Combined midterm practice (1.2.3 actuals)
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
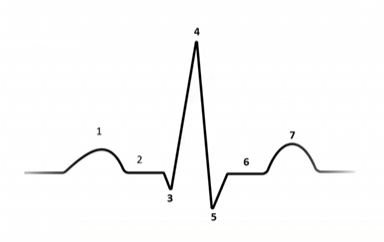
Match the following
1) atrial depolarization
3-5) Ventricular repolarization
7) Ventricular repolarization
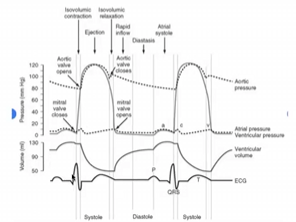
Isovolumic contraction (mechanical) correlates with this portion of the EKG complex (electrical)
R wave
During diastasis, the:
Ventricle filling/atria dumping
While performing an echocardiogram, you are in the parasternal short axis window using an M-mode) you are at the level of the mitral valve) your image contains all structures EXCEPT the:
*Papillary muscles
*interventricular septum
*right ventricle/right ventricular outflow tract
*anterior and posterior mitral leaflets
*pericardium
Papillary muscles
In sequence name the stages of myocardial damage caused by a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle:
Ischemia, injury, infarction
Using the wall motion scoring method, scoring a particular wall segment a “3” represents
Akinetic
using the wall motion scoring method, scoring a wall segment a “3” with no motion and thickening, represents:
Akinetic
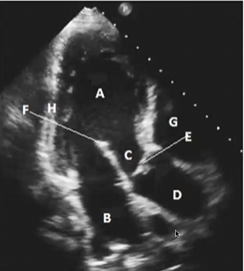
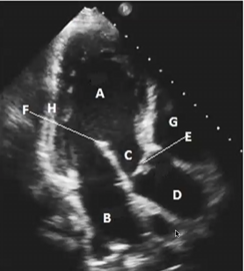
Match the following
A-LV
B-LA
C-LVOT
D-AO ROOT / ASCENDING AO
E-AV
F-ANTERIOR MITRAL VALVE LEAFLET
G-RIGHT VENTRICLE
H-INFEROLATERAL LV WALL
In this image, which portion of the cardiac phase is it in?
Diastole
The signs and symptoms of a myocardial infarction can include all the following except:
1-Hemoptysis
2-Dizziness, syncope
3-Chest pain/ Arm or jaw pain
4-Nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis
5-shortness of breath
Hemoptysis
For a heart attack patient in route to or in the hospital, the first line of defense fro treatment includes all the following except:
1-Nitroglycerin
2-Oxygen
3-Tyenol
4-Morphine
5-Aspirin
Tylenol (remember the MONA acronym)
The sequence in the progression and development of atherosclerosis are:
Fatty steak formation, fibrous plaque formation, complicated lesion
During diastole the:
atrioventricular valves are open and the semilunar valves are closed
When the pressure in the aorta exceeds the pressure in the left ventricle, all the following occurs EXCEPT:
1- chordae tendineae become taught/tight
2-Semilunar valves close
3Ventricular pressure starts to rise
4-Atrial pressure starts to decline
5-Atrioventricuylar valves open
chordae tendineae become taught/tight
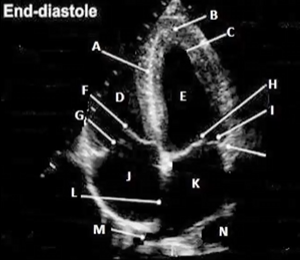
Match the following
A- IVS
B-LV APEX
D-RV
E-LV
F-SEPTAL LEAFLET OF THE TV
G-POST LEAFELET OF THE TV
H-ANTERIOR LEAFLET OF THE MV
I-POST LEAFLET OF MV
K-LA
L-IAS
M-RIGHT UPPER PULMONARY VEIN
N-DESCENINDG THORACIC AO
An ECG can display a STEMI as:
ST segment elevation, inverted T wave, Q wave formation
All the following are complication associated with a myocardial infarction (MI), except:
1- LV aneurysm/ LV thrombus
2-Pap muscle dysfunction / MR
3- Dressler Syndrome
4- LV wall rupture / VSD
5- Aortic insufficiency
Aortic insufficiency
All the following are true facts associated with the anatomy of an artery in comparison to a vein, except:
1- Small lumen
2-Thicker outer wall
3-Carries oxygenated blood
4-Has valves inside the lumen
5-Consists of elastic fibers in the thicker inner wall
Has valves inside the lumen
T or F: Cardiac markers/enzymes and proteins are used to detect myocardia injury and infarct, such as CPK, CK, Troponin T and troponin I
True
The key factors associated with ischemic heart disease or myocardial infarction, include all the following except:
1-Smoking
2-atheroclerosis
3-race/gender
4-renal disease
5-systemic hypertension
6-hyperlipidemia
7-genetic/family history
renal disease
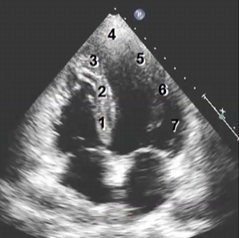
Match the following
1-Basal inferoseptal wall - RCA
2-Mid inferoseptal wall - RCA / LAD
3- Apical septal wall - LAD
4- Apex - LAD
5- Apical lateral wall - LAD/LCX
6- Mid anterolateral wall LAD/LCX
7- Basal anterolateral wall - LAD/LCX
The upper limits of normal for the left ventricular internal dimension in diastole for woman is:
5.3 cm
All the following can result in an increase demand or myocardial workload and can cause IHD or a myocardial infarction, except:
1- Extreme physical exertion
2- severe systemic HTN
3-hypertrohic cardiomyopathy/ HOCM
4-Increase aortic diastolic pressure
5-Severe aortic stenosis
Increase aortic diastolic pressure
The volume of blood in the ventricles at end diastole in diastole is called the:
pre load
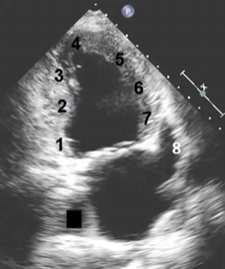
Match the following
1- basal inferior wall - RCA
2- Mid inferior wall - RCA
3- Apical Inferior wall - LAD
4- Apex - LAD
5-Apical anterior wall - LAD
6-Mid anterior wall - LAD
7- Basal anterior wall - LAD
8- Left atrial appendage
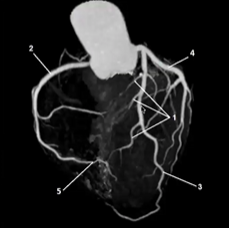
Match the following
1-Spetal perforators
2-RCA
3-LAD
4-Left circumflex
5-Posterior descending artery
The degree of fiber stretch due to the quantity of blood in the chamber prior to contraction at end diastole is known as:
Left ventricular end diastolic pressure
The layer of the arterial wall that consists of loose fibrous connective tissue and provides strength to the vessel is:
Tunica externa
The length tension relationship that refers to the more blood that enters the ventricle during diastole, the greatest the force of contraction required to eject the blood is called the:
Frank starling law
The upper limits of normal for left ventricular end diastolic volume for a man is:
150 mL
Some treatment options used for patients during or following a myocardial infarction (MI), include all the following except:
1-PTCA, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
2-CABG, Coronary artery bypass graft
3-Stress echocardiogram
4-Bed test, telemetry, medical therapy, drugs, oxygen, thermolytic therapy, pain relievers, nitrates
5-AICD, defibrillator, LVAD, RVAD assisted devices
Stress echocardiogram
The upper limits of normal for left atrial volume indexed is:
34 ml/m2
The apical 4 chamber view is used to evaluate all he following except:
1-Aortic valve pathology
2-LV diastolic function
3-chamber sizes
4-pericardial effusion
5-MV and TV pathology
6-LV and RV systolic function
Aortic valve pathology
The upper limits of normal for left ventricular end diastolic volume indexed for a man is:
74 ml/m2
possible causes of myocardial infarction include all the following except:
1-Coronary artery spasm
2-decreased myocardial workload/demand
3-atherosclerosis
4-coronary artery thrombosis
5-decreased blood flow
decreased myocardial workload/demand
The most accurate to calculate the left ventricular ejection fraction is by:
bi plane Simpsons method of discs
The sax aortic level view is used to evaluate all the following except:
1-Aoritc valve pathology
2-TV and PV pathology
3-ASD and VSD
4-MV pathology
5-RVOT, LA, and RA chamber size
MV pathology
Occasionally the origin of the right coronary artery can be visualized by echo in this view(s)
PLAX and PSAX
The wall motion abnormality that demonstrates little or decreased motion and thickening is calls
Hypokinetic
On and ECG, Ischemia is demonstrated as _______, injury as ________ and infarction as ________.
Inverted T wave/ST depression
ST elevation
Deep q wave / ST elevation
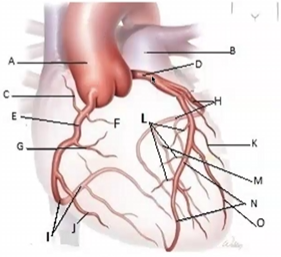
Match the following
A-Aorta
B-Pulmonary artery
D-Left main coronary
E-Right coronary
H-Left circumflex
N-Left anterior descending
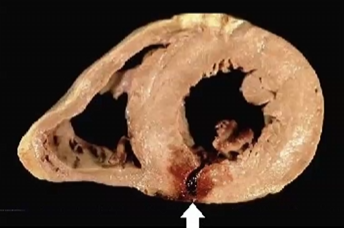
What type of injury has occurred
subendocardial/ Non transmural
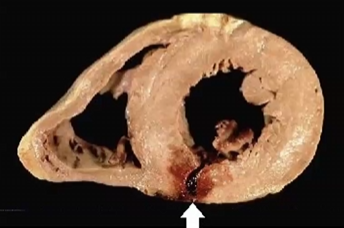
What wall segment is involved in this injury
Inferior wall MI - RCA
The mid inferoseptal territory is supplied oxygenated blood via this artery (ies)
RCA/LAD
From the parasternal short axis view, blood moving through the tricuspid valve during diastole is moving:
Towards the transducer, red
From the parasternal short axis view, blood moving through the pulmonic valve during systole is moving
away from the transducer, blue
From the apical four chamber view, blood moving through the tricuspid valve during diastole is moving
towards the transducer, red
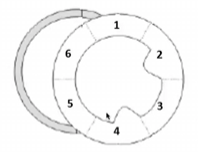
Match the following
1- Mid anterior - LAD
2-Mid anterior lateral - LAD/CX
3-Mid inferior lateral - RCA / CX
4- Mid inferior - RCA
5-Mid inferior septal - LAD/RCA
6-Mid anterior septal - LAD
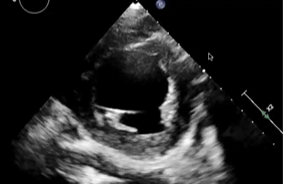
Estimated EF
30-40% (in the clip the more anterior wall is not moving )
M-mode ejection fraction (M-mode EF)
(4.7)3-(3.3)3 x 100 =
(4.7)3
65% (Normal)
Cardiac output indexed (M-mode)
First get SV SV = EDV - ESV
(4.7)3-(3.3)3= 67.89
Second get CO CO = SV x HR
67.89 × 84 / 1000 = 5.7
Third now get COi CO / BSA
5.7 / 1.7 = 3.35 L/min/m2
3.35 L/min/m2 (Normal)
2D Ejection fraction (2D area length EF)
Calculate Diastole and systolic values for EDV and ESV by the area and length methods
EF = EDV - ESV / EDV x 100% =
112.9 - 82.64 / 112.9 × 100% =
26.8% (BAD)
Left atrial volume indexed (2D area length method)
First calculate LA volume
LA volume = 0.85 x (a1 x a2 / L)
0.85 x (21 × 19 / 1.7) = 72.6
Second calculate LA volume indexed
LAVI = LA volume / BSA
72.6 / 1.7 =
42.45 mL/m2 (Dilated)
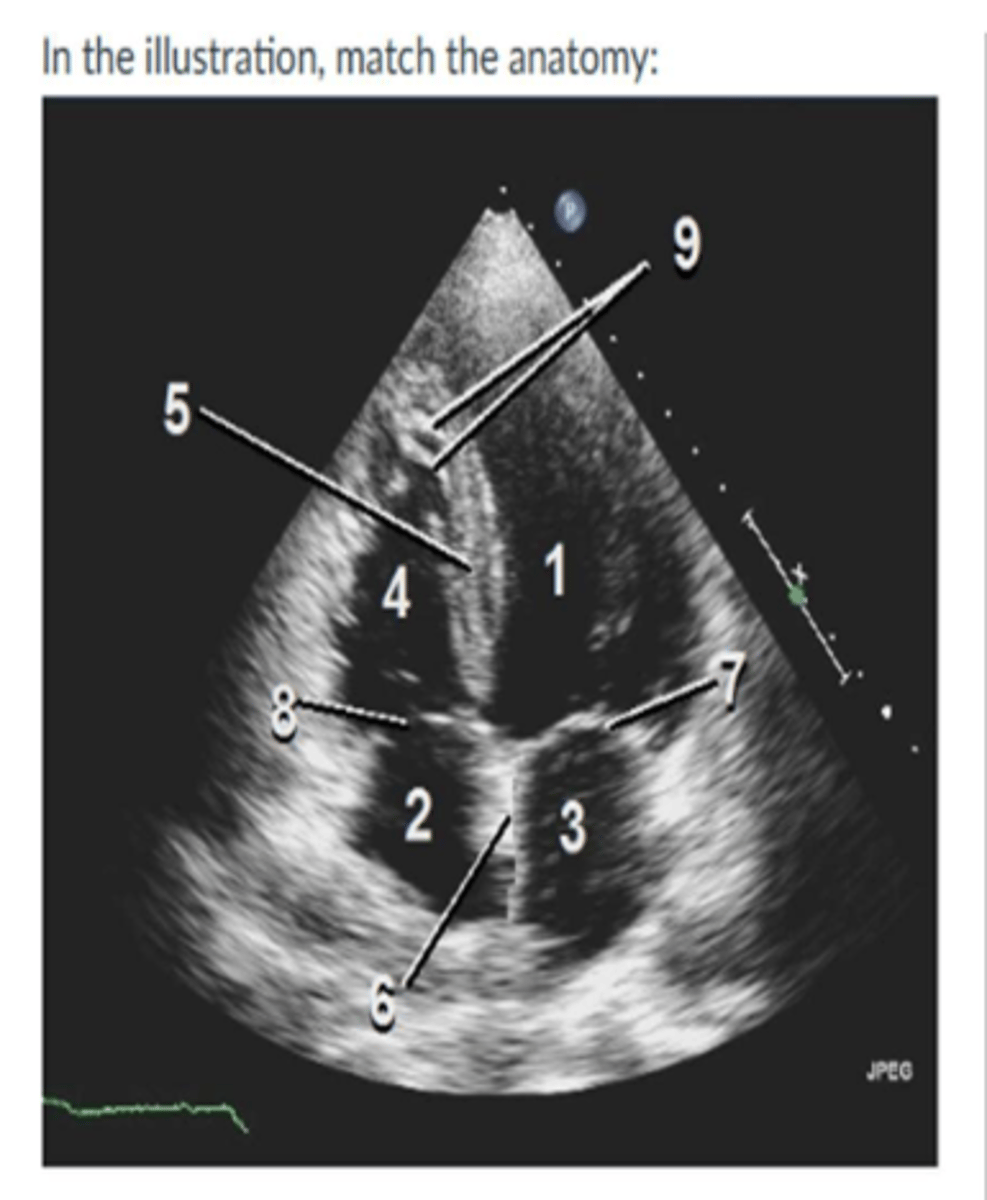
Image:
1. left ventricle
2. right atrium
3. left atrium
4. right ventricle
5. IVS
6. IAS
7. MV
8.TV
9. Moderator Band
The length-tension relationship that refers to the greater the stretch of the cardiac muscle or volume of blood in the ventricles during diastole, the greater the force of contraction required to eject the blood is called the:
Frank-starling law
Your patient has left atrial volume of 45ml, and a body surface area of 1.8m^2. This measurement is considered:
Normal
In M-mode of the aorta, what chamber is above the aortic root.
right ventricular outflow tract
T/F: during the rapid filling phase, the pressure in the aorta is greater than the ventricular pressure.
True
Image:
1. RV
2. TV
3. RA
4. IVC
5. Anterior leaflet
6. posterior leaflet
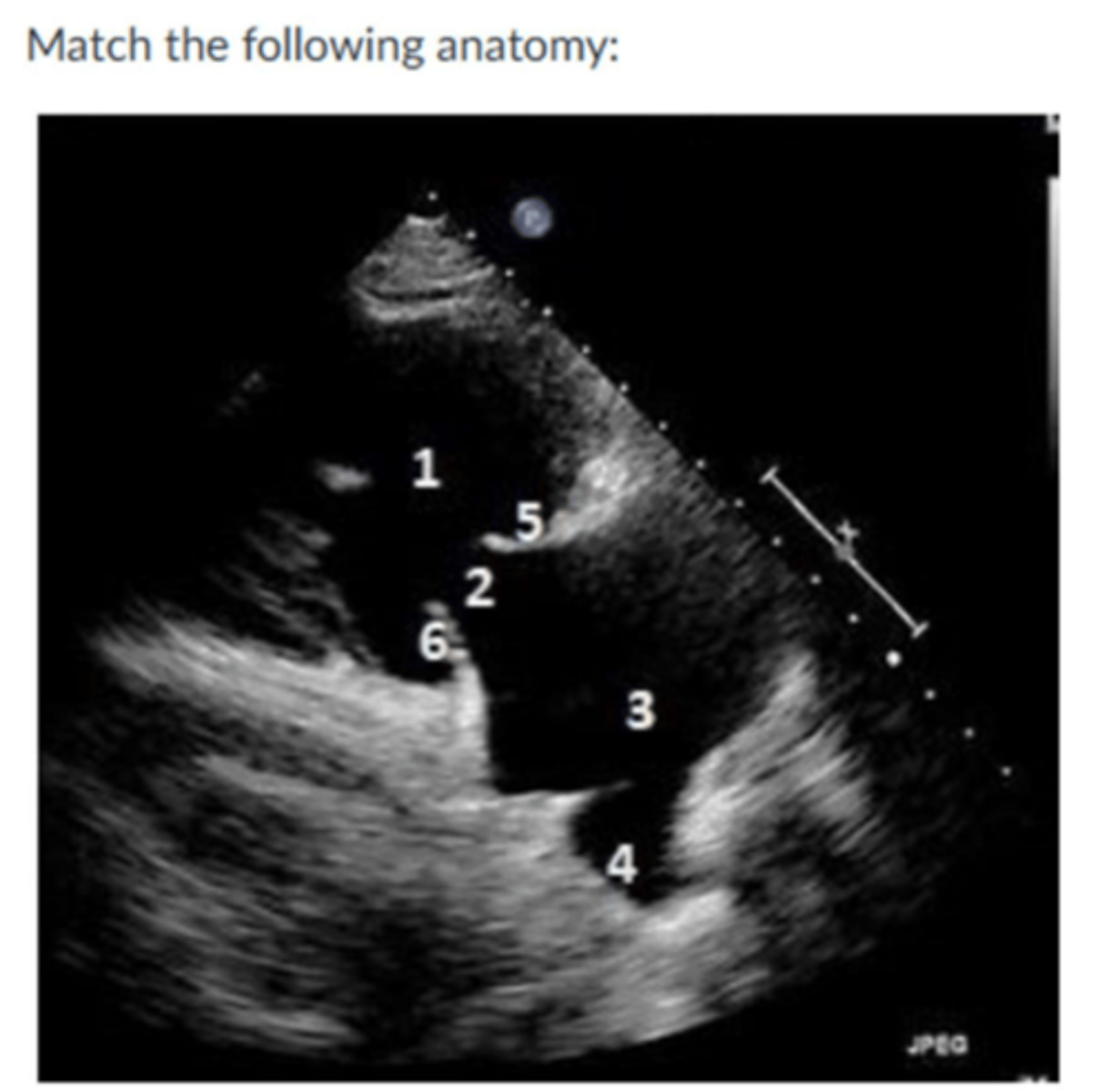
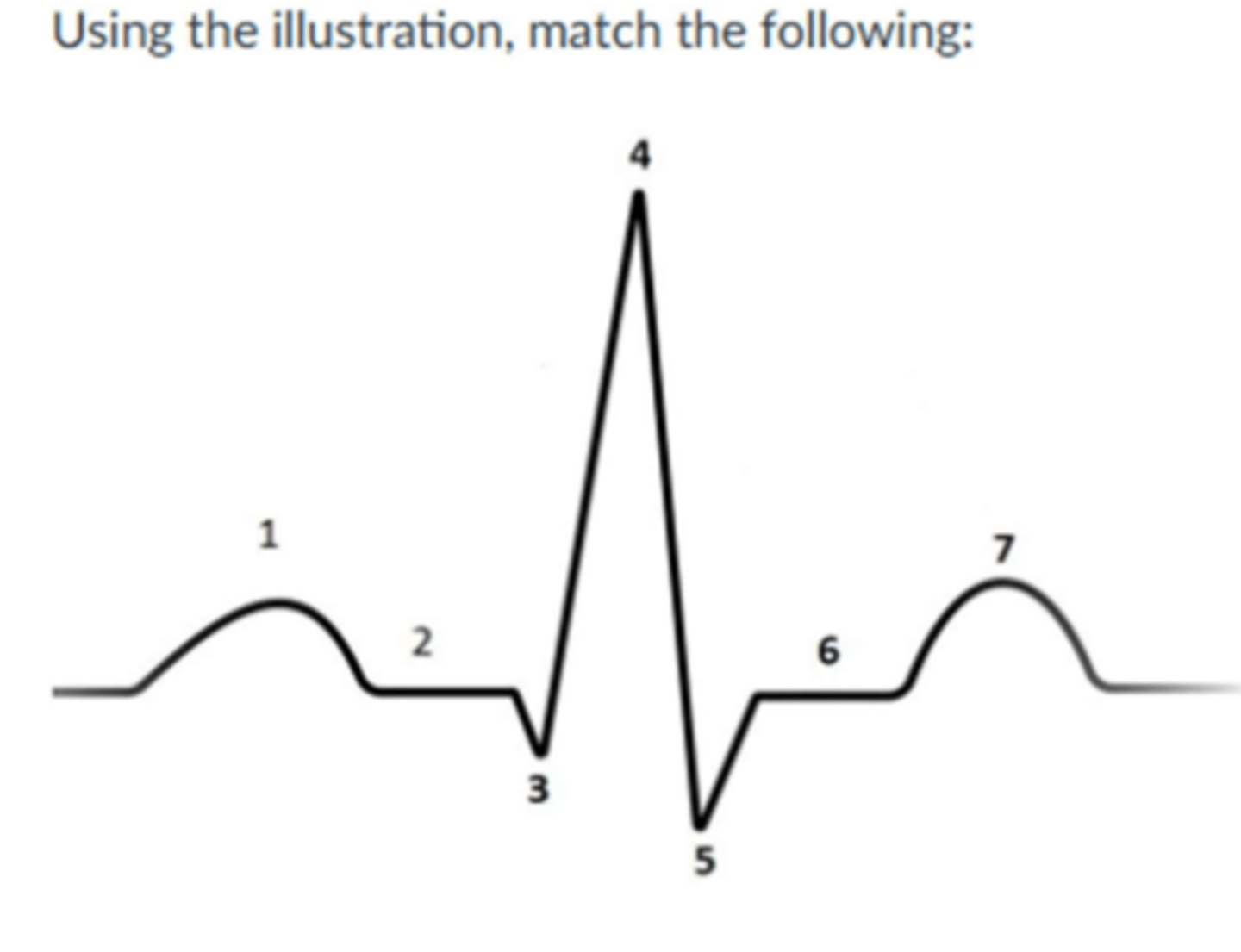
Image:
1. p wave/ atrial contraction
2. QRS complex
3. T wave
4. R wave
All the following are true facts about the left atrial appendage, except::
Helps in the conduction pathway
Stroke volume is defined as:
The volume of the blood pumped out the ventricle per beat or contraction
T/F: The semilunar valves are tethered by chordae tendineae and are attached to papillary muscles
False
Image:
Phase 6
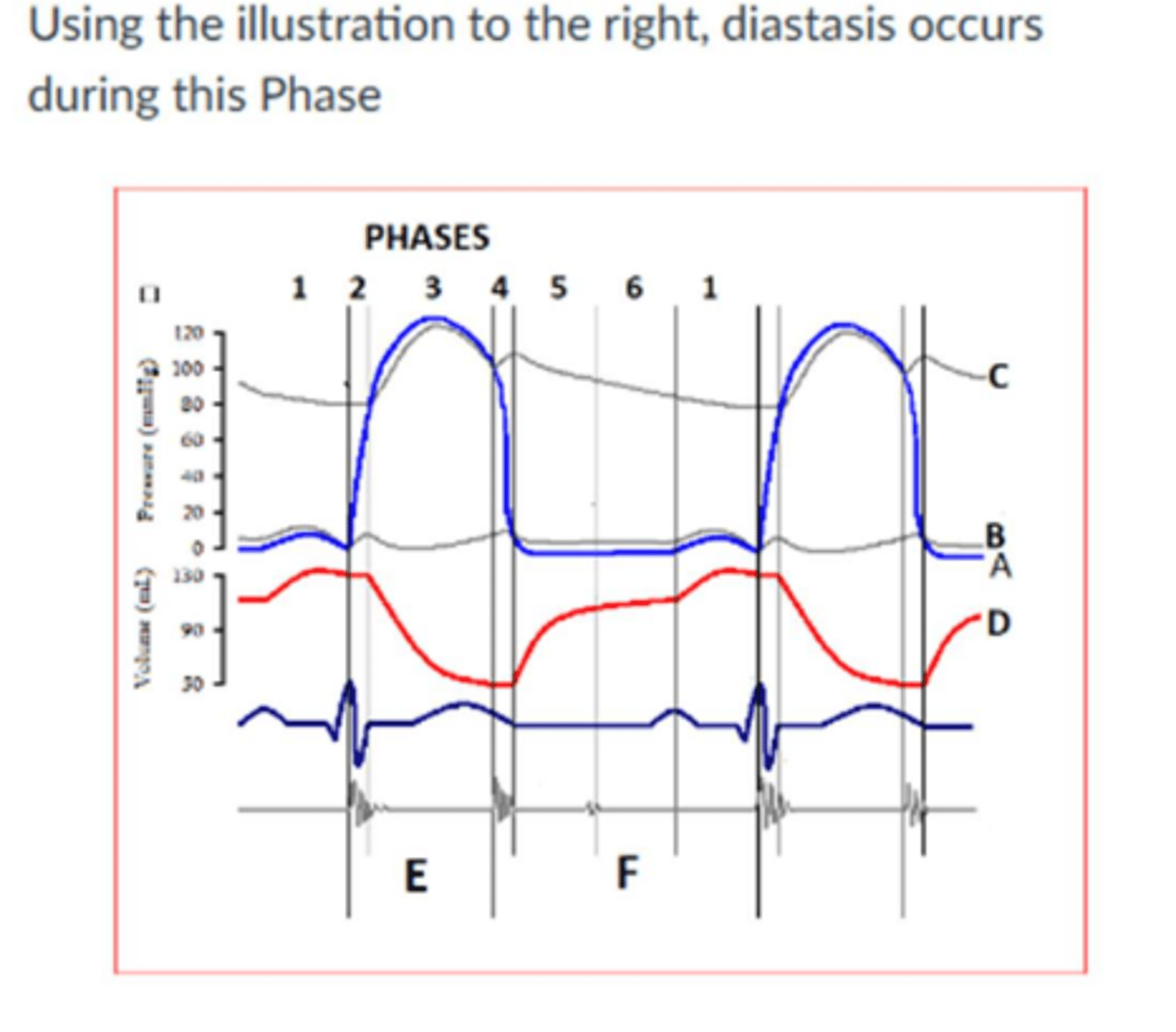
Image:
Left ventricular
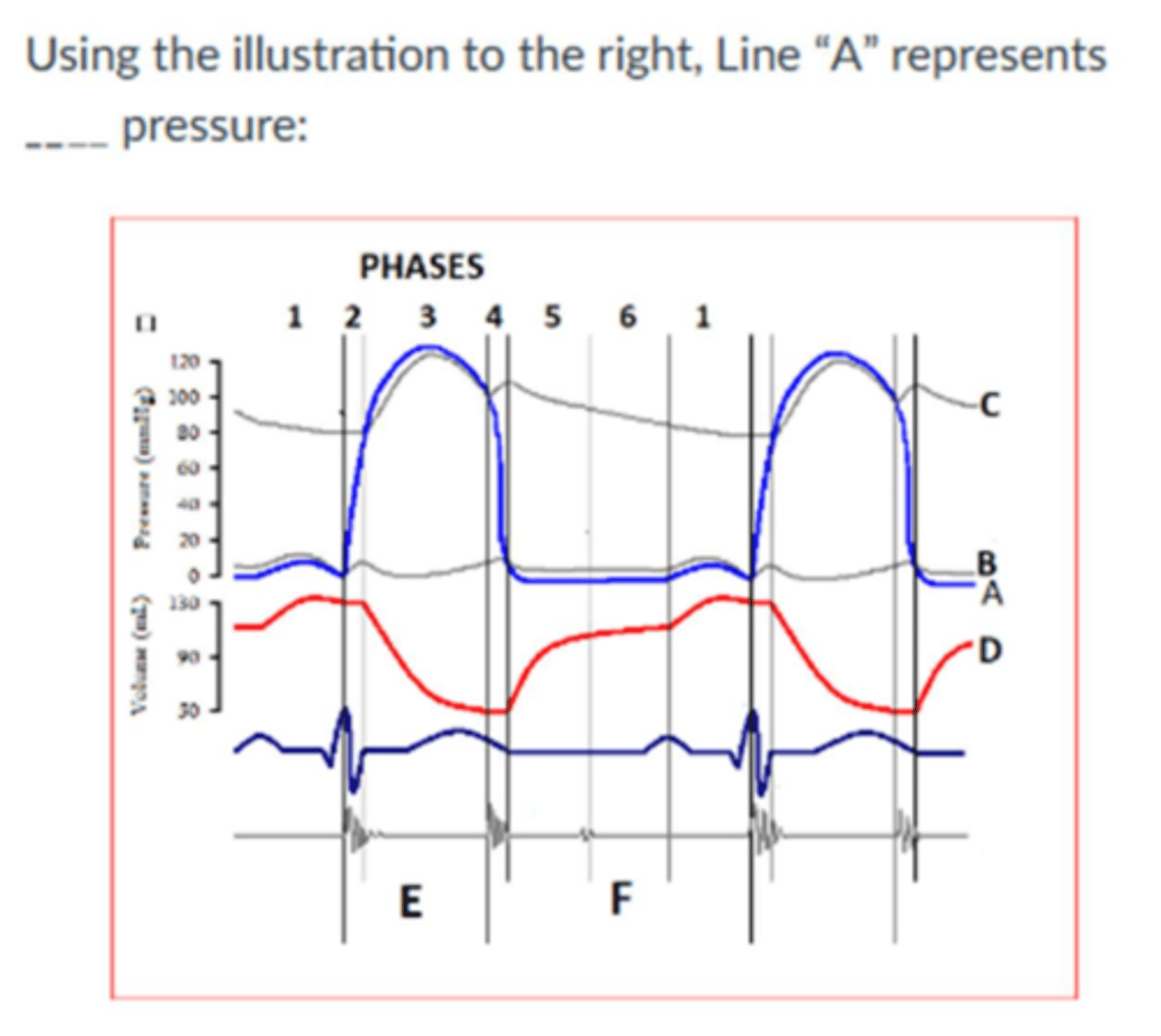
Image:
80 mmHg
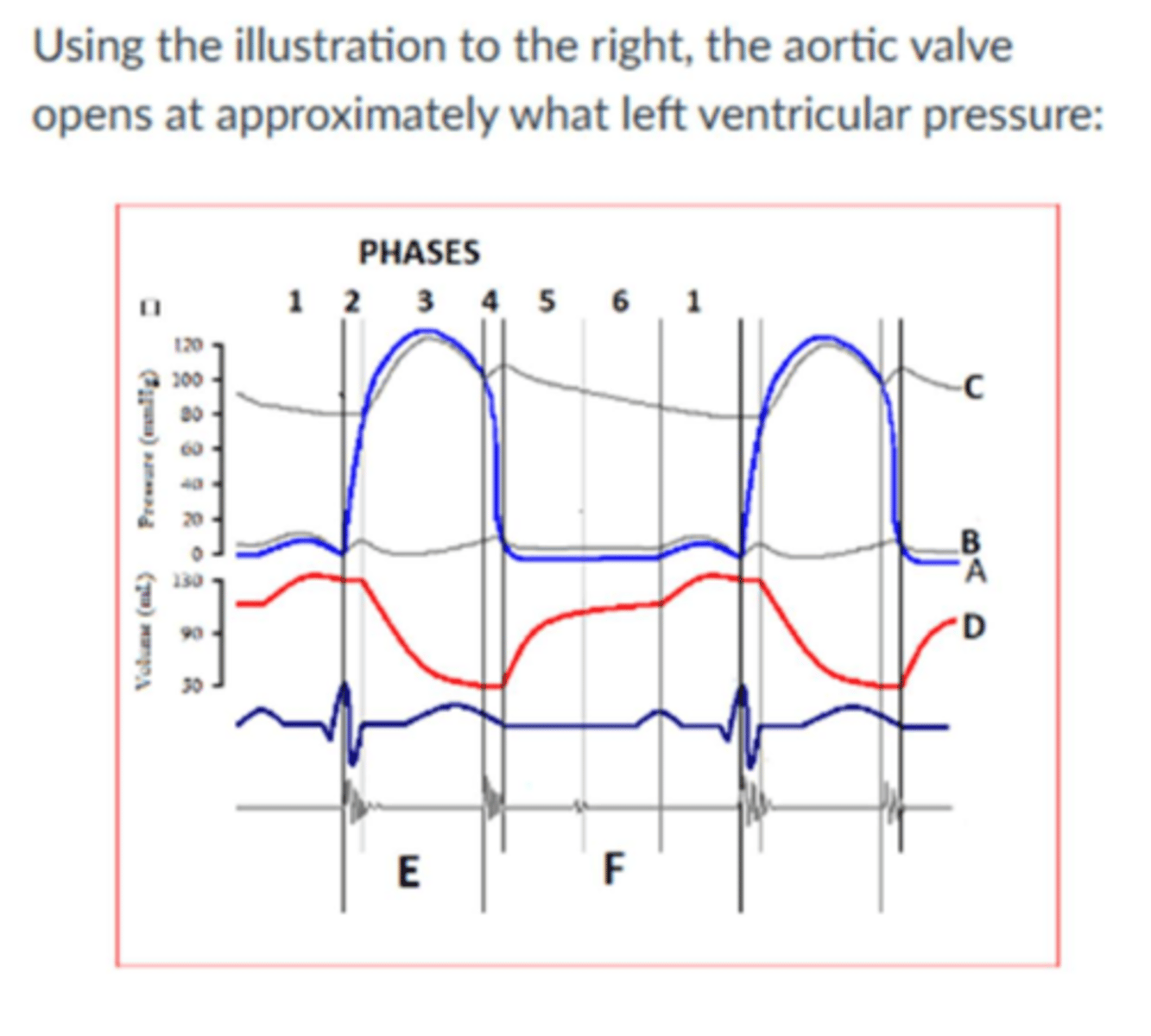
Image:
Aortic root
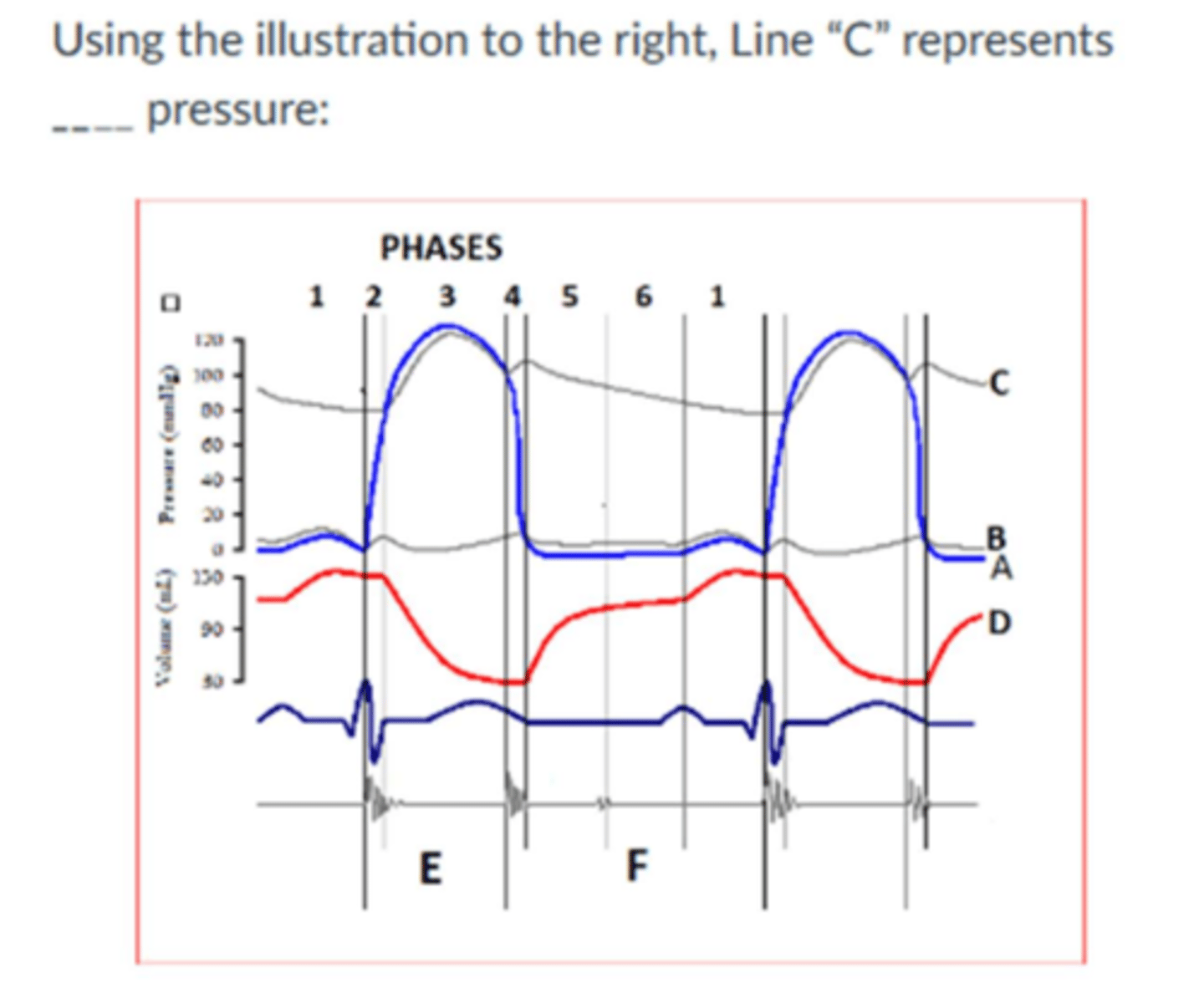
Image:
5 mmHg
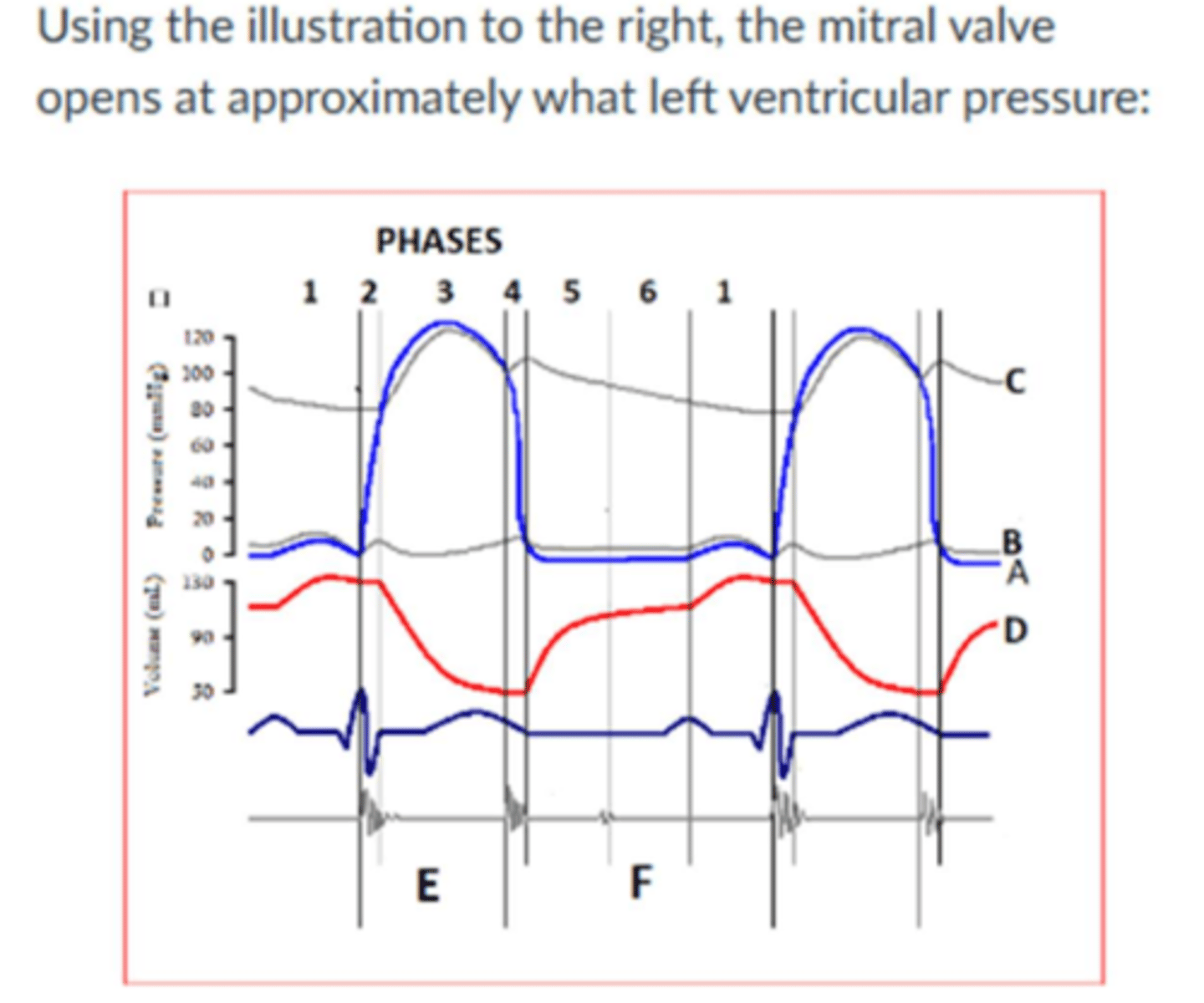
Image:
Phase 4
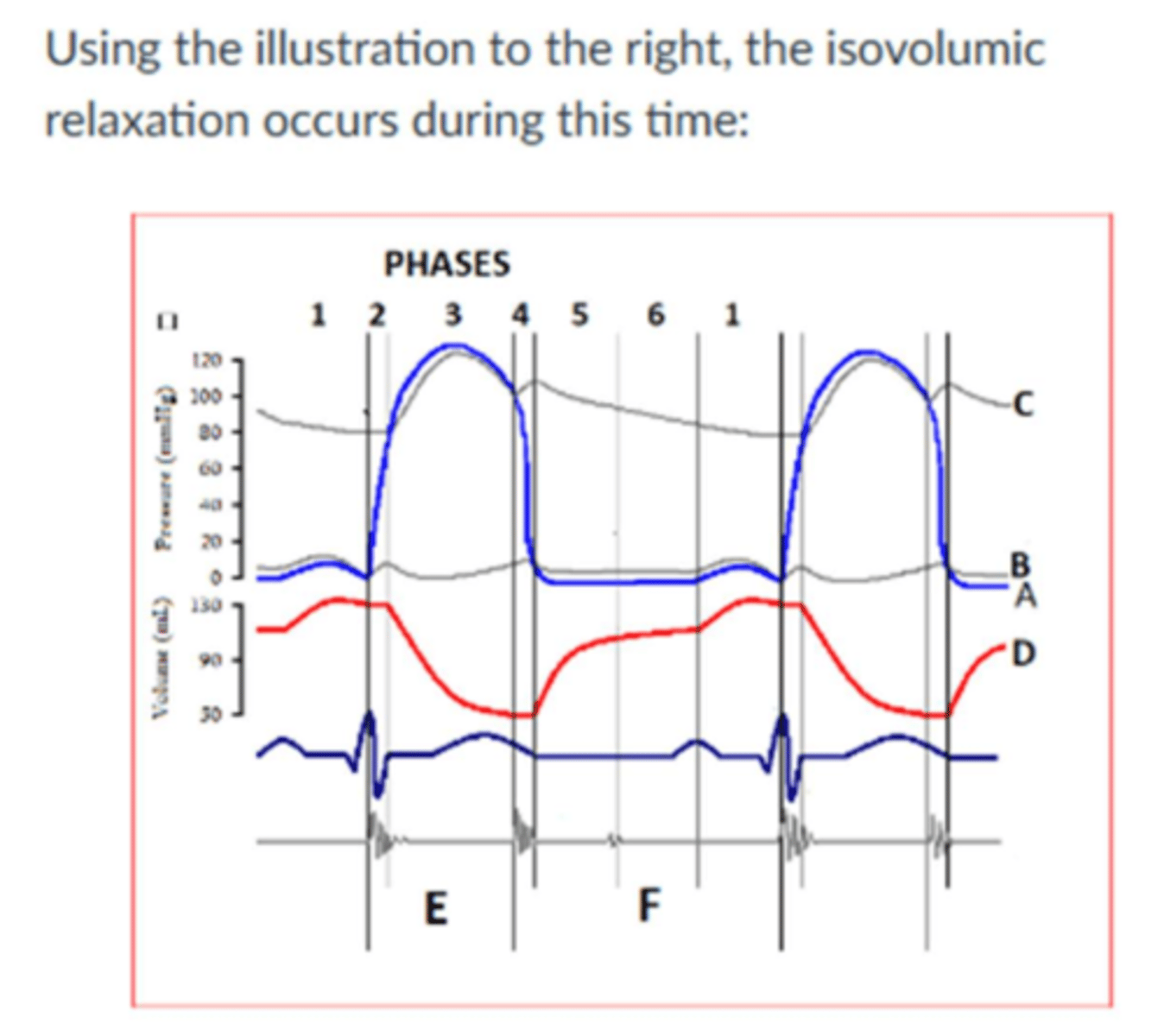
Image:
100 mmHg
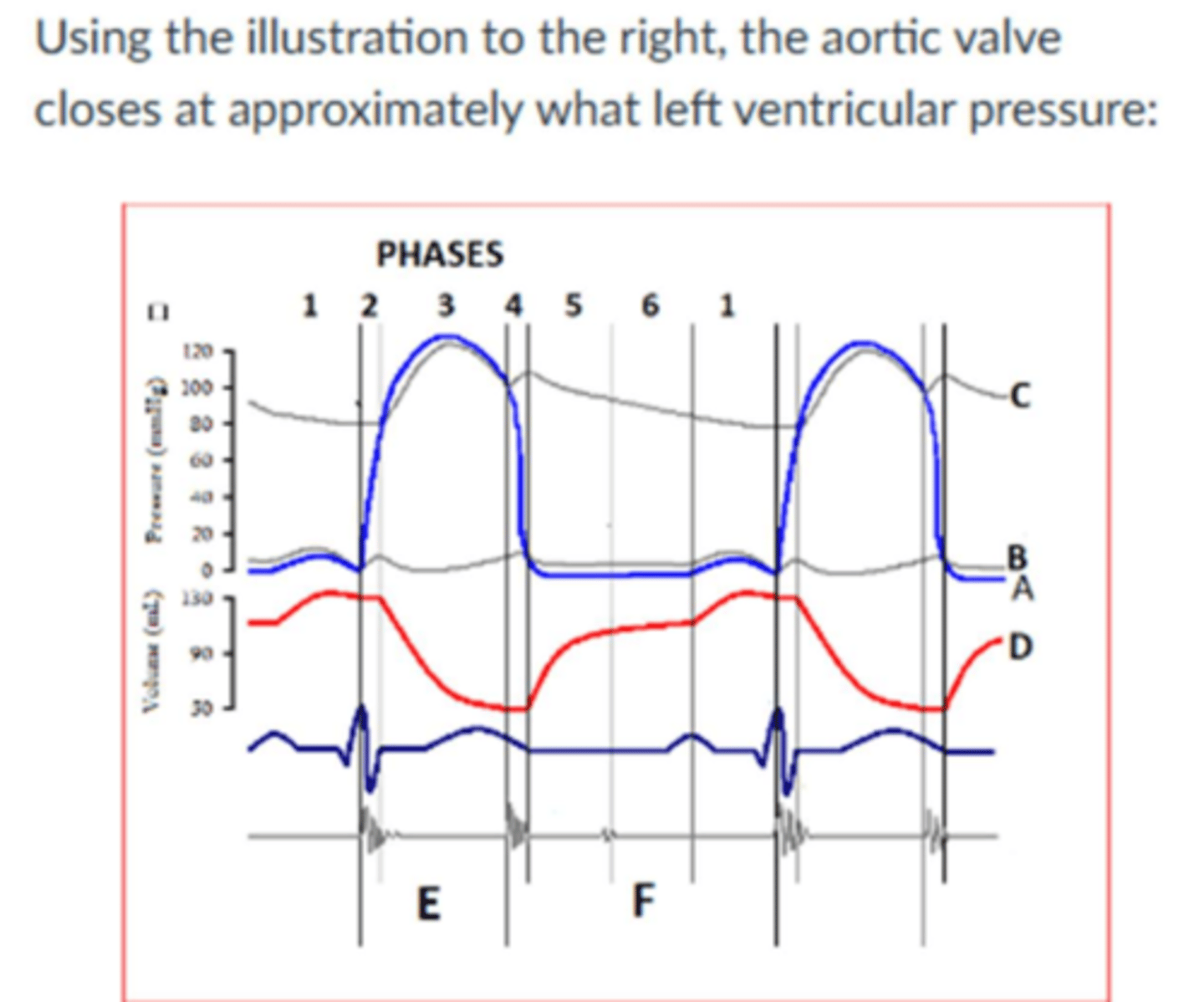
Image:
Phase 2
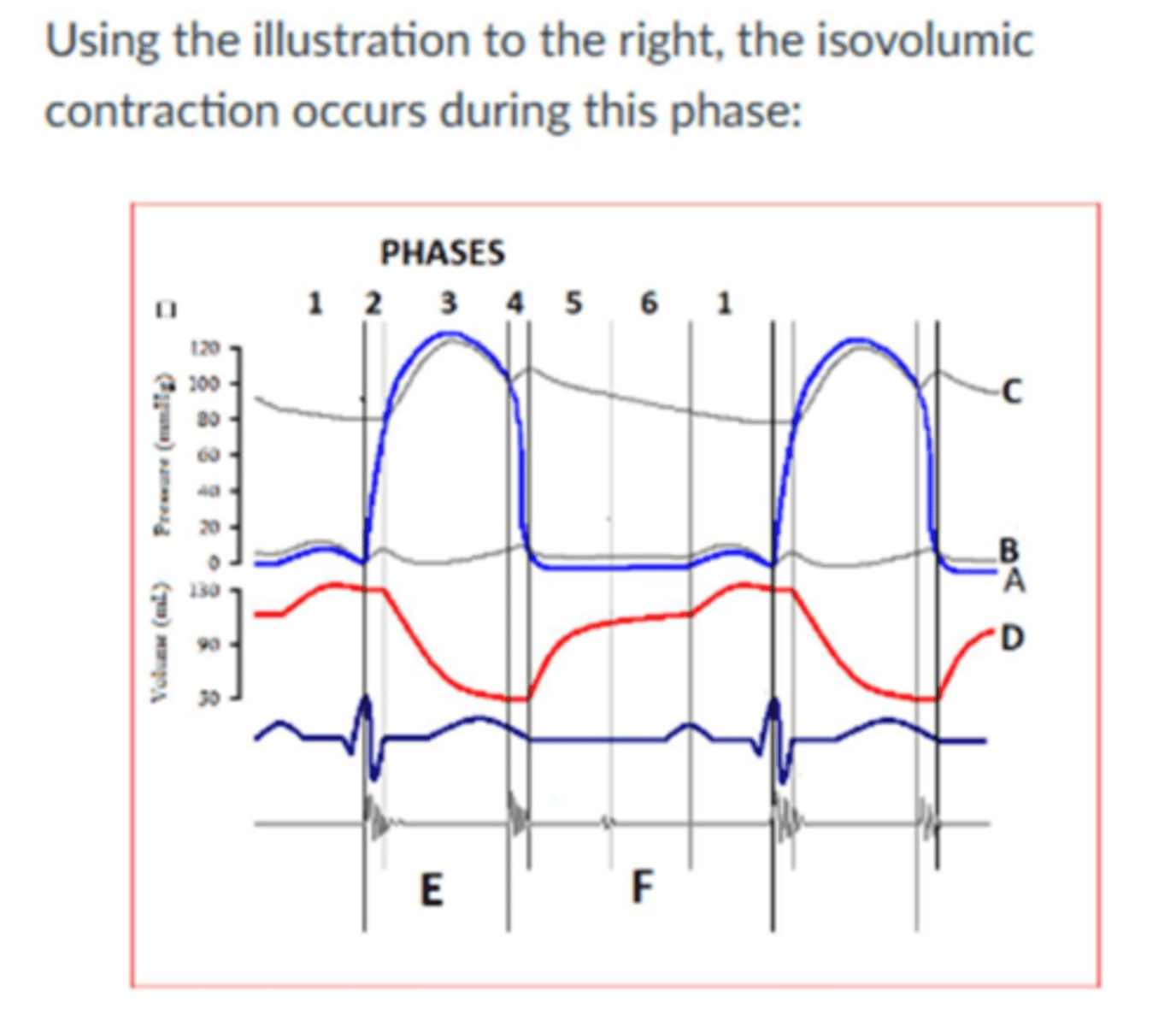
Image:
Left ventricular volume
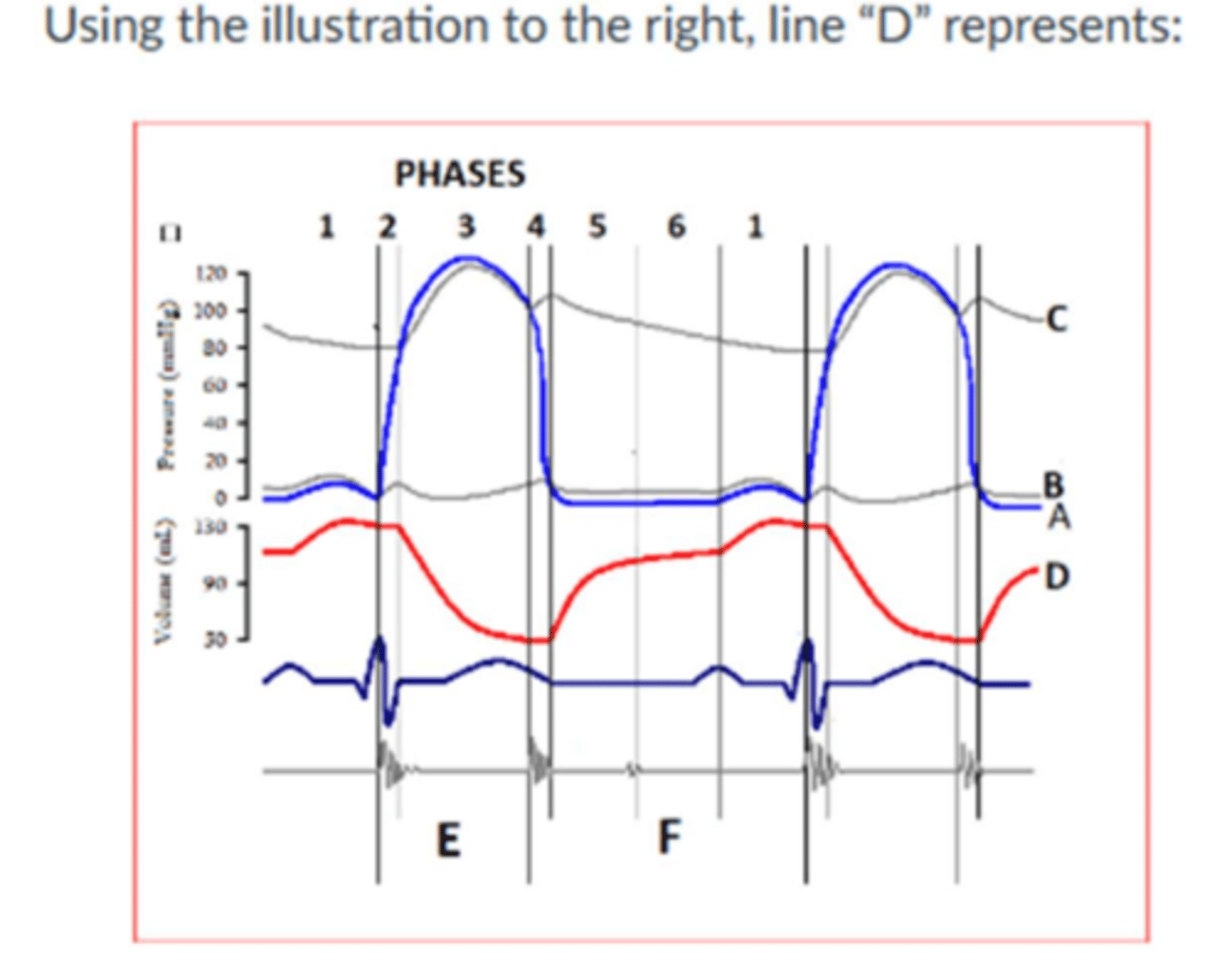
Normal right atrial pressure is ________ mmHg.
2-8
Image:
Isovolumic
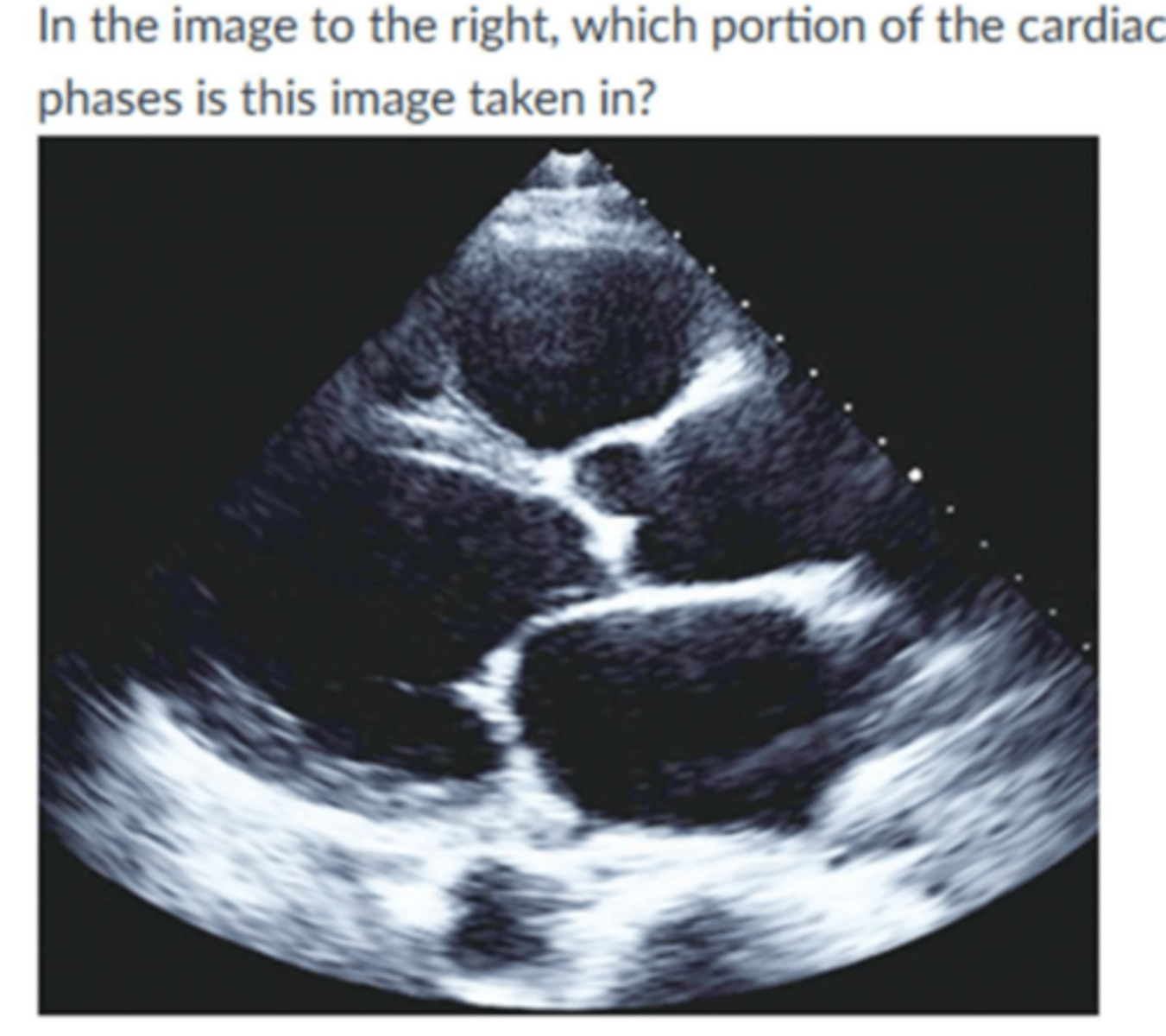
Image:
1. DTA
2. Anterior mitral leaflet
3. Right ventricular
4. Interventricular
5. Chordae Tendinea
During systole:
The semilunar valves are open and the atrioventricular valves are closed
The degree of fiber stretch related to the quantity of blood in the ventricle prior to contraction at end-diastole is:
Preload
The resistance against which the ventricles must pump to eject blood is:
Afterload
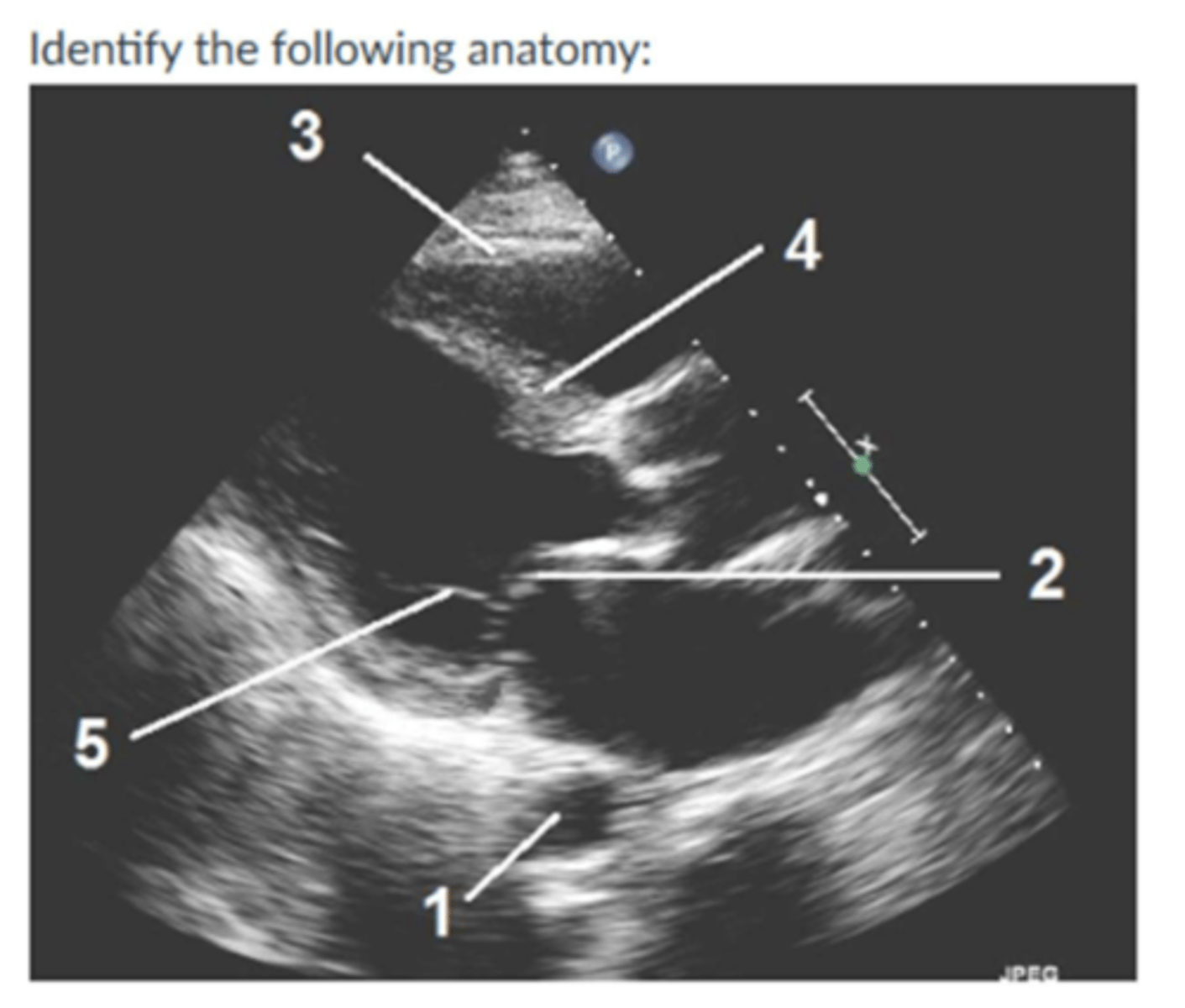
Image:
1. endocardium
2. epicardium
3. pericardium
4.
5. moderator band
7. chordae tendinea
The volume of blood at end-diastole at which the cardiac myofibril is stretched is called:
LV end diastolevolume
T/F: once the ventricular pressure exceeds the great vessels pressure, the atrioventricular valves open.
False
The majority of the heart muscle is a sponge-like meshwork of interwoven myocardial fibers or crisscross muscular bundles or bands on the inner surface of the LV and RV. The term used to describe the surface is:
Trabeculation
The upper limits of normal for left atrial volume indexed is:
34 mL/m^2
The normal range for CO is:
4-8 L/min
In a normal ECG complex, what represents atrial contraction (atrial depolarization)?
P-wave
The sympathetic nervous system ________ the heart rate as part of fight or flight, while the parasympathetic nervous system_____ the heart rate via the vagus nerve.
Increase/decrease
On M-mode of the mitral valve, the E-F segments represents:
Diastasis
In the PLAX view, what direction does blood flow during systole?
From the left ventricle through the aortic valve
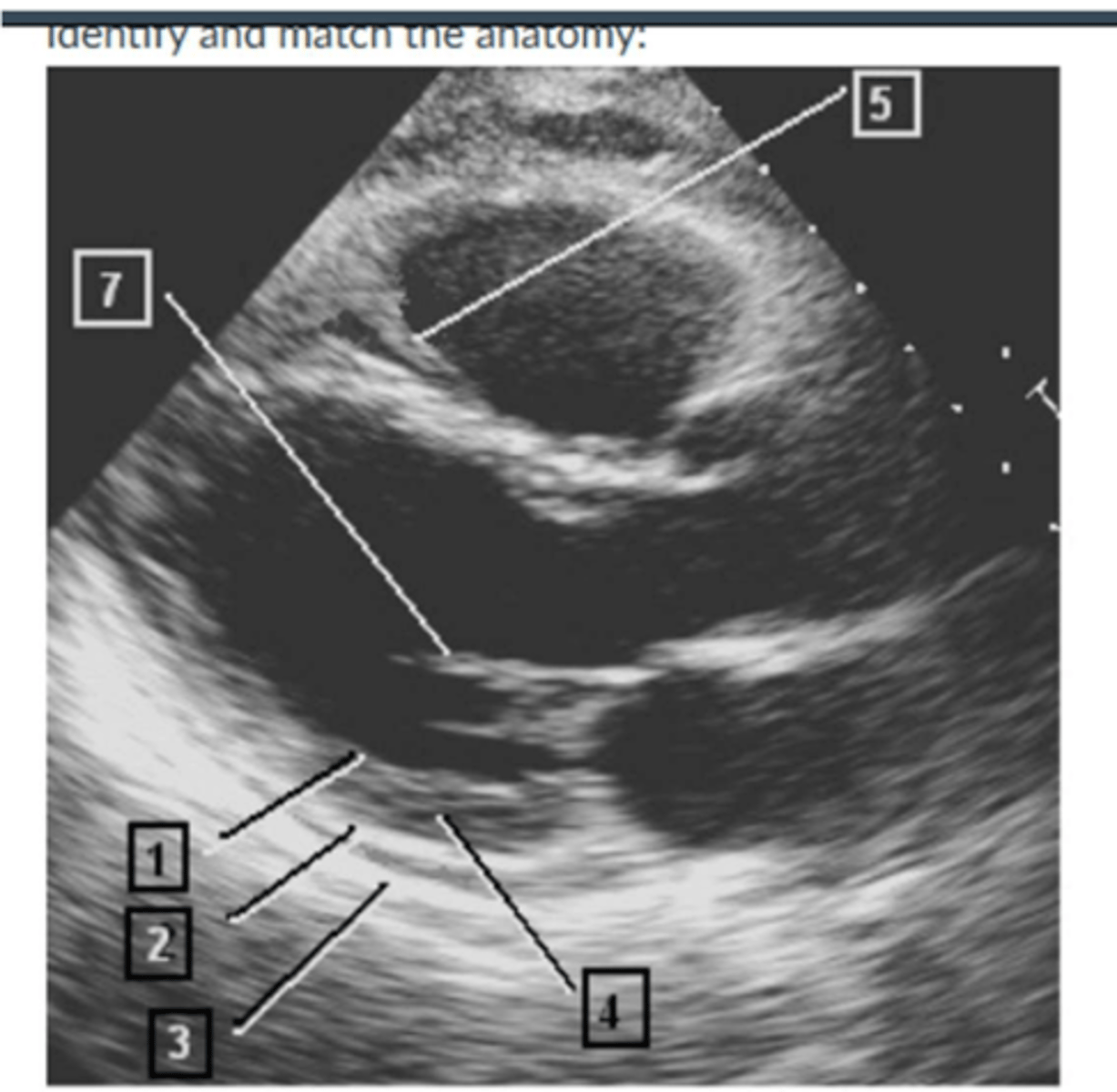
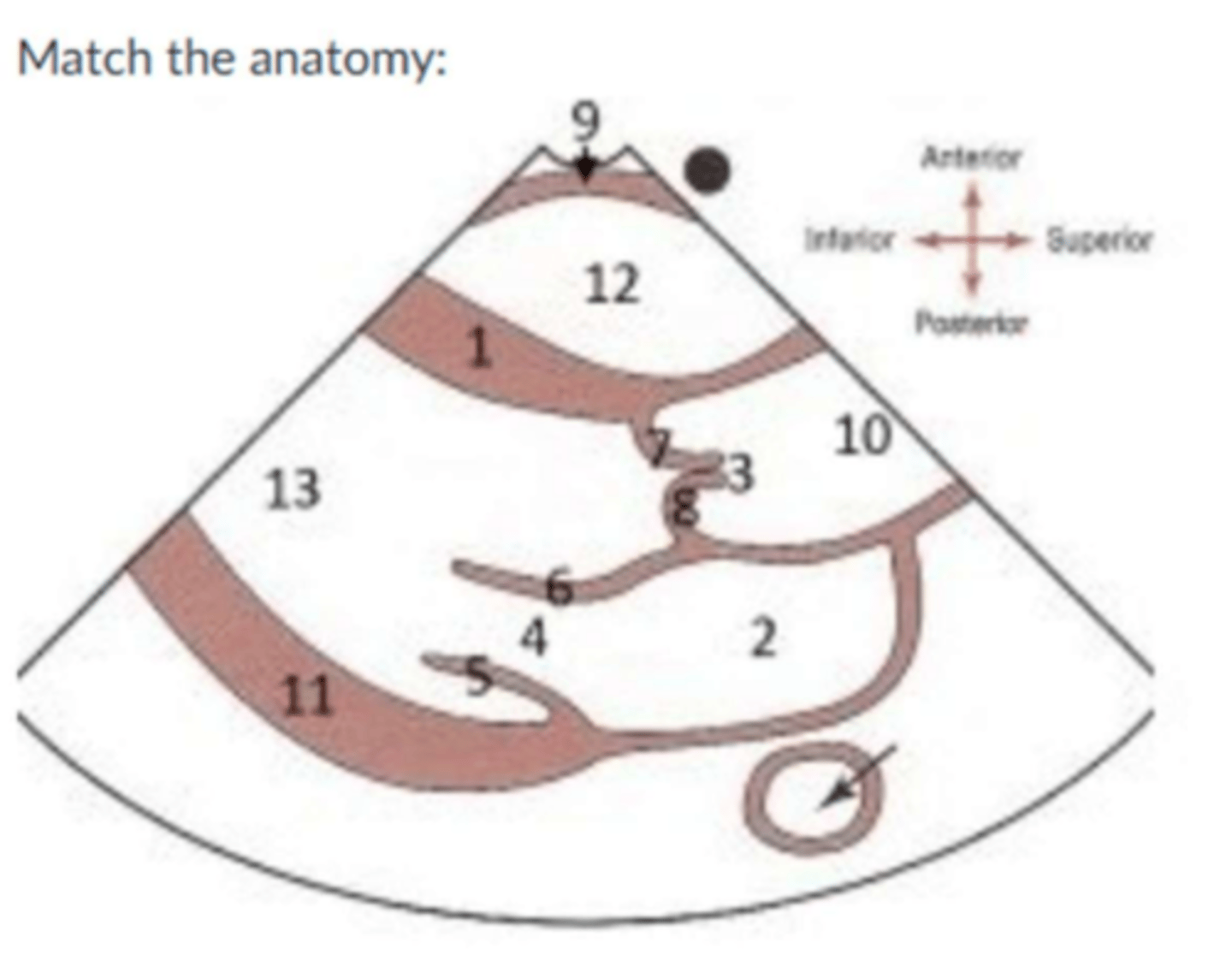
Image:
1. IVS
2. LA
5. PMVL
6. AMVL
7. RCC
8. NCC
10. Aorta
11. LVPW
12. RV
13. LV
9. RV free wall
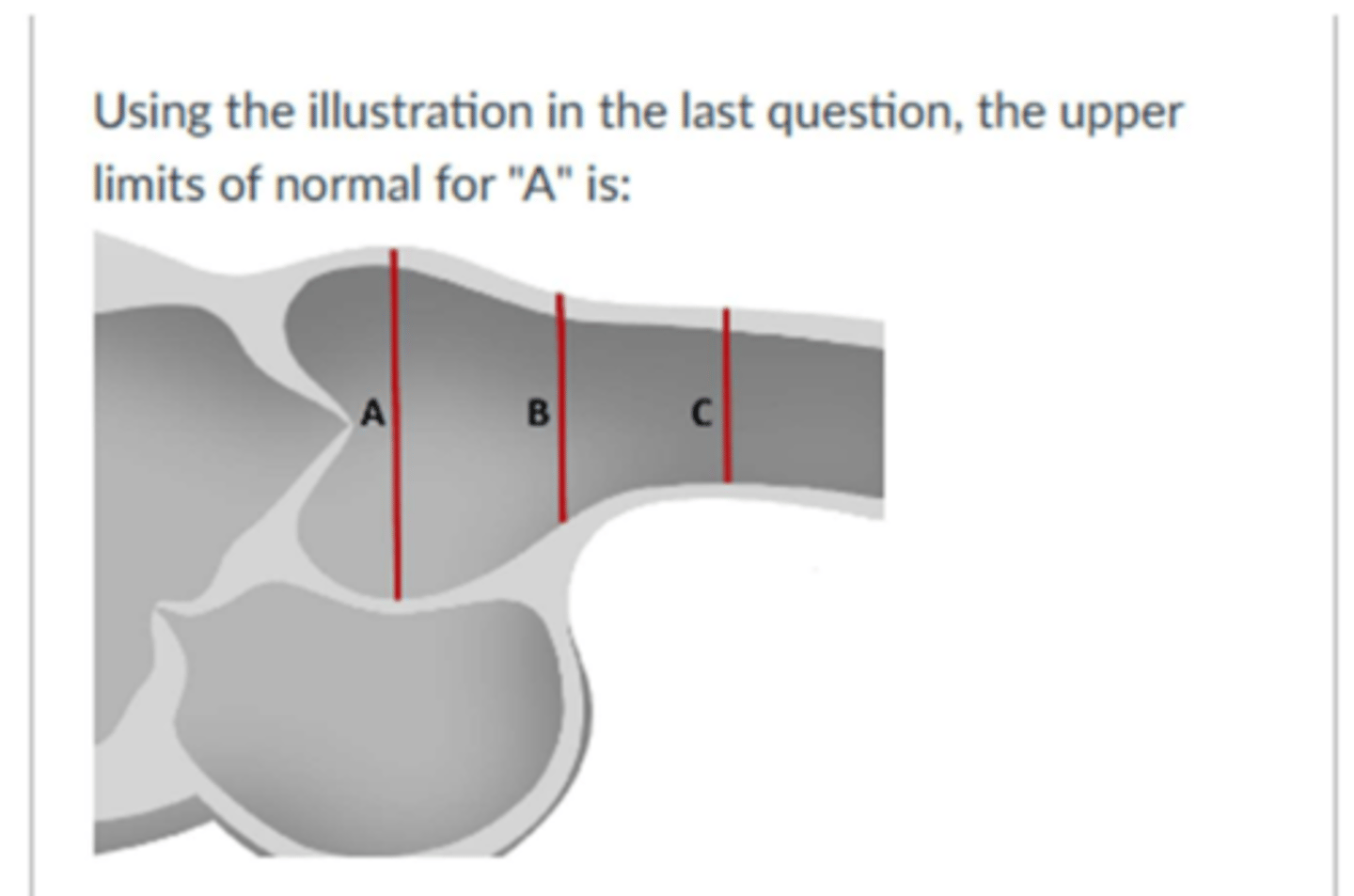
The upper limits of normal for the interventricular septum, for a man is:
1.0cm
In M-mode, the left atrial dimension is measure at:
End-systole
The upper limits of normal for left ventricular internal dimension for a woman is:
5.3cm
You are using M-mode in your echocardiogram examination. you are at the level of the aortic valve. Your image contains all structures except:
Anterior mitral leaflet
The upper limits of normal for left atrium dimension for a man is:
4.0cm
The valve located at the junction of the IVC and the right atrium during fetal circulation and usually disappearing after birth, sometimes visualized as a thin crescentic fold is known as the:
Eustachian Valve
The longer the interval between heart beats, the stronger the contraction required to pump the blood out is known as:
interval-strength relationship
Image:
3.7 cm
Stroke volume is dependent upon all the following except:
Heart rate
During Diastole:
Atrioventricular valves are open ventricular filling occurs
Isovolumic contraction time occurs:
period after mitral valves closes and the aoritc valve has not yet opened.