BIOL 2460 - chapter 16 - PARKS - MICROBIOLOGY
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Parks UTA
Last updated 3:46 PM on 12/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Epidemiology
Field that studies distribution & timing of diseases (infectious & non-infectious); determines etiology, transmission, and susceptible populations
2
New cards
Etiology
study of the causes of disease
3
New cards
Morbidity
# of individuals w/ disease
4
New cards
Morbidity rate
#/pop; %
5
New cards
Mortality
# of deaths from disease
6
New cards
Mortality rate
#/pop; %
7
New cards
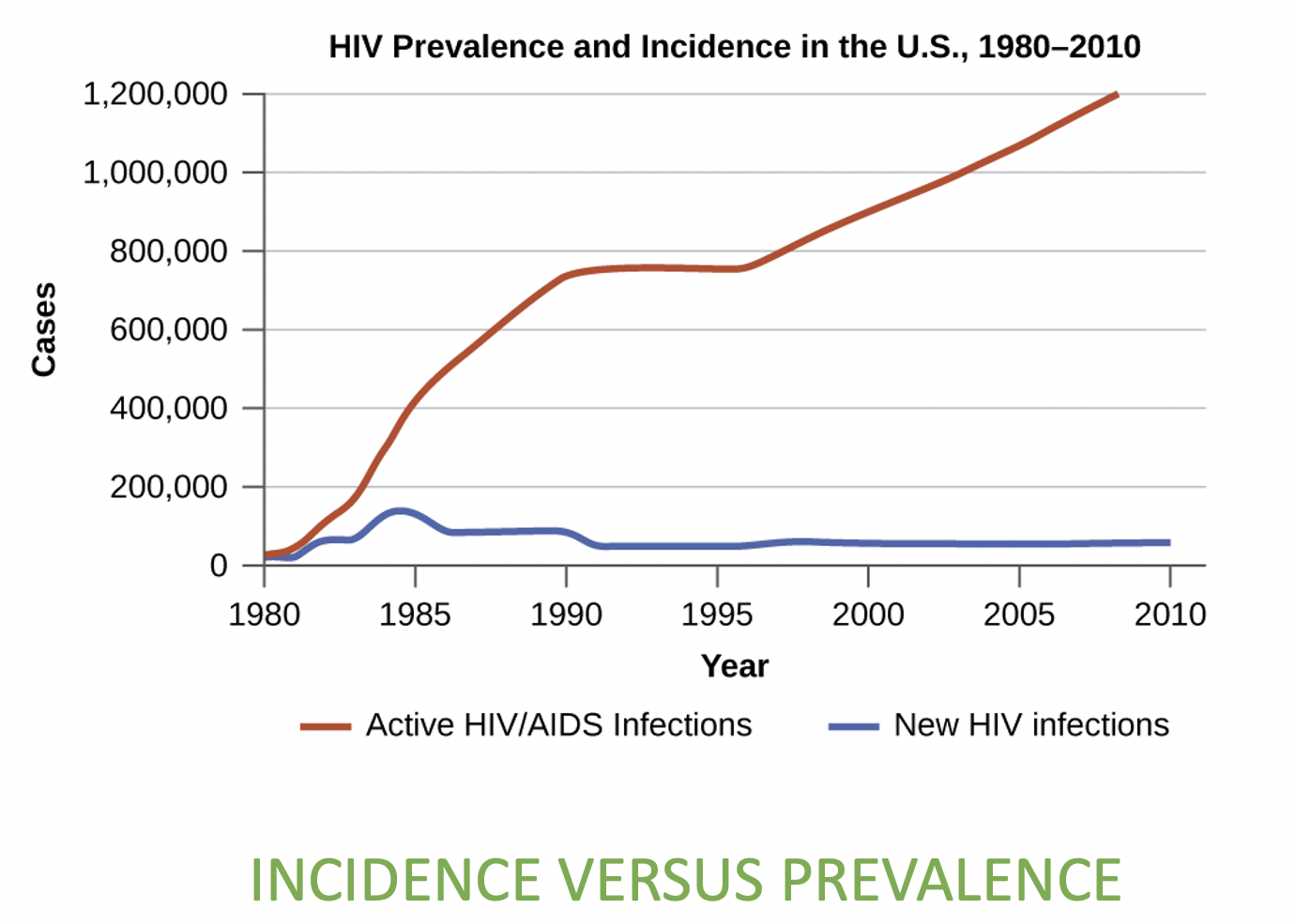
Prevalence
no. individuals at certain time
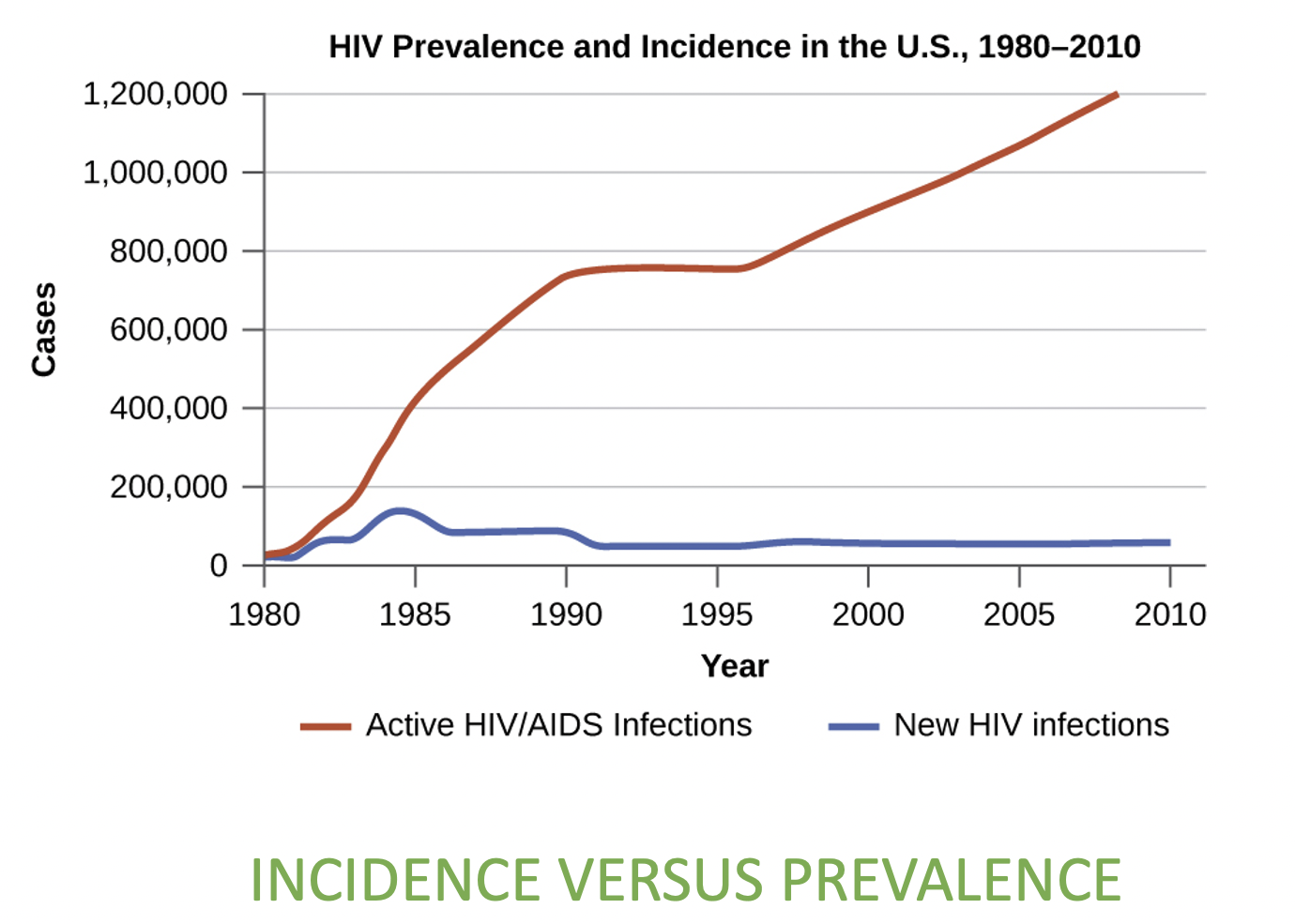
8
New cards
Incidence
no. of new cases
9
New cards
Patterns of Incidence
Sporadic, Endemic, Epidemic, Pandemic
10
New cards
Sporadic
occurs occasionally w/o regional concentration (random)
i.e. Tetanus, rabies, plague
i.e. Tetanus, rabies, plague
11
New cards
Endemic
constantly present in certain region (usually at low levels)
i.e. Malaria, Ebola, chicken pox
i.e. Malaria, Ebola, chicken pox
12
New cards
Epidemic
larger than normal amount of cases
i.e. Influenza, West Nile
i.e. Influenza, West Nile
13
New cards
Pandemic
epidemic that is cross continental
i.e. Virulent influenza, Ebola, etc. (COVID)
i.e. Virulent influenza, Ebola, etc. (COVID)
14
New cards
NNDSS (in the U.S.)
All cases MUST be reported by physicians
Ex: West Nile, HIV, measles, etc.
Studies track notifiable disease to determine risks
Ex: West Nile, HIV, measles, etc.
Studies track notifiable disease to determine risks
15
New cards
CDC
publishes Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR)
Provides physicians and health-care workers with updates on public health issues and latest data on notifiable diseases
Provides physicians and health-care workers with updates on public health issues and latest data on notifiable diseases
16
New cards
John Snow
father of epidemiology; cholera in London 1854
17
New cards
Florence Nightingale
Determined many deaths were from poor sanitation, not battle
18
New cards
Joseph Lister
used epidemiology data of handwashing for better healthcare practices (carbolic acid/aseptic conditions)
19
New cards
Common source
single source for all infected indiv.
Broad Street water pump
Broad Street water pump
20
New cards
Point source
common source that exists for short-time (< pathogen incubation)
potato salad
potato salad
21
New cards
Continuous source
continuous contamination
sewage from upstream of cholera in London
sewage from upstream of cholera in London
22
New cards
Intermittent source
on and off
rainfall runoff
rainfall runoff
23
New cards
Propagated
direct or indirect person to person contact
no single source
no single source
24
New cards
Observational
not manipulated
Descriptive
Analytical
Cohort Method
Case-control
Cross-sectional
Descriptive
Analytical
Cohort Method
Case-control
Cross-sectional
25
New cards
Experimental
subjects are manipulated; clinical trials; ethical concern, best evidence for etiology, double-blind studies
26
New cards
Descriptive
gathers info about disease outbreak
- Includes interviews & examination of medical records (family history)
- Helps develop hypothesis for etiology/causation
- Includes interviews & examination of medical records (family history)
- Helps develop hypothesis for etiology/causation
27
New cards
Analytical
selects group to evaluate hypothesis
Retrospective – data from past groups (history)
Prospective – date from current subjects moving forward (looking at it as it is going forward
Retrospective – data from past groups (history)
Prospective – date from current subjects moving forward (looking at it as it is going forward
28
New cards
Cohort method
group-based
examines individuals who share a particular characteristic
Prospective or retrospective
examines individuals who share a particular characteristic
Prospective or retrospective
29
New cards
Case-control
group-based
compares groups w/ disease to group w/o
Commonly retrospective
compares groups w/ disease to group w/o
Commonly retrospective
30
New cards
Cross-sectional
group-based
group is randomly selected, compares disease and no disease at a point in time
Looks for associations of measurable variable(s) and the disease
group is randomly selected, compares disease and no disease at a point in time
Looks for associations of measurable variable(s) and the disease
31
New cards
Non-living
soil, water; Ex. Clostridium spp. in soil
32
New cards
Living
humans, animals; Ex. Viruses, enteric microbes
33
New cards
Carriers
living reservoirs (Long persisting pathogens must live somewhere)
34
New cards
Passive
transmits mechanically; is not infected
- failing to wash hands
- failing to wash hands
35
New cards
Active
infected host transmits during incubation or convalescence
- transmission before/after fever
Asymptomatic – active carrier w/o symptoms
- early HIV, typhoid Mary aka Mary Mallon
- transmission before/after fever
Asymptomatic – active carrier w/o symptoms
- early HIV, typhoid Mary aka Mary Mallon
36
New cards
Definitive host
Parasitic infection: preferred host; parasite reaches sexual maturity
37
New cards
Intermediate host
Parasitic infection: can include one or more; parasite goes through immature life cycle stages
38
New cards
Contact transmission
Direct contact transmission – person to person
- Vertical – mother to child
- Horizontal – other person to person contact
- Droplet – transmission in droplets at 1 meter or less
Indirect contact transmission – fomite to person
- Ex. Sexually transmitted = direct & horizontal
- Ex. Birth = direct & vertical
- Ex. Cough @ short range = direct & droplet
- Ex. Cough onto desk = indirect
- Vertical – mother to child
- Horizontal – other person to person contact
- Droplet – transmission in droplets at 1 meter or less
Indirect contact transmission – fomite to person
- Ex. Sexually transmitted = direct & horizontal
- Ex. Birth = direct & vertical
- Ex. Cough @ short range = direct & droplet
- Ex. Cough onto desk = indirect
39
New cards
Vehicle transmission
through water, food, or air
Ex. Aerosols; Hantavirus
Ex. Longer lasting droplets; tuberculosis
Ex. Aerosols; Hantavirus
Ex. Longer lasting droplets; tuberculosis
40
New cards
Vector Transmission: Mechanical transmission
animal vector (not infected) carries pathogen from one host to another;
- Mechanical vector ; Ex. fly that lands on feces & food,
arthropod
- Mechanical vector ; Ex. fly that lands on feces & food,
arthropod
41
New cards
Vector Transmission: Biological transmission
pathogen reproduces in vector that transmits pathogen from one host to another
- Biological vector ; Ex. mosquitoes that pick up West Nile
- Biological vector ; Ex. mosquitoes that pick up West Nile
42
New cards
Quarantined
isolation of infected or exposed individuals to prevent transmission of the disease
- Duration is determined by incubation period & evidence
of infection
- Duration is determined by incubation period & evidence
of infection
43
New cards
healthcare-associated infections (HAI)
Nosocomial: Commonly introduced through contaminated medical equipment (e.g. catheters, respiratory ventilators, etc.)
44
New cards
Agencies Monitoring Global Health
WHO, CDC, EU Health Security Committee
- Provide logistical support and response in case of
epidemic/pandemic
- Identify emerging & re-emerging diseases
- Provide logistical support and response in case of
epidemic/pandemic
- Identify emerging & re-emerging diseases
45
New cards
Emerging infectious disease
new to population or shown increase in prevalence in last 20 yrs
Ex: Ebola (2015), Coronavirus (2020)
Ex: Ebola (2015), Coronavirus (2020)
46
New cards
Re-emerging infectious disease
increase after period of decline
Ex: drug resistant tuberculosis
Ex: measles; decline in vaccinations
Ex: drug resistant tuberculosis
Ex: measles; decline in vaccinations