ACRP204 multiple choice questions
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🦴- Exam 1🗿- Exam 2 🕰️ - Exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
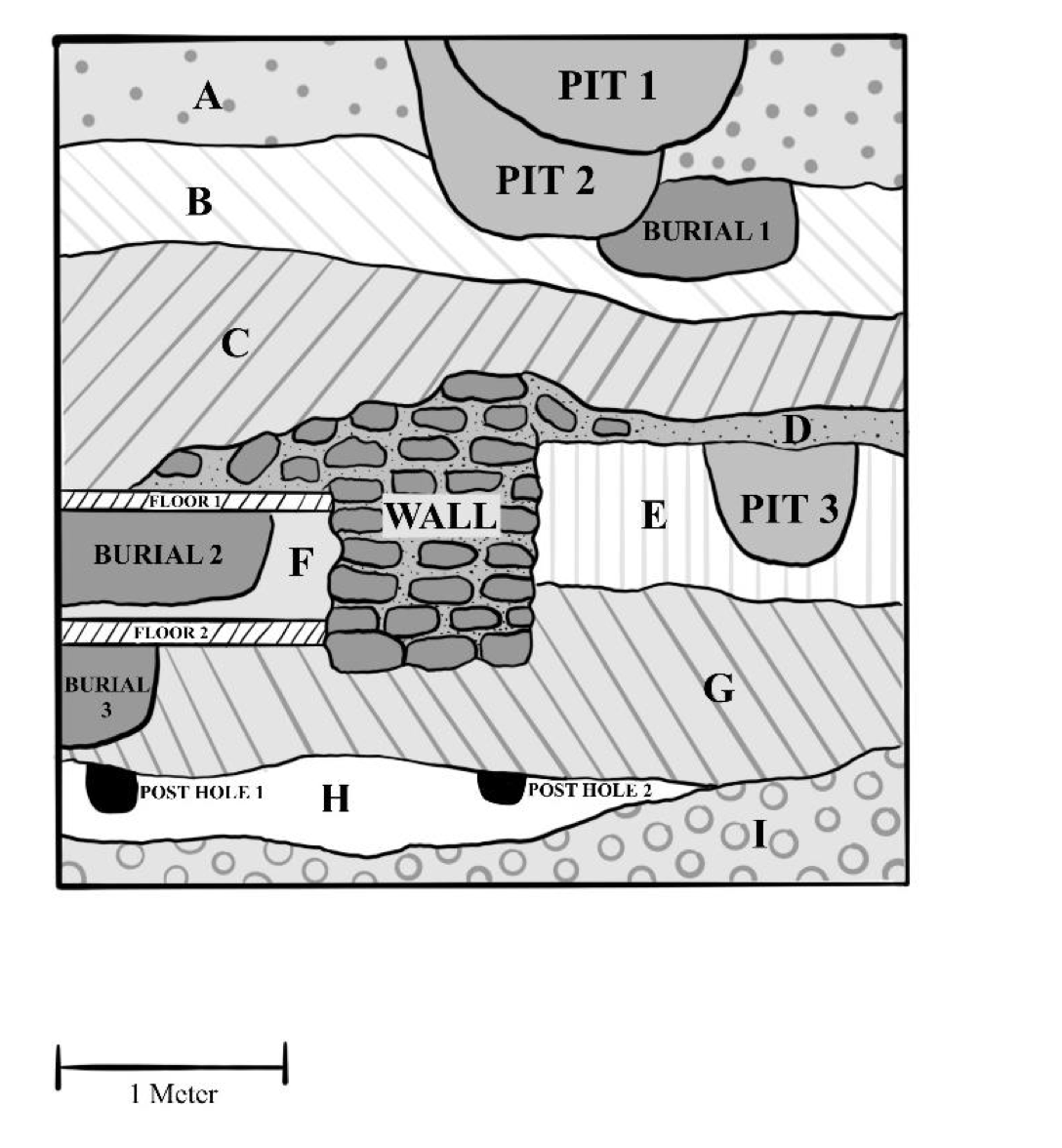
🦴What is the correct chronological order of strata, from oldest to newest? Order Burial 1, Pit 2, A, C, D
D, C, Burial 1, A, Pit 2
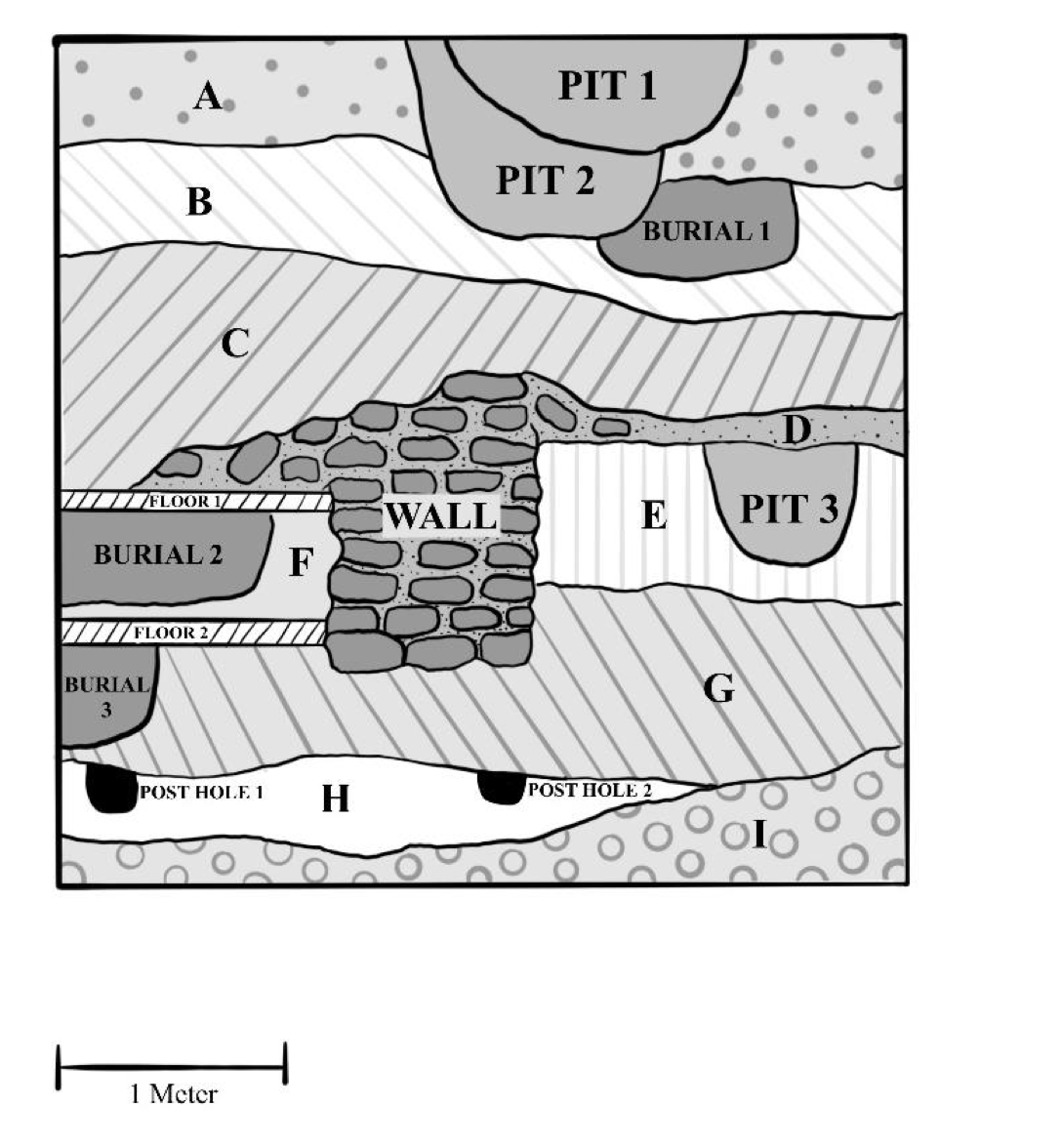
🦴A coin dated to 1875 was found in Burial 2. What is the date for Floor 1?
Sometime after 1875
🦴Which of the following dating methods would be most appropriate for dating a stratigraphic layer of volcanic ash found immediately above an Australopithecus afarensis fossil?
Potassium/argon or argon/argon dating
🦴Which of the following dating methods would be most appropriate for dating a fragment of pottery excavated from a Lapita cultural complex site in Polynesia?
Thermoluminescence
🦴Which of the following dating methods would be most appropriate for determining an absolute date for animal bones excavated from the site of Monte Verde, Chile?
Radiocarbon dating
🦴Which of the following dating methods would be most appropriate for dating a stratigraphic layer of volcanic ash containing the Laetoli footprints?
Potassium/argon or argon/argon dating
🦴Which of the following best describes the concept of stratigraphic association?
Archaeological artifacts found in the same stratigraphic layer have the same date.
🦴Which of the following is NOT an archaeological survey method used to locate sites?
a. Backfilling
b. Satellite imagery
c. Pedestrian surface mapping
d. Magnetometry
e. Mapping with a total station
A. Backfilling
🦴What is the approximate date for the migration of humans onto Sahul?
50,000 years ago
🦴What is the approximate date for the migration of humans out of Africa according to the early “southern route” hypothesis?
100,000 years ago
🦴What is the approximate date for the migration of Homo erectus out of Africa according to finds at sites such as Dmanisi, Georgia?
1.8 million years ago
🦴Which of the following is NOT true about the discipline of archaeology?
a. In the United States, archaeology is usually a sub-field of anthropology; archaeology is concerned with the interpretation of human material culture.
b. Archaeological excavations destroy sites; it is important to record as much contextual information as possible for each excavation locus.
c. Archaeologists do not accept the principle of uniformitarianism; archaeological site formation processes do not include natural geological processes.
d. Archaeologists often struggle to find ways of interpreting past social behaviors based on physical remains; the concept of chaîne opératoire has been developed to analyze the social acts involved in artifact production and use.
e. Many archaeological interpretations are biased by the colonialist history of the discipline; scientific techniques and theories used in archaeology are not objective.
C. Archaeologists do not accept the principle of uniformitarianism; archaeological site formation processes do not include natural geological processes.
🦴The site of Laetoli in Tanzania shows that Australopithecines were:
Fully bipedal
🦴Which hominin is only found in Indonesia, had a small body size due to island dwarfism, and is dated to ca. 700,000-50,000 years ago?
Homo fioriensis
🦴Which hominin was first identified through ancient DNA studies, interbred with humans and Neanderthals in Asia, and lived approximately 40,000 years ago?
Denisovans
🦴Which hominin was fully bipedal, is represented by the famous “Lucy” fossils, had diet and behaviors similar to chimpanzees, and likely made some of the earliest stone tools?
Gracile australopithecines such as Australopithecus afarensis
🦴Which hominin is represented by a female skeleton found in Koobi Fora, Kenya that has skeletal evidence for vitamin A poisoning caused by consumption of large amounts of meat?
Homo erectus
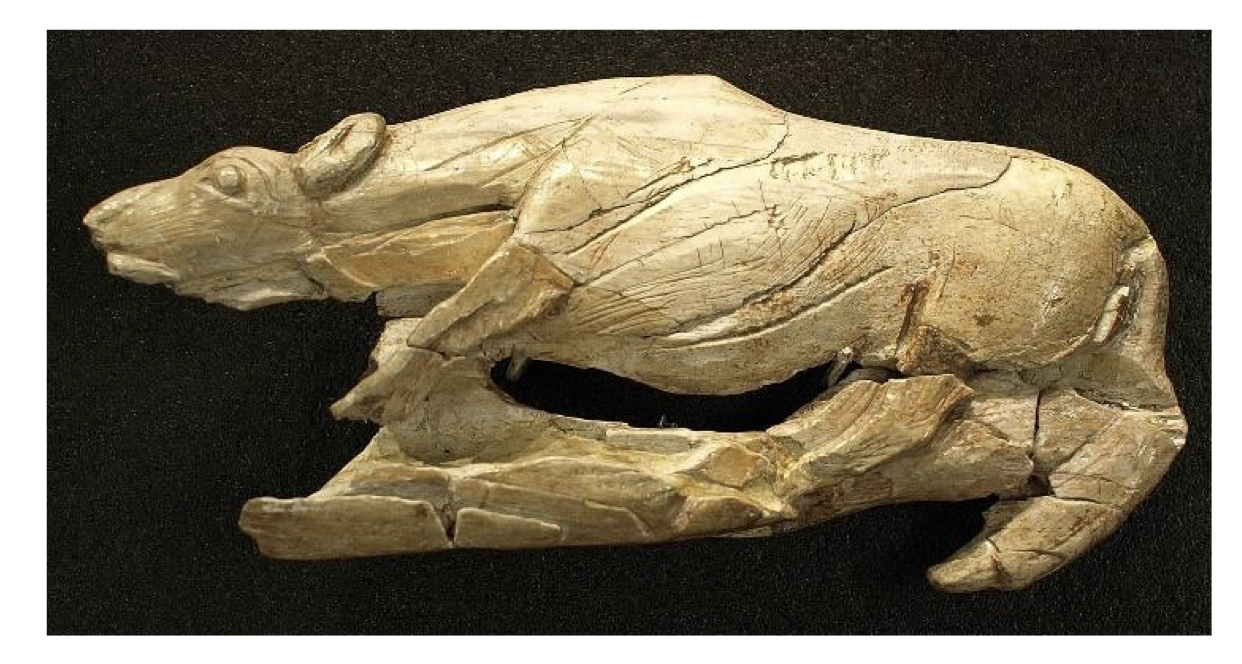

🦴Which hominin likely made this
Homo sapiens
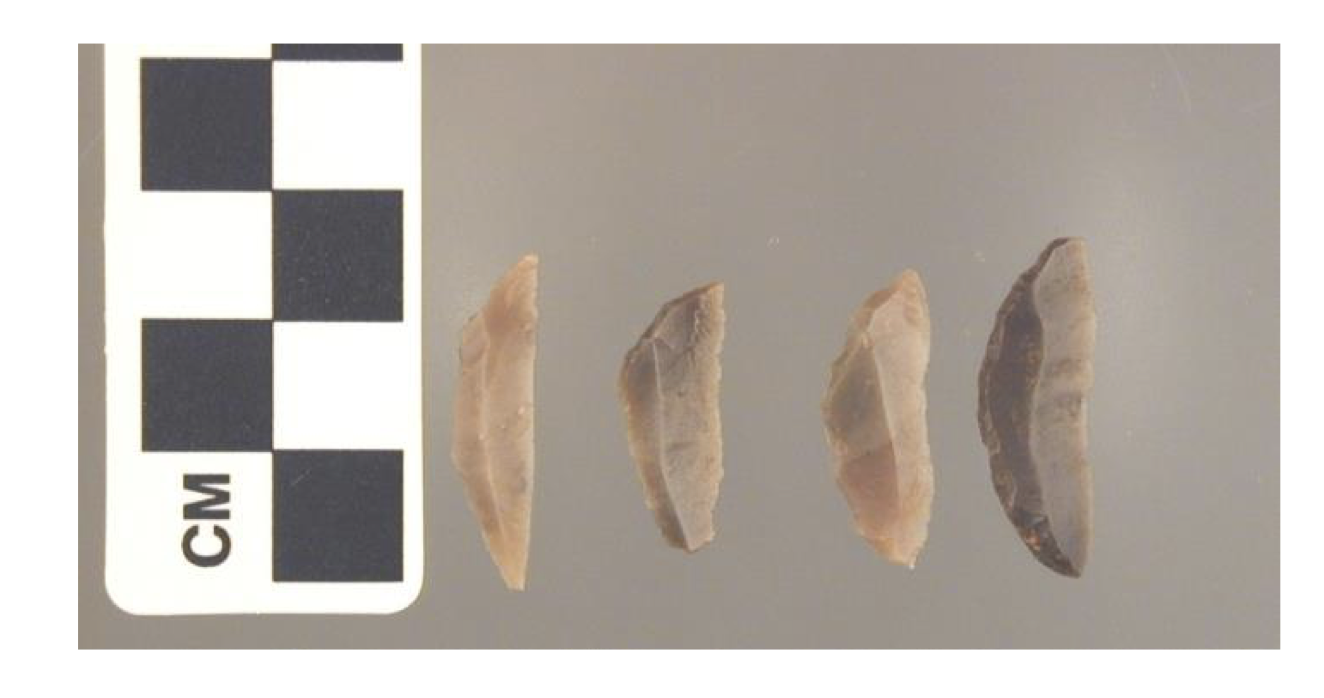
🦴Which hominin likely made this
Homo sapiens
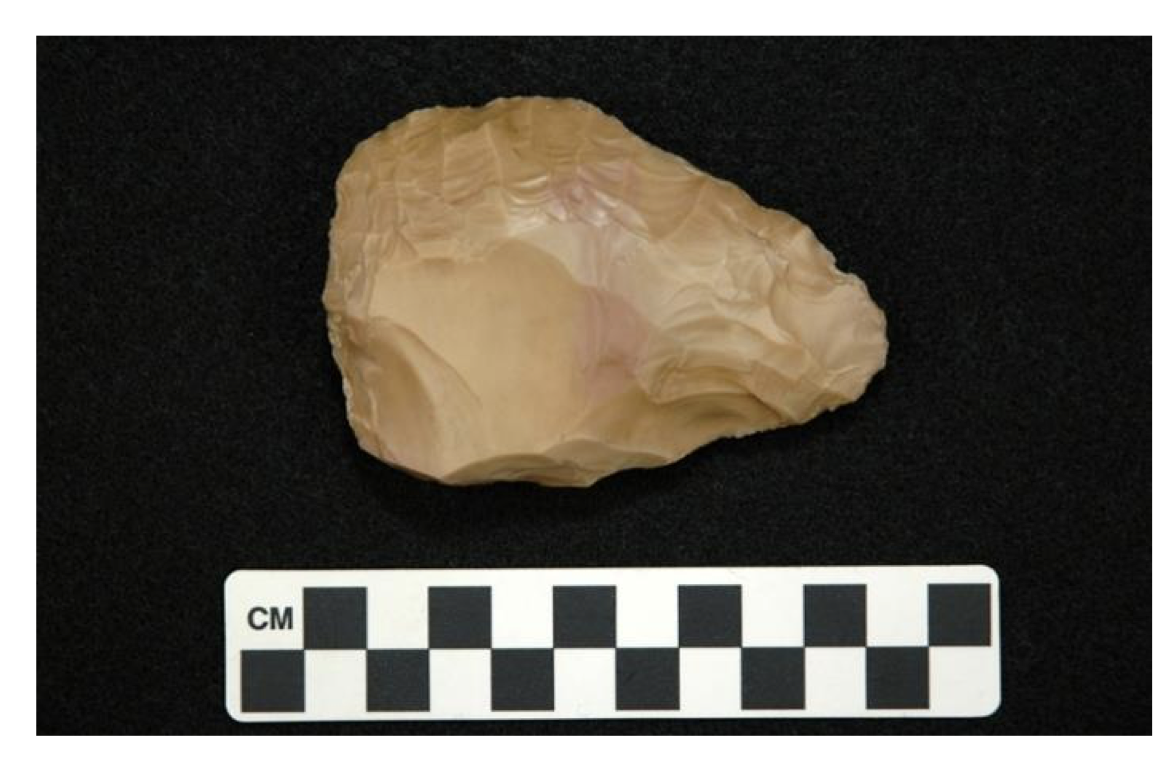

🦴What kind of tool is this
Mode II/Acheulean hand axe

🦴What kind of tool is this
Mode 1/Oldowan core-and-flake
🦴The site of Dmanisi, Georgia is important because…
it contains the earliest modern human bones found outside of Africa, revealing that there was a “early southern route” for human migration.
🦴The site of Sima de los Huesos, Spain is important because…
it contains dozens of Homo heidelbergensis skeletons found at the bottom of a pit, revealing that Middle Paleolithic hominins may have intentionally buried their dead.
🦴Which of the following is NOT true about the site of Zhoukoudian, China?
a. there is debatable evidence for the use of fire by Homo erectus individuals living in the cave.
b. there is debatable evidence for cooking of meat and other foods by Homo erectus individuals living in the cave.
c. some Homo erectus skeletons were probably brought to the cave by other predators.
d. ancient DNA studies of Homo erectus bones in the cave reveal that they may have interbred with Denisovans.
D. ancient DNA studies of Homo erectus bones in the cave reveal that they may have interbred with Denisovans.
🦴Middle Paleolithic/Middle Stone Age industries made by Neanderthals are characterized by the following:
Mode III/Levallois tools
🦴Which of the following is NOT a way that archaeologists recognize human-made stone tools?
Prescence of the cortex
🦴What distinguishes members of the genus Homo from the Australopithecines?
Members of the Homo genus had bigger brains, smaller jaws and teeth, ate more meat, and possibly cooked their food.
🦴According to the reading by Sheela Athreya and Rebecca Rogers Ackermann, which of the following is NOT a feature of the history of paleoanthropological research on human origins?
a. Narratives about human origins tend to ignore important findings from Asia and the research models developed by Asian scholars.
b. Ethnographic and physical comparisons between Paleolithic humans and living hunter-gatherers today have been a constant feature of paleoanthropological research that continues to “other” these populations in harmful ways.
c. The “Out of Africa”/replacement model is frequently interpreted within imperialist frameworks that focus on the supposed intellectual and technological superiority of human populations that left Africa.
d. Western scientists continue to dominate high ranking positions in the field of paleoanthropology and shape the research agenda; it is important to increase the number of indigenous scientists working in the discipline and to highlight indigenous ways of knowing.
e. The discovery of the “Piltdown” fossils shows that the Paleolithic in European pre-dates the Paleolithic in Africa; subsequent research has confirmed the authenticity of the Piltdown finds and revealed that there were more hominin species living in Europe than in Asia and Africa.
E. The discovery of the “Piltdown” fossils shows that the Paleolithic in European pre-dates the Paleolithic in Africa; subsequent research has confirmed the authenticity of the Piltdown finds and revealed that there were more hominin species living in Europe than in Asia and Africa.
🦴According to Richard Wrangham’s book Catching Fire, which of the following is evidence that Homo erectus used fire?
a. Homo erectus had larger brains than earlier hominins.
b. Homo erectus had smaller teeth and mouths than earlier hominins.
c. Homo erectus slept on the ground, and fire helped protect camp sites from predators.
d. Homo erectus had less sexual dimorphism and may have had sexual divisions of labor.
e. All of the above
E. All of the above
🦴Which of the following best describes behavioral archaeology?
Reconstruction of the step-by-step decision-making processes involved in making an object, from raw material selection through the production of a finished product; technological change can be used to study culture change.
🦴Which of the following is an example of a taphonomic cultural transformation (c-transform)?
Humans transporting materials from a secondary trash deposit into a tertiary trash deposit.
🦴Which of the following is NOT an example of a natural cultural transformation (n-transform)?
a. Rodents burrowing through the soils of an archaeological site.
b. Humans transporting materials from a secondary trash deposit into a tertiary trash deposit.
c. Hyenas chewing on bones in a cave.
d. Floods depositing animal bones along the edges of an ancient river.
e. Tree roots moving artifacts between stratigraphic layers.
B. Humans transporting materials from a secondary trash deposit into a tertiary trash deposit.
🦴Which of the following was NOT a potential advantage of bipedalism in early hominins?
a. bipedal hominins were more efficient at climbing very tall trees
b. bipedal hominins had more efficient heat regulation
c. bipedal hominins could walk greater distances
d. bipedal hominins could carry tools or other objects
e. bipedal hominins could more easily spot predators
A. bipedal hominins were more efficient at climbing very tall trees
🗿What is the approximate date for the beginning of the Neolithic transition in the Middle East
12,000 years ago
🗿What is the approximate date for the widespread adoption of maize agriculture among eastern North American mound building societies?
1000 years ago
🗿Which approach would be most appropriate for mapping a site located in a densely forested region?
LiDAR
🗿Which approach would be most appropriate for reconstructing the series of decisions that went into the production of a stone tool?
Chaine operatoire
🗿Which of the following dating methods would be most appropriate for precisely dating a wooden beam from a Kiva in Chaco Canyon, New Mexico?
Dendrochronology
🗿Which of the following artifacts CANNOT be dated using radiocarbon dating?
a. A pig bone found in a trash pit at a 50 CE Roman fortress.
b. A wooden timber found at a 900 CE Kiva in Chaco Canyon,.
c. A burned millet seed found at a 5000 BCE farming village in the Yellow River Valley.
d. A bear bone pendant found at a 70,000 BCE Neanderthal cave site in Europe.
D. bear bone pendant
🗿In general, which of the following is NOT true about the changes in material culture, health, and social organization associated with the Neolithic transition and origins of agriculture?
a. agriculturalists were much healthier than hunter-gatherers; agriculture was necessary to feed the large labor forces that constructed early monuments.
b. people began to live in sedentary villages and invest more in storage of surplus food; a few thousand years later, early cities emerged in the same regions where plants and animals were domesticated.
c. people invested more time in the production of new types of material culture such as pottery and ground stone tools.
d. Neolithic societies tended to have larger population sizes, more social hierarchy, and greater social complexity than hunter-gatherers.
A. agriculturalists were healthier
🗿The site of Monte Verde is important because it shows that people likely first migrated into the Americas…
through Beringia via an inland route after the opening of an ice-free corridor ca. 13,000 years ago
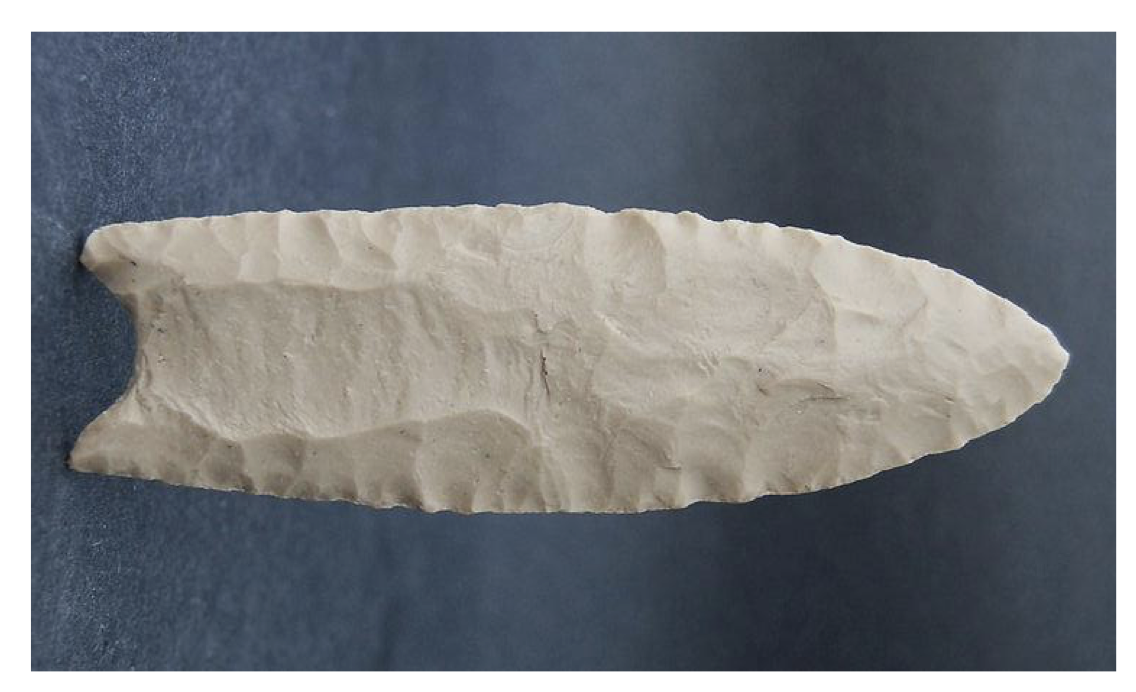
🗿What is this tool?
Clovis point
🗿What best describes the “processual” (New Archaeology) theoretical approach in archaeology?
Hypothesis testing, application of scientific research methods, and development of explanatory laws for cultural changes.
🗿 What best describes the “post-processual” theoretical approach in archaeology?
Non-positivist explanations and a focus on individual agency in the past.
🗿What best describes the “cultural historical” theoretical approach in archaeology?
Research focus on documentation and classification of archaeological “cultures.”
🗿What plant was first domesticated in the Middle East
Wheat
🗿What plant was first domesticated in North America
Sunflower
🗿What plant was first domesticated in Mesoamerica
Maize
🗿What best describes the site of Çatalhöyük, Turkey?
Egalitarian Neolithic village made up of densely packed mud brick houses occupied for multiple generations, burials below house floors, doorways in roofs, and evidence for religious beliefs centered
around wild cattle.
🗿 What best describes the site of Anyang, China?
Urban center with bronze and bone workshops, elaborate royal burials, neighborhoods for various clan lineages, and ancestral rituals involving large numbers of human and animal sacrifices.
🗿What best describes the ancient Maya site of Copan, Honduras?
City-state with carved stone monuments containing hieroglyphic writing and depictions of rulers, ballcourts, pyramids, and imitation of royal architecture by courtiers/nobles.
🗿What best describes South American Andean states such as the Moche and Inka?
Ritualized warfare among elites; extensive road networks and labor taxes; khipu used for bureaucratic record keeping.
🗿Which of the following is NOT true about Teotihuacán, Mexico
a. Teotihuacán may have put rulers in place at Maya centers such as Tikal and Copán.
b. Teotihuacán was already abandoned by the time early Olmec centers such as San Lorenzo emerged.
c. The city was arranged in a grid pattern divided into multi-ethnic neighborhoods.
d. The ceremonial core along the “avenue of the dead” contains some of the largest pyramids in the Americas.
e. The feathered serpent pyramid in the ciudadella complex was built on top of a cave system filled with ritual offerings.
b. Teotihuacán was already abandoned by the time early Olmec centers such as San Lorenzo emerged.
🗿What best describes the South Asian Indus civilization?
Mound sites with mud brick architecture; planned cities with urban water management systems and sacred pools; possible heterarchical leadership structure without images of rulers.
🗿What best describes the ancient Indigenous societies of Southwestern United States?
Sites with well-preserved wooden beams and other organic remains; circular kivas used for group rituals; long-distance trade with Mesoamerican societies.
🗿An art museum in the United States purchased a looted Shang Dynasty bronze ritual vessel from the international antiquities market in 1968. What is true about legal requirements for Repatriation?
The artifact is not subject to repatriation to China because it was purchased prior to the passage of UNESCO Convention on Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Import, Export, and Transfer of Ownership of Cultural Properties (1970).
🗿According to Barbara Fash’s article “Beyond the Naked Eye: Multidimensionality of Sculpture in Archaeological Illustration,” which of the following is NOT true about 3D scanning of ancient Maya monuments?
a. the development of 3D scanning techniques has made traditional archaeological illustration of Maya monuments completely unnecessary.
b. 3D scanning produces extremely accurate renderings of carvings and hieroglyphic inscriptions that can be viewed digitally under different lighting conditions.
c. archaeologists need to plan for the long-term storage and preservation of 3D scans so that the digital data do not become obsolete or unreadable as technologies change.
d. 3D scanning technologies are improving rapidly; it is now possible to use portable 3D scanners to record monuments both in museum settings and in the field.
A. the development of 3D scanning techniques has made traditional archaeological illustration of Maya monuments completely unnecessary.
🗿According to Wendi Field Murray, which of the following is NOT true about Wesleyan’s history and NAGPRA Compliance:
a. Like many universities, Wesleyan used to have a museum that collected human skeletal remains in order to demonstrate the quality of its science curriculum; Native American human remains were used to support cultural evolutionary frameworks and racialized science.
b. Wesleyan’s museum closed in the 1950s; when NAGPRA passed in the 1990s, there was no dedicated staff or institutional support for inventorying Wesleyan’s collections or consulting with tribes.
c. Wesleyan was not in compliance with NAGPRA until the 2010s; in 2013 and 2014, Wesleyan made a formal apology and hired a full-time staff member to manage the Archaeology & Anthropology Collections and serve as NAGPRA coordinator.
d. Since 2014, Wesleyan has repatriated Native American ancestors and has submitted summary letters to hundreds of tribes; Wesleyan no longer houses any Native American skeletal remains, and NAGPRA consultations are ongoing for objects in the collections.
e. Following the newest NAGPRA regulations, Wesleyan must set a timeline for repatriation of all remaining funerary objects in our collections; tribes are required to reply to summary letters within one year of notice in order to ensure the timely return of objects.
E. Following the newest NAGPRA regulations, Wesleyan must set a timeline for repatriation of all remaining funerary objects in our collections; tribes are required to reply to summary letters within one year of notice in order to ensure the timely return of objects.
🗿 According to Wendi Field Murray and our in-class discussions, which of the following is NOT true about the 2023/2024 updates to NAGPRA:
Guidelines for determining cultural affiliation have been broadened; for example, geography alone can be used to determine affiliation with a descendant tribe.
🗿Which of the following is NOT true about the practice of archaeology in the United States?
a. Many Native American tribes are reclaiming their history through activism and legislation that prioritizes repatriation and protection of Native American sites.
b. Most professional archaeologists in the US work in cultural resource management for private companies that conduct survey and excavation of sites prior to new building projects.
c. Laws require archaeological assessment and survey before any public building project.
d. Laws require artifacts found on private land to be reported and repatriated to descendant tribes.
D.Laws require artifacts found on private land to be reported and repatriated to descendant tribes.
🗿According to David Meltzer’s article “Kennewick Man: Coming to a Closure,” which of the following is NOT true about the Ancient One case?
a. Some anthropologists argued that the Ancient One should not be repatriated because of his scientific importance; a projectile point was found embedded in the skeleton, the skeleton had unique physical traits, and the skeleton had a very early date, all of which warranted further study.
b. During legal battles in the 1990s and early 2000s, some courts determined that the Ancient One was not subject to repatriation because it was not possible to tie such an ancient skeleton directly to a federally recognized tribe today.
c. Dietary and skeletal evidence suggests that the Ancient One was a “traveler” from another region; the Ancient One originated in Polynesia, and there is no evidence that he is a Native American ancestor.
d. Ancient DNA extracted from the skeleton showed that the Ancient One was closely related to tribes living in Washington State today.
C. Dietary and skeletal evidence suggests that the Ancient One was a “traveler” from another region; the Ancient One originated in Polynesia, and there is no evidence that he is a Native American ancestor
🕰Which of the following dating methods would be most appropriate for precisely dating a heavily eroded 18th century CE gravestone in the Washington Street Cemetery, Middletown?
A. Seriation
🕰 Which of the following dating methods would be most appropriate for precisely dating a piece of pottery excavated from Djenne-Djenno, Mali?
C. Thermoluminescence
🕰 Which of the following methods or approaches would be most appropriate for conducting archaeological survey of the Beman Triangle, Middletown?
C. Magnetometry
🕰 Which of the following methods or approaches would be most appropriate for studying human skeletal remains excavated from a cemetery?
A. Bioarchaeology
🕰 Which of the following methods or approaches would be most appropriate for reconstructing the steps involved in making a Lower Paleolithic stone tool?
B. Chaine operatoire
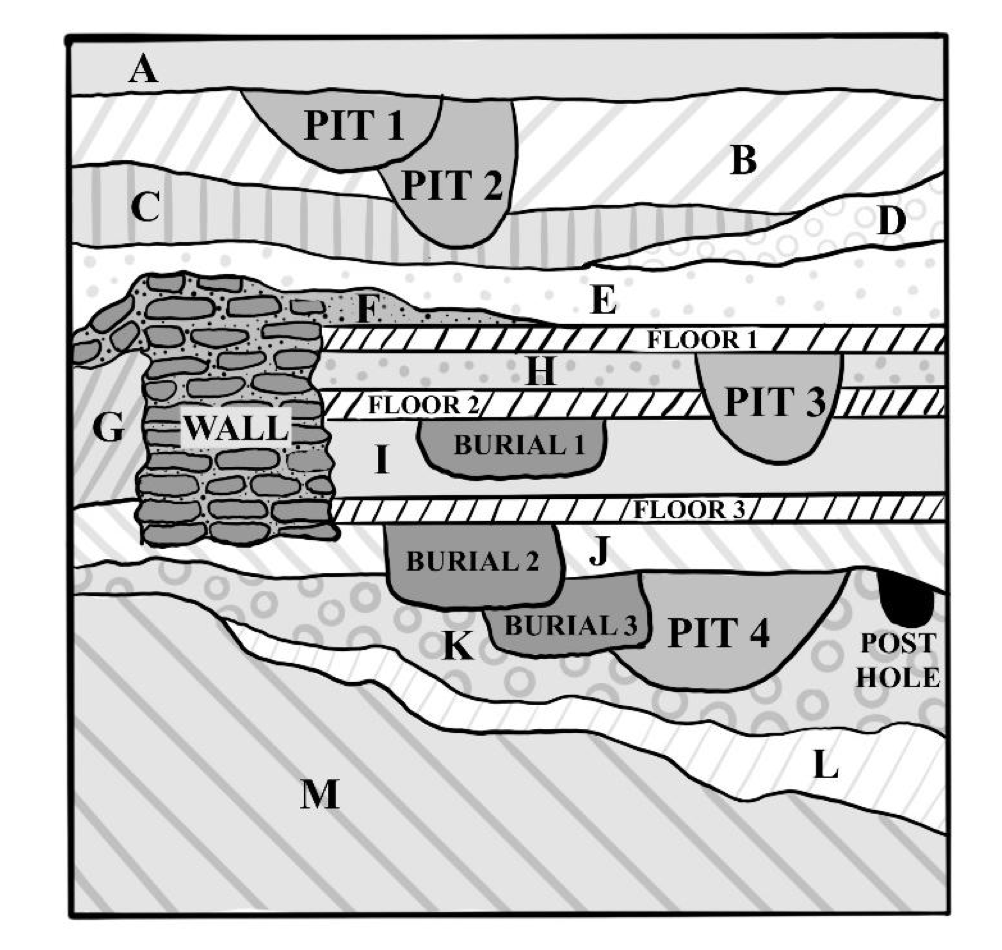
🕰 Order A, B, C, D, Pit 1, Pit 2
e. D→C→B→Pit 2→Pit 1→A
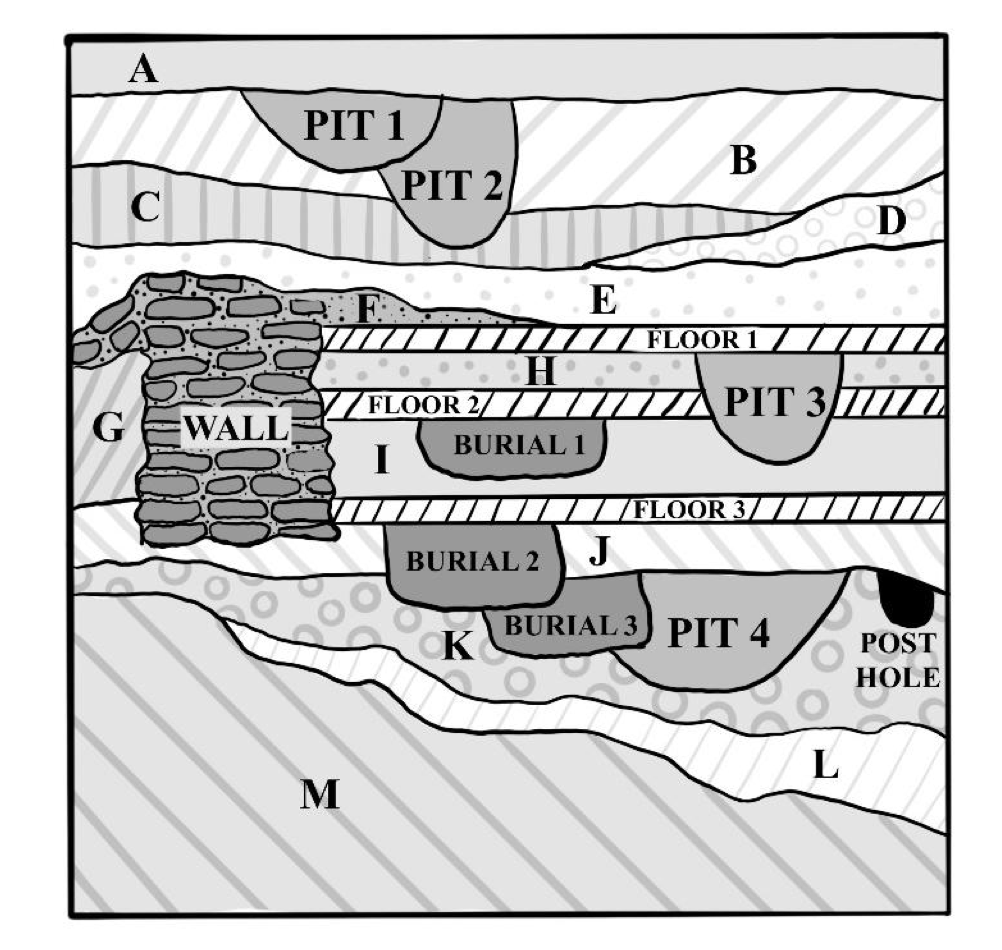
🕰Order J, K, Burial 2, Burial 3, Floor 3, Pit 4
a. K→Pit 4→Burial 3→ J →Burial 2→ Floor 3

🕰An animal bone radiocarbon dated to 1600 BP was found in Pit 4. What is the date for Burial 3?
e. Sometime after 1600 BP
🕰Which of the following best describes Upper Paleolithic (Late Stone Age) material culture associated with behaviorally modern human populations?
d. long blade tools, microliths, and spear throwers (atlatls)
🕰Which hominin is characterized by the use of mode I/Oldowan and mode II/Acheulean tools, possible evidence for the earliest use of fire, and is found in Africa and Eurasia at sites such as Dimanisi, Georgia and Zhoukoudian, China?
c. Homo erectus
🕰Which animal was first domesticated in Mesoamerica?
b. Turkey
🕰Which animal was first domesticated in South America?
d. Llama
🕰Which plant was first domesticated in East Asia?
a. Millet
🕰Which of the following plants was first domesticated in South America?
e. Potato
🕰List the correct chronology for the cultural traditions of Mesoamerica from oldest to most recent
a. Olmec→Teotihuacán→Classic Maya→Aztec
🕰Which of the following is NOT true about the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act?
a. Archaeologists are required to consult with native tribes during excavations of Native American and Native Hawaiian archaeological sites.
b. Federally funded museums and institutions are required to repatriate human remains, funerary objects, sacred objects, and objects of cultural patrimony in their collections to the appropriate federally recognized descendant tribes.
c. After cultural affiliation is established, native tribes are required to rebury human remains and artifacts i mmediately and must consult with museum personnel about the best ways to rebury the remains.
d. Cultural affiliation with a descendant tribe can be established based on multiple lines of evidence including archaeological data, oral histories, traditional knowledge, geography, and genetic evidence.
c. After cultural affiliation is established, native tribes are required to rebury human remains and artifacts i mmediately and must consult with museum personnel about the best ways to rebury the remains.
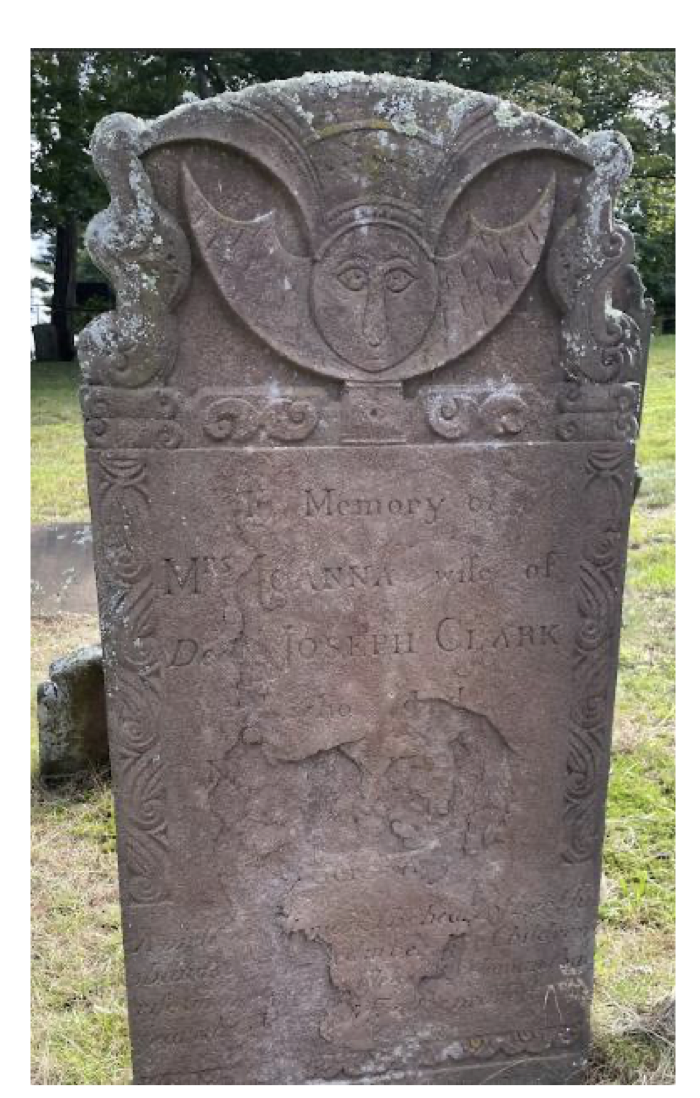

🕰 Approximate date of this gravestone
b. 1775 (?)
🕰 According to the reading by James Deetz, which of the following is true about 18th and 19th Century gravestones in the Connecticut River valley like the ones we observed in the Washington Street Cemetery?
a. The region was a highly productive agricultural zone for tobacco and other crops until the late 1800s; merchant farmers were more affluent and aware of the current styles in England, and were able to afford gravestone markers in the most current English styles.
🕰According to Dr. Jesse Nasta, which of the following is NOT true about historic Middletown and the Washington Street Cemetery?
a. Historical research on the people buried in the cemetery shows that slavery in Connecticut was similar to slavery in the southern US; enslaved people lived in separate houses and were buried in separate cemeteries from those used by white Middletown residents.
🕰Which of the following is NOT true about Spanish colonialism in the Americas during the contact period?
b. Spanish conquistadors quickly conquered and wiped-out indigenous Maya populations living in Mesoamerica without facing significant resistance due to their superior technology.
🕰 describe the site of Cahokia, USA?
e. Large regional ritual and economic center with planned precincts and streets, earthen burial mounds, maize agriculture, public plazas, and long-distance trade for elite goods.
🕰 describe ancient Mesopotamian city-states?
d. Sites in locations with greater plant and animal biodiversity; anthropogenic dark earth; plant familiarization.