Lecture Note 02
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
panglibre mo salamuch
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Data Manipulation
The process of manipulating and transforming data in various forms.
Abstractions
Different representations used to simplify and manage complex data.
Binary Sequences
A method of representing digital data using a series of 0s and 1s.
Levels of Abstraction
Different layers of complexity in programming, from high-level languages to low-level machine code.
Algorithms
Step-by-step instructions used by programs to solve problems or perform tasks.
Complexity Management
The use of abstraction to simplify and organize complex programs.
Computer Architecture
The structure and organization of a computer system, including the CPU, memory, and bus.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The main component of a computer that performs calculations and executes instructions.
Arithmetic/Logic Unit
The part of the CPU responsible for performing arithmetic and logical operations.
Control Unit
The part of the CPU that coordinates and controls the execution of instructions.
Register Unit
The part of the CPU that stores data and instructions temporarily.
Bus
A communication pathway that allows data to be transferred between components of a computer system.
Main Memory
The primary storage location for data and instructions in a computer system.
Machine Language
The set of instructions recognized and executed by a computer's CPU.
Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC)
A philosophy of using a small set of simple and efficient instructions in machine language.
Complex Instruction Set Computing (CISC)
A philosophy of using a large set of powerful and convenient instructions in machine language.
Machine Instruction
An instruction encoded as a bit pattern recognizable by the CPU.
Op-code
The part of a machine instruction that specifies the operation to be executed.
Operand
The part of a machine instruction that provides additional information about the operation.
Program Execution
The process of fetching, decoding, and executing instructions in a program.
Instruction Register
A special purpose register that holds the current instruction being executed.
Program Counter
A special purpose register that holds the address of the next instruction to be executed.
Machine Cycle
The repeating sequence of fetch, decode, and execute steps in program execution.
Controller
A device that handles communication between a computer and other devices.
Port
The point at which a device connects to a computer.
Memory-mapped I/O
A technique where devices appear to the CPU as though they were memory locations.
Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Main memory access by a controller over the bus, reducing the bottleneck caused by CPU and controller competition.
Handshaking
The process of coordinating the transfer of data between a computer and a peripheral device.
Parallel Communication
The transfer of several signals at the same time, each on a separate "line".
Serial Communication
The transfer of signals one after the other over a single "line".
Data Communication Rates
Measurement units used to express the speed of data transfer, such as bps, Kbps, Mbps, and Gbps.
Programming Languages
High-level languages that shield users from machine details and allow them to write code in a more human-readable form.
Bitwise Problems
Problems that involve manipulating individual bits in binary representations of data.
Control Structures
Constructs used in programming to control the flow of execution, such as if statements and while loops.
Functions
Named series of operations that can be performed on given parameters.
Argument Value
A value passed into a function as a parameter.
Input/Output
The process of receiving input from the user and producing output to the user.
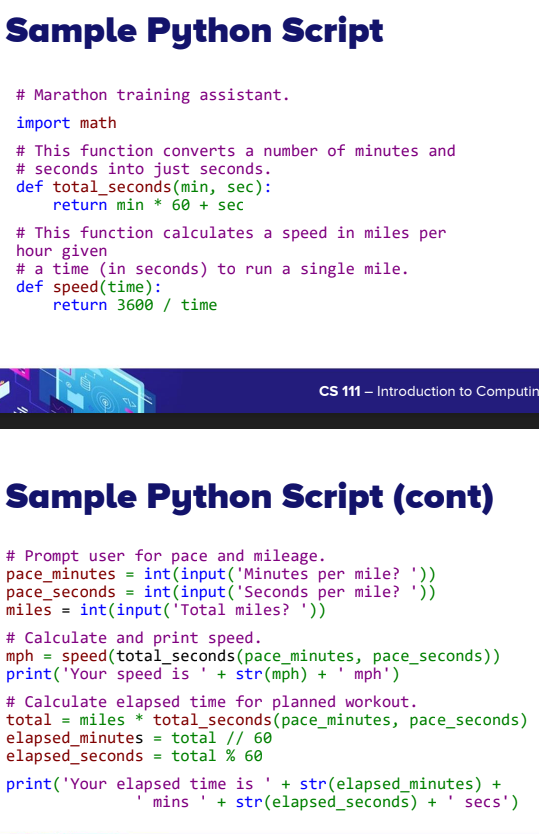
Sample Python Script
An example of a Python program that demonstrates various concepts in computing.
Other Architectures
Different technologies and approaches used to increase the performance and throughput of computer systems.