Chapter 18: Confidence Intervals for Proportions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a confidence interval?
A range of values, derived from sample data, that is likely to contain the true population parameter.
What is the general form of a confidence interval?
Estimate ± Margin of Error
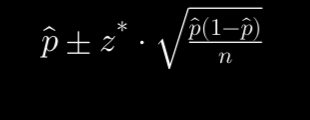
What is the confidence interval formula for a population proportion p?
What conditions must be met to use the confidence interval for proportions?
Random sample
10% Condition: sample size ≤ 10% of population
Success/Failure: np >= 10 and n(1p) >=10
What does the confidence level represent?
The percentage of all possible samples that would capture the true population parameter.
What happens when you increase the confidence level?
The margin of error increases
The interval becomes wider
What happens when you increase the sample size?
The margin of error decreases
The interval becomes narrower
What does the margin of error depend on?
Sample size
Confidence level
Sample proportion ^p
What is ≠*?
The critical value corresponding to the desired confidence level (e.g., 1.96 for 95%).
What’s a key misunderstanding about confidence intervals?
Saying “there’s a 95% chance the true parameter is in this interval” — the parameter is fixed, not random.
What happens if conditions aren’t met for inference on proportions?
The Normal model may be invalid; results might be inaccurate or misleading.
Why is the confidence interval centered at ^p?
Because ^p is the best point estimate of the true population proportion p.