Cell biology exam 3
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
CHP. 11 - Membrane Structure
CHP. 11 - Membrane Structure
micelles do not have
cytosol, we need the lipid bilayer in liposome to have cytosol
cell membranes have the same basic architecture:
phospholipid bilayer (about 3nm wide) with embedded proteins
components of the lipid bilayer
hydrophilic head - interacts with the water-based cytosol and outside environment
hydrophobic core - prevents unassisted movement of water-soluble substances from one side to the other
all membrane lipids are
amphipathic meaning they have a water loving and water hating region
cell membranes act as
selective barriers
in some bacteria, the plasma membrane is the
only membrane
in addition to the plasma membrane, eukaryotic cells also have
internal membranes that enclose individual organelles
all cell membranes prevent
molecules on one side from freely mixing with those on the other
what are the three classes of membrane lipids
phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and sterols
composition of phosphoglycerides
glycerol backbone, tails, and head
phosphoglyceride tails
two hydrophobic fatty acyl chains
commonly 16 or 18 carbon
saturated or unsaturated
phosphoglyceride head
4 major head groups: phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidyethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylserine (PS), and phosphatidylinositol (PI)
plasmalogens composition
one fatty acyl chain attached to glycerol by an ester linkage and one attached by an ether linkage
plasmalogens constitute
10 mol% of the total mass of phospholipids in humans, mainly as membrane structure components
plasmalogens structures
sn-1 vinyl ether
sn-2 polyunsaturated fatty acids
sphingolipids are derivatives of
sphingosine (an amino acid alcohol with a long hydrocarbon chain)
sphingolipids composition
fatty acyl chains connected by an amide bond
sphingomyelines
contain a phosphocholine head
others contain a sugar or oligosaccharide head - glycolipids
glucosylcerebroside
has a glucose head group
sterols are ___ of _____
membrane components of animals (cholesterol), fungi (ergosterol), and plants (stigmasterol)
they are precursors for different hormones
sterol structure
head group - single polar hydroxyl
tail - conjugated four-ring
hydrocarbon and short hydrocarbon chain
purpose of carbohydrates in the membrane
they stick out and serve as receptors
how are cancer cells identified
DNA killed the study of lipids, however cancer cells have unique lipid structures on them so we use those now
amoeba and bacterial DNA would be hard to distinguish, how could we tell them apart?
their membranes could have different lipids that could be separated for profiling
not all cells have the same types of lipids/fatty acids
purpose of phosphoglyceride heads
determine the direction it points on the membrane
plasmalogens are a hybrid version of
archea since they both have ether linkages
how do we obtain plasmalogens
our bodies make them on their own, but people can take supplements to give them bigger pieces of these structures to synthesize them faster
sphingolipid use
retain moisture in the skin
shingomyelin use
cover nerve cells and is useful in the regeneration of cells
simplest sphingolipid has
just an H on the other chain leg
cholesterol role
it stiffens the membrane, decreases membrane fluidity
cholesterol in eukaryotes
sits in between phospholipids in eukaryotes
what determines membrane fluidity in prokaryotes
degree of fatty acid saturation
biological membranes
vary in lipid composition, impermeable to water-soluble molecules and ions
have a viscous consistency with fluid like properties
membrane lipids will spontaneously form
liposomes
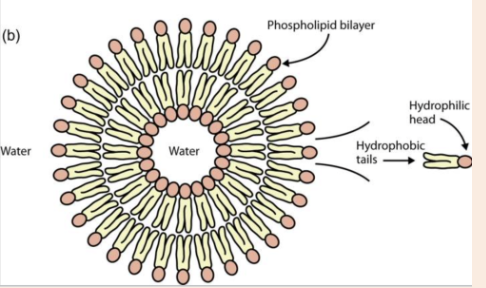
phospholipid bilayers spontaneously
close in on themselves to form sealed compartments
why do phospholipid bilayers spontaneously close in on themselves
in a planar phospholipid bilayer, the hydrophobic tails are exposed to water along the edges which is energetically unfavorable
formation of the sealed compartment shields the hydrophobic tails from water which is energetically favorable
what are the faces of cellular membranes
plasma membrane, vesicle and some organelles, nucleus, mitochondrion, and chloroplast
plasma membrane
single bilayer
cytosolic and exoplasmic leaflets
vesicle and some organelles
single bilayer
internal aqueous space is equivalent to the outside of the cell
nucleus, mitochondrion, and chloroplast
enclosed by two membranes separated by a small intermembrane space
phosphatidyl choline
most common phospholipid in cell membranes
has 3 parts
3 parts of phosphatidylcholine
hydrophilic head: has choline linked to phosphate
two hydrocarbon chains; forms hydrophobic tails
glycerol; links head to the tails
compare different membrane lipids
they are all amphipathic, but differ in their hydrophilic head
galactocerebroside head
sugar galactose plus an -OH group
formation and study of phospholipid bilayers
treatment with organic solvent mix of chloroform and methanol to selectively soluble the phospholipids and cholesterol
mechanical dispersal of extract in water; lipids spontaneously form liposomes
planar bilayer formation over a small hole in a partition separating two aqueous phases; used to study permeability of solutes
the fluidity of a lipid bilayer depends on
its composition
phospholipid synthesis in ER membrane
Step 1: Two fatty acids synthesized on fatty acyl CoA. Hydrocarbon tails anchor the
molecule to the membrane.
• Step 2: Phosphatase – converts phosphatidic acid into diacylglycerol.
• Step 3: Phosphotransferase transfers a polar head group – Choline in this example
• Step 4: Flippase – uses ATP energy to catalyze movement of phospholipids from the
cytosolic leaflet to the exoplasmic leaflet
what does scrambalase do
catalyzes the transfer of random phospholipids from one monolayer to another
flippases mainatin the
asymmetric distribution of phospholipids
certain phospholipids are confined to one side of the membrane
phospholipid translocases
floppase: takes outside and puts in
flippase: takes inside and puts outside
scrambalase: random (activity of this enzyme are increased with calcium ions are increased in the cell)
*floppase and flippase are directed
why does the cell need scrambalase
for when it is undergoing apoptosis