Clin Med - Fungal infections and mycobacterial diseases
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Mycotic or fungal infections are classified as
primary or opportunistic infections.
Primary infections
those that develop in immunocompetent hosts and opportunistic infections develop in immunocompromised hosts.
Fungal infections can also be
local or systemic (aka disseminated).
Local infections
involve one part of the body including the skin, oral cavity, and vaginal and occur in immunocompetent or immunocompromised hosts.
Systemic infections are
infections that are noted in more than one area of the body and spread in the bloodstream.
Most fungi are
opportunists and are typically not pathogenic except in an immunocompromised host.
What are candidiasis, aspergillosis, and mucormycosis
opportunistic systemic fungal infections
What is a common cause of primary fungal infections
inhalation of fungal spores, causing localized pneumonia.
What has a geographic distribution
many primary fungal infections (dimorphic fungi)
Coccidioidomycosis
noted in the southwest United States, northern Mexico, and Central and South America
Histoplasmosis
noted in the Midwestern United States and areas of Central and South America, Africa, Asia, and Australia
Blastomycosis
noted in North America and Africa
Paracoccidioidomycosis
noted in South America
Cryptococcosis
fungus that can lead to chronic meningitis
Histoplasmosis
fungus that can disseminate involving the reticuloendothelial system
Blastomycosis
fungus that can lead to skin lesions or involve the central nervous system and bone
Coccidioidomycosis
fungus that can cause bone and joint infections, skin lesions, and meningitis
Systemic infections are important due to
increased number of immunocompromised patients and antibiotic overuse.
Yeast and mold differ in structural complexity and reproduction, yeast is and reproduces by __
unicellular (single-celled), budding
Yeast and mold differ in structural complexity, mold is and reproduces by _
multicellular (forms hyphae and mycelium), sexually (spores or hyphae) and asexually (fusion of hyphae)
Candida Species
Fungal infection cause by a yeast (candida albicans common)
What can occur with indwelling urinary catheter, focal renal infection, or disseminated disease
Candiduria
What is the work up for candiduria
urinalysis and urine culture treatment focused if needed
What would you prescribe for candiduria for a patient with normal renal function
oral fluconazole 200 mg QD x 7-14 days
What imaging would you order for candida albicans
endoscopy indication, esophagitis (white plaques in esophagus)
What is the 1st line of treatment for candida albicans, localized infection and immunocompetent
Nystatin
What is the 1st line of treatment for candida albicans, more severe local and systemic infections
Azoles (if fungus not resistant)
What is useful in detecting the presence of cerebral histoplasmosis prior to performing a lumbar puncture
CT scanning
What is useful if adrenal involvement is suspected
Abdominal CT scanning
What is the surgical management of histoplasmosis
Resection of pulmonary cavitary lesions when repeated relapses or progressive disease occurs despite repeated intensive medical therapy.
What is the emergency management of histoplasmosis
Perform thoracentesis or pericardiocentesis with severe pleural effusions or pericardial tamponade
What would you use to treat histoplasmosis with AIDS and HIV
lifelong itraconazole suppression 200 mg daily
What would you use to treat patient with histoplasmosis with mild pulmonary disease
observation
What causes dissemination of cryptococcosis
immunocompromised state (HIV, long term steroids, treatment of hematologic cancer (hodgkin’s), and solid organ treatment (b/c of drugs that cause immuno-suppression)
What is the surgical management of cryptococcosis
Rarely, patients develop complete obstruction of the ventricles and require a CSF shunt to relieve intracranial pressure.
What is the emergency management of cryptococcosis
not applicable
What is used as maintenance treatment of cryptococcosis
Fluconazole x 6 months (HIV or immune compromised up to 12 months)
What would you diagnose for a patient who presents with a cough with hemoptysis
Aspergillomas
Fungal infections are acquired through:
Inhalation of spores into lungs and paranasal sinuses
Direct contact
What is this referred to
Candida albicans
Candida glabrata
Candida lusitaniae
Candida krusei
Candida auris
Cryptococcus
Yeasts: eg, Candida sp. (Pathologic fungi)
What is this referred to
Aspergillus, mucor
Aspergillus flavus
Aspergillus niger
Rhizopus
Molds (pathologic fungi)
What is this referred to
Blastomyces
Paracoccidiodomycoses
Coccidiodomycoses
Histoplasma
Fungi
What has the risk factors below
Patients with neutropenia
Immunocompromised
Indwelling (intravascular) catheter
Hospital admission
Recent use of antibiotics (abx)
Recent use of corticosteroids
Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM)
Risk factors
What is the etiology below
Yeast with budding and pseudohyphae
Common gut flora
Opportunistic infection if immunocompromised
Incubation period unknown
Vulvovaginal candidiasis associated with pregnancy
Candida Albicans
In Candida Albicans, who does this apply to
Usually present with systemic disease
Esophagitis
Endocarditis
Immunocompromised
In Candida Albicans, who does this apply to
Usually present with skin and mucous membrane infections
Oral thrush
Inhaled corticosteroids
HIV patients CD4+ cell count < 500/mm3
Candidal intertrigo
Diaper rash
Vulvovaginitis
Perleche or angular cheilitis
Immunocompetent
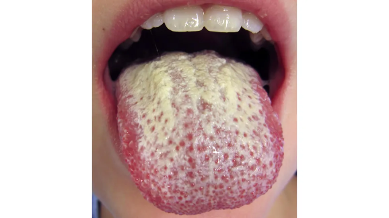
What causes oral thrush
Candida Albicans
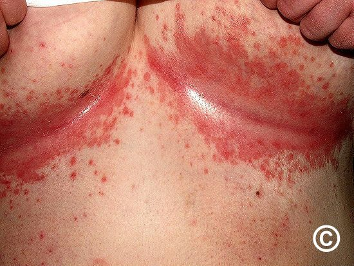
What is this physical exam
intertrigo from Candida Albicans
What is this physical exam
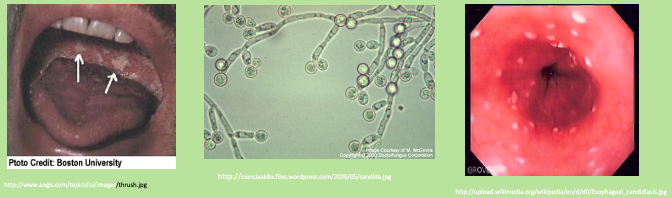
Esophageal candidiasis
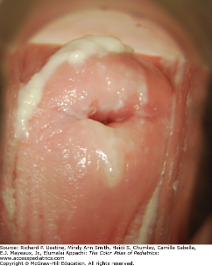
What is this physical exam
Vulvovaginitis from candida albicans
What causes macronodular skin lesions associated with hematogenously disseminated Candida
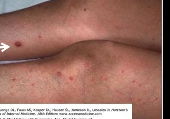
Invasive Candidias
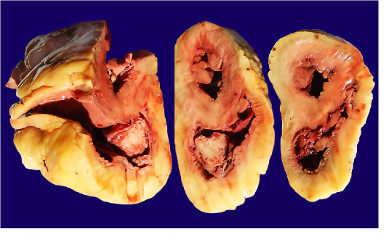
What can cause endocarditis
Candida Albicans
What is the below
Bacterial infection
Other fungal pathogen
Cutaneous
eczema, psoriasis, cellulitis, seborrheic dermatitis
Esophageal
Cardiac origin (MI,
GI origin gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
Vulvovaginal
Herpes simplex, molluscum contagiosum
Deep invasive
Bacterial or viral origin
Oral thrush
Strep throat, abscess
Developing abscess
Candida Albicans
What is the lab work up for candida albicans
Blood/tissue culture
KOH (wet mount)
Biopsy
Systemic Illness/Sepsis
CBC w. diff
CMP
Lactic Acid
Blood culture
UA + urine culture
+/- Procalcitonin
EKG/Cardiac biomarkers/echocardiogram
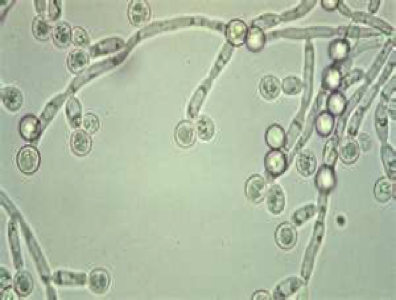
How is Candida Albicans diagnosed
Germ tube formation at 37°C (98.6F)
True hyphae sprout from yeast
Definitive diagnosis
Blood or other tissue culture
Wet mount (vaginal fluid)
Yeast and pseudohyphae KOH
Biopsy
What is the clinical intervention of Candida Albicans
Remove any central vascular or urinary catheters if possible
Consult with Infectious Disease
Limit use of systemic steroids if possible
What is the surgical management of candida albicans
______________
Surgical drainage of abscess + antifungal therapy
Prosthetic joint infection → removal of prosthesis
Splenic abscess → splenectomy
Endocarditis → valve replacement
What should you use to treat fungus resistant to azoles
Echinocandins
Can also use with systemic infections
Could be considered 1st line due to increased resistance to azoles
Amphotericin B
More severe systemic infections
Typically considered 2nd line
Safe for use in pregnancy
What is the prognosis of candida albicans
complication of infection → disseminated
Invasive candidiasis has a high mortality
What does this refer to
Histoplasma capsulatum is a dimorphic fungus
Grows in soil as spore-bearing mold
Converts to yeast phase at body temperature
Etiology of histoplasmosis
What does this refer to
Worldwide
Endemic in eastern and central U.S. Mostly Ohio, Mississippi, Missouri river valleys.
Most common endemic mycosis in the U.S.
Facilitated by bird, bat and chicken droppings
Inhalation of spores causes infection
No person-to-person transmission
Variable incubation period, but usually 1 to 3 weeks
Epidemiology of histoplasmosis
What does this refer to
Think in terms of
Site
Pulmonary (MC), extrapulmonary or disseminated
Duration
Acute, chronic
Pattern
Primary vs. reactivation
Often Asymptomatic
Symptomatic mild flu-like illness across the spectrum to an atypical pneumonia presentation
Post infection recognized by incidental findings on chest x-ray - calcifications
Clinical Presentation of Histoplasmosis
What does this refer to
Epidemics can occur after contaminated soil disturbed
Primary histoplasmosis
Often asymptomatic
May present with fever, chills, non-productive cough, myalgia, and chest discomfort
Diffuse pneumonia on chest x-ray
Rarely fatal
Acute histoplasmosis
What causes this
Most often affects the severely immunocompromised (HIV)
Multiorgan involvement
Fever
Cough
Dyspnea
Weight loss
Often fatal
Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis (PDH)
What does this refer to
Older patient
Variety of lesions on chest x-ray
Cavitation nodules, etc
History of COPD, fever, fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, productive cough, and night sweats.
Death from retraction and cavitation of the lungs can occur.
Chronic Progressive Pulmonary Histoplasmosis
What does this apply to
Tuberculosis
Pneumocystosis
Lung cancer
Pneumonia
Lymphoma
Mycoplasma
Blastomyces
Aspergillosis
Blastomycosis
Differential Diagnosis of Histoplasmosis
What does this refer to
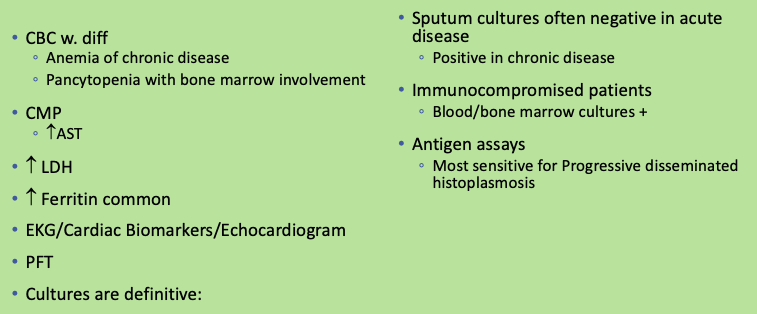
Workup for histoplasmosis
What does this refer to
Primary ______
Hilar adenopathy
Acute pneumonia
Chronic pulmonary
Unilateral or bilateral upper lobe infiltrates with multiple cavities and extensive fibrosis in the lower lobes
Disseminated _________
Diffuse pulmonary infiltrates
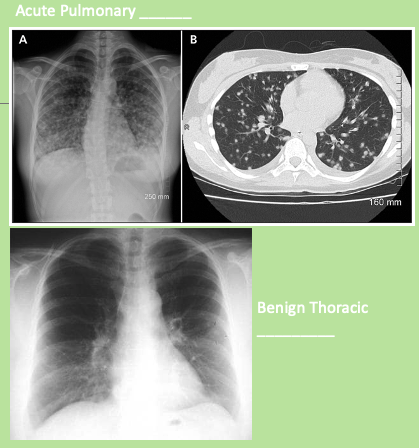
Histoplasmosis
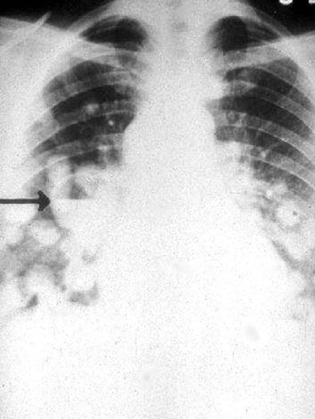
What is the arrow pointing at
Histoplasmosis on CXR
What will show you
if valvular involvement is suspected;
endocarditis with Histoplasma species is rarely associated with positive blood cultures.
echocardiography of histoplasmosis
What does the following refer to
Determine the extent of pulmonary involvement by evaluating
the degree of restrictive defect
the presence of a small airway obstruction
the extent of diffusion impairment
the presence of hypoxemia.
Pulmonary function tests of Histoplasmosis
What would you use to treat histoplasmosis in mild to moderate Disseminated Non-Meningeal Disease
Itraconazole 200mg TID for 3 days then
qd – bid for weeks to months depending on severity
What would you use to treat histoplasmosis for patients with the following
Unable to take p.o.
Failed itraconazole
Meningitis
Severe disseminated disease in immunocompetent patients
Amphotericin b
What does the following refer to
Educate individuals residing or traveling in endemic areas
Exposure risks, including both leisure and work activities
Advance preparation reduces exposure to contaminated soil, bat and bird dwellings, and inoculum.
Many exposed immunocompetent individuals from endemic areas do not develop extensive clinical manifestations
Reactivation can occur
Patient education/maintenance/prevention for histoplasmosis
What does the following refer to
Prior infection does not prevent future reinfection
Take precautions when facing increased exposure risk.
Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis is associated with a good outcome.
Relapse rate in chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis ~20%.
Prognosis histoplasmosis
What is the following
Pulmonary or disseminated infection acquired by inhalation of soil contaminated with the encapsulated yeasts
Encapsulated yeast
C. Neoformans
Predominately seen in immunocompromised
C. Gatti
Rarely seen in humans
When found more likely in immunocompetent
Cryptococcosis
What is this referring to
Seen worldwide
Affects 5-10% of adults with HIV/AIDS
Epidemiology of cryptococcosis
What does this refer to
Found in
Soil
Bird (pigeon) droppings
Inhalation
No person-to-person transmission
Incubation period unknown
Etiology
that cause immuno-suppression)
What clinical presentation is below
Cough
Chest Pain
Nausea
Fever
Cutaneous Nodules or Ulcers
Lytic Bone Lesions
Dissemination to any organ
CNS is the major concern
Meningitis
Slow Onset Headache
Mental status changes
Behavior changes
Nuchal rigidity
Cryptococcosis
What does this refer to
Acanthamoeba
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Histoplasmosis
Lipomas
Molluscum Contagiosum
Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia
Syphilis
Toxoplasmosis
Tuberculosis
Differential diagnosis of cryptococcosis
How is cryptococcosis diagnosed
Culture
Isolate organism from body fluids or tissue
CSF stain
Encapsulated yeast cells
Cryptococcal capsular antigen in CSF plus
Positive culture gives a 90% diagnosis rate
MRI is better than CT for CNS abnormalities
What do these images refer to
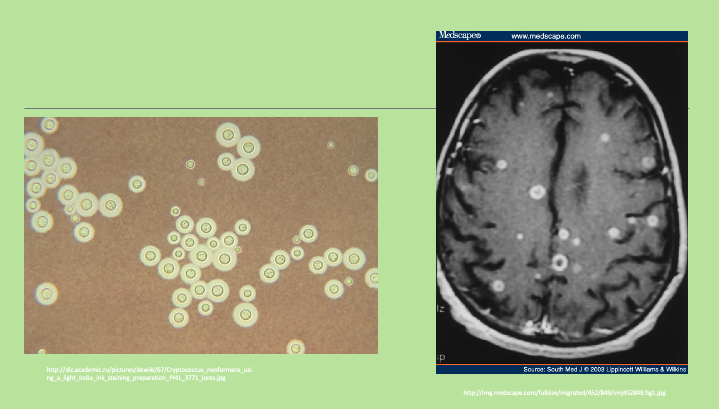
Cryptococcus
What is used as treatment of cryptococcosis in patient with Meningitis or other serious (usually systemic) infection
Amphotericin B PLUS Flucytosine or Fluconazole
Change from Amphotericin B when clinically improved and sterile CSF
What is patient education/maintenance/prevention for immunocompromised patients with cryptococcosis
Early medical treatment
Onset of severe HA or neurologic sx
May allow for tx of cryptococcal disease before permanent damage occurs
What does the following refer to
Clinical syndromes
Invasive aspergillosis (lung)
Aspergilloma
Mycetoma (“fungal ball”)
Non-invasive
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
MC in patients with cystic fibrosis
Found in soil and decomposed material
Transmission via spore inhalation
Aspergillus
What does this refer to
Risk Factors
Immunocompromised status
Neutropenia
Steroids or cytotoxic drugs
Hematologic malignancy
Chronic granulomatous disease
Asthma
Pre-existing lung disease
Aspergillus Epidemiology
What would you diagnosis a patient with
Persistent fever
Cough (hemoptysis)
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Invasive Aspergillosis
What does this refer to
Invasive aspergillosis
MC immunocompromised (suppressed) patients
Spores germinate and produce invasive hyphal structures
ABPA
Local inflammatory reaction that can result allergic response
Cystic Fibrosis and Asthma are significant RF
Etiology of Aspergillosis
What does this refer to
Atopic diseases
Atopic dermatitis
Allergic rhinitis
Asthma
Food allergies
Hyper IgE syndrome
Associated conditions of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
What does this refer to
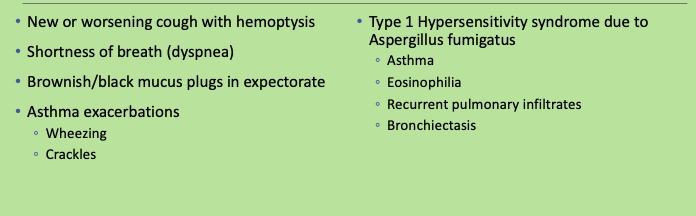
Clinical presentation Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
What labs would you order for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
_____ skin test
Hypersensitivity screening
+ skin test = wheal
Eosinophilia and ↑ IgE
Aspergillus-specific antibodies
IgG and IgE
Precipitin antibodies
What imaging would you order for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
CXR often initial imaging
Transient consolidations
CT chest
Gold standard
Central bronchiectasis and normal peripheral bronchi
What does this refer to
Patient’s WITHOUT Cystic Fibrosis (Rosenberg-Patterson diagnostic criteria) at least 6
Asthma
Transient pulmonary opacities on imaging
Positive Aspergillus skin testing
Peripheral eosinophilia
Positive Aspergillus-specific antibodies IgG or IgE
Elevated peripheral IgE
Bronchiectasis on imaging
Positive precipitin antibodies
Patient’s WITH cystic fibrosis
New findings on imaging that do not clear with antibiotics
How to diagnose allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
What does this refer to
1st line management
Systemic corticosteroids
2nd line management
Itraconazole
Severe disease refractory to monotherapy with systemic steroid therapy
Other treatment
Omalizumab (Xolair)
Reduce exacerbations
Clinical pharmcotherapeutics allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
What does this refer to
Pneumocystis pneumonia
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome)
Differential diagnosis for aspergillosis
What does this refer to

Labs/work up for aspergillosis
What does this refer to

Imaging/workup for aspergillosis
What does this refer to
Invasive ______
Pathology + invasive hyphae in tissue OR
Aspergillus positive culture
ABPA
Clinical findings
+ eosinophilia OR IgE
_________
Abnormal sputum culture OR aspergillus positive culture or serology
Aspergilloma seen on imaging
Aspergillosis (how its diagnosed)
What does this refer to
Infectious disease consult
Pulmonology consult
Surgical resection may be indicated for aspergilloma
Clinical intervention Aspergillosis
What does this refer to
ABPA
Steroids 1st line
Invasive _______
Voriconazole (Vfend)
Caspofungin (Cancidas)
If voriconazole CI
Amphotericin B may be used as adjunct with voriconazole
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Aspergillosis