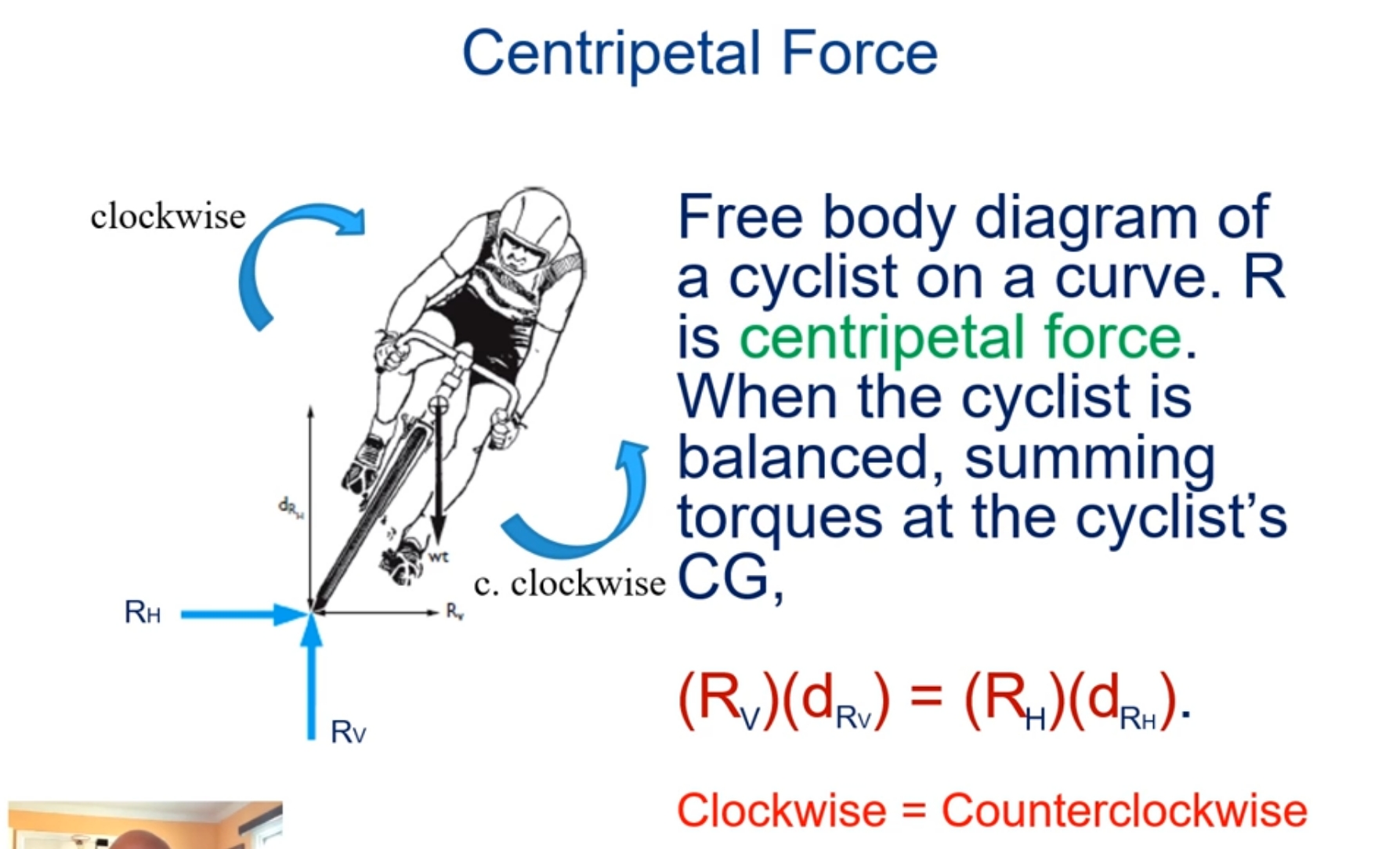
Chapter 14 Angular Kinetics of human movement (KNES 361)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
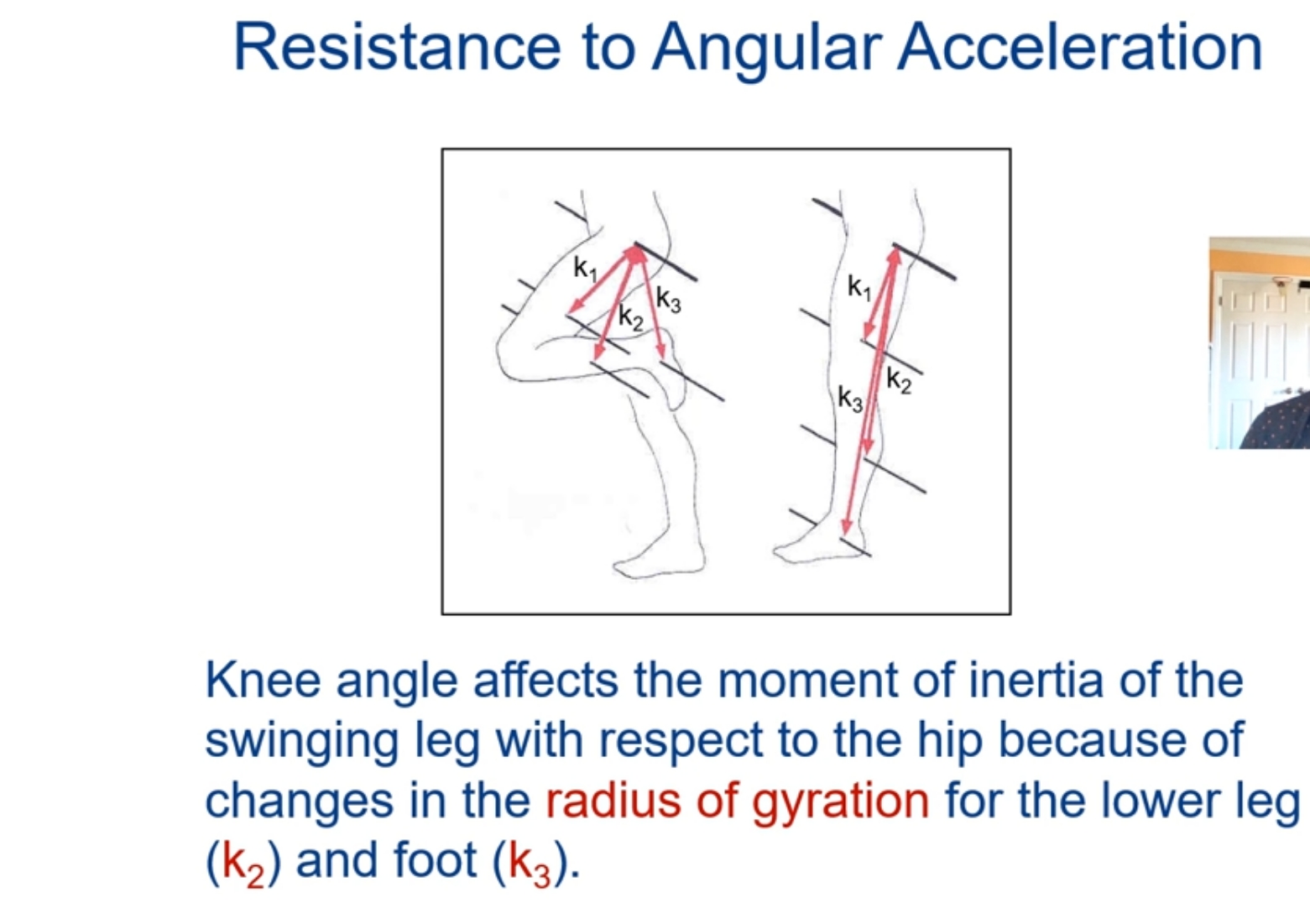
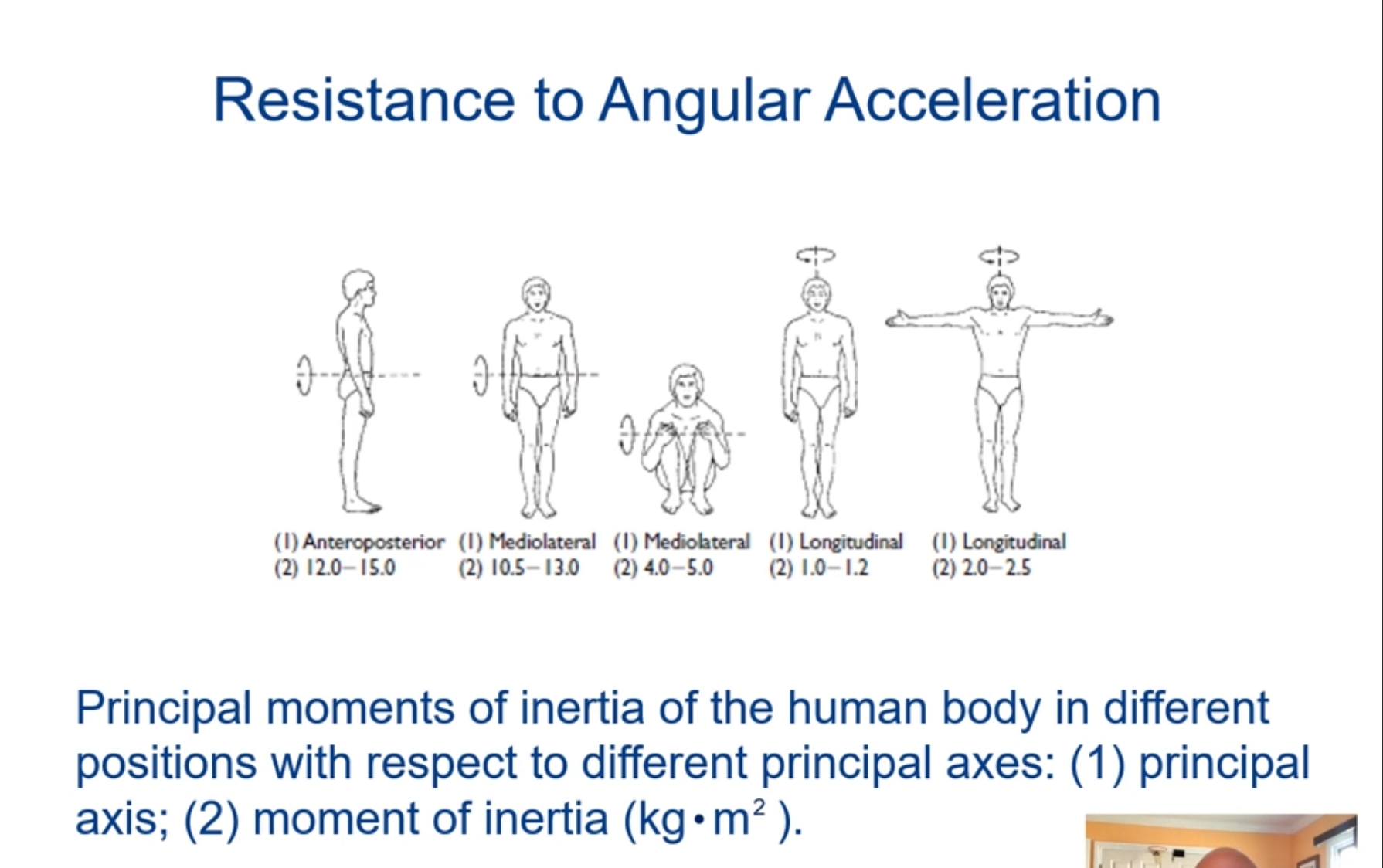
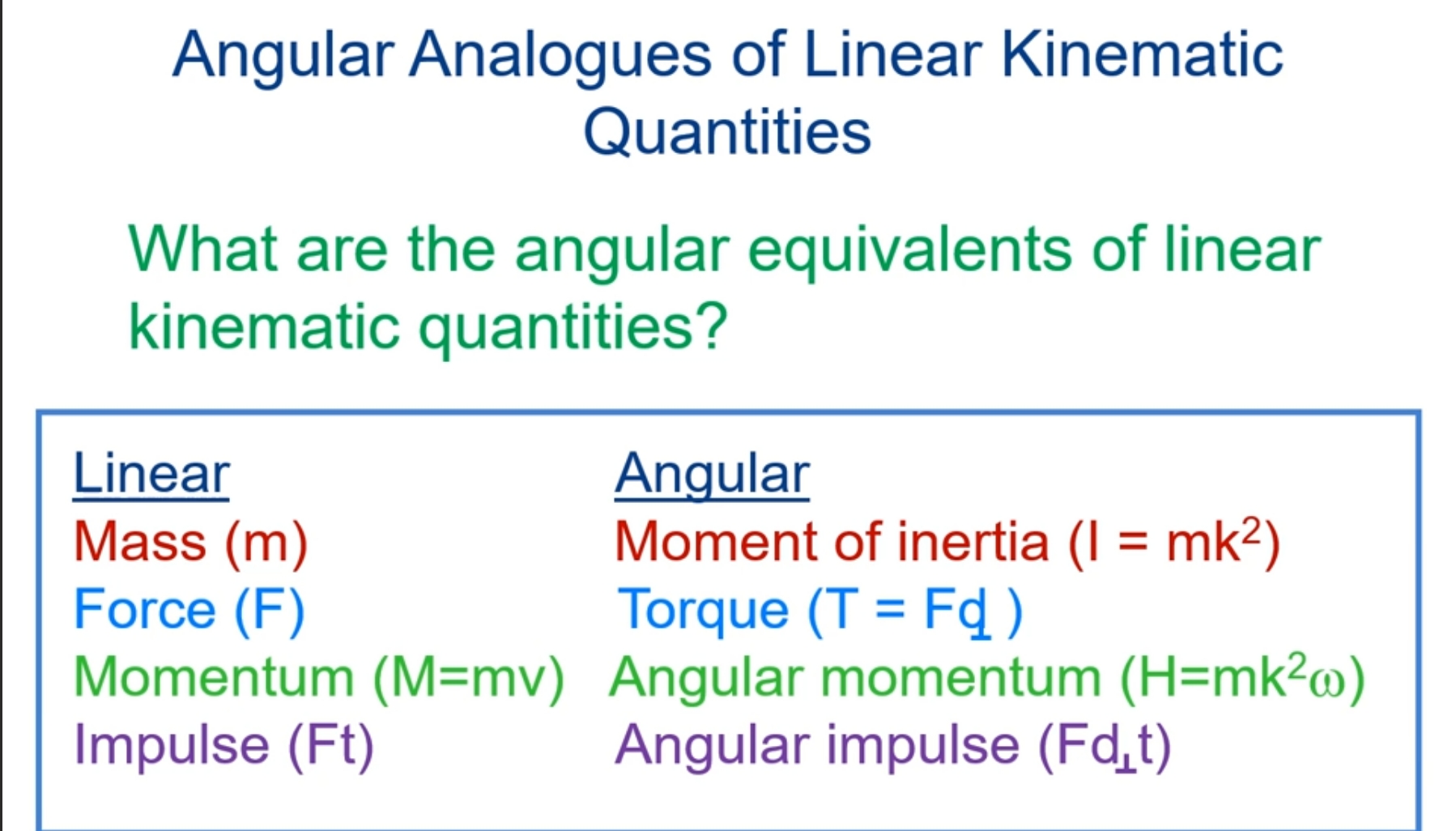
What is moment of inertia?
(Resistance to Angular Acceleration)
The inertial property for rotating bodies represents resistance to angular acceleration based on both mass and distance the mass is distributed from the axis of rotation
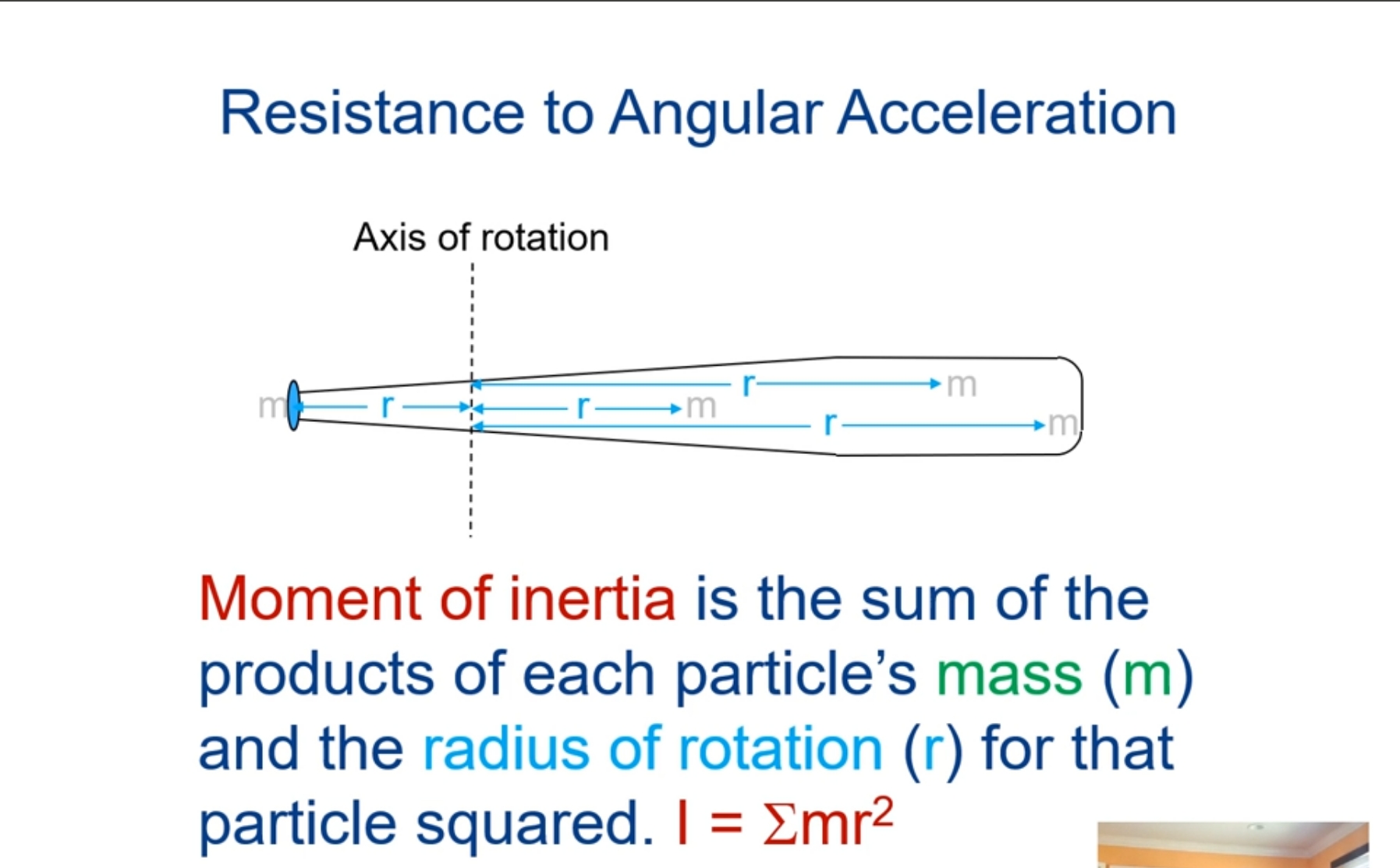

What is the radius of gyration?
Distance from the axis of rotation to a point where the body’s mass could be concentrated without altering its rotational characteristics
Used as the index for mass distributions for calculating moment of inertia:
I = mk²


What is angular momentum?
Quality of angular motion possessed by a body
Measured as the product of moment of inertia and angular velocity
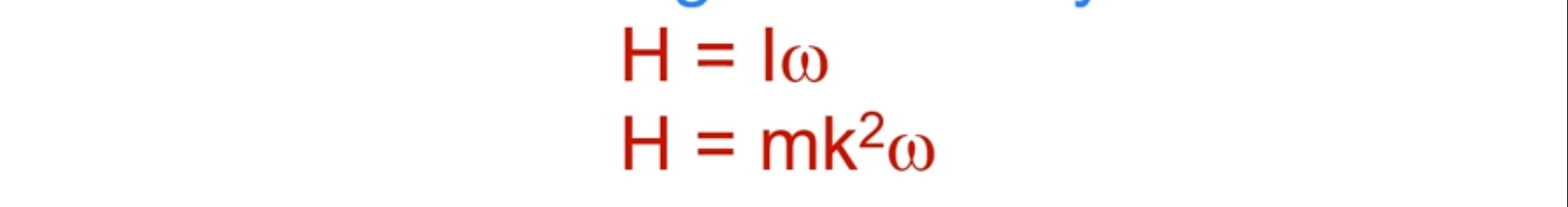
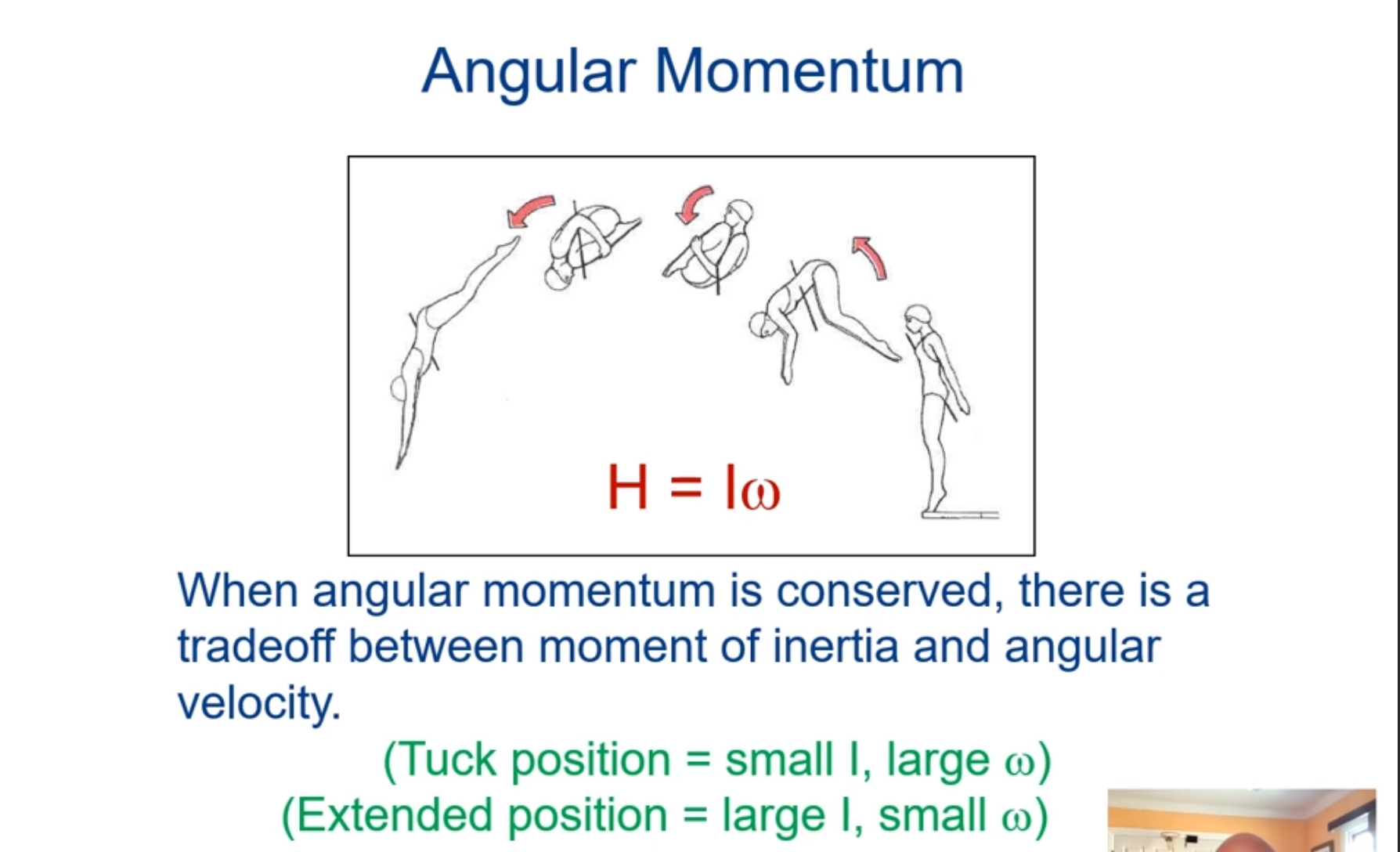
What is the principle of conversation of angular momentum?
The total angular momentum of a given system remains constant in the absence of external torques


What produces change in angular momentum?
Angular impulse- The product of torque and the time interval over which the torque acts:
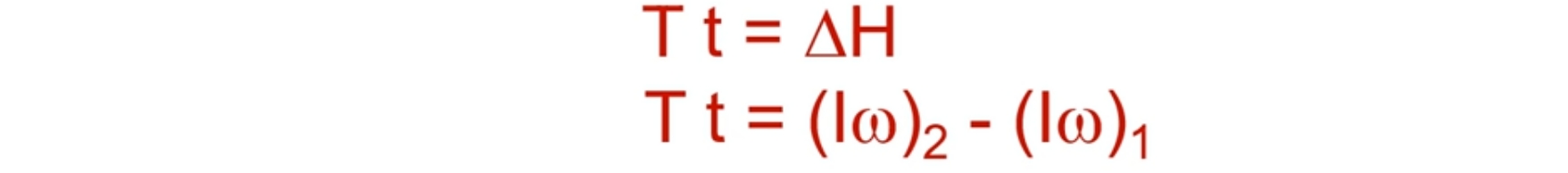



What is the angular law of inertia?
A rotating body will maintain a state of rest or constant rotational motion unless acted on by an external torque that changes the state
What is the angular law of acceleration?
A net torque causes angular acceleration of a body that is
of a magnitude proportional to the torque
in the direction of the torque
Inversely proportional to the body’s moment of inertia

What is the angular law of reaction?
For every angular action, there is an equal and opposite angular reaction
When one body exerts a torque on a second, the second body exerts a reaction torque that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction on the first body