RAID 3.3
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What does RAID stand for?
Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
What are the two main reasons to implement RAID?
To improve system performance and create data redundancy.
What are the two ways RAID can be implemented?
Using hardware RAID (RAID controller) or software RAID (CPU and OS).
What is a hardware RAID controller?
A physical card with its own processor that manages RAID arrays, providing better performance and flexibility.
What is software RAID?
RAID managed by the CPU and OS, more affordable and easier to implement, though it may be slower.
Why is hardware RAID generally preferred?
It offers better performance and fault tolerance despite being more expensive.
What is RAID 0 also known as?
Disk striping.
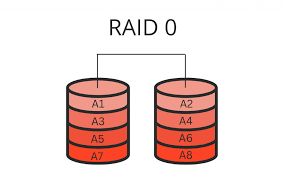
How does RAID 0 work?
Data is split and written across two or more drives simultaneously for increased speed.
What is the downside of RAID 0?
No redundancy or fault tolerance; if one drive fails, all data is lost.
What is the storage capacity of RAID 0?
Sum of all drives, but limited to smallest drive size per disk.
What does RAID 1 implement?
Disk mirroring for redundancy.
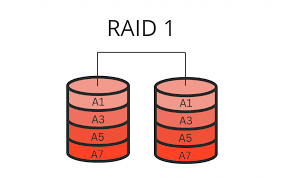
How does RAID 1 work?
Exact copies of data are written to two drives at the same time.
What happens if one drive fails in RAID 1?
The other drive contains the full copy, allowing continued operation.
What is the downside of RAID 1?
Uses two drives but only gives the storage capacity of one.
What is disk duplexing?
RAID 1 setup with each mirrored drive connected to its own controller for added fault tolerance.
Why is duplexing better than mirroring?
It adds fault tolerance by removing the RAID controller as a single point of failure.
What is parity in RAID?
A calculated value used to rebuild data in case of a drive failure.
What is RAID 5?
Striping with distributed parity across all drives, requiring at least 3 drives.
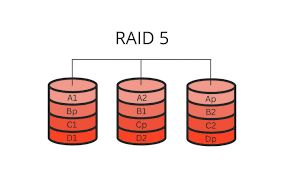
What are the benefits of RAID 5?
Offers speed, redundancy, and fault tolerance.
How does RAID 5 handle drive failure?
Parity info on remaining drives can be used to rebuild data from the failed drive.
What is the storage capacity formula for RAID 5?
Number of drives minus one, times the smallest drive size.
What happens if two drives fail in RAID 5?
The array becomes unrecoverable.
What is a hot spare?
A standby drive in a RAID 5 array that takes over automatically if another drive fails.
What is RAID 6?
A RAID level similar to RAID 5 but can tolerate two simultaneous drive failures.
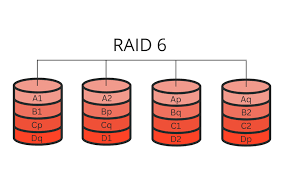
What is RAID 10?
A combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0; mirroring plus striping.
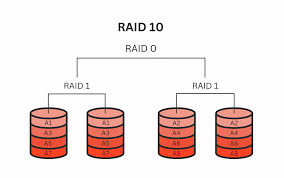
What is the minimum number of drives for RAID 10?
Four.
Why is RAID 10 preferred for performance-heavy applications?
It provides fast read/write speeds and redundancy without parity management.
What is the main downside of RAID 10?
Only 50% of total storage capacity is usable due to mirroring.
Can Linux support non-standard RAID 10 arrays?
Yes, the Linux MD driver allows 2–4 disk configurations for RAID 10.
Which RAID level offers no redundancy?
RAID 0.
Which RAID level offers full redundancy but no speed gain?
RAID 1.
Which RAID level offers balanced speed and redundancy?
RAID 5.
Which RAID level offers best performance and redundancy but at the cost of usable capacity?
RAID 10.
JBOD (Just a Bunch of Disks)
Combines multiple disks into one logical volume (also called spanning). Disks can be different sizes. Data saved sequentially, typically filling one disk before moving to the next. Uses all available space (no overhead). No striping, performance boost, or fault tolerance. If a disk fails, some data may be recoverable.
What is an advantage of RAID 5 over RAID 1?
RAID 5 improves performance over RAID 1.