Chapter 27: Assessment: Respiratory System
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
A patient with acute shortness of breath is admitted to thehospital. Which action should thenurse take during theinitial assessment of thepatient? a. Ask thepatient to lie down for complete a full physical assessment. b. Complete thehealth history and check for allergies before treatment. c. Briefly ask specific questions about this episode of respiratory distress. d. Delay thephysical assessment to first complete pulmonary function tests
ANS: C If respiratory distress is severe, only obtain pertinent information and defer a thorough assessment until thepatient's condition stabilizes. Obtaining a comprehensive health history or full physical examination is unnecessary until theacute distress has resolved. Brief questioning and a focused physical assessment should be done rapidly to help determine thecause of thedistress and suggest treatment. Checking for allergies is important, but it is not appropriate to complete theentire admission database at this time. theinitial respiratory assessment must be completed before any diagnostic tests or interventions can be ordered.
The nurse prepares a patient who has a left-sided pleural effusion for a thoracentesis. How should thenurse position thepatient? a. High-Fowler's position with theleft arm extended b. Supine with thehead of thebed elevated 30 degrees c. On the right side with theleft arm extended above the head d. Sitting upright with thearms supported on an over bed table
ANS: D The upright position with thearms supported increases lung expansion, allows fluid to collect at thelung bases, and expands theintercostal space so that access to thepleural space is easier. theother positions would increase thework of breathing for thepatient and make it more difficult for thehealth care provider performing thethoracentesis.
The arterial blood gas (ABG) results of a patient with diabetes show metabolic acidosis. Which compensatory finding would thenurse expect? a. Intercostal retractions b. Kussmaul respirations c. Low oxygen saturation (SpO2) d. Decreased venous O2 pressure
ANS: B Kussmaul (deep and rapid) respirations are a compensatory mechanism for metabolic acidosis. Acidosis does not cause intercostal retractions, a low oxygen saturation rate, or a decrease in venous O2 pressure.
On auscultation of a patient's lungs, thenurse hears low-pitched, bubbling sounds during inhalation in thelower third bilaterally. How should thenurse document this finding? a. Inspiratory crackles at thebases b. Expiratory wheezes in both lungs c. Abnormal lung sounds in theapices of both lungs d. Pleural friction rub in theright and left lower lobes
ANS: A Crackles are low-pitched, bubbling sounds usually heard on inspiration. Wheezes are high-pitched sounds. They can be heard during theexpiratory or inspiratory phase of therespiratory cycle. thelower third of both lungs are thebases, not apices. Pleural friction rubs are grating sounds that are usually heard during both inspiration and expiration.
The nurse palpates theposterior chest and notes absent fremitus while thepatient says "toy boat". Which action would thenurse take next? a. Palpate theanterior chest and observe for barrel chest. b. Encourage thepatient to turn, cough, and deep breathe. c. Review thechest x-ray report for evidence of pneumonia. d. Auscultate anterior and posterior breath sounds bilaterally
To assess for tactile fremitus, thenurse uses thepalms of thehands to palpate for vibration while thepatient repeats a word or phrase such as "toy boat." After noting absent fremitus, thenurse would then auscultate thelungs to assess for thepresence or absence of breath sounds. Absent fremitus may be noted with pneumothorax or atelectasis. thevibration is increased in conditions such as pneumonia, lung tumors, thick bronchial secretions, and pleural effusion. Turning, coughing, and deep breathing are appropriate interventions for atelectasis, but thenurse needs to first assess breath sounds. Fremitus is decreased if thehand is farther from thelung or thelung is hyperinflated (barrel chest). theanterior of thechest is more difficult to palpate for fremitus because of thepresence of large muscles and breast tissue.
A patient with a chronic cough is scheduled to have a bronchoscopy with biopsy. Which intervention will thenurse implement directly after theprocedure? a. Encourage thepatient to drink clear liquids. b. Place thepatient on bed rest for at least 4 hours. c. Keep thepatient NPO until thegag reflex returns. d. Maintain thehead of thebed elevated 90 degrees
ANS: C Risk for aspiration and maintaining an open airway is thepriority. Because a local anesthetic is used to suppress thegag and cough reflexes during bronchoscopy, thenurse should monitor for thereturn of these reflexes before allowing thepatient to take oral fluids or food. thepatient does not need to be on bed rest, and thehead of thebed does not need to be in thehigh-Fowler's position.
The nurse completes a shift assessment on a patient admitted in theearly phase of heart failure. Which sounds would thenurse most likely hear on auscultation? a. Continuous rumbling, snoring, or rattling sounds mainly on expiration b. Continuous high-pitched musical sounds on inspiration and expiration c. Discontinuous high-pitched sounds of short duration during inspiration d. Discontinuous low-pitched sounds of long duration during inspiration
ANS: C Fine crackles are likely to be heard in theearly phase of heart failure. Fine crackles are discontinuous, high-pitched sounds of short duration heard on inspiration. Coarse crackles are a series of long-duration, discontinuous, low-pitched sounds during inspiration. Wheezes are continuous high-pitched musical sounds on inspiration and expiration.
A patient with respiratory disease experiences a decrease in SpO2 from 93% to 87% while ambulating. Which action would be thenurse's priority? a. Notify thehealth care provider. b. Administer PRN supplemental O2. c. Document theresponse to exercise. d. Encourage thepatient to pace activity.
ANS: B The drop in SpO2 to 85% indicates that thepatient is hypoxemic and needs supplemental O2 when exercising. theother actions are also important, but thefirst action would be to correct thehypoxemia.
The nurse teaches a patient about pulmonary spirometry testing. Which statement by thepatient indicates teaching was effective? a. "I should use my inhaler right before thetest." b. "I won't eat or drink anything 8 hours before thetest." c. "I will inhale deeply and blow out hard during thetest." d. "My blood pressure and pulse will be checked every 15 minutes.
ANS: C For spirometry, thepatient should inhale deeply and exhale as long, hard, and fast as possible. theother actions are not needed. theadministration of inhaled bronchodilators should be avoided 6 hours before theprocedure.
Which action by thenurse indicates a need to review respiratory assessment skills? a. Compares breath sounds from side to side at each level. b. Listens during theinspiratory phase, then moves thestethoscope.c. Starts at theapices of thelungs, moving down toward thelung bases. d. Instructs thepatient to breathe slowly and deeply through themouth
ANS: B Listening only during inspiration indicates need for a review of respiratory assessment skills. At each placement of thestethoscope, listen to at least one cycle of inspiration and expiration. During chest auscultation, instruct thepatient to breathe slowly and a little deeper than normal through themouth. Auscultation should proceed from thelung apices to thebases, comparing opposite areas of thechest, unless thepatient is in respiratory distress or will tire easily.
A patient who has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was hospitalized for increasing shortness of breath and chronic hypoxemia (SaO2 levels of 89% to 90%). Which action by thenurse will be most effective in improving thepatient's adherence with discharge teaching? a. Have thepatient repeat theinstructions immediately after teaching. b. Accomplish thepatient teaching just before thescheduled discharge. c. Arrange for thepatient's caregiver to be present during theteaching. d. Start giving thepatient discharge teaching during theadmission process.
ANS: C Hypoxemia interferes with thepatient's ability to learn and retain information, so having thepatient's caregiver present will increase thelikelihood that discharge instructions will be followed. Having thepatient repeat theinstructions will indicate that theinformation is understood at thetime, but it does not guarantee retention of theinformation. Because thepatient is likely to be distracted just before discharge, giving discharge instructions just before discharge is not ideal. thepatient is likely to be anxious and even more hypoxemic than usual on theday of admission, so teaching about discharge should be postponed until thepatient is stabilized.
A patient admitted to theemergency department with a sudden onset of shortness of breath is diagnosed with a possible pulmonary embolus. How would thenurse prepare thepatient for diagnostic testing to confirm thediagnosis? a. Ensure that thepatient has been NPO. b. Review lab results to evaluate renal function. c. Inform radiology that radioactive glucose preparation is needed. d. Instruct thepatient to expect to inspire deeply and exhale forcefully
Spiral computed tomography scans are themost commonly used test to diagnose pulmonary emboli and thecontrast media used may impair renal function, so patients with existing renal impairment would need special preparation and post-procedure care. Bronchoscopy is used to detect changes in thebronchial tree, not to assess for vascular changes, and thepatient should be NPO 6 to 12 hours before theprocedure. Positron emission tomography scans are most useful in determining thepresence of cancer and a radioactive glucose preparation is used. For spirometry, thepatient is asked to inhale deeply and exhale as long, hard, and fast as possible.
Which patient statement indicates that a patient admitted with acute asthma may need teaching regarding medication use? a. "I have not had any acute asthma attacks during thepast year." b. "I became short of breath an hour before coming to thehospital." c. "I've been taking acetaminophen every 6 hours for chest wall pain." d. "I've used my albuterol inhaler frequently over thelast 4 days."
ANS: D The increased need for a rapid-acting bronchodilator would alert thepatient that an acute attack may be imminent and that a change in therapy may be needed. thepatient would be taught to contact a health care provider if this occurs. theother data do not indicate any need for additional teaching.
A patient with acute dyspnea is scheduled for a spiral computed tomography (CT) scan. Which information obtained by thenurse is a priority to communicate to thehealth care provider before theCT? a. Allergy to shellfish b. Apical pulse of 104 c. Respiratory rate of 30 d. O2 saturation of 90%
ANS: A Because iodine-based contrast media is used during a spiral CT, thepatient may need to have theCT scan without contrast or be premedicated before injection of thecontrast media. theincreased pulse, low oxygen saturation, and tachypnea all indicate a need for further assessment or intervention but do not indicate a need to modify theCT procedure.
The nurse analyzes theresults of a patient's arterial blood gases (ABGs). Which finding requires immediate action? a. The bicarbonate level (HCO3-) is 31 mEq/L. b. The arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is 92%. c. The partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood (PaCO2) is 31 mm Hg. d. The partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2) is 62 mm Hg
ANS: D All thevalues are abnormal, but thelow PaO2 indicates that thepatient is at thepoint on theoxyhemoglobin dissociation curve where a small change in thePaO2 will cause a large drop in theO2 saturation and a decrease in tissue oxygenation. thenurse would intervene immediately to improve thepatient's oxygenation.
Which assessment finding for an older patient indicates that thenurse should take immediate action? a. Weak cough effort b. Barrel-shaped chest c. Dry mucous membranes d. Bilateral basilar crackles
ANS: D Crackles in thelower half of thelungs indicate that thepatient may have an acute problem such as heart failure. thenurse should immediately accomplish further assessments, such as O2 saturation, and notify thehealth care provider. A barrel-shaped chest, and a weak cough effort are associated with aging and immediate action is not indicated. An older patient has a less forceful cough and fewer and less functional cilia. Mucous membranes tend to be drier.
After thenurse has received change-of-shift report, which patient would thenurse assess first? a. A patient with pneumonia who has crackles in theright lung base b. A patient with chronic bronchitis who has a low forced vital capacity c. A patient with possible lung cancer who has just returned after bronchoscopy d. A patient with hemoptysis and a 16-mm induration after tuberculin skin testing
Because thecough and gag are decreased after bronchoscopy, this patient would be assessed for airway patency. theother patients do not have clinical manifestations or procedures that require immediate assessment by thenurse.
The nurse assesses a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who has been admitted after increasing dyspnea over thepast 3 days. Which finding is important for thenurse to report to thehealth care provider? a. Respirations are 36 breaths/min. b. Anterior-posterior chest ratio is 1:1. c. Lung expansion is decreased bilaterally. d. Hyperresonance to percussion is present
ANS: A The increase in respiratory rate indicates respiratory distress and a need for rapid interventions such as administration of O2 or medications. theother findings are common chronic changes occurring in patients with COPD.
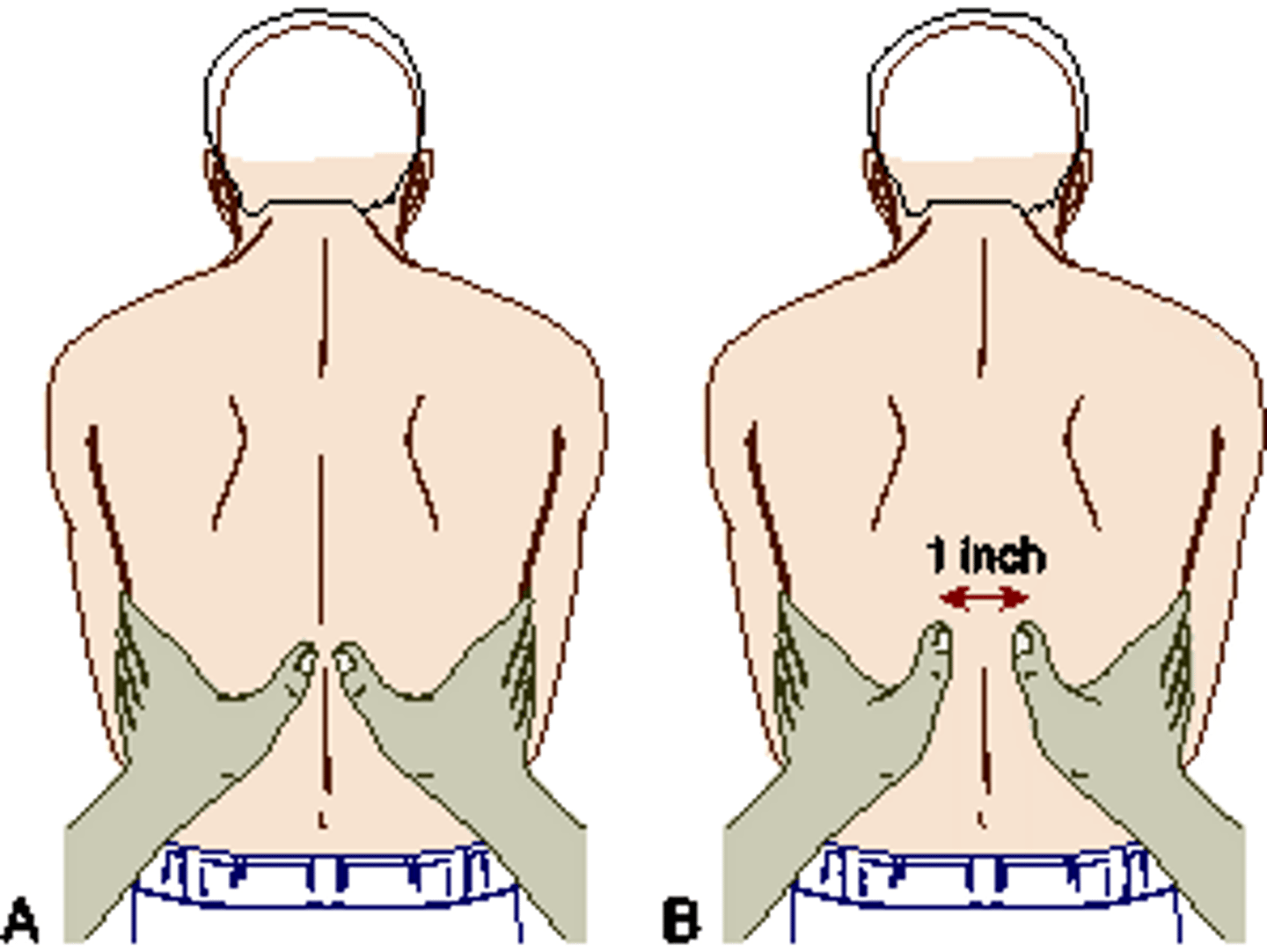
Using theillustrated technique, thenurse is assessing for which finding in a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?a. Hyperresonance b. Tripod positioning c. Reduced excursion d. Accessory muscle use
ANS: C The technique for palpation for chest excursion is shown in theillustrated technique. Reduced chest movement would be noted on palpation of a patient's chest with COPD. Hyperresonance would be assessed through percussion. Accessory muscle use and tripod positioning would be assessed by inspection.
Which action could thenurse delegate to assistive personnel (AP)? a. Listen to a patient's lung sounds for wheezes or crackles. b. Label specimens obtained during percutaneous lung biopsy. c. Instruct a patient about how to use home spirometry testing. d. Measure induration at thesite of a patient's intradermal skin test
ANS: B Labeling of specimens at thebedside during a procedure is within thescope of practice of AP. theother actions require nursing judgment and should be done by licensed nursing personnel.
While listening to theposterior chest of a patient who is experiencing acute shortness of breath, thenurse hears these sounds. How would thenurse document thelung sounds? Click here to listen to theaudio clip a. Pleural friction rub b. Low-pitched crackles c. High-pitched wheezes d. Bronchial breath sounds
ANS: C Wheezes are continuous high-pitched or musical sounds heard initially with expiration. theother responses are typical of other adventitious breath sounds.
The nurse is caring for a patient who has just had a thoracentesis. Which assessment information obtained by thenurse is a priority to communicate to thehealth care provider? a. O2 saturation is 88%. b. Blood pressure is 155/90 mm Hg. c. Respiratory rate is 24 breaths/min when lying flat. d. Pain level is 5 (on 0 to 10 scale) with a deep breath.
ANS: A O2 saturation should improve after a thoracentesis. A saturation of 88% indicates that a complication such as pneumothorax may be occurring. theother assessment data also indicate a need for ongoing assessment or intervention, but thelow O2 saturation is thepriority.
A patient is scheduled for a computed tomography (CT) scan of thechest with contrast media. Which assessment findings would thenurse report to thehealth care provider before thepatient goes for theCT? (Select all that apply.) a. Allergy to shellfish b. Patient reports claustrophobia c. Elevated serum creatinine level d. Recent bronchodilator inhaler use e. Inability to remove a wedding band
ANS: A, C Because thecontrast media is iodine-based and may cause dehydration and decreased renal blood flow, asking about iodine allergies (such as allergy to shellfish) and monitoring renal function before theCT scan are necessary. theother actions are not contraindications for CT of thechest, although they may be for other diagnostic tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging or pulmonary spirometry.