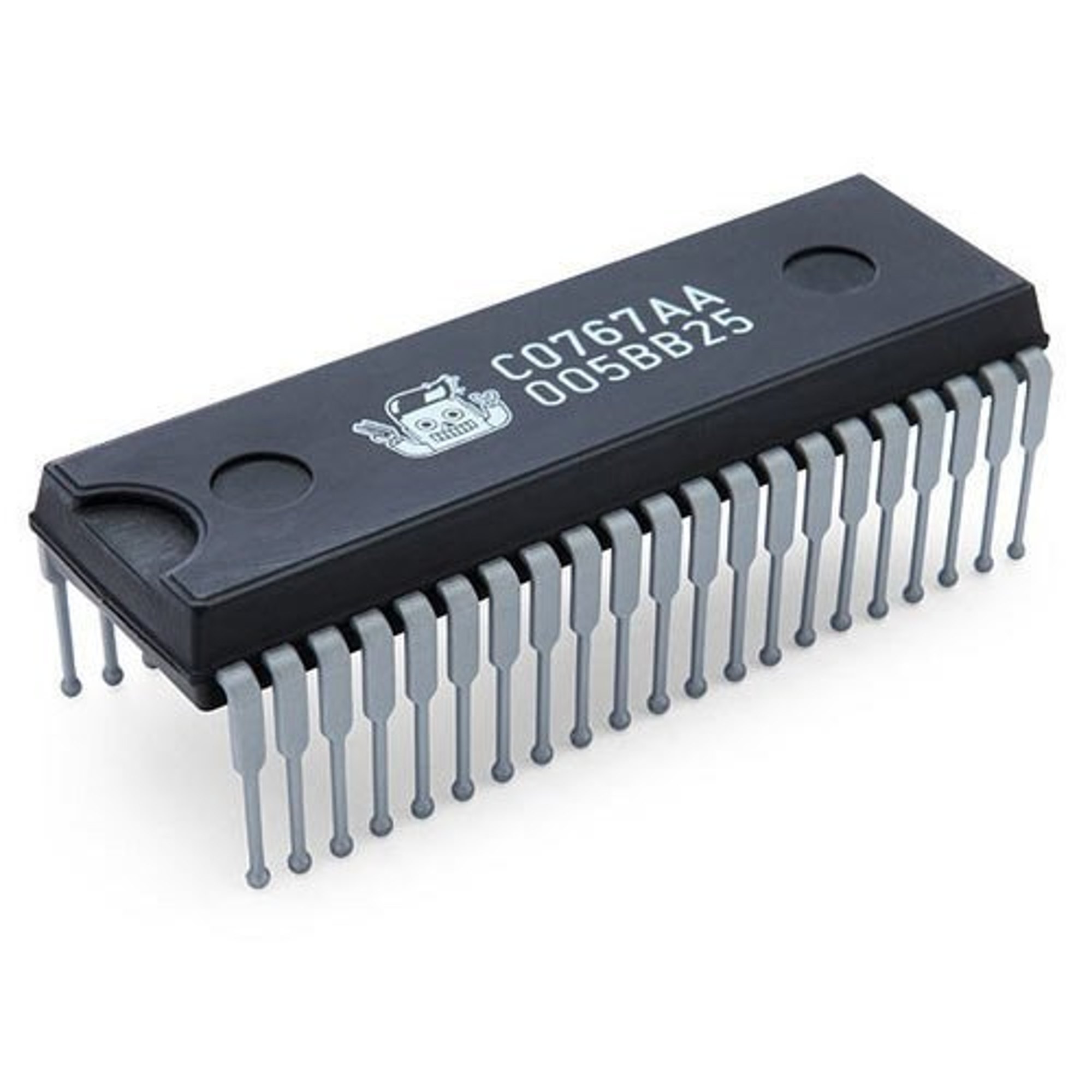
integrated circuit
a tiny piece of silicon that contains a large number of transistors

silicon
a semiconductor made of clay and sand
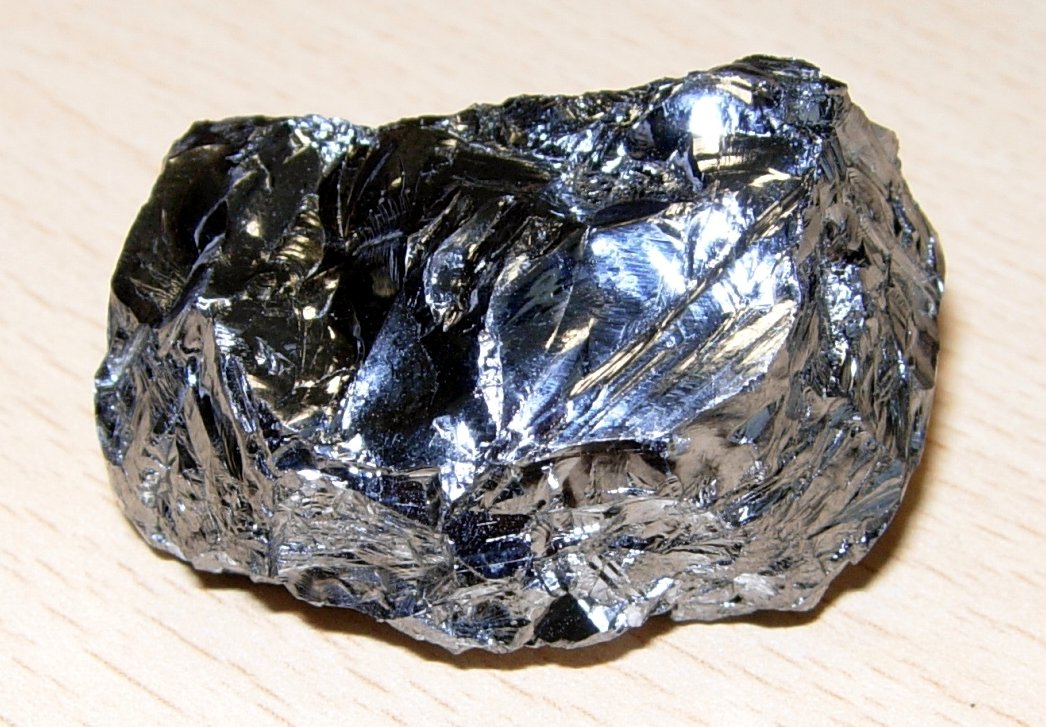

semiconductor
a material whose electrical properties are immediate between a good conductor and a nonconductor of electricity
transistor
a tiny electric switch that can be turned on or off millions of times per second; the building block of any integrated circuit

memory
the storage area in which programs are kept when they are running and that contains the data needed by the running programs
central processor unit
active part of the computer, contains the datapath and control and which adds numbers, test numbers, signals I/O devices to activate, and more

northbridge
connects the CPU to high-speed components; deals with performance-critical components

southbridge
handles slower peripherals and I/O functions; slow runtime because it deals with less performance-sensitive tasks

accelerated graphics port
dedicated slot for graphics cards

peripheral component interconnect
general expansion slots for devices like sound cards, network cards, and modems
serial ata
connects modern storage drives to the motherboard, faster than the ide

basic input output system
firmware stored on a chip, boots up the operating system when the pc turns on
integrated drive electronics
an old storage interface for hard drives and optical drives

processor socket
the physical slot where the CPU is installed, electrical connection from CPU to the rest of the motherboard

electronic numerical integrator and computer
the first programmable, general-purpose, electronic digital computer that was only used for calculations; made in 1945
abstraction
lower level details are hidden to offer a simpler model at high levels

make the common case fast
enhance performance better than optimizing the rare cases

parallelism
compute operations at the same time

pipelining
break tasks into different stages that execute simultaneously

prediction
anticipate future operations to minimize delays, it might be faster to guess and start working rather than waiting to know for sure

hierarchy of memory
the fastest and smallest memory per bit are closest to the CPU. multiple levels of cache bridge the speed gap between the CPU and slower memory (registers - l1 - l2 - l3 - ram - ssd - hdd)
dependability via redundancy
when you include redundant components that can take over when failure occurs (or even detect failures), you make the system more dependable

moore’s law
the number of transistors doubles about every 2 years, leading to faster, smaller, and more powerful computing devices

personal computer
designed for an individual to use, good performance for low costs; drove the evolution of many computing technologies

servers
network based, high capacity, performance, and reliability. high emphasis on dependability. running larger programs for a multitude of people at the same time

super computer
highest performance and cost computers, hundreds and thousands of processers, usually for high end calculations in science and engineering

embedded computer
hidden computers that work as components to a system; widest range of applications and performance

volatile memory
storage that retains data only if it is still receiving power

non volatile memory
a form of memory that retains data even in the absence of a power source

secondary memory
nonvolatile memory used to store programs and data between runs

execution time
the total time required for the computer to complete a task, including disk access, memory access, I/O activities, operating system overhead, CPU execution time, and so on.
throughput or bandwidth
measure of performance, the number of tasks completed per unit time

CPU execution time
the actual time the CPU spends computing for a specific task
user CPU time
the CPU time spent in a program on itself

system CPU time
the CPU time spent in the operating system performing tasks on behalf of the program

clock cycle
the time it takes for one clock period to complete, usually the processor clock, which runs at a constant rate
clock period
the length of each clock cycle
clock cycles per instruction
average number of clock cycles per instruction for a program or program fragment
instruction count
the number of instructions executed by the program