chemistry--ch.1
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
science
place of naturalism and materialism
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass (that weighs something)
pure substances and mixtures
two types of matter?
pure substances
elements or compounds
mixtures
homogeneous or heterogeneous
pure substance
made up of only ONE type of substance; one chemical formula or symbol
element
SIMPLEST type of matter; made up of only one type of atom
ex) Nitrogen, Oxygen…
atom
smallest unit of matter; keeps it unique characteristics
compound
pure substance made of TWO OR MORE elements chemically joined together
mixture
combination of two or more substances; can be separated into its different components
homogeneous mixture
one whose composition is the SAME throughout
heterogeneous mixture
one whose composition is NOT UNIFORM but VARIES throughout
periodic table of the elements
listing of all the elements on earth; each block holds a different element, has a letter or two, have numbers above and below these letters
chemical symbol
letters on the periodic table; ex) Na = sodium, Au = gold
group
vertical column; have SIMILAR chemical behaviors; A designations for main-group elements, B designations for transition elements
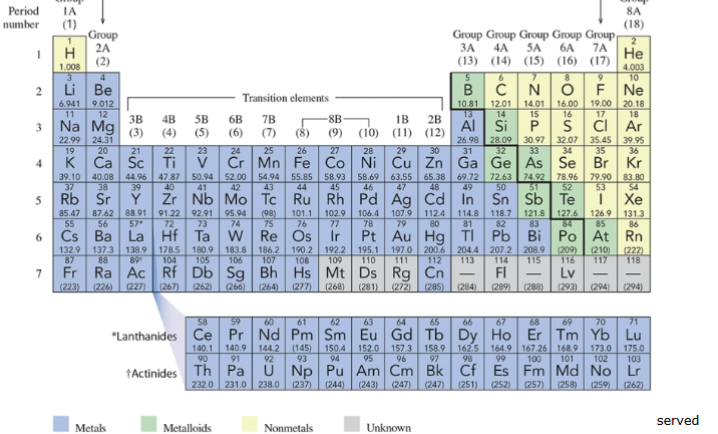
IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry)
system using numbers 1 through 18 for the columns
period
horizontal row on periodic table; numbered from 1 to 7; staircase-shaped line which begins at boron, separates metals from nonmetals; elements bordered by the line, with the exception of aluminum (Al) are metalloids
largest quantity
how much do you need the elements of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N)
macronutrients
needed in quantities greater than 100 mg per day; ex) Sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), and chlorine (Cl)
micronutrients
needed in quantities less than 100 mg per day; ex) Iodine (I), fluorine (F), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn)…
hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen
most common elements in living things?
chemical formula
identifies which elements and how many atoms of each element are present in a compound; ex) H2O or NaCl
gas
state of matter composed of particles that are not associated with each other and are rapidly moving, NO definite volume or shape
liquid
state of matter composed of particles that are loosely associated and freely moving, DEFINITE volume but NO definite shape
solid
state of matter composed of particles that have an orderly arrangement and very little motion, DEFINITE shape and DEFINITE volume
physical change
change in the STATE; form of the matter is changed, but not its identity
chemical change
change in the chemical identity of a substance; substance undergoes such a change it is a chemical reaction
chemical reaction
change in the chemical identity of a substance
reactants and products
2 terms in what happens in a chemical reaction?
law of conservation of mass
mass either created or destroyed; number of atoms of each element in the reactants equals the number of atoms of each element in the products (number of atoms must be the same on BOTH SIDES of the equation = balanced)
matter only changes form
coefficients
numbers in front of the chemical formula in order to balance a chemical equation
systeme international d’Unites (SI)
modern-day version of the metric system
kilogram (kg)
SI unit for mass
liter (L)
SI unit for volume
meter (m)
SI unit for length
giga
x 1,000,000,000
mega
x 1,000,000
kilo
x 1,000
base unit
1 (gram, liter, meter)
deci
divided by 10
centi
divided by 100
milli
divided by 1000
micro
divided by 1,000,000
nano
divided by 1,000,000,000
equivalent units
quantities that can be related to each other by an equal sign; 1 dL = 0.1 L
conversion factors
equivalencies that can be used to convert one unit to another using one or more of these factors
dimensional analysis
use of converting units to an equivalent unit
significant figures
all digits in a number representing data or results that are known with certainty plus one uncertain digit
measuring matters; important to be reasonably; nondigital device, there is some level of uncertainty in the measurement; the sig figs are the digits with certainty plus one estimated digit; digital devices automatically show us the number of sig figs; all NONZERO numbers are considered significant
C
unit for coefficient
n
exponent telling us the number of tens places that apply
scientific notation
C x 10^n
positive
? exponent that tells us that the actual number is greater than 1
negative
? exponent tells us that the number is between 0 and 1
sig figs
in scientific notation, only ? ? are shown in the coefficient
percent
%; part out of 100 total, or hundredths; directly compare two sets of numbers that have different total sizes
% = part/whole x 100
mass
measure of the amount
gram (g)
common unit for mass
pull of gravity
weight is determined by ? ? ? on the object; force changes depending on location
volume
measure of the SPACE occupied by matter
milliliter (mL)
SI unit used for volume in the lab
cubic centimeter
unit used in the clinical setting for volume; 1 mL = 1 cc or cm³
density (d)
ratio of mass (m) to its volume (V)
d = m/V
constant at a given temperature
specific gravity (spgr)
ratio of the density of a sample to the density of water
= density of sample/density of water
refractometer
measures the specific gravity of a liquid
temperature
measures the hotness or coldness; SI unit for temperature = Kelvin
measure also by Fahrenheit and Celsius
hyperthermia
person’s temperature is ABOVE 40.0 deg C (104 deg F)
cause convulsion, coma, or permanent brain damage
hypothermia
person’s temperature DROPS BELOW 35 deg C (95 deg F)
feels cold, has an irregular heartbeat, and slow breathing rate
energy
capacity to do work or supply heat
potential energy
stored energy
kinetic energy
energy of motion
law of conservation of energy
energy takes various forms, but it is never created or destroyed
joule (J)
SI unit for energy
calorie
amount of energy required to raise the temperature of ONE gram of water by one degree Celsius; 1 calorie = 4.184 joules
Calorie (Cal)
1000 times larger than a calorie; 1 Calorie = 1000 calories
heat
kinetic energy; flows from a warmer body to a colder one
every substance has the ability to absorb or lose this as the temperature changes
specific heat capacity
amount of heat NEEDED to raise the temperature of 1 g of that substance by 1 deg C
SH = heat/grams x delta T
metals
low specific heat values
water
very high specific heat; 1.00
state of matter
physical form in which the matter exists; most common are solid, liquid, and gas
accuracy
degree of agreement between the true value and the measured value
error
difference between the true value and our estimation
can be random or systematic
precision
measure of the agreement of REPLICATE measurements
deviation
amount of VARIATION present in a set of replicate measurements
12 in
1 ft =
5280 ft
1 mile =
16 oz
1 lb =
drop factor
used to determine drip rates when a prescribed volume of medicine is required in a given time period
drop
gtt means…