Industrial Growth and Railroad Expansion in the Gilded Age
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
What was the economic trend in the United States from 1865 to 1900?
The United States experienced a significant economic transformation, shifting from an agriculture-based economy to an industrial powerhouse.
What was the primary reason talented individuals were drawn away from politics during this period?
They were attracted to the booming private economy and the potential for profits in the industrial sector.
What was the value of manufactured goods the U.S. exported by 1900?
More than $600 million worth of manufactured goods.
What was the extent of railroad construction in the U.S. by 1900?
The U.S. had 192,556 miles of steam railways, more than all of Europe combined.
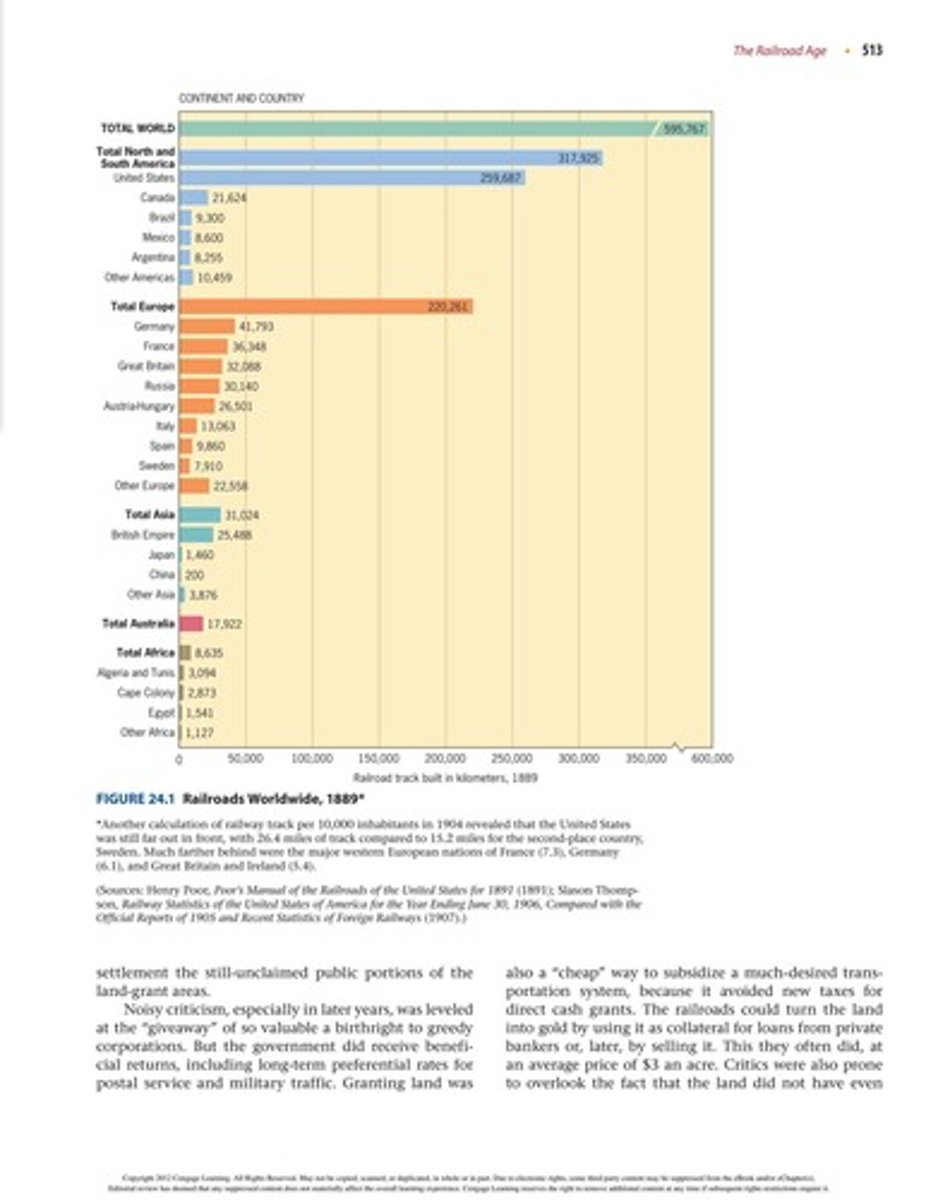
What role did government subsidies play in railroad construction?
Government subsidies were essential for funding the costly and risky transcontinental railroad projects.
What was the total area of land granted to railroads by the U.S. government?
155,504,994 acres, with an additional 49 million acres from western states.
What was the impact of railroads on land use and settlement?
Railroads facilitated the growth of cities in newly accessible areas while bypassed areas often became ghost towns.
What was the significance of the Union Pacific Railroad?
It was commissioned by Congress to connect the Pacific Coast to the rest of the Republic, enhancing national unity.
What incentives were provided to the Union Pacific Railroad for construction?
For each mile of track, the company received 20 square miles of land and federal loans based on the terrain.
What was the outcome of the deadlock over the transcontinental railroad in the 1850s?
The deadlock was broken when the South seceded, allowing Congress to proceed with the railroad.
By 1900, what percentage of the national economy was accounted for by agriculture?
Less than half.
How did foreign investment contribute to the U.S. economy during this period?
Foreign investment, along with labor, trade, and technology, played a crucial role in the economic transformation.
What were the financial benefits for railroad companies from land grants?
Railroad companies could use the land as collateral for loans or sell it, often at an average price of $3 an acre.
How did President Grover Cleveland impact land grants to railroads?
He ended the practice of railroads withholding land from other users in 1887.
What was the criticism regarding land grants to railroads?
Critics viewed it as a giveaway of valuable land to corporations, although it provided beneficial returns to the government.
What was the relationship between railroads and community development?
Communities competed to attract railroads, often offering monetary incentives, leading to rapid urban development.
What was the role of the Crédit Mobilier construction company?
Insiders of the company profited significantly from the construction of railroads, often through corrupt practices.
What was the significance of the term 'Iron Colt' in the context of this chapter?
It refers to the rapid development and importance of railroads in transforming the U.S. economy.
What was the impact of railroads on the economy and society by 1900?
Railroads were crucial for economic growth, national unity, and the transformation of American society.
What company profited significantly from the construction of the transcontinental railroad?
The Crédit Mobilier construction company, which pocketed $73 million for $50 million worth of work.
What was the primary labor force used for the construction of the transcontinental railroad?
Many Irish laborers, referred to as 'Paddies', who had fought in the Union armies.
What was the purpose of the federal land grants to railroads?
To provide specific parcels of land to encourage railroad construction and expansion.
What was the significance of the 'wedding of the rails' in 1869?
It marked the completion of the transcontinental railroad, joining the Union Pacific and Central Pacific railroads.
What challenges did the Central Pacific Railroad face during construction?
They encountered formidable barriers in the Sierra Nevada, requiring extensive tunneling through solid rock.

Who were the 'Big Four' in the context of the Central Pacific Railroad?
Leland Stanford, Collis P. Huntington, and two other financial backers who managed the railroad's construction and profits.
What role did Chinese laborers play in the construction of the Central Pacific Railroad?
They provided a cheap and efficient labor force, often facing dangerous working conditions.
What was the impact of the transcontinental railroad on American trade?
It facilitated a flourishing trade with Asia and connected the West Coast more firmly to the Union.
What was the reaction of Native Americans to the construction of the railroad?
They attempted to protect their land, leading to conflicts that resulted in loss of life on both sides.
What were the 'hells on wheels' in the context of railroad construction?
Tent towns that sprang up along the railroad, often filled with workers and various forms of entertainment.

How long was the Union Pacific Railroad upon completion?
1,086 miles.
How long was the Central Pacific Railroad upon completion?
689 miles.
What was the significance of the completion of the transcontinental railroad in American history?
It was one of America's most impressive peacetime undertakings and transformed the nation's infrastructure.
What were some of the dangers faced by railroad workers during construction?
Workers faced premature explosions, accidents, and attacks from hostile Native Americans.
What was the public perception of railroad magnates during the construction of the transcontinental railroad?
They were often viewed as greedy and unscrupulous, prioritizing profits over public welfare.
What was the role of bribery in the construction of the transcontinental railroad?
Insiders of Crédit Mobilier bribed congressmen to overlook their financial misconduct.
What were the time zones introduced in 1883 related to the railroads?
Time zones were established to standardize timekeeping across the country for railroad schedules.
What was the impact of the transcontinental railroad on the settlement of the West?
It paved the way for the phenomenal growth of the Great West and facilitated westward migration.
What was the significance of the golden spike ceremony?
It symbolized the completion of the transcontinental railroad and was celebrated with a ceremonial event.
What was the financial strategy of the Big Four regarding the railroad's profits?
They operated through construction companies to avoid direct involvement in bribery while profiting immensely.
What was the public's reaction to the completion of the transcontinental railroad?
It was celebrated as a monumental achievement, comparable to the Declaration of Independence.
What was the relationship between the Union Pacific and Central Pacific railroads?
They were two competing railroads that ultimately connected to form the first transcontinental railroad.
What were the land grants provided to railroads intended to do?
They were meant to incentivize railroad construction by granting land for development.
When was the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe railroad completed?
1884
What railroad stretched from New Orleans to San Francisco?
Southern Pacific
What year was the last spike of the last transcontinental railroad hammered home?
1893
Who was the prominent builder of the Great Northern railroad?
James J. Hill
What was a common issue faced by pioneer railroad builders?
Gross overoptimism leading to bankruptcies
Who was known as 'Commodore' and contributed significantly to railroad consolidation?
Cornelius Vanderbilt
What was one of the major improvements in railroad technology during the post-Civil War era?
The steel rail
What safety device was generally adopted in the 1870s to improve railroad efficiency?
The Westinghouse air brake
What was the significance of the joining of the Union Pacific and Central Pacific railroads at Promontory Point?
It created the nation's first transcontinental railroad.
What was the impact of railroads on American economic growth after the Civil War?
They spurred economic growth by connecting markets and facilitating resource distribution.
How did railroads affect the settlement patterns in the United States?
They led to the establishment of farm settlements along the rail lines.
What was the effect of railroads on the mining and agriculture sectors in the West?
Railroads stimulated both sectors by transporting goods and resources.
What change did railroads bring to timekeeping in the United States?
They established four standardized time zones.
How did railroads influence immigration to the United States?
They advertised land grants in Europe and sometimes offered free transport to settlers.
What ecological impact did railroads have on the Great Plains?
Settlers plowed up prairies and displaced buffalo with cattle ranching.
What was the role of railroads in the creation of millionaires in America?
Railroads were a major factor in wealth accumulation during the industrial era.
What was the name of the golden spike tapped into the last tie at Promontory Point?
The golden spike was a symbolic gesture marking the completion of the transcontinental railroad.
What was the primary purpose of the Pullman Palace Cars introduced in the 1860s?
They were designed as luxurious traveling accommodations.
What was one of the criticisms of the Pullman Palace Cars?
They were considered unsafe due to their wooden construction and kerosene lamps.
What was the significance of the iron horse in American society?
It symbolized the unification of the nation and the growth of the railroad industry.
What percentage of investment dollars did railroads consume?
Nearly 20 percent
What was a major consequence of the railroads for cities in the late 19th century?
They facilitated urbanization by transporting food and resources to growing populations.
How did the railroads contribute to the steel industry?
They generated the largest single source of orders for steel production.
What was the impact of railroads on the distribution of manufactured goods?
They enabled the rapid transport of finished goods across the continent.
What replaced the old southern 'lords of the lash' in the railroad industry?
A new aristocracy consisting of 'lords of the rail.'
What was the role of Wall Street in the railroad industry?
Wall Street became involved in the railroad industry, leading to the accumulation of colossal wealth by stock speculators and railroad wreckers.
What was the Crédit Mobilier scandal?
It was one of the first instances of corruption in railroad construction, involving fleecings administered by railroad construction companies.
Who was Jay Gould?
Jay Gould was a prominent figure in railroad speculation, known for manipulating the stocks of various railroads for nearly thirty years.
What does 'stock watering' refer to in the context of railroads?
It refers to the practice of inflating claims about a railroad's assets and profitability to sell stocks and bonds far exceeding the railroad's actual value.
What were 'promoters' profits' in the railroad industry?
Profits made by railroad promoters that often dictated the operations and financial strategies of the railroads.
How did railroad managers respond to their financial obligations?
They charged extortionate rates and engaged in ruthless competition to meet their exaggerated financial obligations.
What was the public perception of railroad magnates like Cornelius Vanderbilt?
They were seen as powerful industrial monarchs who disregarded the law and public interest.
What was the purpose of 'pools' in the railroad industry?
Pools were agreements among railroad companies to divide business in a given area and share profits.
How did railroads discriminate against small farmers?
Small farmers often paid the highest rates while large customers received better deals through rebates and kickbacks.
What was the reaction of impoverished farmers to railroad monopolies?
Farmers began to protest against being 'railroaded' into bankruptcy, questioning if they had escaped one form of slavery only to fall into another.
What was the significance of the Wabash case in 1886?
The Supreme Court ruled that individual states could not regulate interstate commerce, necessitating federal regulation of railroads.
What did the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 accomplish?
It prohibited rebates and pools, required railroads to publish rates, and established the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) to enforce the law.
What was Richard Olney's perspective on the Interstate Commerce Commission?
He believed it could be used to satisfy public demand for regulation while still benefiting the railroads.
What was the primary goal of the Interstate Commerce Act?
To provide an orderly forum for resolving conflicts among business interests and stabilize the railroad industry.
How did the Interstate Commerce Act impact the relationship between government and business?
It marked the first large-scale attempt by the government to regulate business in the interest of society.
What did the Interstate Commerce Act signify for future regulatory commissions?
It heralded the arrival of independent regulatory commissions that would monitor and guide the private economy.
What major factor contributed to the post-Civil War industrial expansion in the U.S.?
The railroad network facilitated rapid industrial growth.
By 1894, where did the U.S. rank among manufacturing nations?
The U.S. ranked first among manufacturing nations.
What caused the increase in liquid capital in the U.S. during the late 19th century?
Profiteering during the Civil War created immense fortunes, leading to increased liquid capital.
Which countries primarily invested in U.S. industry during the post-war period?
Investors primarily from Britain, France, Germany, the Netherlands, and Switzerland.
What was the impact of innovations in transportation on industrial growth?
Innovations brought natural resources like coal, oil, and iron to factories, fueling growth.
What was the significance of the Mesabi Range in Minnesota?
It was a rich source of iron deposits transported to Chicago and Cleveland for refining.
Who was known as the 'Wizard of Menlo Park'?
Thomas Alva Edison.
What was one of Edison's major contributions to industry?
He established the first major industrial research laboratory and applied mass production principles.
What was the impact of Edison's inventions on society?
Inventions like the phonograph and electric lightbulb transformed daily life and industry.
What was the 'American System' in manufacturing?
It involved using specialized machinery to create interchangeable parts.
What innovation did Henry Ford develop in 1913?
The fully developed moving assembly line for the Model T.
What was the primary labor source for the steel industry during this period?
Low-priced immigrant labor from eastern and southern Europe.
How many patents were issued between 1860 and 1890?
Approximately 440,000 patents were issued.
Who invented the telephone and in what year?
Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 1876.
What was the social impact of the telephone?
It created a vast communications network and changed social roles, particularly for women.
What did Thomas Edison believe was the key to genius?
He believed it was 'one percent inspiration and ninety-nine percent perspiration.'
What business strategy did Andrew Carnegie pioneer?
Vertical integration, controlling all phases of manufacturing from mining to marketing.