BME 2200 EXAM 1
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapters 7 & 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
True or False: A body is in steady state if the parameters that define it (i.e., mass, volume, temperature) do not change with time.
True
True or False: Mass balance can be described as ACC=IN-OUT+GEN-CON. At steady-state, ACC=0
True
True or False: If a system is at equilibrium, it will stay the same forever, as long as no other forces act on or are introduced into this system
True
True or False: Our body temperature is maintained at 37 ºC. This is equilibrium.
False - maintaining body temperature at 37*C is homeostasis or steady state.
What are the major differences between open system and closed system?
Open systems have mass exchange with surroundings (mass flow in or flow out) while closed systems do not exchange mass with surroundings
True or False: In a closed system, on energy is exchanged.
True
True or False: our blood pH is maintained at pH 7. This is homeostatic.
True
True or False: In a steady-state, accumulation with ACC=IN-OUT+GEN-CON is zero because the mass system doens’t change.
True
ATP + H2O —> ADP +Pi
if Pi = H3PO4, find ADP
ADP = C10H15N5O10P2
Tracer elimination follows first-order kinetics. Let M represent the total mass of the tracer in the body at time t, M0 the initial mass at t=0, and k the rate constant. Write down: (a) The formula to calculate M as a function of M0, k, and t. (b) The formula to calculate the half-life (t1/2) in terms of k.
M = M0exp(-kt), t(1/2)=0.693/k
True or False: Internal respiration refers to that air flows into our lung.
False - internal respiration refers to cell exchange O2 and CO2 with surroundings.
True or False: Total lung capacity does not include residual volume.
False - total lung capacity includes residual volume
True or False: The exchange of air between the alveolus and the atmosphere is called ventilation.
True
True or False: Just as electric currents flow from areas of high voltage to low voltage, air flows from areas of high pressure to low pressure. When the pressure inside the lungs exceeds atmospheric pressure (1 atm or 760 mmHg), air flows out of the lungs
True
True or false: the half-life first order reaction is constant regardless of the initial concentration
True
True or False: first-order reaction the plot ln(A) v.s. time is a straight line
True
True or False: If a person breathes faster, he or she may increase the delivery of oxygen into the lung.
True
True or False: Assuming a steady-state condition for O₂ exchange between the alveoli and the surroundings and considering the system as the alveolar gas excluding the vasculature, there is one inlet (O₂ entering the alveoli from the atmosphere) and one outlet (O₂ exiting the alveoli back to the atmosphere) for this system.
False - 2 outlets for this system (alveoli gas), including atmosphere and vasculature (venous blood) in the lung.
True or False: if the partial pressure of O2 in lung’s venous blood is 40 mmHg and the partial pressure of O2 in alveolar gas is 100 mmHg, O2 flows from the alveolar gas into the venous blood
True
if the pressure in the lung is 1.1 atm, will air flow into or out of the lungs?
out of the lungs because 1atm, the pressure outside of the lung, is greater than 1.1 atm. Therefore, it will flow outward to follow the pressure gradient.
If the concentration of hydrogen ion [H+] in a solution is 10-6 mol/L, what is the pH of this solution?
pH=-log[H+]=6
True or False: CO2 in the red blood cells (RBCs) has three possible fates: some remains dissolved (4%), some combines with other molecules (such as hemoglobin, 21%), and some combines with water to form carbonic acid and then bicarbonate (64%).
True
True or False: In Fick’s law, the flux is a constant, the diffusion coefficient D is a constant, and the derivative dc/dx is also a constant
True
True or False: During digestion, solid foods are mechanically pulverized into small pieces, which are further dissolved into molecules. Large molecules, such as proteins and polysaccharides, are broken down into monomer units to allow for absorption into the body
True
True or False: The small intestine includes three parts: duodenum, jejunum, ileum. Ileum connects to the stomach.
False - the duodenum connects to the stomach
True or False: Digestive enzymes are rich in the small intestine to facilitate converting large molecules into small subunits, a process called hydrolysis. These enzymes are mainly secreted by the liver
False - digestive enzymes are mainly secreted by pancreas
True or False: Zymogens are protein that are secreted in an inactive form and then converted into an active enzyme at the site of function
True
True or False: Proteins and starch can be directly absorbed by the small intestine
False - they need to break down to peptides and amino acids or oligo/monosaccharides for absorption by the small intestine.
The conversion of ATP to ADP (ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + energy) is condensation
False - water is a reactant, so it is a hydrolysis reaction
The function of stomach in digestion is converting solid food to small particles through physical grinding or chemical reaction.
True
True or False: Digestive enzymes are rich in large intestines to facilitate digestion and nutrient absorption.
False - enzymes are rich in the small intestine
True or False: Ribonucleases break down nucleic acids while peptidase break down proteins.
True
T/F: Monosaccharides and proteins are both polymers.
False - monosaccharides are monomers while polysaccharides are polymers
T/F": Triglycerides and proteins can be absorbed by small intestine without breaking down into smaller molecules.
False - They need to break down to be absorbed
T/F: Liver secretes most digestive enzymes.
False - pancreas secretes most digestive enzymes
T/F: Bile acids are secreted by gall bladder.
False - bile acids are secreted by liver and stored in the gall bladder
T/F: Digestive systems use 5-7L of water per day for digestion. Most water is reabsorbed by large intestines.
True
T/F: Anabolism builds up new molecules while catabolism breaks down molecules.
True
True or False: Ideal batch reactor is a closed system
True
True or False: the extent of reaction X in an ideal reactor increases with reactor volume V and reaction rate vmax/Km, and decrease with inlet/outlet flow rate Q
True
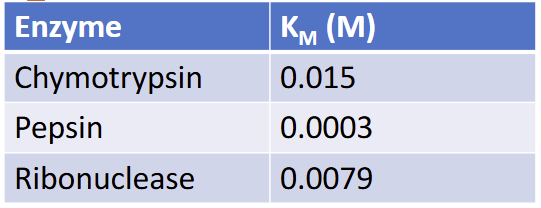
Michaelis constant Km determined for three enzymes are shown. Which has the highest affinity for its substrate?
Pepsin - a low Km suggest a higher enzyme affinity
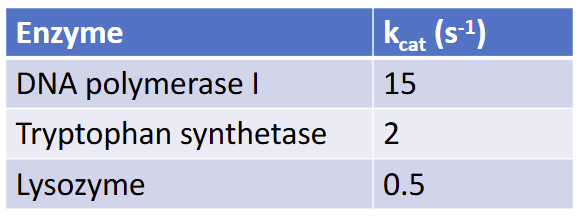
The turnover number kcat determined is shown. Which is the most efficient in reacting with substrates.
DNA polymerase - higher Kcat relates to a more efficient reaction rate with substrates.
True or False: Blood flow in the blood vessels is driven by pressure drop and the heart creates the pressure gradient.
True
list the following four fluids in order from highest to lowest viscosity: olive oil, blood, plasma, and water (37 degree Celsius)
oilve oil>blood>plasma>water
True or False: The total cross-sectional area of arterioles is greater than that of capillaries
False
True or False: Local blood flow to a tissue is controlled by constriction and dilation of capillaries because the greatest overall resistance is provided by them, and they have muscular layers
False - arterioles rather than capillaries
If pressure is consistent within a system, how does the diameter and the length change with the flow rate?
Hose with short length and large diameter will produce low resistance to water flow, resulting in higher flow rate at the same pressure difference.
Describe the difference between axial pressure and transmural pressure
axial pressure - aligned with blood flow direction, and the drop in it will drive flow.
transmural pressure - direction perpendicular to blood flow, and difference between blood vessel and interstitial fluid drives fluid flow in/out of vessels.
T/F: many vessels have smooth muscle layers so that they can contract and dilate. For this reason, these vessels can change their resistance to blood flow and regulate blood flow rate
True
T/F: The most significant pressure drop in the blood vessels occurs in the aorta and venae cavae.
False - more significance in arterioles and capillaries
List three structures of capillaries and address which structure provides big leaks and allows macromolecular exchange.
Fenestrated
Sinusoidal: allows macromolecular exchange
Continuous
T/F: water and very small solutes can move cross capillary walls because of the transmural pressure gradient.
True