Semester 2 exam
4.0(6)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Last updated 12:49 AM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
how are Genes, DNA, and Chromosomes related?
Chromosomes are made of DNA and Genes are made of Chromosomes.
2
New cards
DNA
Made of subunits called nucleotides, Have Deoxyribose as their sugar, And is the shape of a double helix
3
New cards
RNA
Made up of subunits called nucleotides, Has ribose as their sugar, and its shape depends on the type of RNA.
4
New cards
Nucleotide structure
Made up of a sugar, phosphate group, and a base nitrogen.
5
New cards
Base pair rules for DNA
Adenine pairs with Thymine, Guanine pairs with cytosine.
6
New cards
base pair rules for RNA
Adenine pairs with uracil, Guanine pairs with cytosine.
7
New cards
DNA Helicase
this enzyme binds to a replication origin on the DNA and begins unwinding the DNA helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
8
New cards
topoisomerase
Works ahead of the Helicase cutting the sugar phosphate backbones of one or both DNA strands.
9
New cards
single stranded binding proteins
Binds to the single strands of DNA at the fork and prevents them from rejoining.
10
New cards
RNA primase
this enzyme builds short complementary segments of RNA (primers) on template strands
11
New cards
DNA polymerase III
Adds Nucleotides at the end of RNA Primers.
12
New cards
Nucleotide Triphosphates
provides energy needed by DNa poly III to catalyze the senthesis reaction that adds a DNa nucleotide to the newly forming strand
13
New cards
leading strand
DNA strand built in the direction of the replication fork
14
New cards
lagging strand
built in the opposite direction of the replication fork
15
New cards
DNA polymerase I
removes every RNA nucleotide in each primer and replaces them with the appropriate Nucleotides
16
New cards
DNA ligase
joins unattached sections of DNA by phosphodiester bonds between them
17
New cards
Exonucleus
proofreaders during DNA polymerisation in DNA replication
18
New cards
DNa replication
the process by which the genome's DNA is copied in cells.
19
New cards
Okazaki fragments
short sections of DNA formed at the time of discontinuous synthesis of the lagging strand during replication of DNA
20
New cards
mRNA
singlestranded, carries instructions from nucleus to robosomes . Is located in the nucleus .
21
New cards
tRNA
hair pin shape, brings amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis. located in cytoplasm .
22
New cards
rRNa
ribosomes are made of rRNa and proteins. located in the nucleus.
23
New cards
does translation/Protein synthesis happen
happens in ribosome in cytoplasm or rough ER
24
New cards
what type of nucleic acids are involved in translation?
amino acids
25
New cards
what is a mutation?
Changes in DNA that affects an organism’s physical characteristics.
26
New cards
Asexual reproduction
Offspring created **without fusion** of gametes.
Genes come from **ONE individual**
Genes come from **ONE individual**
27
New cards
Sexual reproduction
Offspring created created by **union of male and female gametes** (egg and sperm)
28
New cards
type of cells
Diploid, Haploid
29
New cards
Haploid
when the egg and sperm cells fuse in the process of fertilization
30
New cards
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
31
New cards
advantages of sexual reproduction
genetic variation and ability to adapt
32
New cards
purpose of meiosis
to produce gametes, the sperm and eggs, with half of the genetic complement of the parent cells.
33
New cards
crossing over
a cellular process that happens during meiosis when chromosomes of the same type are lined up
34
New cards
what is produced at the end of crossing over?
a hybrid chromosome with a unique pattern of genetic material
35
New cards
where do offspring get their chromosomes
they obtain half from each parent
36
New cards
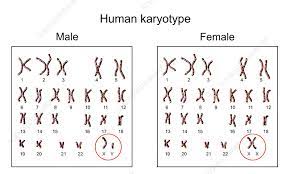
boy and girl karyotype
boy and girl karyotype
37
New cards
nondisjunction
the failure of one or more pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate normally during nuclear division
38
New cards
genotype
the genetic makeup of an organism
39
New cards
phenotype
the set of observable characteristics of an individual
40
New cards
Gregor Mendel’s contribution
he discovered the 3 laws of inheritance
41
New cards
Gregor Mendel’s 3 principles from his work.
the Law of Dominance and Uniformity, the Law of Segregation, and the Law of Independent Assortment
42
New cards
Law of Dominance an Uniformity
some alleles, which are variants of a particular gene found at the same chromosomal locus or location, are dominant over the other alleles for a given gene.
43
New cards
Law of Segregation
alleles segregate randomly into gametes-alleles of one trait had no influence of another.
44
New cards
Law of Independent Assortment.
the alleles of a gene for one trait segregate independently of the alleles of a gene for another trait
45
New cards
complete dominance
in the dominant allele completely masks the effect of the recessive allele in heterozygous conditions
46
New cards
incomplete dominance
results from a cross in which each parental contribution is genetically unique and gives rise to progeny whose phenotype is intermediate
47
New cards
codominance
a type of inheritance in which two versions (alleles) of the same gene are expressed separately to yield different traits in an individual
48
New cards
multiple alleles
Three or more possible phenotypes or genotypes for the same trait.
49
New cards
sexlinked inheritance
characteristics (or traits) that are influenced by genes carried on the sex chromosomes
50
New cards
Taxonomy
science of classifying living things
51
New cards
How to make scientific name
using the system that describes the genus and species of the organism. The first word is the genus and the second is the species. The first word is capitalized and the second is not.
52
New cards
what are the 6 kingdoms
Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista
53
New cards
kingdom Plantae
Multiellular,Autotrophic through photosynthesis.Have cell walls made off cellulose and large central vacuole
54
New cards
Kingdom Animalia
Muticellular, 0 cell walls, They are heterotrophic, Aqutic and terrestrial.
55
New cards
Kingdom Fungi
Eukaryotic,Multi/unicellular. Heterotrophic, Have cell walls made of Chitin. Terrestrial and by dead damp stuff
56
New cards
Kingdom Eubacteria
Unicellular,Prokaryotic. Asexually through binary fission. Has Peptidoglycan in their cell wall.
57
New cards
Kingdom Archaebacteria
unicellular,Prokaryotic. Have cell walls with 0 Peptidoglycans. Found in extreme enviornments.
58
New cards
Kingdom Protista
Kingdom of things that dont belong in any other kingdoms.
Some have cell walls some dont. Both heterotrophic and photosynthetic, Uni/Multicellular, sexually and asexually. Found in aquatic and terrestrial.
Some have cell walls some dont. Both heterotrophic and photosynthetic, Uni/Multicellular, sexually and asexually. Found in aquatic and terrestrial.
59
New cards
carl Linnaeus
"Father of Taxonomy"; established his classification of living things;
60
New cards
why have changes been made to the taxonomic group over the years?
scientist make discoveries.
61
New cards
first life forms on earth and why?
Prokaryotes because they could perform photosynthesis.
62
New cards
order of major vertrate groups appearance in the fossil record
Fishes, amphibians, mammals and reptiles
63
New cards
major evolutionary events:
photosynthesis, amniotic egg, exoskeleton, first eukaryotes, first vertibrates, first cells, earths formation, humans
64
New cards
natural selection
a process whereby species which have traits that enable them to adapt in an environment survive and reproduce, and then pass on their genes to the next generation
65
New cards
how do mutations occur that lead to natural selection?
If a trait is advantageous and helps the individual survive and reproduce
66
New cards
causes of evolutionary change
mutation, non-random mating, gene flow, and natural selection
67
New cards
what does being “fittest” in natural selection mean
organisms best adjusted to their environment are the most successful in surviving and reproducing
68
New cards
evolution
the process by which species adapt over time in response to their changing environment
69
New cards
3 types of natural selection
directional selection, stabilizing selection, or disruptive selection
70
New cards
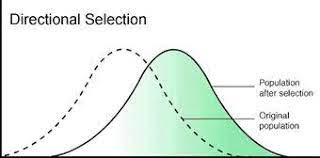
Directional selection
occurs when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or reproduce more than those on the other
71
New cards
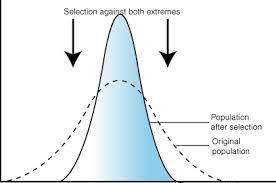
stabilizing selection
tends to remove the more severe phenotypes, resulting in the reproductive success of the norm or average phenotypes
72
New cards
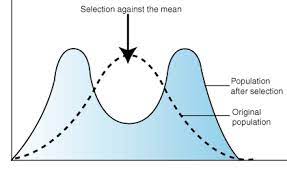
disruptive selection
when more extreme phenotypes (or genotypes) within a population have a fitness advantage over intermediate individuals
73
New cards
what is ecology
the scientific study of interactions among organisms with each other and with the environment
74
New cards
Primary succession
on land where no soil previously existed
75
New cards
secondary succession
occurs in an area where soil exists,but has been damaged or disturbed(EX- a change to an existing community that does not affect the soil.
76
New cards
producer
Autotrophs- produce energy by capturing sunlight or using chemicals(EX- plants,algae,and some bacti
77
New cards
consumer
Heterotrophs-organisms that consume other organisms for food(EX-rabbit,cat,fish
78
New cards
goals of competition
to survive and produce the mos offspring
79
New cards
Mutualism
a type of symbiotic relationship where all species involved benefit from their interactions
80
New cards
parasitism
Association between two different organisms wherein one benefits at the expense of the other
81
New cards
commensalism
a relationship between individuals of two species in which one species obtains food or other benefits from the other without either harming or benefiting the latter
82
New cards
predation
one organism kills and consumes another
83
New cards
food chain
a hierarchical series of organisms each dependent on the next as a source of food
84
New cards
food web
big web of food chains
85
New cards
energy pyramid
Diagram that shows the amount of energy stored in trophic levels(shows how energy moves through levels and how food chain works.)
86
New cards
10% law
90% of the energy left behind at each level
87
New cards
limiting factors
density dependant, density independant
88
New cards
density dependent
any force that affects the size of a population of living things in response to the density of the population
89
New cards
density independent
earth quakes floods tornadoes ect
90
New cards
abiotic
nonliving things
91
New cards
biotic
living organisms
92
New cards
Niche
the entire amount of conditions that an organism can endure
93
New cards
habbitat
where things live
94
New cards
invasive species
brought to a new habitat by human means.They could kill off entire species or help them
95
New cards
coevolution
back and forth evolutionary adjustments between species. it produces balance between communities.
96
New cards
order of levels of organization
Individual/species, Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biome, Biosphere.
97
New cards
erosion
in carbon cycle when carbon dioxide is returned to the ground and limestone is broken down
98
New cards
combustion
burning of fossil fuels in carbon cycle
99
New cards
nitrogen fixation
bacteria combine hydrogen and nitrogen to make a amonea in the nitrgoen cycle.
100
New cards
percipitation
returning waqter back to earth in water cycle